Chemical analysis
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What is chromatography
technique that separates out all different compounds in a mixture
what are the two phases in chromatography
stationary phase = column or paper (hydrophillic)
mobile phase = solvent (hydrophobic)
in chromatography how do we know which spot is more polar
spot with the smaller rf value so attracted more to the stationary phase
how do we calculate Rf value
distance moved by sample/ distance moved by solvent
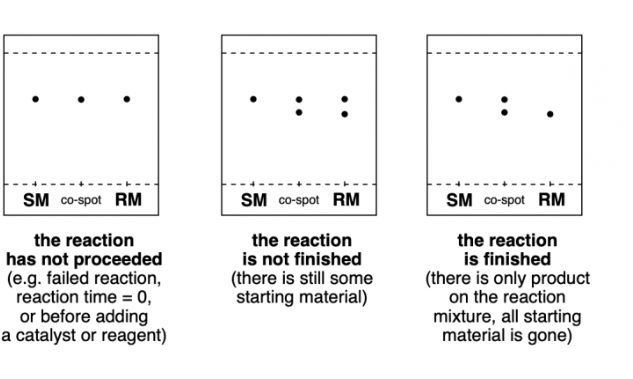
how do we know if the reaction is complete OR not complete in thin layer chromatography
complete = there is no more of the starting material
incomplete = there is still some of the starting material left
impurities do what to the melting point
they lower it
what is empirical formula
what is molecular formula
formula showing simplest ratio of atoms of each element present in a compound
formula showing the Actual number of atoms of each element present in a compound
how to work out molecular formula
empirical formula x whole number
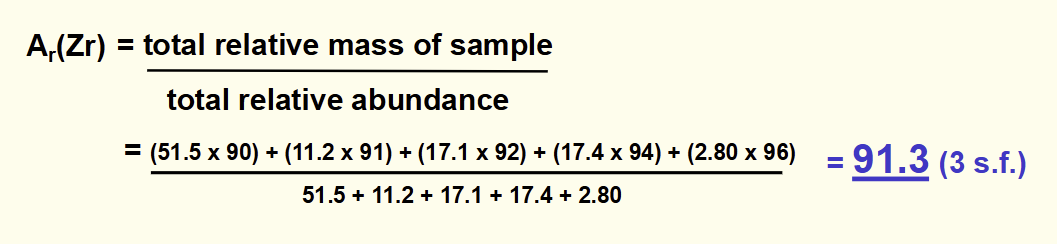
formula for relative abundance
total relative mass of sample / total relative abundance
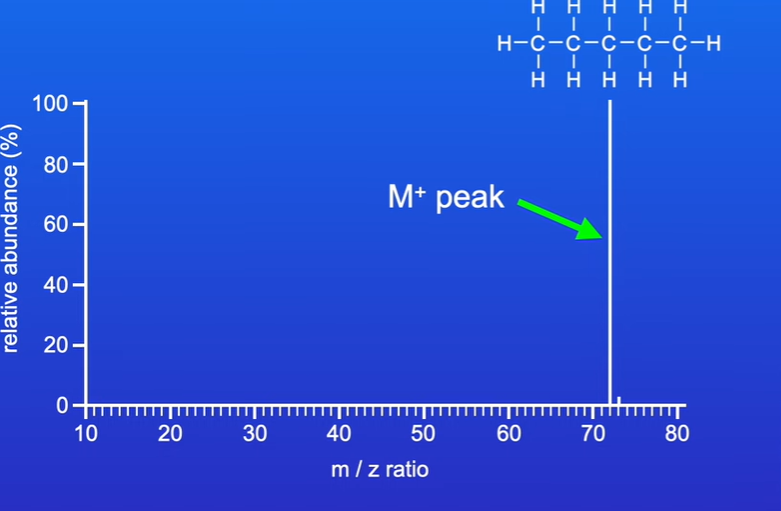
what is the molecular ion peak
peak on the furthest right of spectrum and highest m/v value and also represents molecular weight
in mass spectrum the peak on the far right is the what
why is there a peak there
M+ peak
presence of isotope carbon 13 which represents 1% of carbon atoms
the peak to the right of the M+ peak is the what
M+1 peak and doesnt play a role in fragmentation
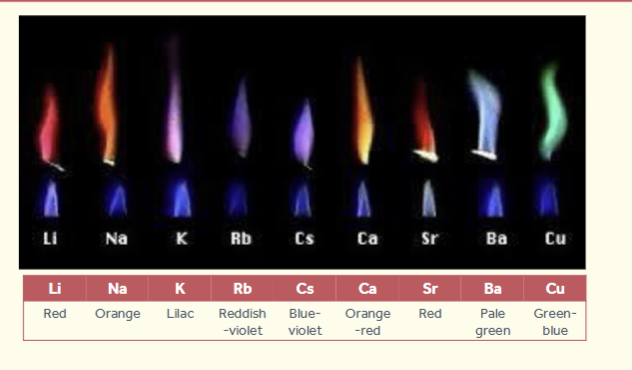
in flame tests what colours do these metals produce:
lithium
sodium
potassium
rubidium
caesium
calcium
strontium
barium
copper
red
orange
lilac
violet
blue-violet
orange-red
red
pale green
green-blue
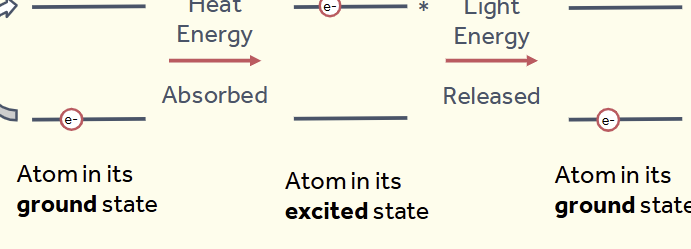
what happens inside the atom when heated
The heat of the flame excites an electron - promotes an outer
electron to a higher energy level
The excited atom then relaxes back to the ground state by
releasing light energy
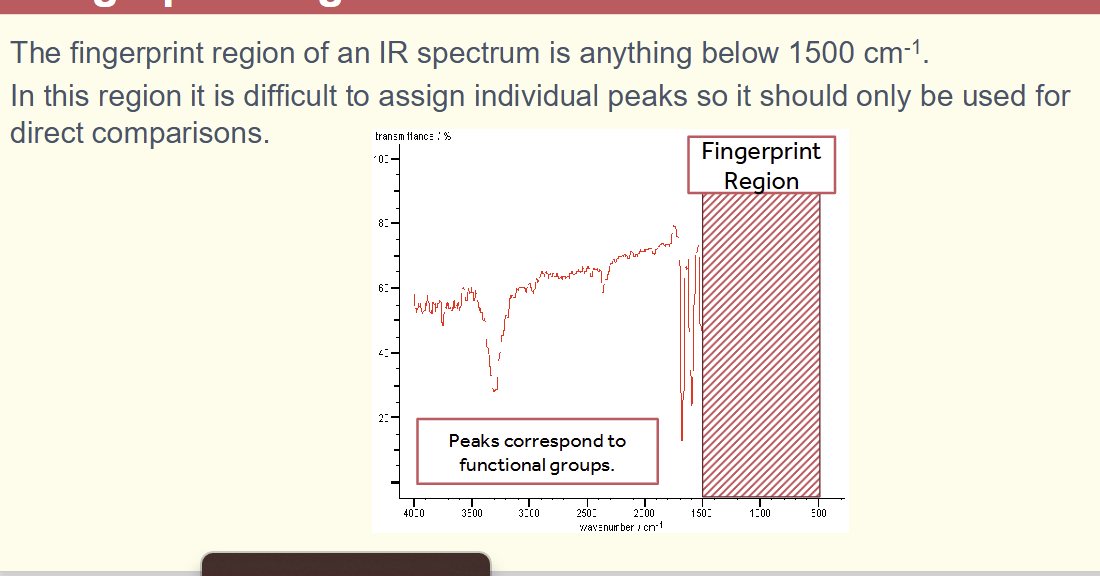
in the infrared spectrum what is the fingerprint region
below 1500
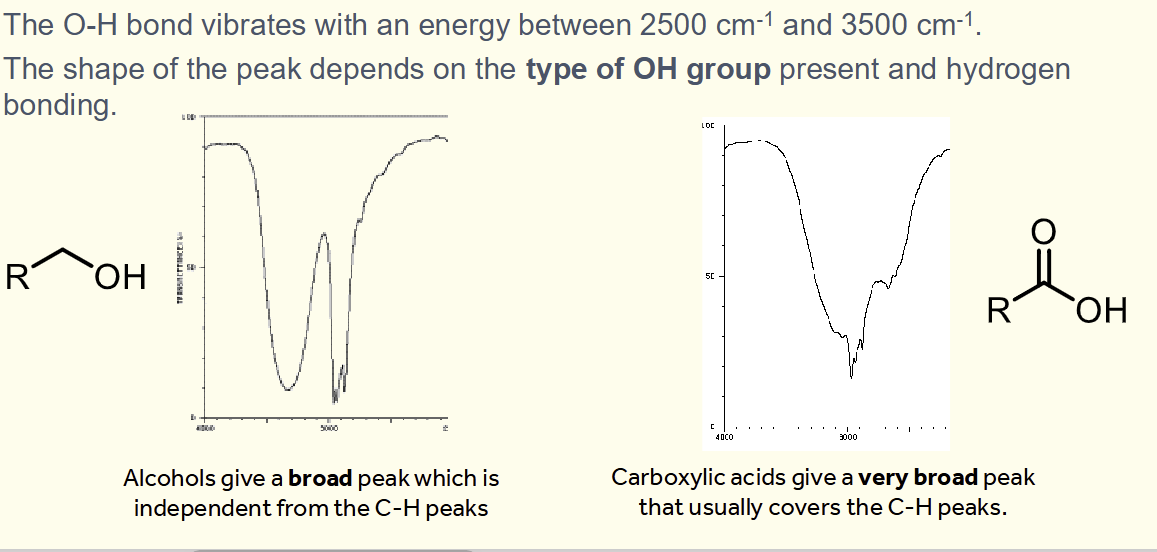
what do the OH on an alcohol and OH of a carboxylic acid look like