Nucleotides and phosphodiester bonds
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
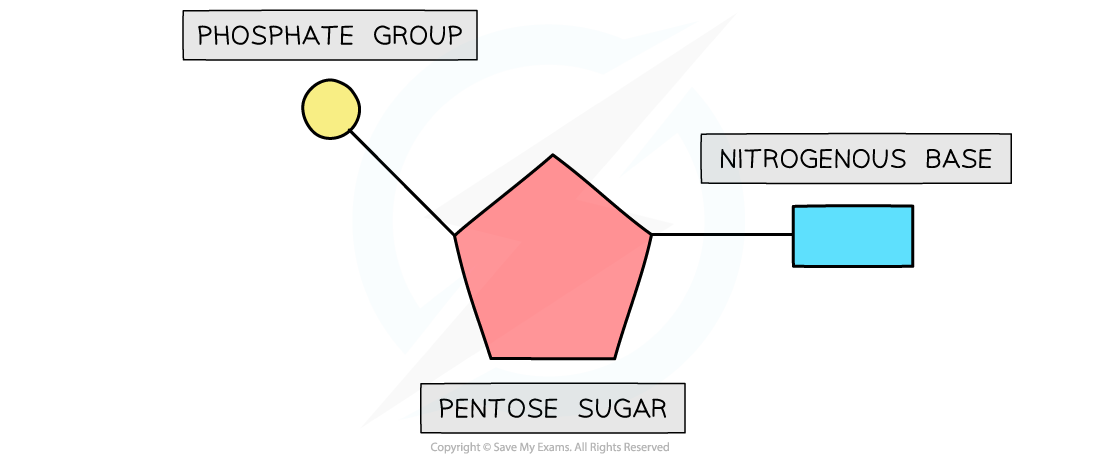
What is a nucleotide and what are its three components? ( draw diagram of structure too)
A nucleotide is the monomer of DNA and RNA.
It consists of:
Pentose sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
Nitrogen-containing base
Phosphate group
Nucleotides join to form polynucleotides (DNA/RNA).
What are the components of DNA and RNA nucleotides?
DNA nucleotide:
Pentose: Deoxyribose
Bases: A, C, G, T
Phosphate group
RNA nucleotide:
Pentose: Ribose
Bases: A, C, G, U
Phosphate group
DNA contains thymine; RNA contains uracil
DNA has deoxyribose; RNA has ribose
Which bases are purines and which are pyrimidines? What is the difference?
Purines (double-ring):
Adenine (A)
Guanine (G)
Pyrimidines (single-ring):
Cytosine (C)
Thymine (T)
Uracil (U)
What is the structural difference between ribose and deoxyribose?
Both are pentose sugars.
Ribose has –OH on carbon 2
Deoxyribose has –H on carbon 2
Therefore, deoxyribose has one fewer oxygen atom.
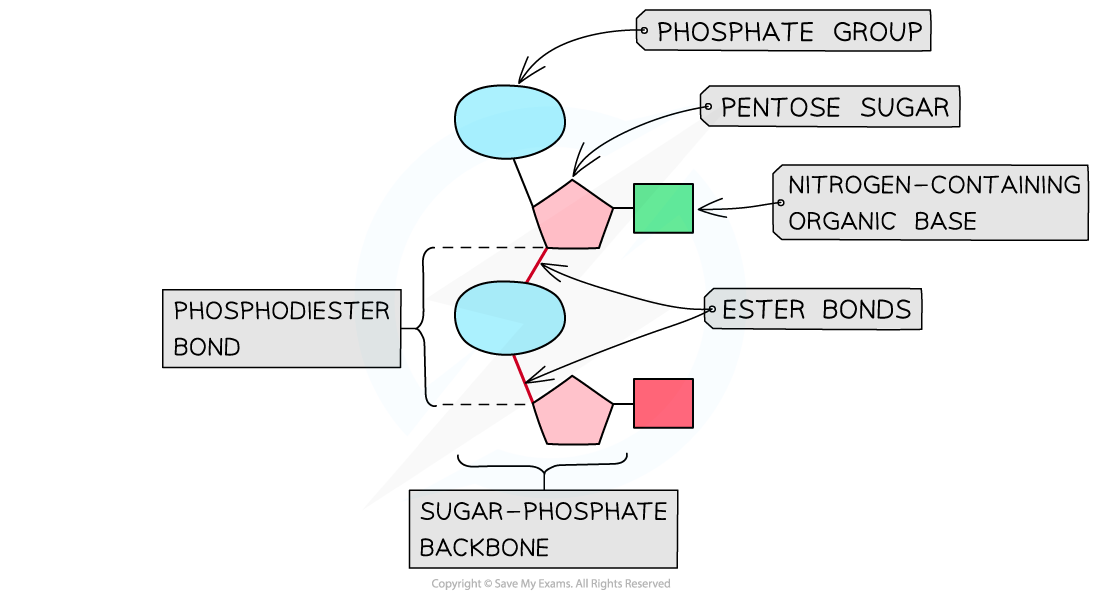
How are nucleotides joined to form DNA/RNA?
Nucleotides join in a condensation reaction
Between phosphate of one nucleotide and carbon 3 of the next sugar
Forms a phosphodiester bond (phosphate + two ester bonds)
Repeated bonding forms the sugar-phosphate backbone
How are DNA or RNA chains broken down?
The reverse of condensation
Hydrolysis reactions
Break phosphodiester bonds
Releases individual nucleotides
List three structural differences between DNA and RNA.
Sugar: DNA has deoxyribose; RNA has ribose.
Bases: DNA uses thymine; RNA uses uracil.
Strands: DNA is double-stranded (double helix); RNA is single-stranded.