Ochem Midterm 1
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Which holds electrons more tightly, s orbitals or p orbitals?
s orbitals
What two orbitals can form pi bonds?
p orbitals
What are the 4 criteria for evaluating resonance forms?
max number of octets
max number of bonds
plus charge on less EN atoms, negative charges on more EN atoms
minimum charge separation
What does induction (sigma bonding network) consider?
electrongetativity, senstive to distance (up to 2C away)
What are the two methods for determinin gwhich side is favored in acid-base equilibrium?
pKa of acids (weaker acid side is favored, higher pKa)
Conjugate base stability (more stable CB is favored)
How do you know a conjugate base is more stable?
stabilizies/delocalizes the lone pair of electrons the best
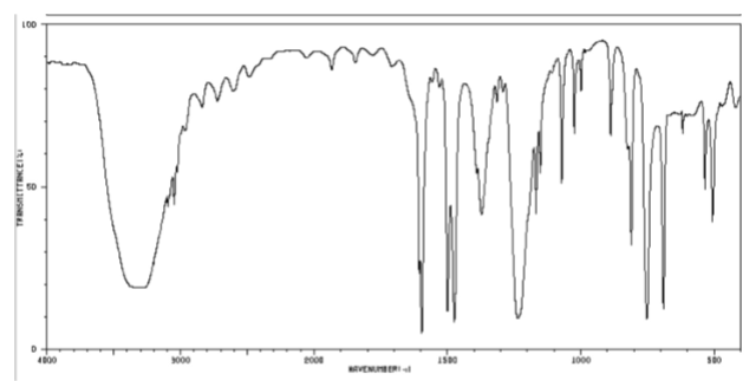
OH bond in cm-1
33200-32500 (broad)
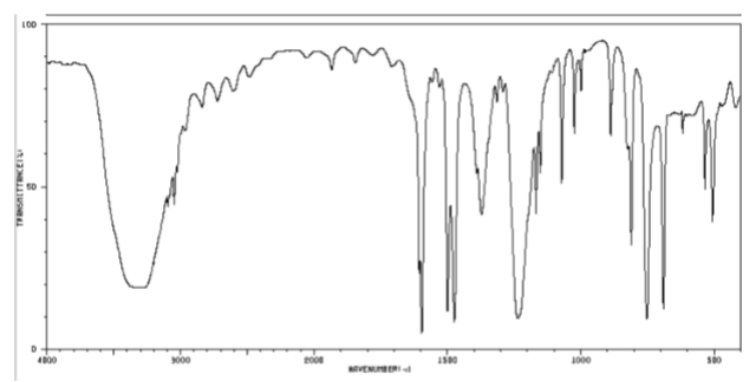
NH2 bond in cm-1
3300-2500 (skinty)
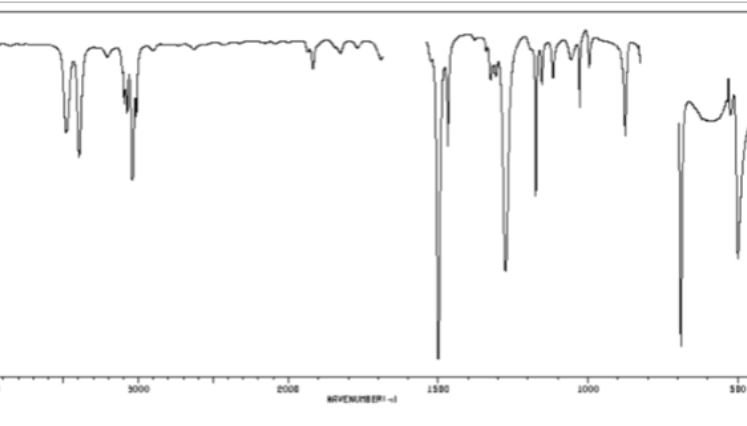
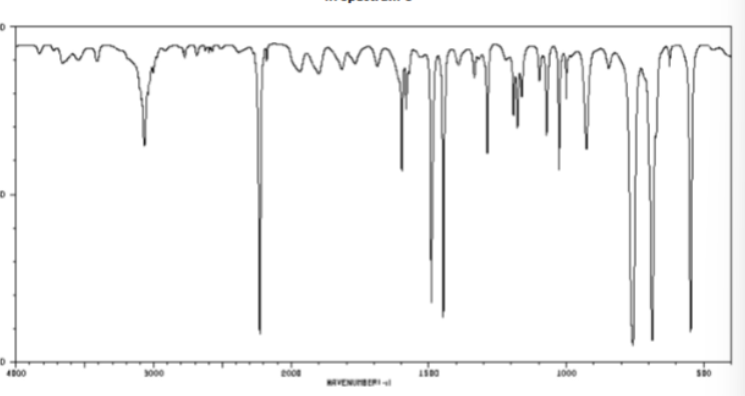
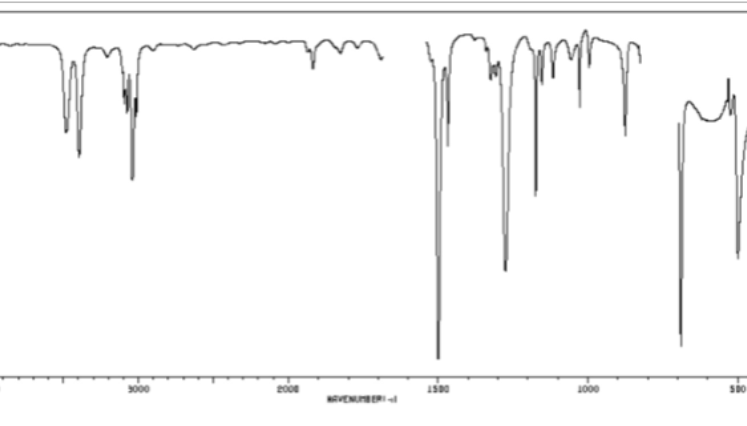
CC triple bond or CN triple bond in cm-1
2200-2250 (sharp)
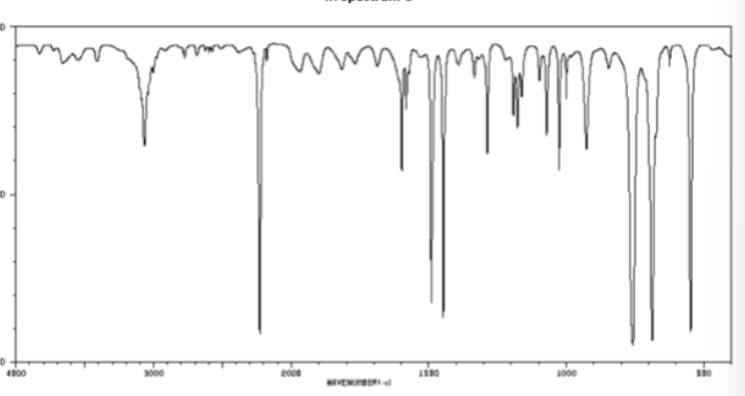
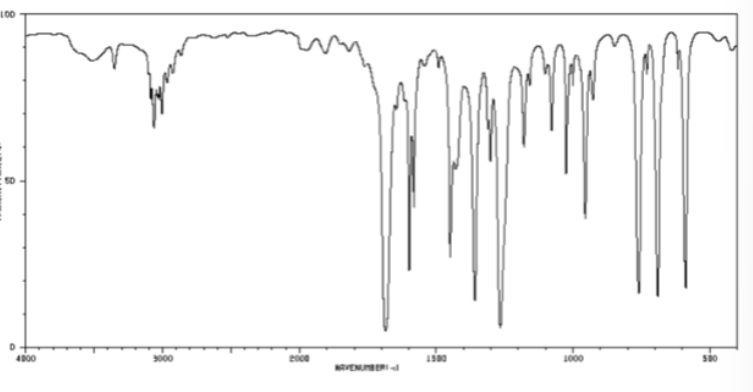
O=C bond in cm-1
1700 sharp
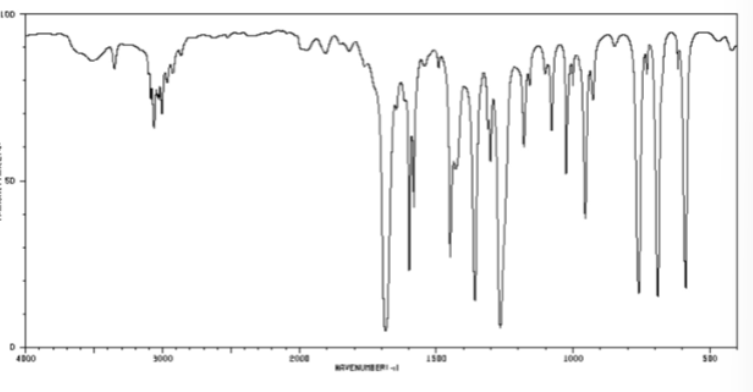
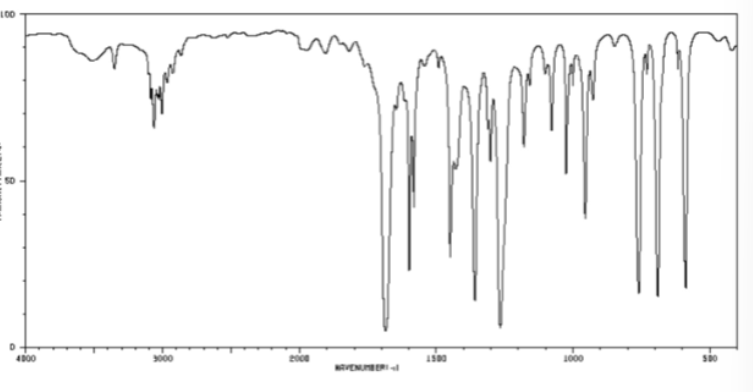
ketone bond in cm-1
1700-1725
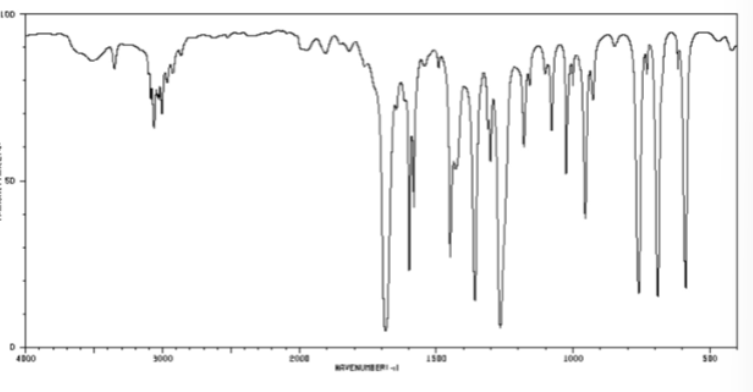
Aldehyde bond in cm-1
2750 and 2850
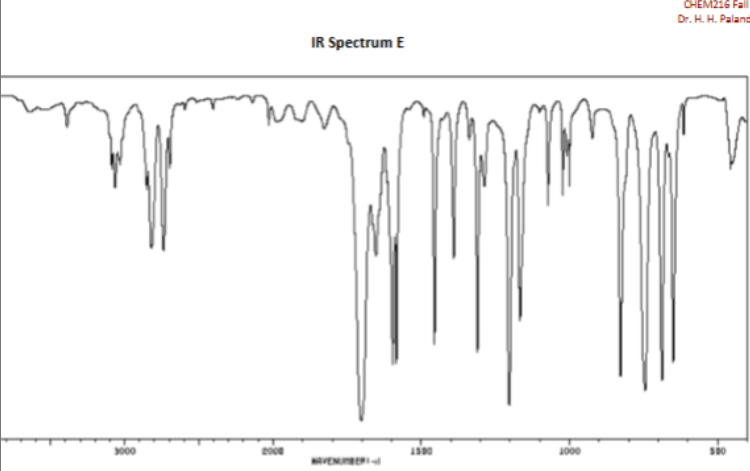
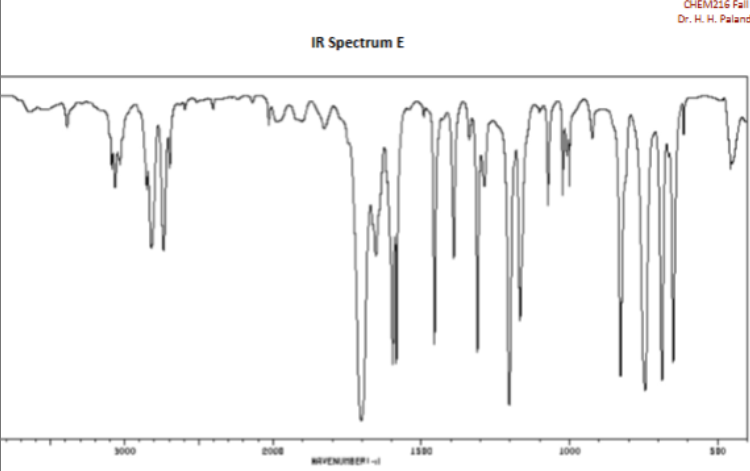
Carboxylic Acid bond (0=C) and (O-H) in cm-1
1700
3000-3600 (Very broad)
Amide bond in cm-1
1650
acylhalide bond in cm-1
1800
Why do acylhalides have a stronger bond than ketones?
EN of Cl
What do resonance forms do to bond order and wavelength?
weaken bonds and reduce bond order
lower wavelength and lower energy bonds