Prosth: POST Midterm Practice Questions
1/157
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
What is the most commonly used impression materials?
Alginate, PVS, polyether
Tissue supported segments are needed to capture functional boarders, so for trays, what should we use?
custom tray
What are some custom tray indications?
history of bone loss, capturing functional boarders, arch shape
When making a custom tray, why do we block out undercuts with baseplate wax ?
so tray material doesn't get locked onto cast
The purpose of the baseplate wax layers is to ...
create space for impression material
What do bubbles or voids in and around the rest seat preparations, occlusal surfaces, or anywhere will cause...
the RPD will contact the tissue
Teeth need to be impressed in which form, vs soft tissues need to be impressed in which form?
anatomical form (teeth), functional form (soft tissues)
What type of impression is a way to capture the functional soft tissues in correct relationship to the teeth>
altered cast impression
Altered cast impressions are most commonly used for what?
distal extension RPDs in the mandible (because mandibular extensions rely on the ridge and buccal shelf for support)
True or False: Altered cast impressions present more equitable distribution of forces between teeth and soft tissue, theoretically less torque in the long-term on abutment teeth
True
When do we use an altered cast impression?
If pressing on the tissue stops intraorally causes anterior portion of the framework to lift away from the teeth
When using an altered cast impression, the original framework tissue stops will no longer be contacting the cast, so what must be placed between the tissue stops and cast for DE support for the remaining clinical try-in steps?
cold-cure acrylic
What do we call the cast the framework will be made from (compare with preliminary cast)?
master cast
When filling out the Rx in DDX (axium), what must you including?
major connector, type of acrylic retention area, rest seats, plates, clasp assemblies, undercuts
What is used to ensure that the framework will not impinge on soft tissues or extend into embrasures which would prevent it from seating?
wax block out (relief)
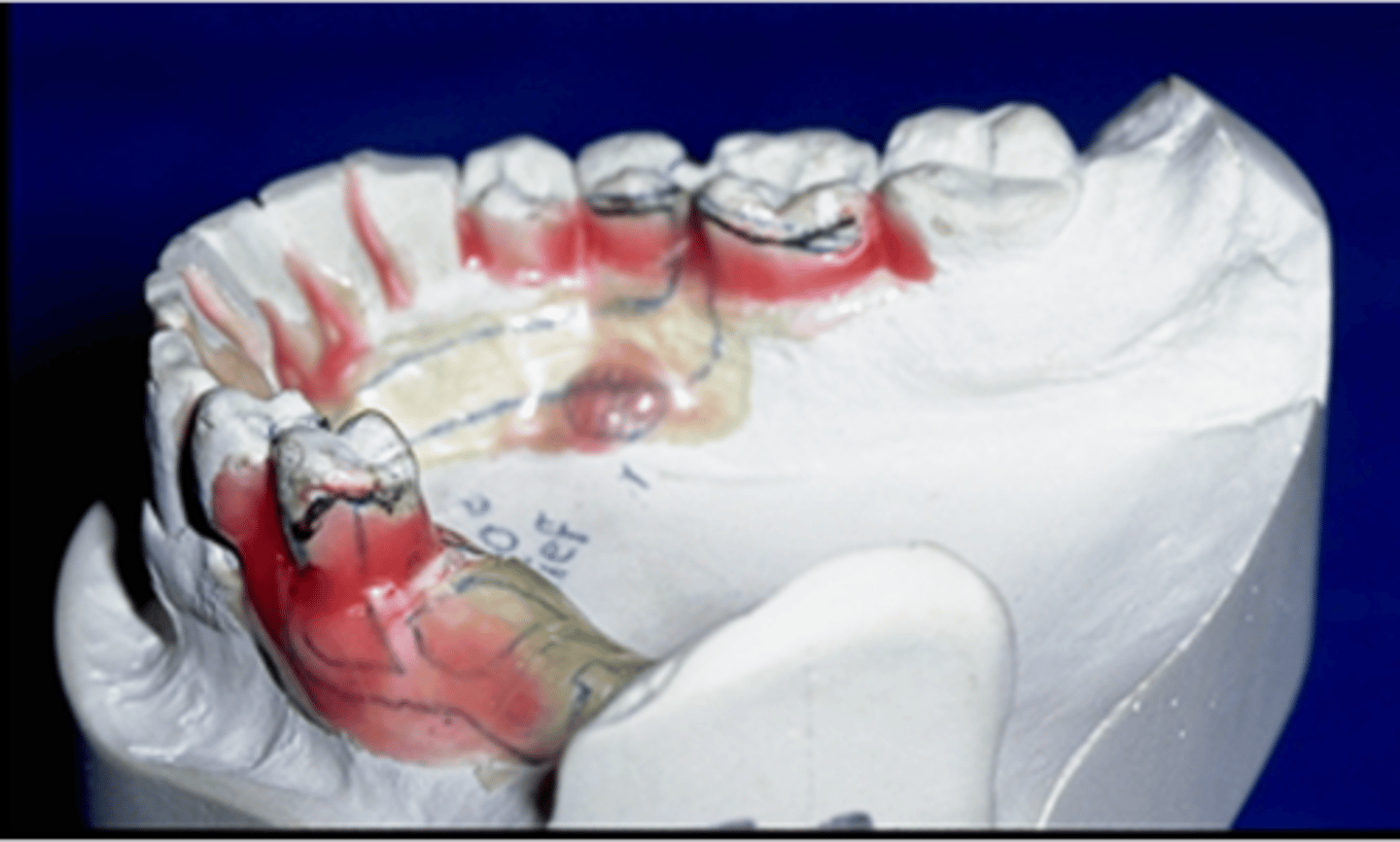
What is necessary to provide space for acrylic between the framework and the soft tissue to allow acrylic retention?
relief wax
What is relief wax also necessary for?
under mandibular major connectors and over small tori
the wax-up of the RPD framework is completed on which cast?
refractory cast
What are placed on the refractory cast?
preformed wax shapes
What is the only portion of wax visible when everything is encased?
Sprue
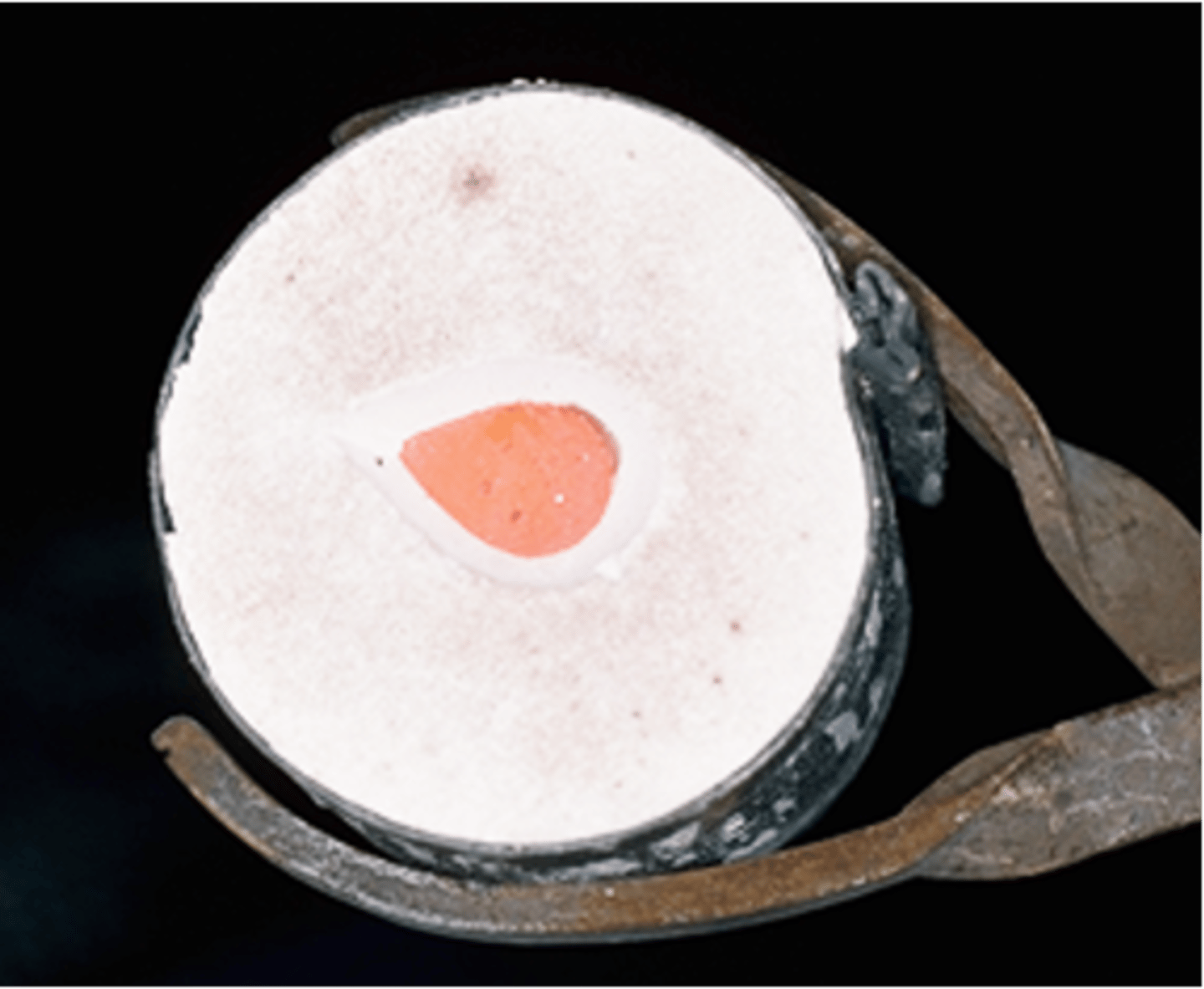

The purpose of the sprue is, after burnout, to ...
provide a pathway for molten metal to flow into the space where the wax previously was
What are the benefits of the digital process of designing framework
eliminates the refractory cast, takes less time, has the advantage of preservation of framework "waxup"
T or F: casting of resin 3D printed pattern is More reliable than Selective laser melting
False (Selective laser melting is more reliable)
Criteria for selecting framework materials
Biocompatibility, Biologically Inert, Versatility, Rigidity, Resilient
What are some framework casting alloys?
Co-Cr (Vitallium), Co-Cr-Ni, Ni-Cr (and Ni-Cr-Be) (Ticonium)
What are the advantages of:
•Co-Cr (Vitallium)
•Co-Cr-Ni
•Ni-Cr (and Ni-Cr-Be) (Ticonium)
lightweight, corrosion resistant less expensive than gold alloys, high strength and modulus of elasticity
What are the disadvantages of:
•Co-Cr (Vitallium)
•Co-Cr-Ni
•Ni-Cr (and Ni-Cr-Be) (Ticonium)
production of dental appliance is complex, high-fusing temperature, extremely hard, not usually adaptable to a laboratory in a dental office
What are the brand names for Co-Cr
Jelenko JD, Nobilium, Vitallium
From the Co-Cr framework, what percent is cobalt?
60%
What part of the Co-Cr framework increases elastic modulus, hardness, and strength?
cobalt
From the Co-Cr framework, what percent is chromium?
25-30%
What part of the Co-Cr framework by its passivating effect, insures corrosion resistance acts in solid solution hardening?
Chromium
Co-Cr-Ni element percents
50% cobalt, 25% chromium, 19% nickel (and minor components)
Ni-Cr (Ticonium) element percents
70% nickel
16% chromium
(aluminum and beryllium are important minor components)
What is the main disadvantage when using Co-Cr-Ni or Ni-Cr as your framework material?
nickel sensitivity or allergy
Which alloy does this effect describe: effects precipitation hardening and increases ultimate tensile strength and yield strength
Al
Which alloy does this effect describe: hardener and grain structure refiner, generally added to reduce fusion temperature
Be
Which alloy does this effect describe:
deoxidizer and hardener, reduces ductility and markedly increases hardness, widens melting range and reduces solidus temperature
Bo
Which alloy does this effect describe:
small variations (0.2% can affect strength, hardness, ductility), small amounts increases strength, excess produces severe brittleness
C
Gold Alloys: Type IV gold (hardest gold alloy) advantages
Casts well into crowns with semi-precision attachment components, Less likely to break
Gold Alloys: Type IV gold (hardest gold alloy) disadvantages
high cost, Heavier, Less corrosion resistant
What framework step does this describe: Disinfect the framework, and place in the mouth. DO NOT let the patient insert and remove the framework AT ANY POINT during this appointment.
1. Evaluate and adjust intaglio
T or F: Most frameworks do not require adjustment to fully seat in the mouth
False (they do!)
Should you adjust a proximal plate?
NO
Should you adjust contact at the base of the lingual plate at the FGM?
YES
What is step two in the framework try-in sequence?
Evaluate occlusion with opposing dentition
T or F: Even if the framework does not seat completely, you can still continue to check the occlusion
False (Only proceed with checking occlusion if the framework seats completely. If it does not, new framework is indicated.)
What should you note for occlusion before checking occlusion with framework in the mouth?
Note occlusion of dentition with framework not in the mouth
What is each side of the horseshoe articulation paper used for?
one side for natural dentition and other for when framework is in place
Which type of movements should you check with articulating paper?
static and excursive
The rest-minor connector junction cannot be less than how many mms?
1.5mm
In step 3 of the framework try in, you Evaluate need for altered cast impression by pressing towards the tissue near the tissue stop. What indicates if an altered cast impression is required?
if the base can be depressed enough that the indirect retainer or lingual plating lifts away from the teeth,
What must there be around the arch in order to relate the upper to the lower cast?
tripod of opposing contacts
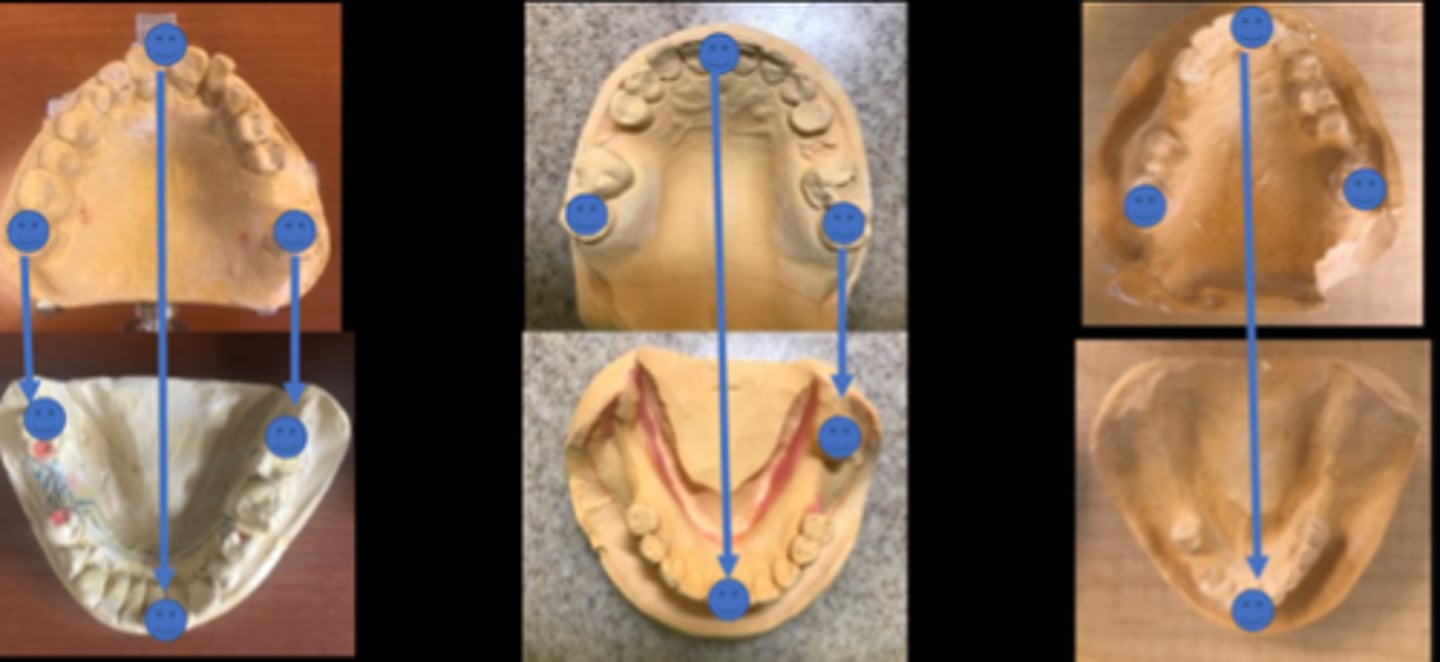
What is necessary when there aren't enough opposing contacts?
wax rim and record base
When should you use record bases and wax rims?
There are opposing distal extensions, Tooth-bound edentulous area is large, When remaining teeth are not opposing one another
What on a denture tooth can cause unseating of other components, and/or make the tooth more susceptible to fracture off the base?
Canine guidance
T or F: Ideally, there should be no contact on denture teeth in excursive movements if the patient has enough natural dentition.
True
Generally, if a patient has canine guidance without the RPD, should it be maintained?
yes (this should be maintained with the RPD)
If the patient has group function without the RPD, what should you consider before deciding if denture teeth will contact in excursive movements?
overjet and overbite requirements
What do you check in a tooth try in?
Esthetics, Phonetics, Occlusion
T or F: The doctor, not patient, should insert and remove the RPD until the very last step
True
What are the RPD delivery steps?
1. Adjust intaglio
2. Adjust peripheral extension
3. Adjust occlusion
4. Check for instability/rocking
5. Adjust clasp
6. Have the patient practice insertion and removal
If the patient has pain when you attempt to insert the RPD, what may need to be relieved first?
flange undercuts
White paste used to locate pressure points on the tissue side of a denture
PIP (pressure indicating paste)
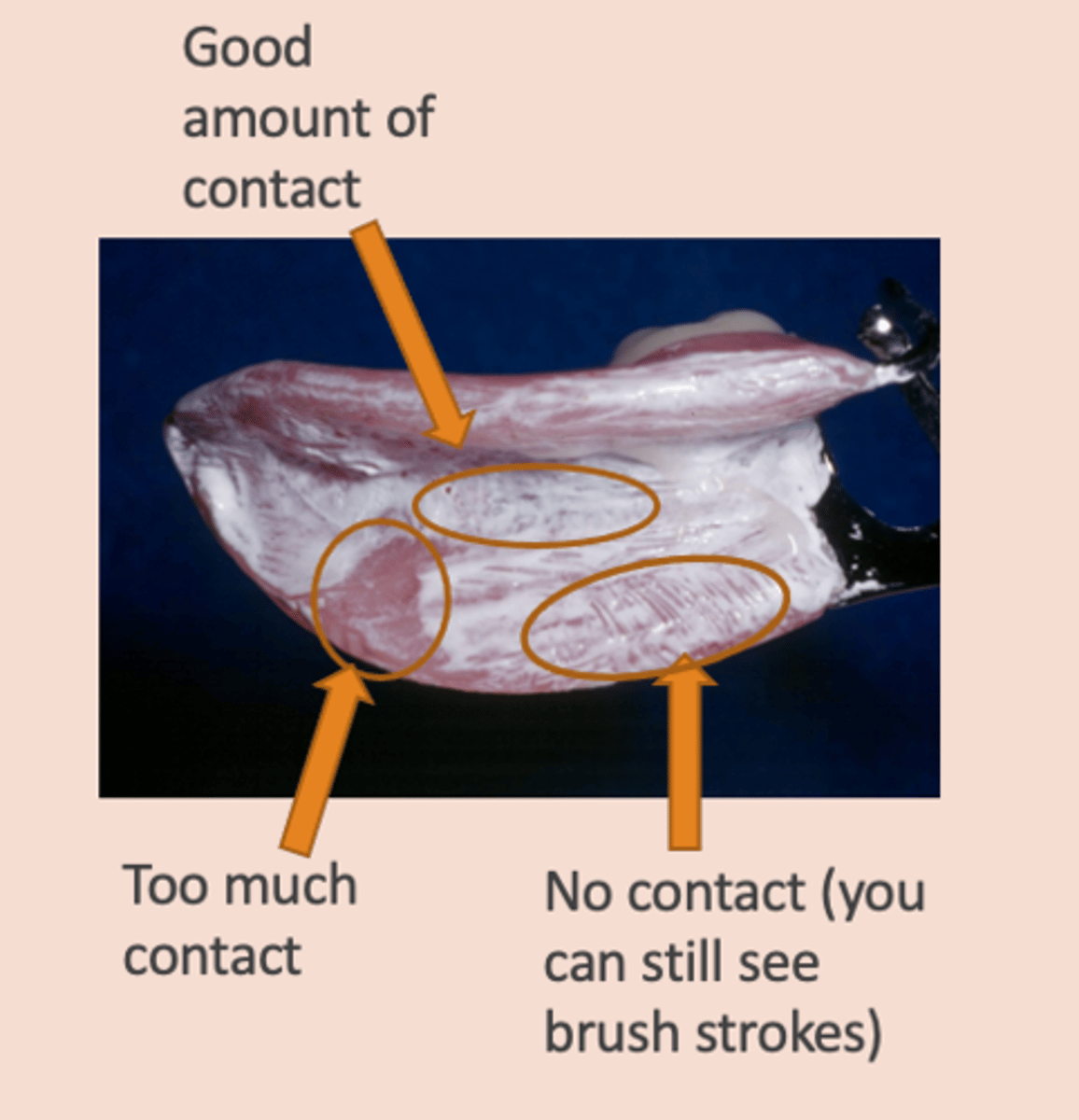
Adjusting peripheral extensions: Overextension of the denture bases may lead to ...
irritation of the soft tissue, displacement of the RPD, or cause RPD to not seat completely
T or F: there should be no contact on denture teeth in excursive movements if the patient has enough natural dentition
True
Excursive contacts cause denture teeth to do what?
de-bond from the acrylic
Non-centric forces on an RPD are what type of force?
unseating forces (RPD may fall out and/or clasps will loosen sooner)
If distal or mesial extension, check for what?
A-P rocking
(similar to evaluating for need for altered cast impression)
Watch to see if anterior rest seats rise up off of rest preps. If not, you're fine.
If yes, need to consider reline impression)
T or F: During a RPD delivery, you need to confirm that there is no clasp contact with the teeth
False (there must be clasp contact with the teeth)
Reasons there may not be contact between clasp and teeth
Numerous framework removals from master cast (during fabrication process), Induced during deflasking procedure, Induced during polishing procedure
What should you use to adjust the clasps if necessary?
wire benders/pliers
What happens if you overbend/rebend cast metal multiple times?
fracture
RPD follow up times
24 hour, 1 week, 1 month
If there is Soft tissue pain Irritation, Inflammation, or ulceration Adjacent to flange edge, what is the cause?
overextension
If there is soft tissue pain Irritation, Inflammation, or ulceration on soft tissues OTHER than on flange edge, what is the cause?
Roughness of the denture base (use PIP to identify), Occlusal discrepancies or prematurities
Adjust RPD adjacent to any ulcerations, after using what to disclose contact of ulceration with RPD?
indelible ink stick (Thompson stick)
What are the causes of abutment tooth pain?
Occlusal prematurities, Clasp too tight, mobility of RPD (tooth abutment adjacent to distal extension, lack of soft tissue support), increased loading of abutment (extension bases), (caries, fracture, endo issue, perio issue)
What are the causes of gagging?
Vertical dimension of occlusion too high,
(Maxillary RPD) Poor adaptation or overextended posteriorly,
(Mandibular RPD) Poor adaptation or overextended distally and/or lingually
What are the causes of change in phonetics?
Improper placement of the teeth (usually anterior tooth placement but could be premolars), Changes in contour of the anterior palate / rugae coverage
(Give patient 1 - 2 weeks to adapt)
What does insufficient horizontal overlap of the posterior teeth, Long-term absence of posterior teeth, or Teeth set too far lingually lead to?
cheek or tongue biting
Fatigue and mishandling of retentive clasps, overextended flange, OR diet - sticky foods and gum can lead to what issue for RPD?
Instability of the RPD or lack of retention
At every periodic oral exam, what should you check?
occlusion, adaptation, stability, prosthesis
When should you consider replacing the RPD?
Teeth are very worn, Teeth have no occlusion when patient is in CR
or MIP, Major connector maladapted to soft tissues
If the only issue is edentulous areas are not in contact, what is necessary?
reline or rebase (helps decrease torqueing forces to abutment teeth, especially for extension base situations)
How many mm of alginate needs to be present under the denture base/ if the indirect retainer lifts how many mm or more, will the patient be considered a candidate for a reline or rebase?
2mm
The re-adaptation of the intaglio of a prosthesis after tissue changes occur to re-establish contact with tissues. Used when denture teeth and base are in good condition.
Reline
The re-adaptation of the intaglio of a prosthesis after tissue changes occur to re-establish contact with tissues, replacing the entire pink acrylic (sometimes the teeth too). Used when denture teeth and/or base are NOT in good condition, OR denture bases are underextended
Rebase
In which process, reline or rebase, is direct or chair-side maintenance not possible?
rebase
Interim RPDs
Which type of RPD is used while other dental treatment is being performed; usually followed by definitive metal framework RPD?
-function for a limited period of time, after which it is to be replaced by a definitive RPD
medical problems, allergy (Ni), refuse metal showing, previous success with non metal framework
Why would you use "other" RPDs?
caries control, extraction healing, implant placement, perio tx, unexpected loss of teeth, finance issues, occlusal support during fixed removable cases
When do you use interim RPDs?
wrought wire
interim RPDs most often uses which clasp assembly for retention?
False (because acrylic is not as strong as metal, and it will crack)
T or F: For interim RPDs you can use an open plate or A-P strap design for the maxillary
full palate to horseshoe
What does the maxillary coverage for interim RPDs usually consist of?
always use a plate
What is the design (major connector) you use for a mandibular interim RPD?
NO!
Can you use lingual bars, sublingual bars, or labial bars for a mandibular interim RPD?
flipper
a term used to describe an interim RPD replacing only 1 or 2 front teeth, with or without clasps, and in these cases the acrylic on the hard palate may terminate short of where a metal framework would terminate
True
T or F: "Flippers" are weak and can break easily so therefore are not a long-term solution to a missing tooth
you survey to determine where heights of contour will allow wrought wire
For an interim RPD, during the first step in the LAB, what do you do differently than a regular removable denture procedure?