Lecture #1 Post-mortem Toxicology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
PMFT stands for...
Post-Mortem Forensic Toxicology
What are the four manners of death?
1. Homicides
2. Accidental
3. Natural
4. Suicides
What is the difference between a coroner and a medical examiner?
A coroner is elected by people or appointed by government while a ME is often appointed by health department.
What are some of the duties that coroners and MEs perform?
1. Performs autospies
2. Conducts investigations
3. Performs toxicological tests
4. Employs services of forensic experts to determine cause and manner of death.
What is the advantage of vitreous fluid?
It is resistant to putrefaction.
What are some things to consider when choosing a specimen?
•Ease of use
•Putrefaction
•PM redistribution
•Matrix issues
•Interferences
•Specimen preparation
•Ease of collection
•Potential for automated analysis
•Sample volume
•Interpretive value
What are the two types of blood specimens?
Peripheral and central
What is the disadvantage of urine as a specimen?
It indicates past drug use and not the "effect".
What are endogenous and exogenous interferences?
Endogenous interference originates from substances present in the patient's own specimen. Exogenous interferences are substances introduced into the patient's specimen.
What are the two types of analysis in PMFT?
Screening (Presumptive) and Confirmation
What are some characteristics of screening tests?
They are rapid, automated, IA-based, require moderate skill level, qualitative, not specific or forensically defensible.
What are some characteristics of confirmatory tests?
They are labor intensive, require a high skill level, quantitative, highly specific and sensitive, and forensically defensible.
What instrument is used to conduct confirmatory testing in toxicology labs?
GC/MS
OTC stands for...
Over-the-counter
T/F: Anything of forensic significance should be confirmed using a second specimen.
TRUE
What are the issues with ethanol as an analyte?
1. PM production
2. Contamination
3. Trauma
What are the three testing levels for drugs?
1. Common drug screen
2. Comprehensive drug testing
3. Specialty testing
Name three drugs in a common drugs screen.
•Opiates
•Cocaine
•Benzodiazepines
•Cannabinoids
•Methamphetamine
•Methadone
•Barbiturates
•PCP
•Propoxyphene
•Acetaminophen
•Salicylate
Name three drugs types in a comprehensive drugs screen, aside from common drugs
•Antidepressants
•Cardiac drugs
•Antihistamines
•Anticonvulsants
•Sedatives
•Hypnotics
•Muscle relaxants
•Opioids
OSAC stands for...
Organization of the Scientific Area Committees
What are some drug interpretation issues?
•Postmortem redistribution
•Trauma
•Contamination
•Antemortem vs postmortem drug concentration
•Parent/metabolite ratios
•Active metabolites
•Polypharmacy interpretation
•Additive, synergistic or antagonistic effects
What are some PM toxicology issues?
1. Putrefaction/decomposition
2. Postmortem production of alcohol
3. Postmortem redistribution of drugs
4. Trauma/contamination
5. Overlap of therapeutic - toxic - fatal concentrations
T/F: Strychnine is a stimulant with convulsant effects.
TRUE
How is strychnine used today?
For veterinary preparations and rodenticides
What are the effects of strychnine?
Heightened stimulation, awareness and muscle spasms.
What is bupivacaine used for?
It is used as a long-acting local anesthetic for surgery
and obstetrics
LSA stands for...
Last Seen Alive
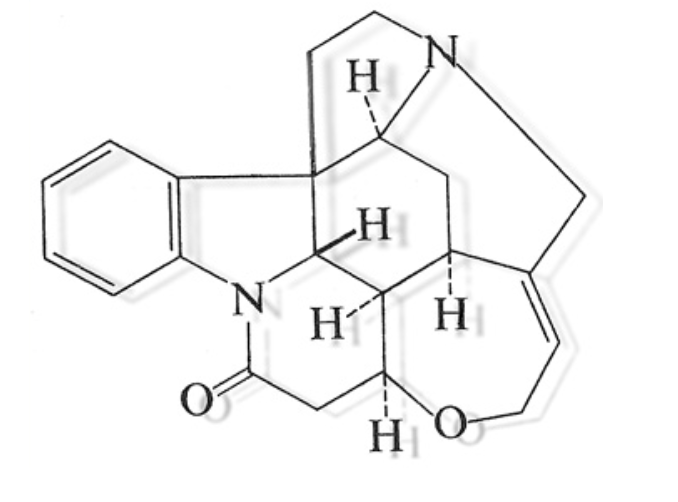
What is the name of this drug?
Strychnine
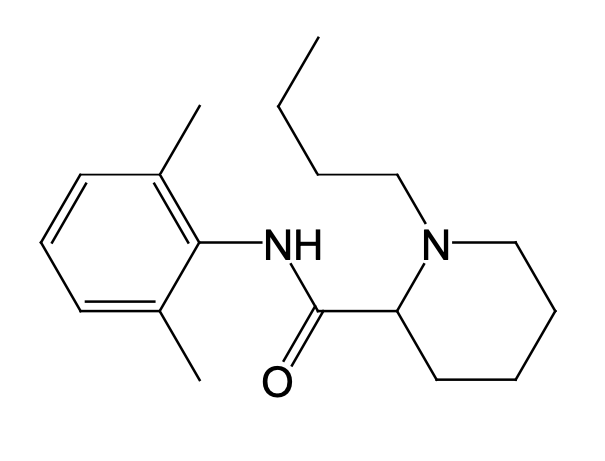
What is the name of this drug?
Bupivicaine