Organization of the nervous system
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
What are the two subdivisions of the nervous system?
CNS and PNS
What are cell bodies in the CNS called? PNS?
Nuclei for CNS and Ganglia for PNS
What are the functions of the somatic PNS?
Sensation(afferent) and Motor(efferent)
What are the functions of the somatic motor neurons?
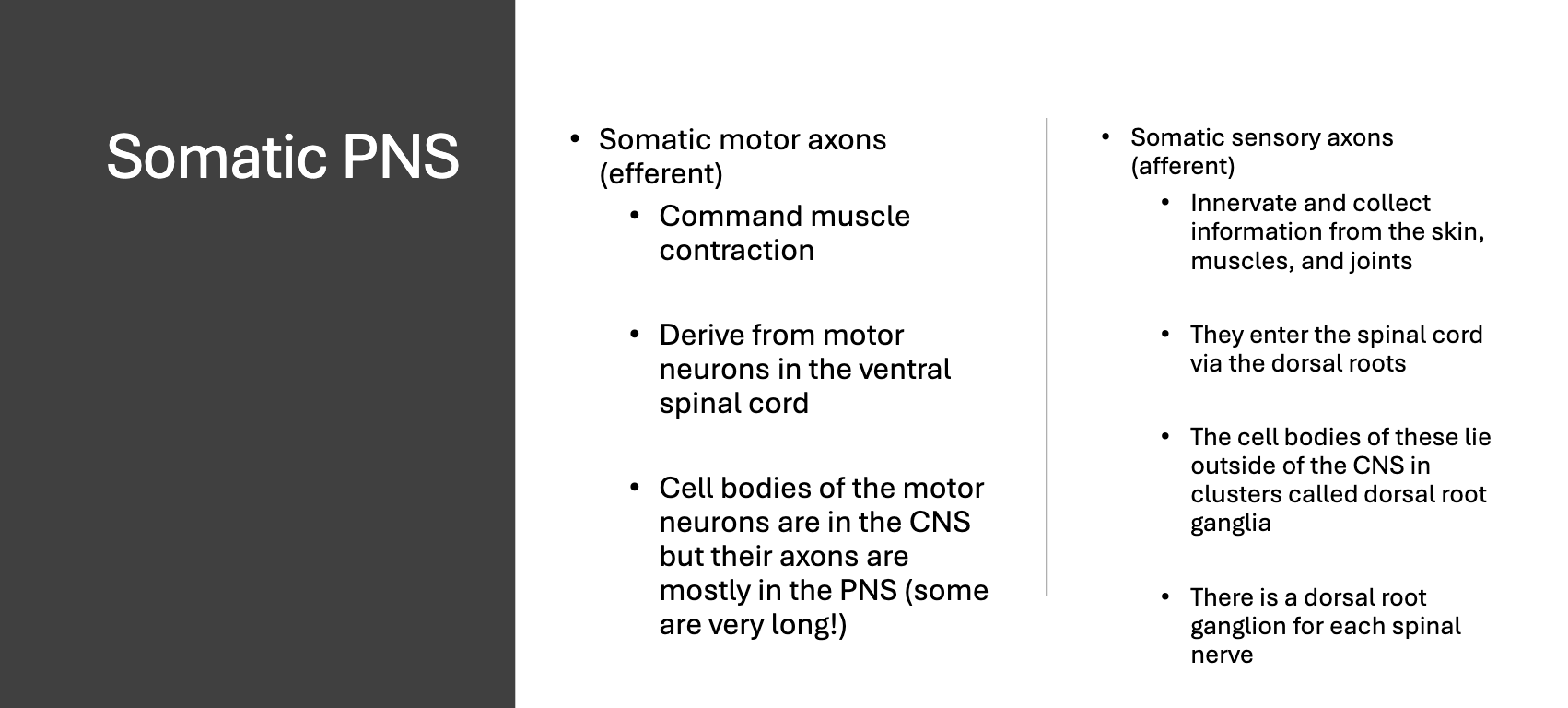
What are the functions of the somatic motor neurons?
What are the three divisions of the autonomic PNS?
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
Enteric NS(GI)
What does the autonomic PNS sense?(afferent)
Sensation from visceral organs
What does the autonomic PNS do?(efferent)

What are 4 responses that the sympathetic nervous system elicits?

When is the sympathetic nervous system on?
It is constantly on.
Tonic stimulation of blood vessels
Active during respiratory cycle. - acts during inspiration to dilate airways.
What tissues does the sympathetic nervous system innervate
Every tissue in the body
What are 5 responses that the parasympathetic nervous system elicits?

What tissues does the parasympathetic nervous system innervate?
Innervates head, viscera, and external genitalia
What does the vagus nerve do?
it makes up 75% of the parasympathetic nervous system
provides parasympathetic input to most of the thoracic and abdominal viscera
Enteric neurons have no direct innervation from the….
CNS
How is the enteric NS organized?
microcircuits that contain intrinsic primary afferent neurons that can respond to local stimuli to integrate information and coordinate motor output
What are the different reflex pathways that control digestive function?
• muscle contraction/relaxation
• Secretion/absorption
• Blood flow
What are the functions of CSF?
cushion the brain from impact
speedy removal of waste from extracellular fluid
What are some important medical uses for CSF?
Measuring CSF pressure
Analyzing CSF for pathology
Drug targeting for brain
High contrast in digital scans
Is CSF creation regulated?
No, it is constantly made
Where does CSF exit?
Specialized out pocketings on the superior surface of the brain called arachnoid granules. It can enter venous blood here.
Where is the choroid plexus found?
it is found as vascularized secretory tissue in every ventricle
It is highly organized tissue consisting of epithelial cells and surround a core of capillaries and connective tissue
What does the BBB regulate?
ion concentrations, fluid volume balance, pH, and immune cell activity
via tight junctions
What is some pathology associated with a “leaky” BBB
BBB breakdown allows neurotoxic blood-borne molecules and cells (e.g. leukocytes) to enter the brain, which subsequently initiates neuroinflammatory as well as innate and adaptive immune responses (microglia and astrocytes)
• Also can lead to dysfunctional efflux and impaired clearance of metabolic waste
• Implicated in aging-related dementia (vascular dementia) and potentially some neuropsychiatric conditions such as depression (when associated with neuroinflammation)
What does the DL PFC control?
•Cognitive/executive processing and control: Higher executive thought, planning, intelligence.
•Governs behavior dealing with abstract, cognitive goals: ambition, future plans.
What does the OM PFC control?
•Emotional processing and control
•Governs behavior dealing with social behavior and social/emotional goals
What are the 3 divisions of the brainstem?
Medulla Oblongota
Pons
Midbrain
What does the Medulla oblongota do?
Functions – sensory input for touch, pain and temperature. Motor control over throat and pharynx. Handles respiration, digestion, and circulation and reflexes such as swallowing, coughing, and sneezing.
What does the midbrain do?
Midbrain: Eye movements, motor control, reward systems, control over pain. Vision- and hearing- related reflexes. Massive tracts passing through
What does the Pons do?
Sensation and motor for the face, hearing, eye movements. Significant role in cerebellar motor processing. Continuation of medulla functions. Helps control breathing rhythms.
Sensory data flows into the ________ from the brainstem,
along with emotional, visceral, and other information from
different areas of the brain
Thalamus
What does the thalamus do?
The thalamus relays these messages to the appropriate
areas of the cerebral cortex
• Almost all axons going to the cortex synapse on neurons
in the thalamus
• The thalamus coordinates signaling, including timing
The hypothalamus is connect to what system?
Endorcrine
What are the 3 components of the limbic system?
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Septum
What are the amygdala’s functions?
• the recognition of facial emotions, especially
fear
• learned fear pathways
• emotional memory formation
• It is thought of as the structure assigning
emotional valence (emotional value) to sensory
experiences.
Habit learning doesn’t require _______
Hippocampus
What are the things that inhibit hypothalamus?
Negative feedback
Hippocampus/frontal cortex
What brain area activates the HPA axis?
amygdala
What changes in the brain happen with PTSD?
Amygdala is hyperreactive to trauma-related stimuli
• Loss of hippocampal volume
• Loss of prefrontal cortex volume, hypoactivity
• Higher brain structures don’t dampen amygdala driven emotional responses
What do spinal cord layers I to VI do?
Dorsal horn: sensory processing
What do spinal cord layers VII do?
Intermediate zone: Some spinocerebellar info + sympathetic and
parasympathetic motor
What do spinal layers VIII and IX do?
ventral horn: motor neurons
What do spinal layers X do?
Central gray(interneurons)
What are the general steps the brain does once it receives sensory infromation?
Compares input with existing memories(new or not)
Integrate information from all sensory fields
The amygdala and memories are used to assign an
emotional significance to the experience and the
hippocampus records it. Limbic lobe.All this information is finally sent to the frontal lobes for processing
What is transductions?
Cells convert an external signal into membrane voltage difference
Explain the dorsal column lemniscal pathway
1st neuron starts from DRG and ascends to the brainstem where it synapses in caudal medulla
2nd neuron crosses the midline at the brainstem and ascends to the thalamus
3rd neuron goes straight up to the Primary somatosensory cortex(parietal lobe)
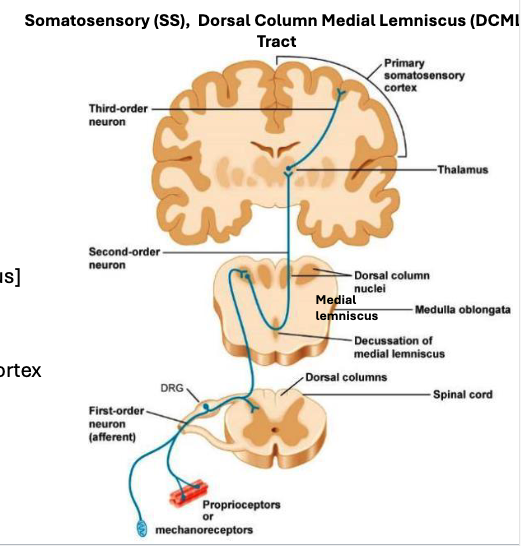
What does the DCML sense?
- carries touch / proprioceptive information
- dorsal columns (and dorsal column nuclei) organized somatotopically
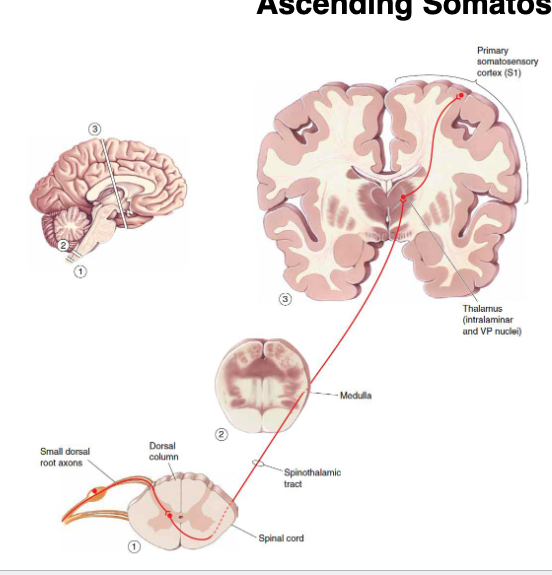
What does the spinothalamic pathway sense?
- carries pain/temperature information
- also exhibits somatotopy
- sensory input crosses midline at spinal cord
Explain the spinothalamic pathway
1st neuron crosses over at the spinal cord level and synapses on the thalamus
2nd neuron goes from thalamus to primary somatosensory cortex
Explain the auditory pathway
spiral ganglion—>ventral cochlear nucleus—>superior olive—>inferior colliclus—>MGN—>Auditory cortex
How is the auditory cortex mapped?
tonotopically
What does tonotopic and somatotopy have in common
They are both plastic, can be changed
What are the first neurons that rods and cons synapse on?
Bipolar cells
What do bipolar cells synapse onto? Where do these neurons synapse?
retinal ganglion cell bodies, these synapse onto thalamic structure(LGN)
Lesions in LGN cause…
blindness in part or all of the visual field
What does the superior colliculus do?
It coordinate the orientation of the eyes and head in space during rapid , reflex eye movements
Ensures rapid reactions without cortical input
Explain cortical blindness
visual field deficits that include macular sparing (V-I)
Explain central color blindness
Color information can be detected by the retinas (retinal pigments, reactions and detection are OK), but color is perceived only as shades of gray. (V-II)
Explain visual discrimination disorders
Difficulties matching lines of different types, unfamiliar faces that have different emotional expressions and are viewed from different angles, discriminating overlapping figures, etc. (V-II)
Explain visual agnosias
Cannot identify person, place or thing, although might be able to identify if using touch or sound.
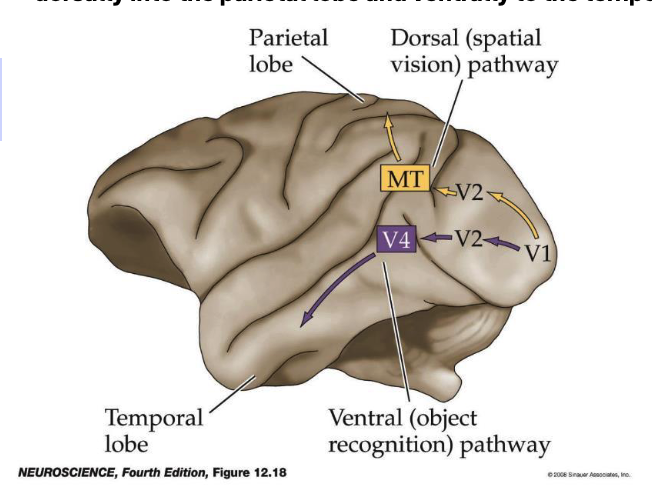
What is the difference between the dorsal and ventral vision pathways?
Dorsal pathway – processing of object motion, navigation, directing eye movements, motion perception
Ventral pathway – color and form perception, visual perception and visual memory