Medsurg 1 (CH 5) - neurological disorders PT 2
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Hemorraghic stroke
ruptured blood vessel in the brain (usually aneurysm rupture) causing pool of blood in the brain to reduce O2 supply to brain tissue
ischemic stroke
thrombotic/embolic blockage in the brain constricts O2 supply causing brain tissue death
Hemorraghic stroke s/s
- HTN (BIG INDICATOR)
- N/V
- slurred speech
- facial drooping
- impaired movements
- confusion
ischemic stroke s/s
- slurred speech
- facial drooping
- impaired movements
- confusion
stroke risk factors
- high cholesterol
- HTN
- inactivity
- excessive alc use
- smoking
- cocaine
- hx TIA
- hx afib
- valve problems
- CVD
- diabetes
modifiable risk factors for stroke
- smoking
- cocaine
- alcohol abuse
- immobility
primary stroke preventions
GOAL: preventing a stroke in pts who have never had a stroke but are at risk
- control HTN/BP
- diabetes/cholesterol management
- increase activity/dietary education
- smoking secession
secondary stroke preventions
GOAL: preventing strokes in pts who have already had a stroke w/ preventative/palliative measures in a more aggressive way
- more agressive risk factor control
- agressive BP/cholesterol/diabetes monitoring
- invasive therapies (stents, BV filters)
- agressive modifiable/lifestyle changes
TIA
transient ischemic attack (mini stroke) w/ complete recovery
- temporary attach <24hrs
TIA risk factors
- same as stroke risk factors
- THROMBOEMBOLISM most common
- ulcerated plaque buildup
right sided TIA manifestations
The left side of the brain is affected
- spatial/perceptual deficit
- denies problems
- short attention span
- impulsive behaviors
- impaired judgements
left sided TIA manifestations
The right side of the brain is affected
- aphasia
- dysarthria (slurred speech, difficulty forming words)
- anxiety
- impaired comprehension
- memory problems w/ languages
- vision changes
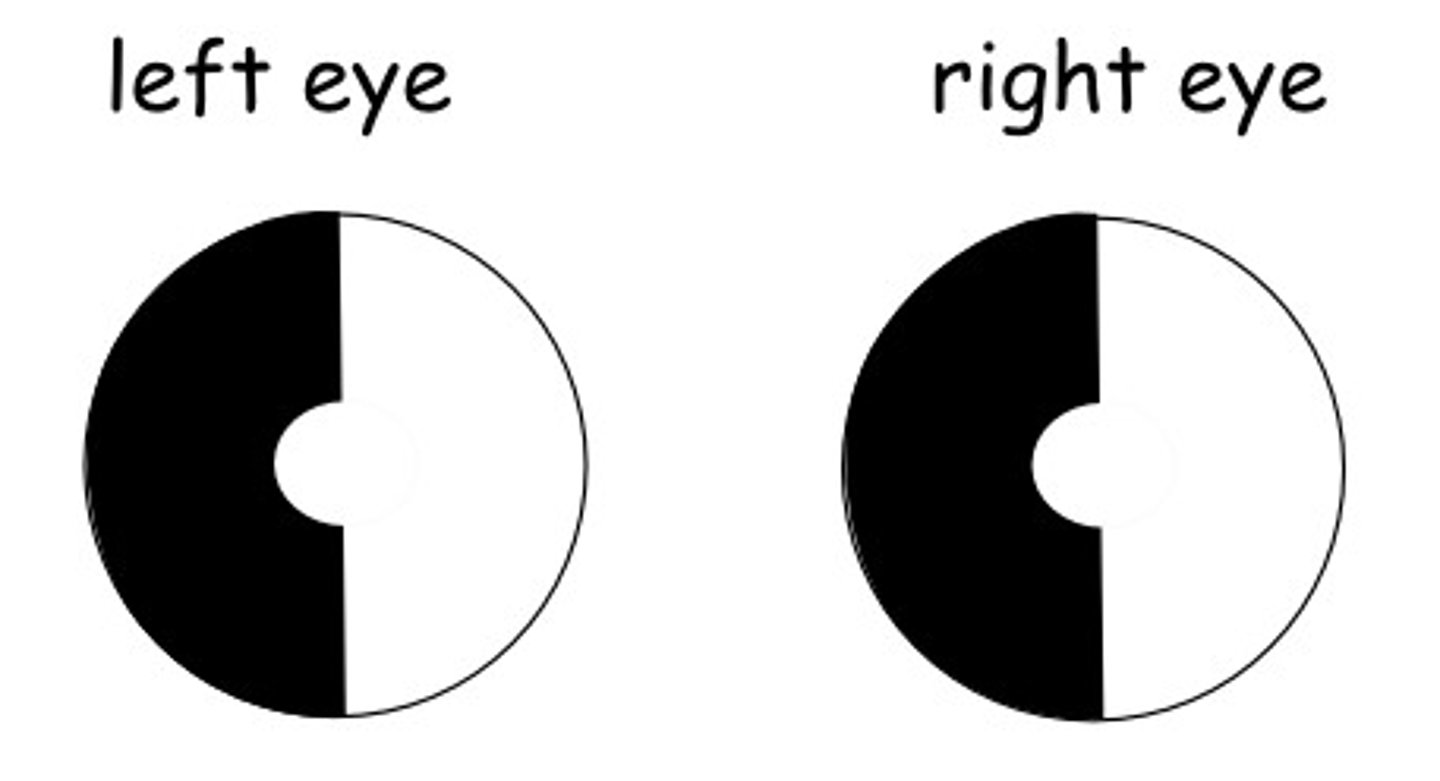
TIA vision changes s/s and nursing priority
- homonymous --> loss of vision in half of the visual field in both eyes
- hemianopia --> vision loss
NURSING:
- RAPID neurological assessments
- determine baseline neurological functioning
- safety assessments
- time length of TIA
nursing care for TIA
- RAPID neurological assessments
"BE FAST"
- determine baseline neurological functioning
- safety assessments
- time length of TIA
- access the airway
- Post TIA, educate preventative/modifiable lifestyle changes

aphasia education
dependent on damaged area, brain loses cohesive speech functioning (w/ subclasses):
- werknies aphasia
- brocas aphasia
- global aphasia
werknies aphasia s/s
left-temporal damage:
- does not understand your speech/writing
- speaks cohesively but not appropriate to situation/ no meaning of words
- word salads/made up words

broca's aphasia s/s
frontal lobe damage:
- comprehends what is being said/wrote
- unable to properly say words/sentences
- non fluet speech
- frustrated and aware of broken speech

global aphasia
SEVERE DEFICIT:
- unable to understand speech/writing
- unable to properly say words/sentences
- facial expressions, gestures, vocal tone is completely impaired

global aphasia nursing priorties
- simplify speech
- visual aids
- safety assessments
- determine swallowing/aspiration risk
- create a system for emergency scenarios
post TIA/stroke nursing interventions
- ABCs --> ensure airway/ monitor O2
- CT scan STAT
- BP management
- thrombolytic therapy
- determine underlying causes (stroke, tissue damage, injury, meds)
- TIMING: CRUCIAL to determine cause of symptoms within 4.5 hrs of onset