Gilded Age US History
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Gilded Age
A time period during the late 1800s that saw an increase in immigration, rapid industrialization, and urbanization. This was also the time of Big Business, Political Machines, and Corruption.

Monopoly
A business with an exclusive possession or control of the supply or trade in a commodity or service. Monopolies eliminate competition and can charge high prices. These are also known as trusts.

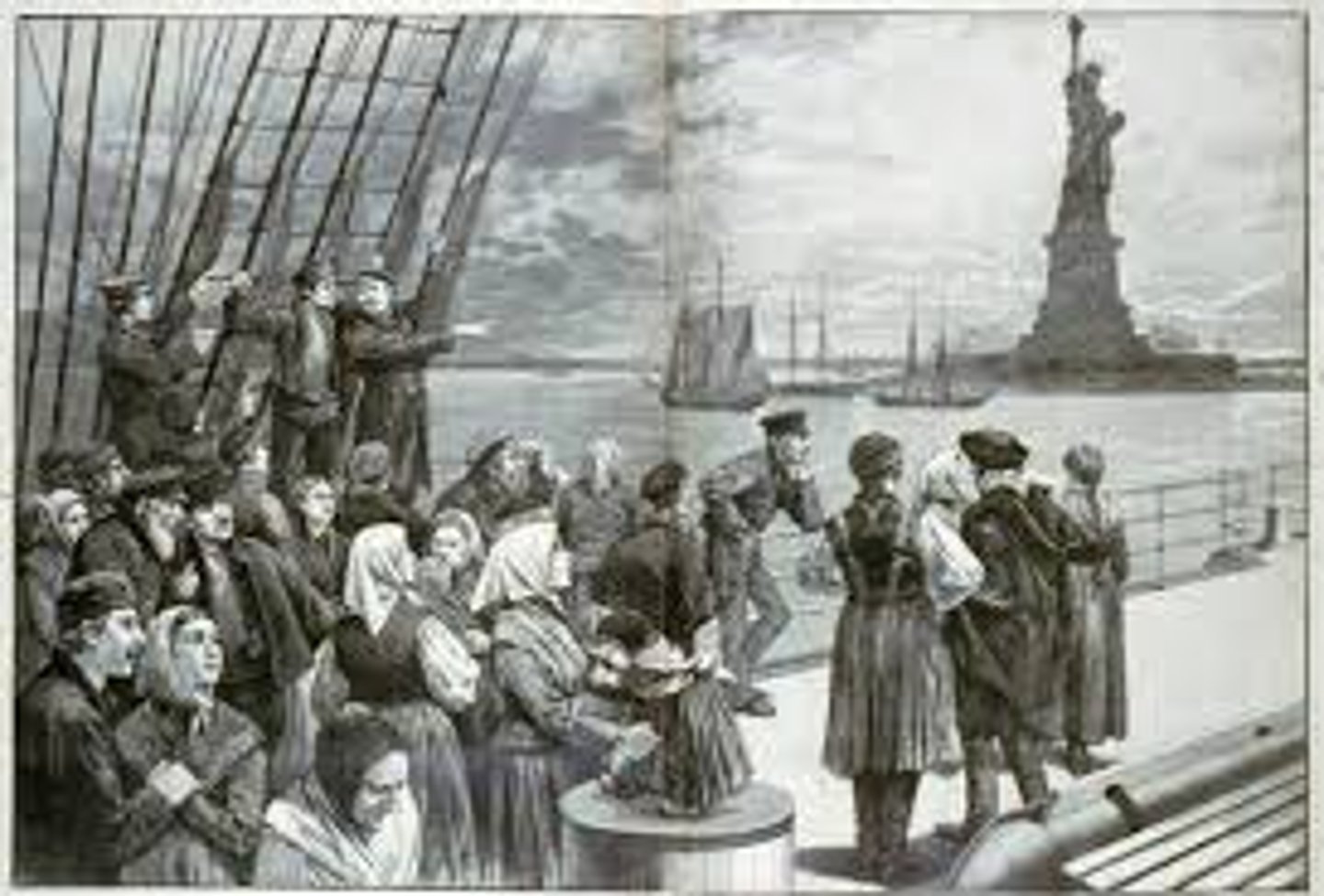
Immigration
The process of foreign people moving to a new place. The Gilded Age saw large amounts of people migrate to the United States.

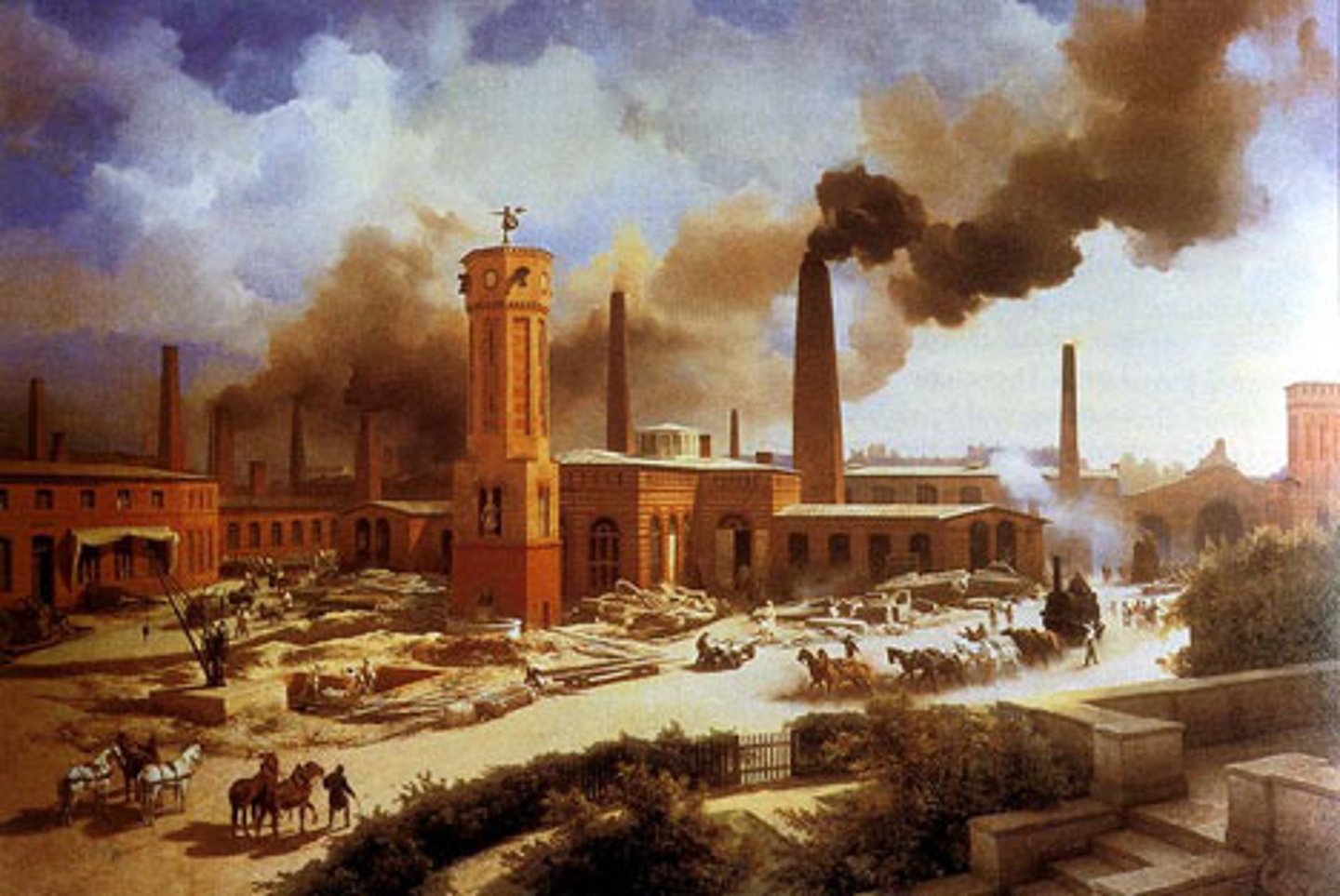
Industrialization
The process of transition from an agriculture-based economy to one of manufacturing (production of items).term-7

Trust
A business with an exclusive possession or control of the supply or trade in a commodity or service. Trusts eliminate competition and can charge high prices. These are also known as monopolies.

Urbanization
The process of people moving from rural to urban areas. During the Gilded Age, cities such as New York, Boston, and Chicago grew rapidly as people moved into cities to find work.

Migration
movement of people from one place to another

Robber Barons
A negative view on Captains of Industry (Big Business leaders).

Captains of Industry
A positive term for Big Business owners.

John D. Rockefeller
The oil tycoon who bought up or destroyed all of his competition. Proponent of Horizontal Integration.

Andrew Carnegie
The Steel tycoon controlled the iron mines, methods of shipping, steel refineries, and stores selling steel (vertical integration).

Cornelius Vanderbilt
A railroad tycoon who had a monopoly on rail travel in the United States.

J.P. Morgan
A Gilded Age banker who purchased Carnegie Steel and turned it into U.S. Steel.
He is the inspiration for the Monopoly Man character.

Sherman Anti-Trust Act
An 1890 law that enables the government to break apart companies that have an unfair control over part of the economy. It is not used much during the Gilded Age, but will be used often during the Progressive Era.

Thomas Edison
A famed Gilded Age inventor. He invented the light bulb, phonograph, and motion pictures (movies).

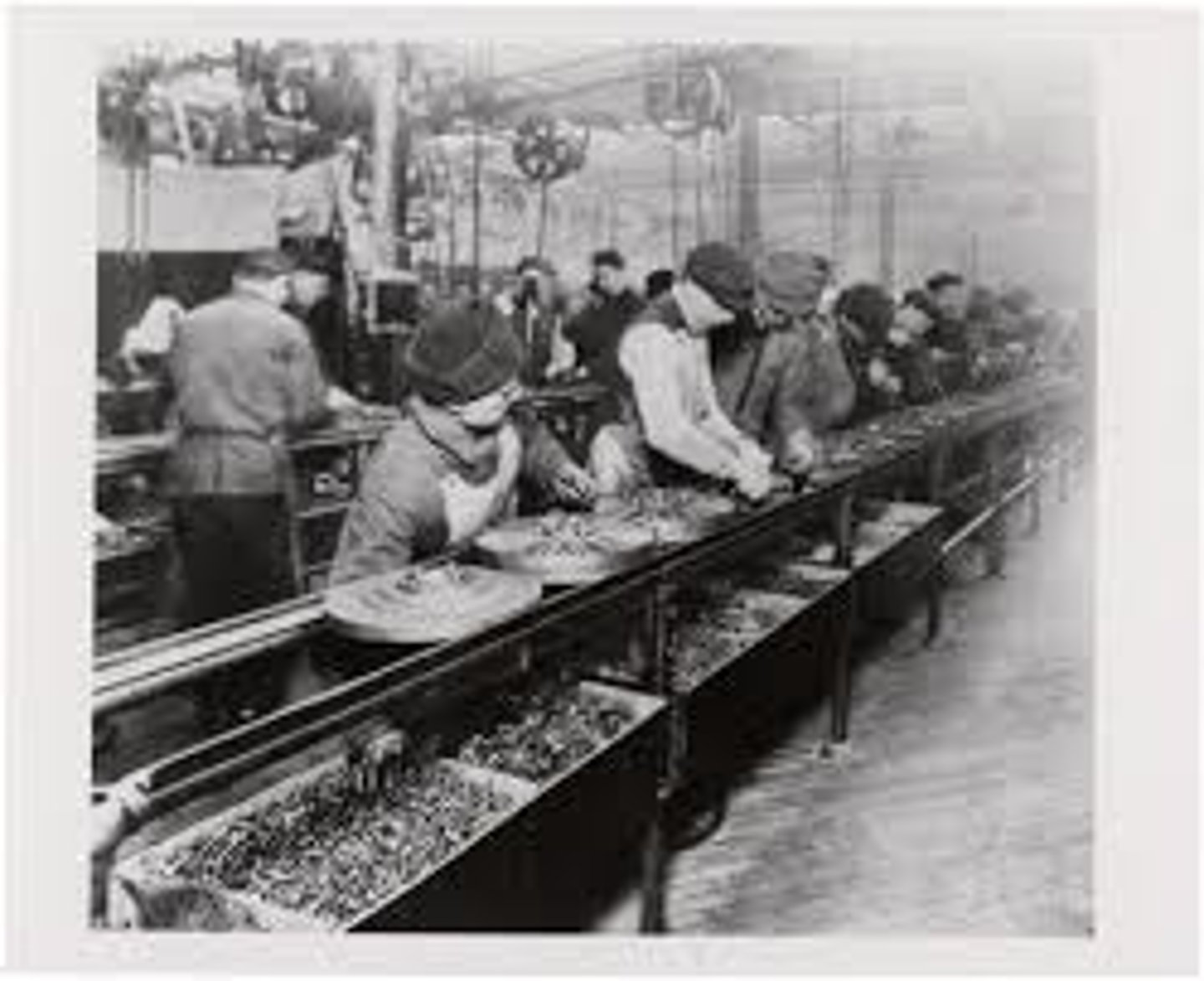
Henry Ford
A famous entrepreneur and founder of the Ford Motor Company. His use of the assembly line allowed for quick and cheap production of cars.

Labor Unions
Groups formed to protect the rights of workers. These groups used strikes to force owners to make changes to work hours, safety, and wages.

Laissez-Faire
An economic approach where the government has little or no control over business. A hands-off policy.

Entrepreneur
Individuals or groups that create or invest in their own businesses.

Free Enterprise
An economic system in which private business operates in competition and largely free of state control. People can buy and sell what they want to whomever they wish.

Big Business
A term for the emergence of large businesses during the Gilded Age. These large corporations exert strong influence on the government.

Gospel of Wealth
The idea that the wealthy have a duty to help those in need. Andrew Carnegie is the person associated with this term.

Philanthropy
The act of giving back or helping people, usually through donating money.

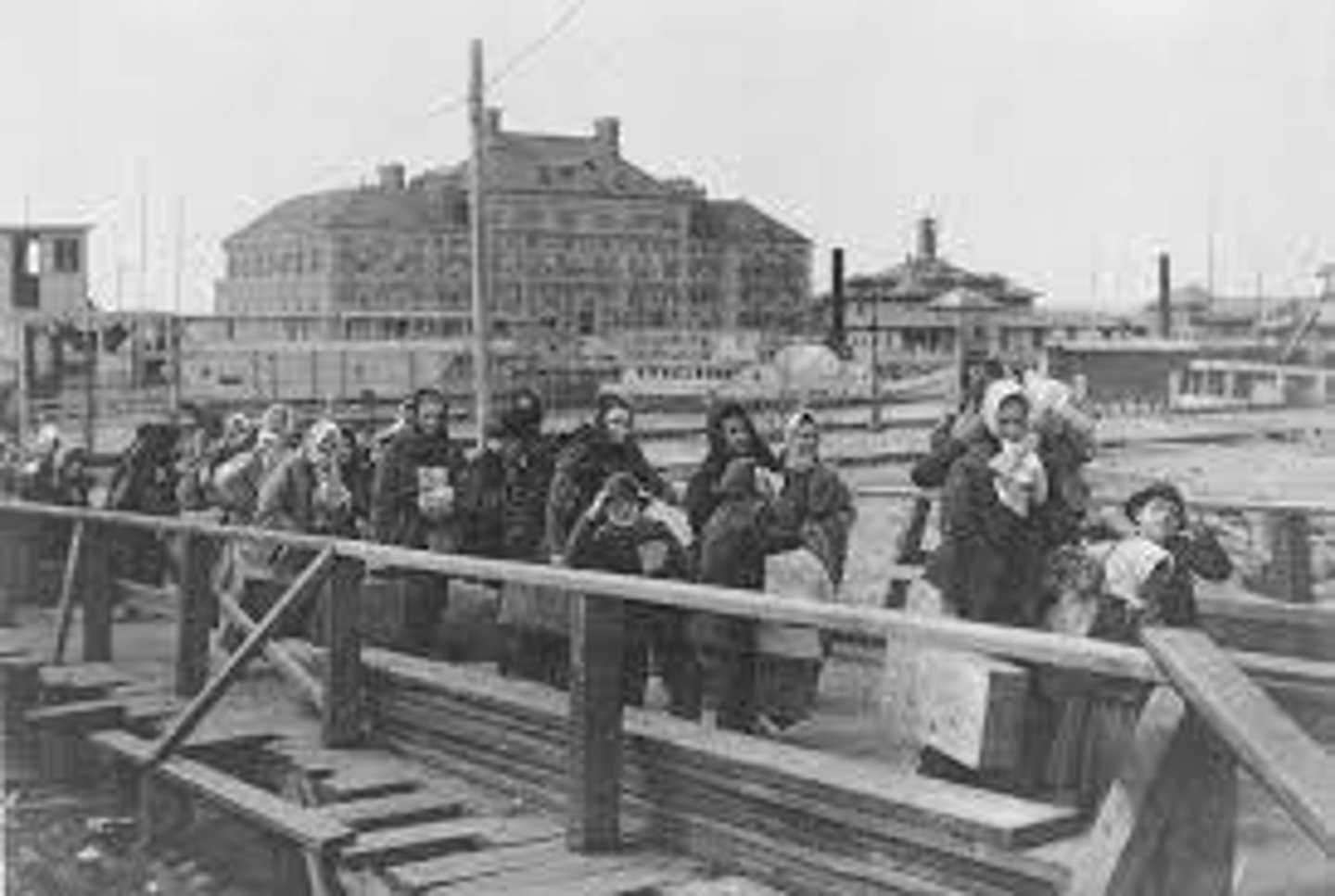
Ellis Island
The first stop in the United States for immigrants from Europe and Africa. Here immigrants were given medical exams, and had their names and countries of origin recorded before gaining entrance to the United States.

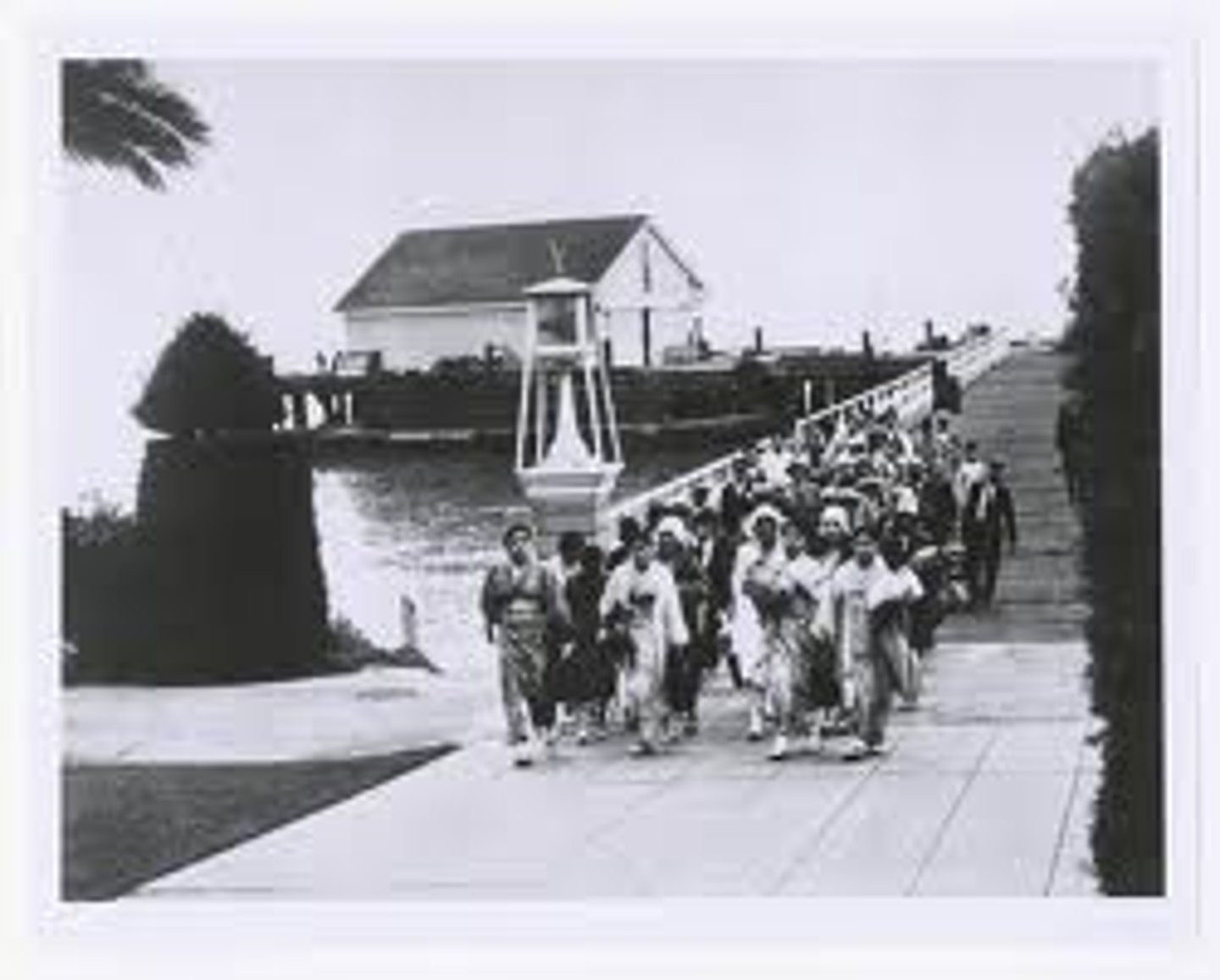
Angel Island
This island, off the coast of California, is where immigrants from Asia would gain entrance into the United States.

Chinese Exclusion Act of 1882
A law forbidding Chinese immigrants from coming to the United States to reduce job competition

Bessemer Process
A process that allows for the creation of very cheap and very strong steel. This process allows for the rapid growth of railroads and industrialization in the United States.
Assembly Line
Items are made in sequence by large groups of people who specialize in making one part of an item. Businesses such as the Ford Motor Company will use this process to make automobiles quickly and cheaply.

(American Indians) Dawes Act
1887 law that distributed reservation land to individual Native American owners

Homestead Act
1862 law that gave 160 acres of land to citizens willing to live on and cultivate it for five years

Populism
a belief in more rights for people and limits to the power of big business and monopolies

Political boss
A corrupt party organization that gets voter support through immigration & infrastructure

Transcontinental Railroad
Railroad connecting the west and east coasts of the continental US. Led to more trade, people moving westward

Nativism
A policy of favoring native-born individuals over foreign-born ones

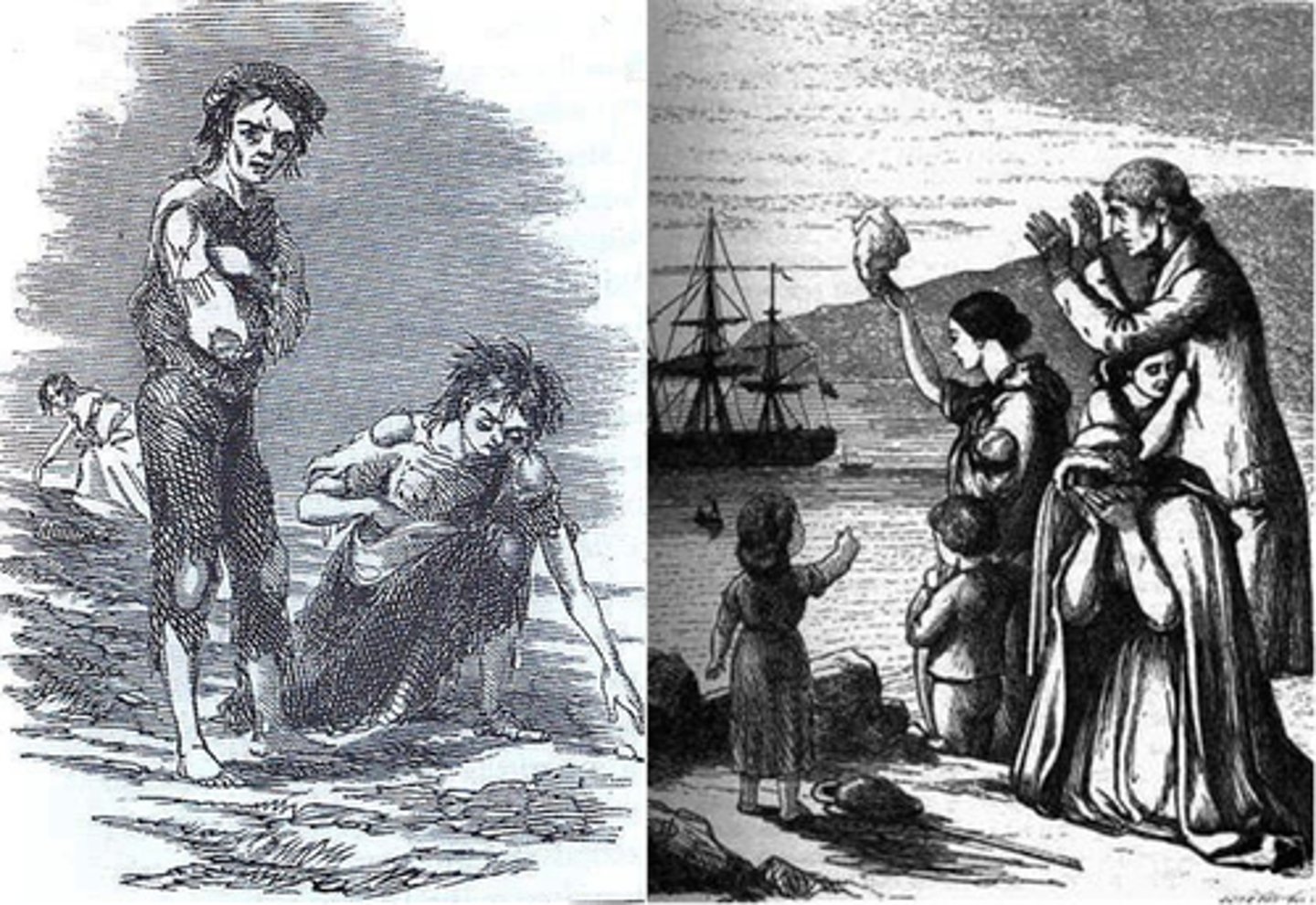
Irish
Group that was Irish Catholic and suffered a potato famine in their home country. Immigrated in large numbers to the US

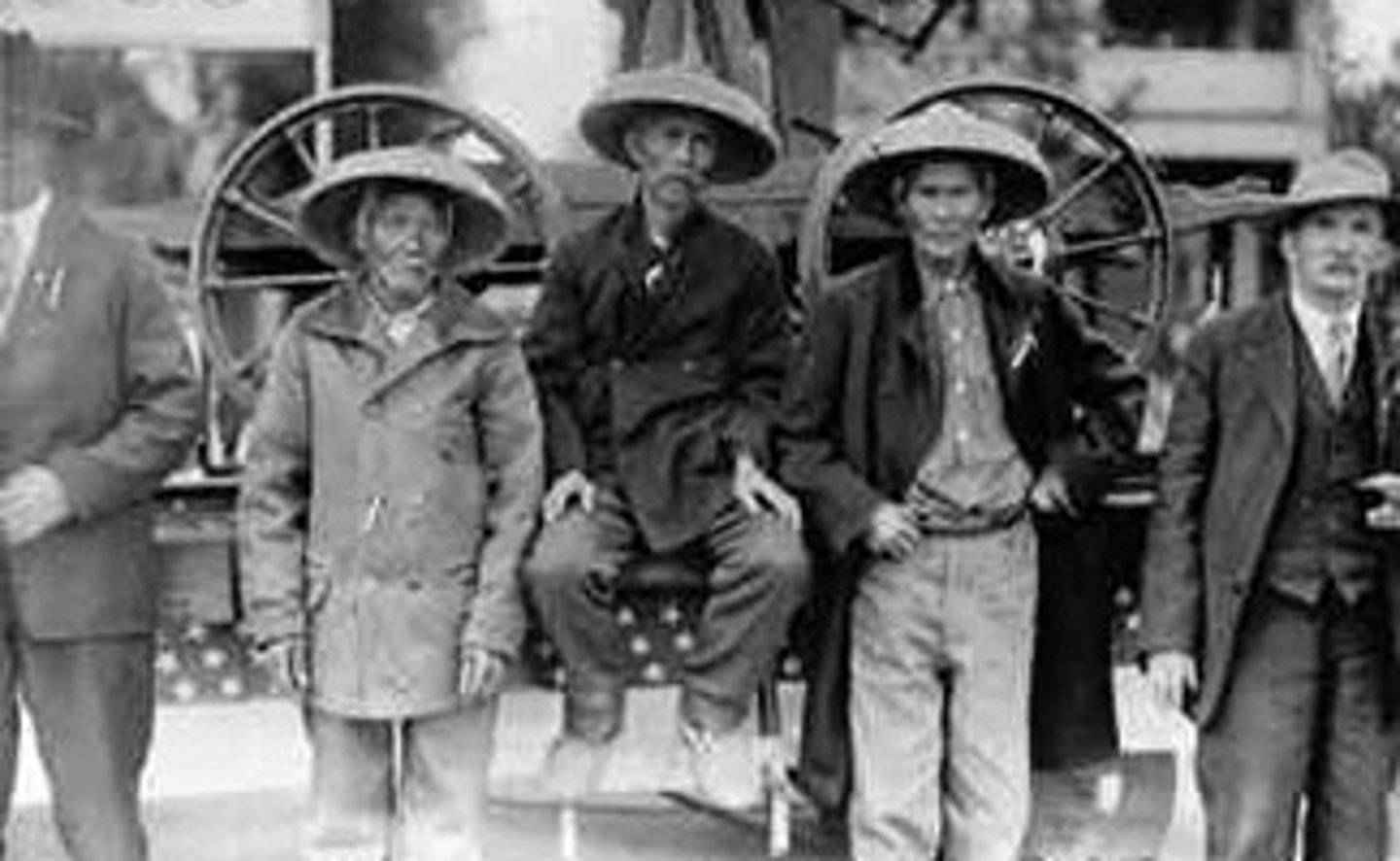
Chinese Immigrants
Came to the U.S. from Angel Island in San Francisco and mainly worked on the railroads for unfair pay and conditions

Social Gospel
Movement led by Washington Gladden - taught religion and human dignity would help the middle class over come problems of industrialization

Anti-trust laws
laws to control monopoly power and to preserve and promote competition

American Federation of Labor (1886)
1886; founded by Samuel Gompers; sought better wages, hrs, working conditions; skilled laborers, arose out of dissatisfaction with the Knights of Labor, rejected socialist and communist ideas, non-violent.

Interstate Commerce Act
1887 law passed to regulate railroad and other interstate businesses

Knights of Labor
First Union Led by Terence V. Powderly; open-membership policy extending to unskilled, semiskilled, women, African-Americans, immigrants; goal was to create a cooperative society between in which labors owned the industries in which they worked

Assimilation
Adopting the culture of a dominant group

Free Enterprise
Economic system in which individuals and businesses are allowed to compete for profit with a minimum of government interference

Political machine
tightly run political operation that allows the head-called a boss- to control elections and government contracts within a city

Plessy v. Ferguson
a 1896 Supreme Court upheld segregation laws, which remained in effect for many decades, particularly in the South

Americanize
one social push of the late 1800's was an effort to assimilate immigrants and American Indians by teaching them white American culture

Advocate
to recommend; to speak in favor of
Corruption
dishonest or fraudulent conduct by those in power, typically involving bribery.

Labor Unions and Strikes
groups of workers who wanted to obtain better working conditions, strikes were held in order to obtain such conditions.

Rural society
Living in the countryside or outside the city

Knights of Labor
labor union that sought to organize all workers and focused on broad social reforms, failed due to diverse goals and being blamed for the Haymarket Square Riot

American Federation of Labor (AFL)
a national organization of labor unions founded in 1886 by Samuel Gompers

Eugene V. Debs
Leader of the American Railway Union, he voted to aid workers in the Pullman strike. He was jailed for six months for disobeying a court order after the strike was over.

Pullman Strike
in Chicago, Pullman cut wages but refused to lower rents in the "company town", Eugene Debs had American Railway Union refuse to use Pullman cars, Debs thrown in jail after being sued, strike achieved nothing

Homestead Steel Strike
In 1892- one of the most violent strikes in America at the Carnegie Steel Company. 7 people died. 300 Pinkerton detectives were hired and there was a battle where they ultimately surrendered.
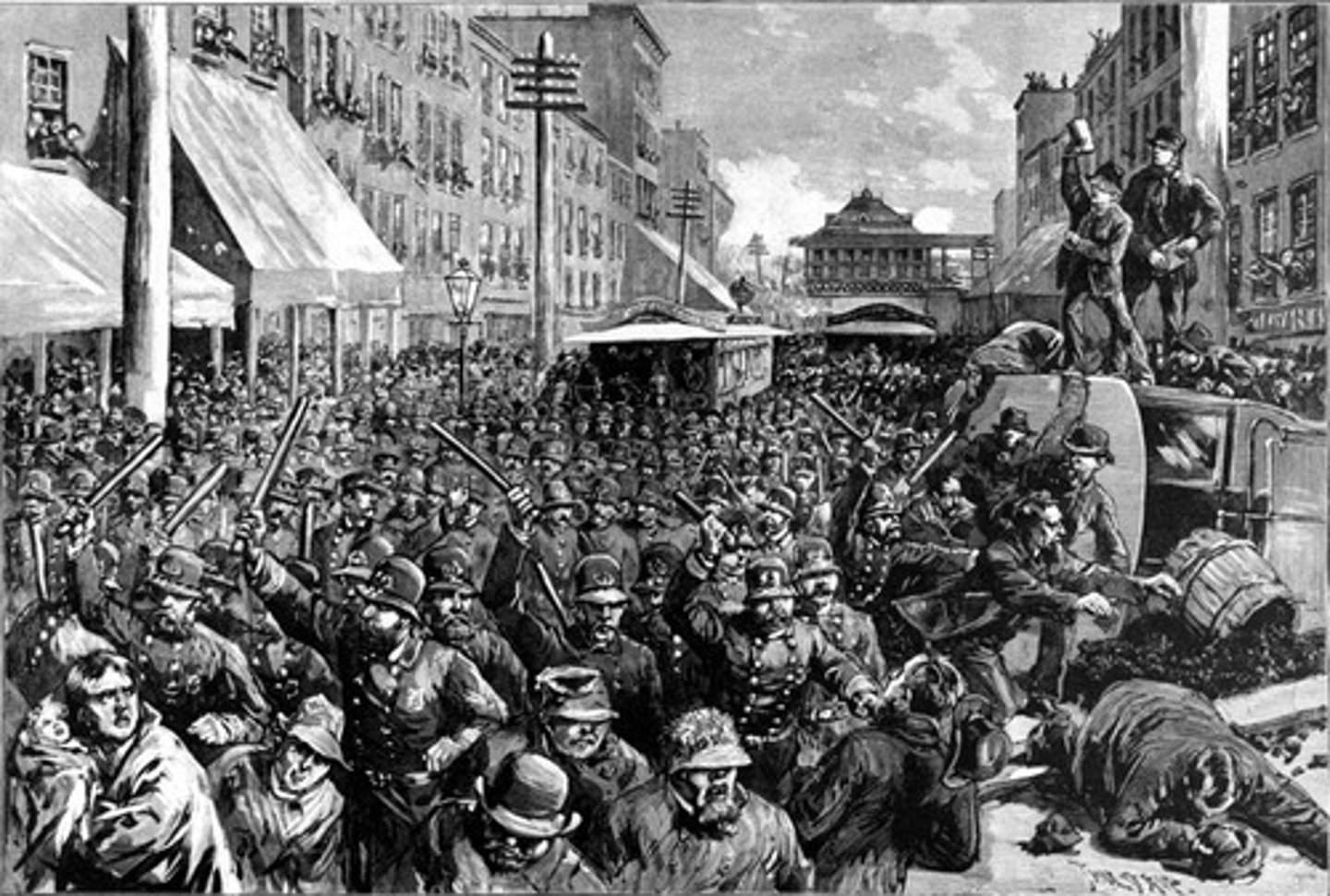

Haymarket Square Riot, 1886
bomb is thrown at a squad of policemen attempting to break up a labor rally. The police responded with gunfire, killing several people in the crowd and injuring dozens more. It set off a national wave of hysteria, as hundreds of foreign-born radicals and labor leaders were rounded up in Chicago and elsewhere. A grand jury indicted 31 suspected labor radicals in connection with the bombing, and eight men were convicted. The Knights of Labor were also blamed for the riot which decrease their popularity.
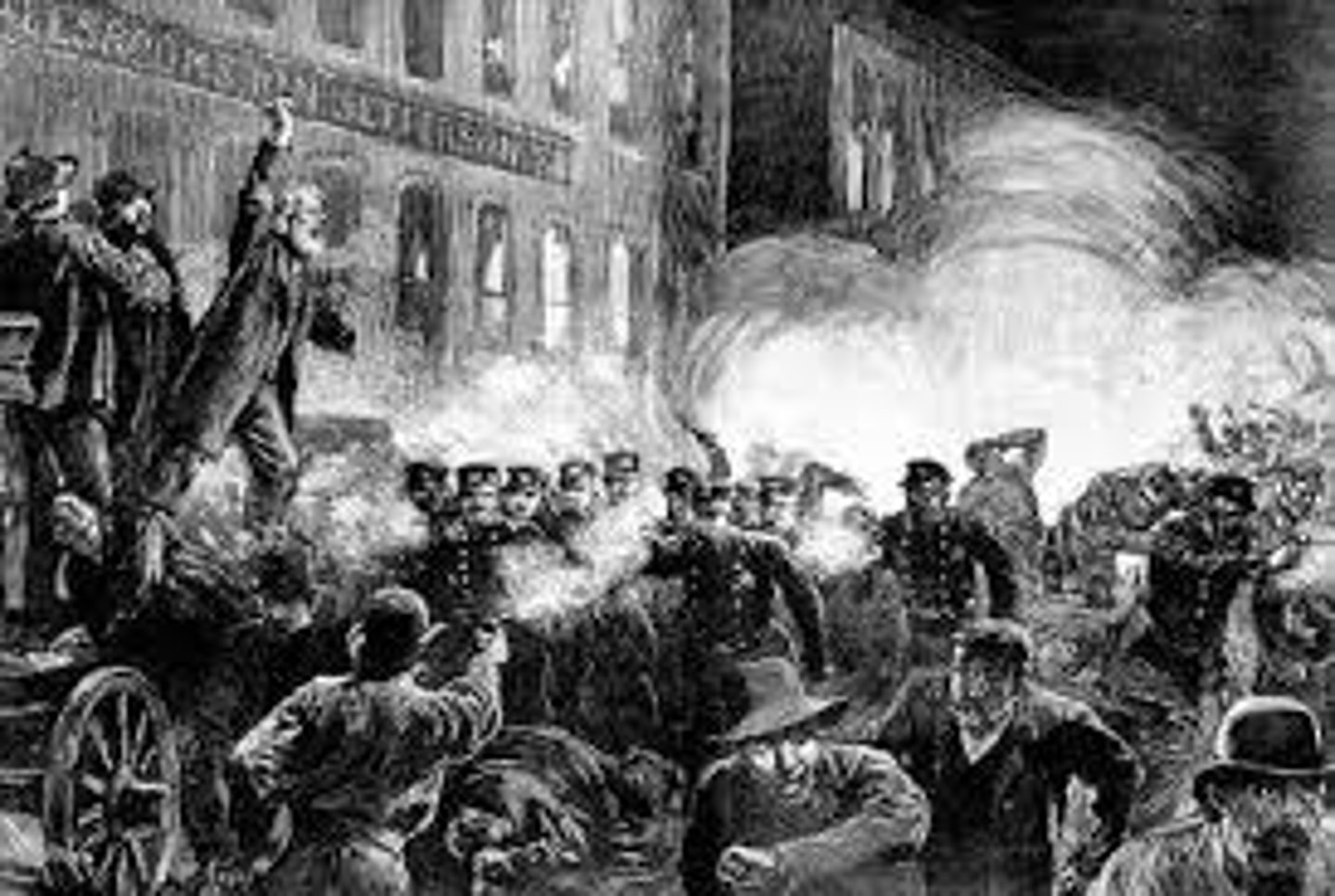

Great Railroad Strike of 1877
A large number of railroad workers went on strike because of wage cuts. After a month of strikes, President Hayes sent troops to stop the strike (example of how government always sided with employers over workers in the Gilded Age). The worst railroad violence was in Pittsburgh, with over 40 people killed by militia men
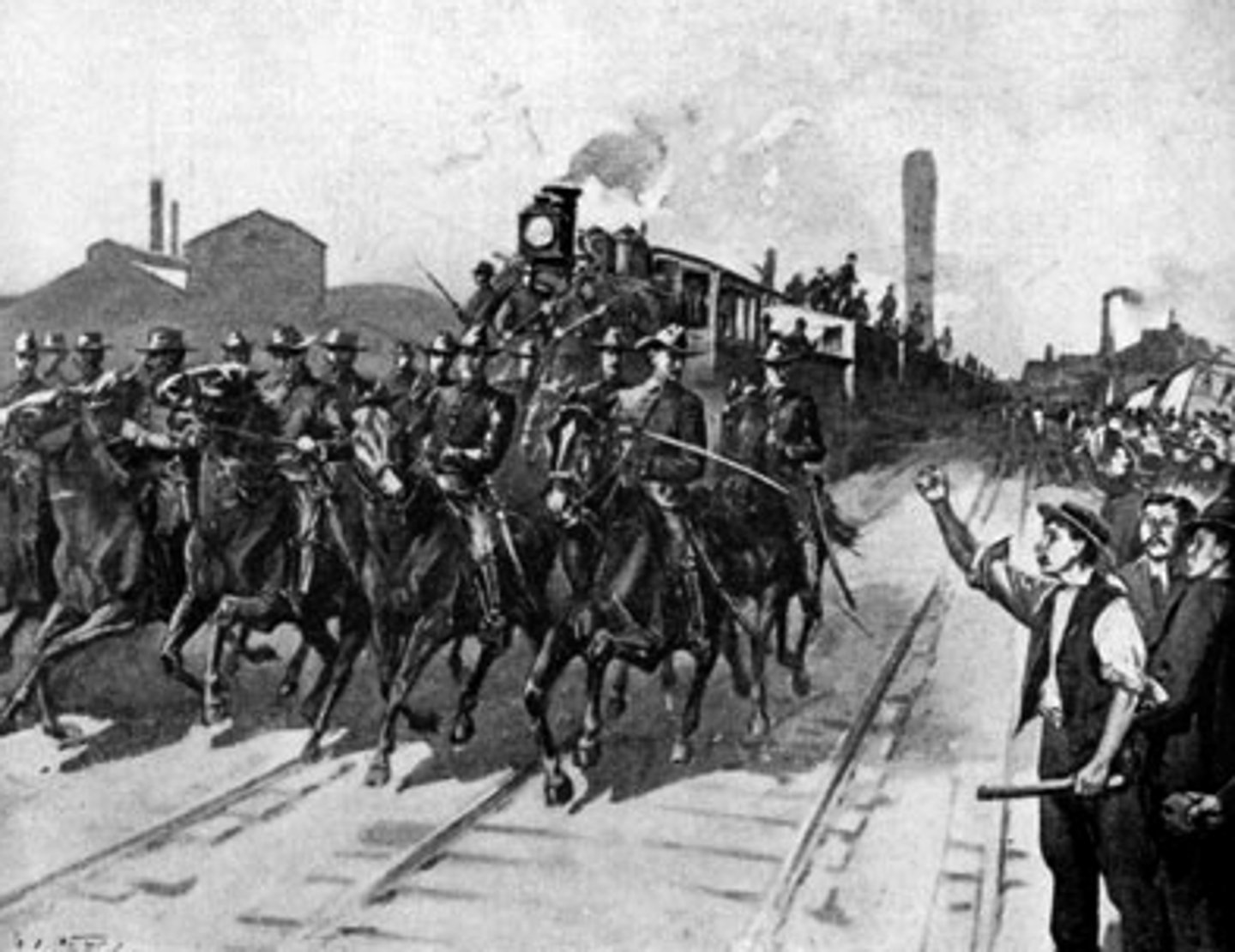

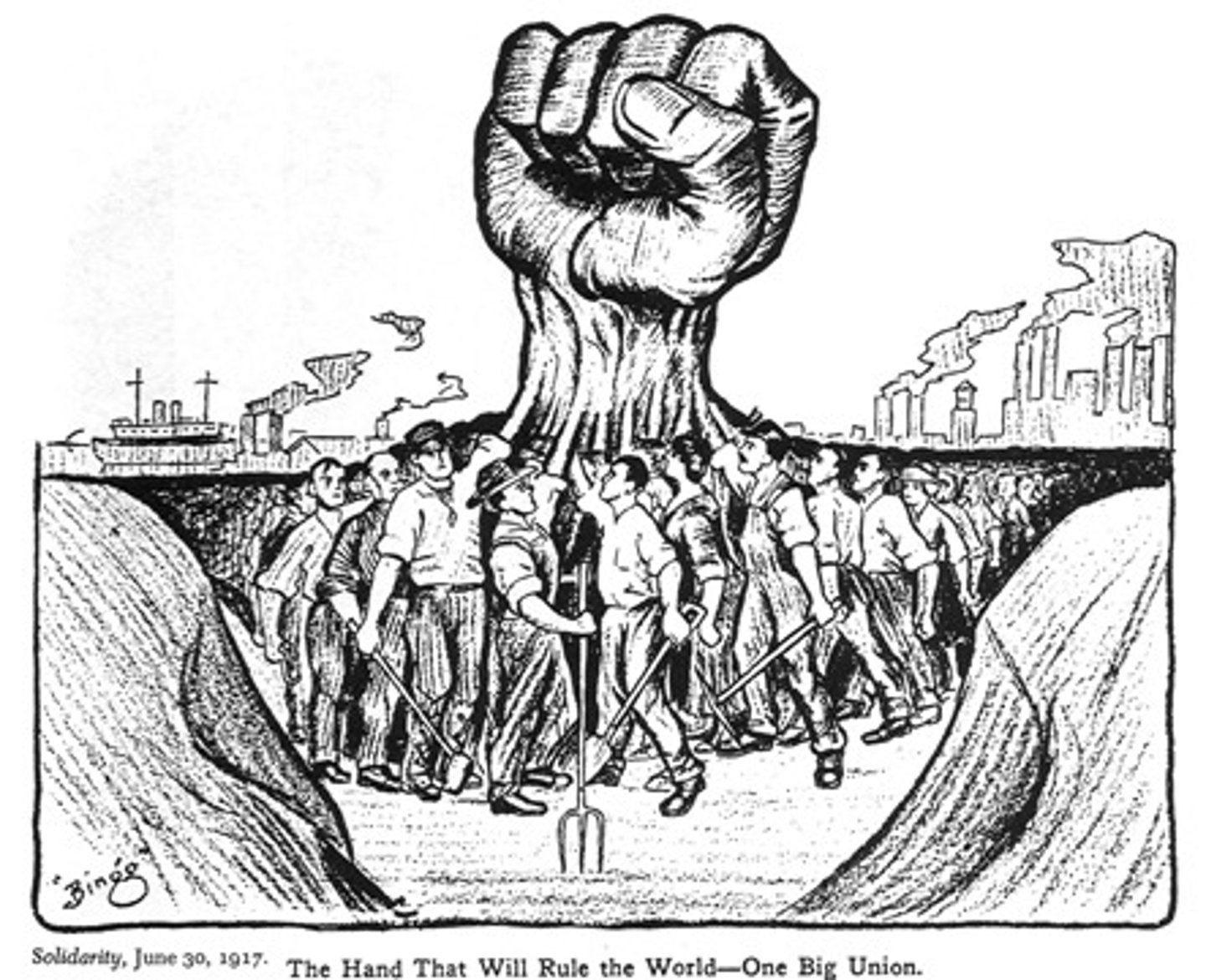
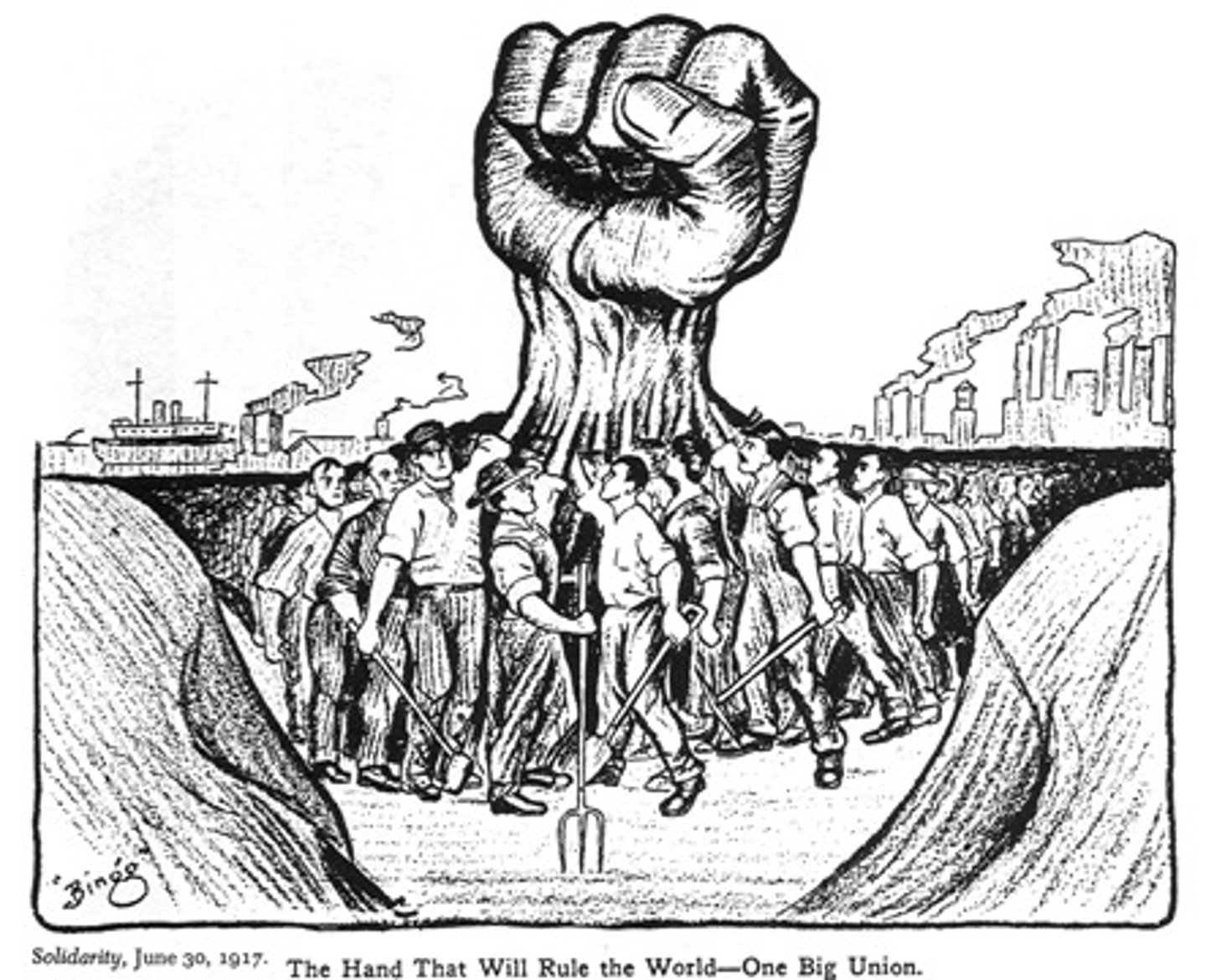
Industrial Workers of the World (IWW)
Founded in 1905, this radical union, also known as the Wobblies aimed to unite the American working class into one union to promote labor's interests. It worked to organize unskilled and foreign-born laborers, advocated social revolution, and led several major strikes. Stressed solidarity.

New immigrants vs. old immigrants
old immigrants from northern and western Europe came seeking better life; new immigrants came from southern and eastern Europe searching for opportunity to escape worse living conditions back home and often did not stay in the US

Pendleton Civil Service Act (1883)
Brought about by the assassination of James Garfield by an immigrant who was angry about being unable to get a government job. The assassination raised questions about how people should be chosen for civil service jobs.
Provided that Federal Government jobs be awarded on the basis of merit and that Government employees be selected through competitive exams. The act also made it unlawful to fire or demote for political reasons employees who were covered by the law. The law further forbids requiring employees to give political service or contributions. The result was more expertise and less politics. An unintended result was the shift of the parties to reliance on funding from business, since they could no longer depend on patronage hopefuls.