MCB Ch 13 Cell Communication
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
If a cell receives no signal…
death by apoptosis
Requirements for cell-cell communication:
signal
receptor
signaling proteins
modification of target proteins
Gap junctions
the cytoplasms of adjacent cells are connected through connexons
occur in animals
Connexons
hollow transmembrane complexes of connexin proteins
Plasmodesmata
occur in plants
no transmembrane protein systems
plasma membranes of adjacent cells are fused through holes in the cell walls
Juxtacrine
direct cell-cell contact
signal and receptor are both surface molecules
Endocrine signaling
hormones
the secreted signals enter the circulatory system
the signals are stable and can reach distant target cells
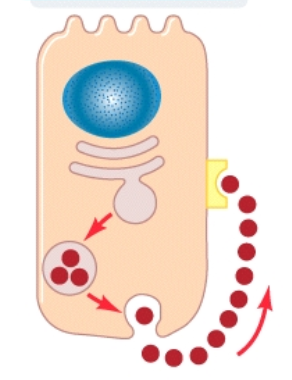
Autocrine signaling
the secreted signal can trigger responses in the same cell that secretes it
Paracrine Secretion
secreted signals can only reach neighboring cells
signals do not enter circulatory system
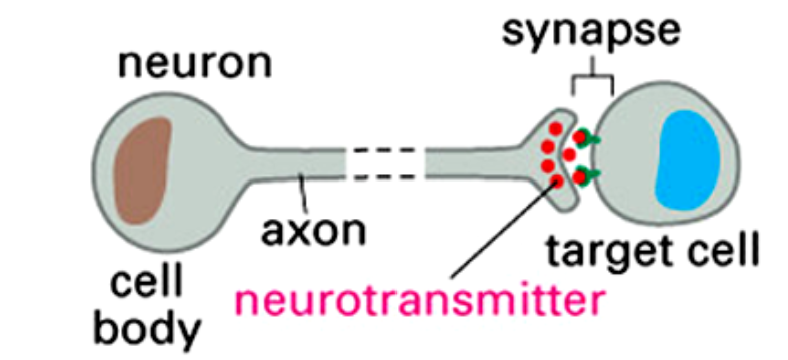
Synaptic signaling
special type of paracrine signaling: the target is the postsynaptic cell, in a permanent interaction
signals are neurotransmitters (stored in synaptic vesicles at the axon terminal of the neuron) that are released and reach the target cell over a small gap : chemical synapse
The propagation of electric signals is caused by ____ through the axon membrane by the alternating opening, inactivation, and closing of _______
ion currents
voltage-gated ion channels
Presynaptic membrane =
axon terminal
Postsynaptic membrane =
target cell
Ions that flow through the postsynaptic membrane after a neurotransmitter opens ion channels may have an ___ or ___ effect
Excitatory ; inhibitory
Excitatory neurotransmitters
cause the depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
open Na+ channels and cause inflow of ion
can trigger action potentials
Membrane Polarization = EPSP
Inhibitory neurotransmitters
cause the hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic membrane
they open Cl- channels on the membrane and cause inflow of ion
prevents action potentials
Membrane Depolarization = IPSP
Acetylcholine (ACh)
neurotransmitter that crosses the synapse b/w motor neuron and skeletal muscle
excitatory neurotransmitter in neuromuscular junctions
opens ACh - gated Na+ channels
depolarizes muscle cells (EPSP)
triggers action potentials and the contraction of the muscle cell
Which enzyme degrades ACh to terminate the signal and allow the muscle to relax?
Acetylcholinesterase
Glutamate
Excitatory neurotransmitter in CNS
glutamate receptors are Na+ and Ca2+ channels
modulated by reuptake into neuron
excessive stimulation by glutamate results in neurodegeneration (Huntington’s disease)
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
inhibitory neurotransmitter in CNS
receptors are gated Cl- channels
important for neural control of body movements and brain functions
modulated by reuptake into neuron
Valium and Xanax enhance binding of GABA to receptor
Dopamine
excitatory biogenic amine in the CNS
causes EPSP (depolarization)
controller of body movements and pleasure sensations
activity is controlled by reabsorption
if dopamine-releasing neurons degenerate, tremors occur (Parkinson’s disease)
molecules removed from synapse by transporters
Dopamine is active in what pleasure pathways in the brain?
amygdalae, part of the limbic system
Reabsorption of dopamine can be blocked by…
cocaine
Down-regulation
response by post-synaptic cell, decreasing number of surface dopamine receptors due to overstimulation by cocaine
Serotonin
EPSP/IPSP depending on the receptor
regulator of sleep and emotional stress
activity is controlled by reuptake into neuron
insufficient serotonin activity may result in clinical depression
Which drug is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor?
Prozac
→ it blocks reabsorption of serotonin so more is available for the stimulation of post synaptic cells
Ecstasy causes..
massive release of serotonin
LSD
psychoactive drug that acts on some excitatory serotonin receptors
Neuropeptides
short chains of amino acids
Substance P
released at synapses in the CNS by sensory neurons and are activated by painful stimuli (P = pain)
excitatory(EPSP): results in pain sensations
Intensity of pain is modulated by …
endogenous opiates
Endorphins
are endogenous opiates. produced by brain to block pain perception
Morphine & Heroin
are exogenous opioids
they have analgesic (pain reducing) effect because they can bind to endorphin receptors
Synthesis and diffusion of NO (nitric oxide) results in:
relaxation of the smooth muscles surrounding blood vessels
dilatation of blood vessels and increased blood flow
Synthesis of NO (nitric oxide) is stimulated by
acetylcholine