Earth Systems Exam I
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
188 Terms
Geography
The study of all physical and human phenomena at individual places and how interactions among places form patterns and organize larger spaces
Foundations of geography
Where is something located?
Why is it there?
How did it get there?
How does it interact with other things?
Physical geography
Studies the characteristics of the physical environment.
Human geography
Studies human groups and their activities
Environmental system
A collection of things and processes that operate as a whole.
Closed system
Allows energy to flow in and out freely, but keeps all matter contained.
Open system
Allows both matter and energy to exit the boundaries of the system.
Output
Feedback that is released from a system
Input
Feedback that is absorbed into a system
_____ released from systems and are then returned back to the system as input.
Outputs are….
Negative feedback is…
Also known as balancing feedback.
Positive feedback is…
Also known as reinforcing feedback
Negative feedback
When system inputs and outputs counteract each other. This has a dampening effect and stabilizes the system.
Ex: being to warm and turning on a fan, and then becoming too cold and turning on a heater.
Positive feedback
When the system inputs and outputs strengthen each other. It has an amplification effect. This produces extreme conditions.
Equilibrium
When inputs = outputs so that conditions within the system remain the same. Not to be confused with a similar concept, despite the fact that it is promoted by it.
Atmosphere
Contains clouds, climate
Related heavily to the hydrosphere
Thin layer of gas that envelopes the earth and allows it to breathe
Biosphere
Contains all living organisms
Soil, microbes, birds, humans etc.
Lithosphere
The rock solid surface of the earth
Concerned with geology, mountains, soil etc.
Hydrosphere
All of the water contained on earth, including that inside of living organisms or the air.
light detection and ranging
LiDAR stands for _____
LiDAR
a technique of collecting data that involves using a laser to scan precise measurements of elevation
Oblate spheroid
The shape of the earth is ___, which is where the rotation of the earth causes an equatorial bulge
Equatorial plane
The plane interesting the earth at the equator.
The angle from the core center of the earth to the point on the surface.
What angle determines the degree of latitude or longitude?
Parallels
Lines of latitude that run east to west across the globe
Meridians
Lines of longitude that run north to south.
Equator
Line of latitude at the center of the earth
Tropic of Cancer
Line of latitude at 23.5 degrees N
(Maximum northern declination of the sun)
Tropic of Capricorn
Line of latitude 23.5 degrees South
(Maximum southern declination of the sun)
Arctic Circle
Line of latitude at 66.5 N
Antarctic circle
Line of latitude at 66.5 S
Prime Meridian
The international meridian located in Greenwich which was a major trade point.
Considered the starting point for longitude or 0 degrees E or W.
Degree°, minute’, second”, direction
What is the way to write out a location based on latitude and longitude?
69 miles
How many miles are in 1 degree of latitude
101.2 ft
How many ft are there in a second of latitude?
0° to 90°
What is the range for latitude (not including direction N or S)
0° to 180°
Range of degree for latitude
Thirty five degrees four minutes and fifty three point eighteen seconds north, ninety two degrees and twenty seven minutes and thirty point zero two seconds west.
How would this be read: 35°, 4’53.18”N, 92°, 27’30.02”W
North West Cartesian plane
+-
South West Cartesian plane
— —
North East Cartesian plane
++
Southeast Cartesian plane
-+
Cartesian plane organization
What organization places degrees only in decimals and uses positives and negatives to signal directions?
Ex: 35.080524, 92.455896 -
Cartesian plane
a map layout that has a lot of distortion at the poles
Size
Shape
Distance
Direction
The basic properties of a map are _____
thematic maps
represents a specific kind of information (restaurant locations or locations of public bathrooms in the covered area)
Graphic scale
represented by a bar style graph that shows a physical representation of the map’s scale
Verbal scale
representation of the map’s scale that is written out in words and numbers
distorted
all maps are _____
isolines
lines connecting points of equal value on a map (ex: elevation)
Closer
the elevation grade is steeper when the contour lines are _____ in distance to each other.
further
the elevation grade is less steep when the contour lines are _____ in distance to each other
contour interval
the amount of physical distance represented in between each contour line
isotherm
a type of isoline that connects equal data points that can exist at a point (ex: elevation, atmospheric pressure, temperature)
Isopleth
a type of isoline that connects equal data points that cannot exist at a point (ex: population density, average tornadoes in an area)
isobar
map showing equal atmospheric pressure
isohyet
map showing equal rainfall
isotherm
map showing equal temperature
more pronounced
the ______ the gradient of an isoline map is, the more dramatic the change in data.
Change/Distance
Gradient
Conic Projection
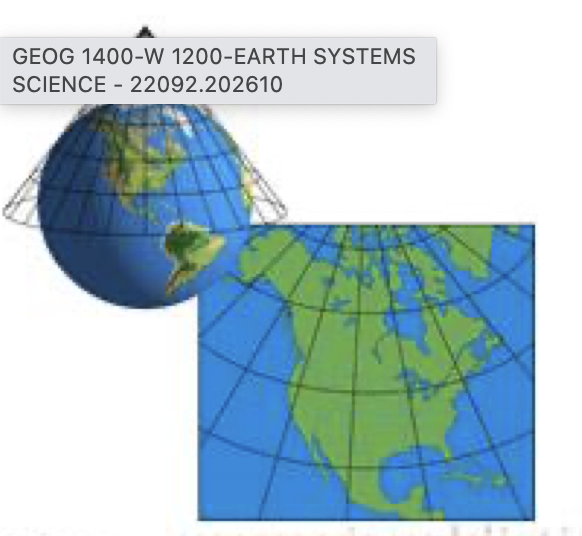
Cylindrical Projection
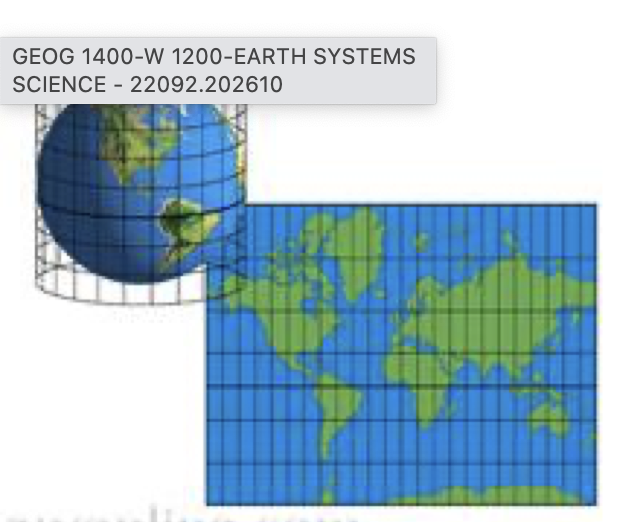
Plane Projection

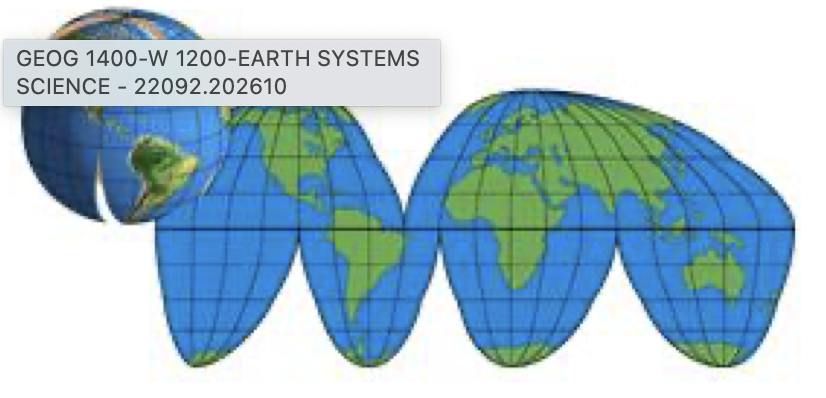
Interrupted projection
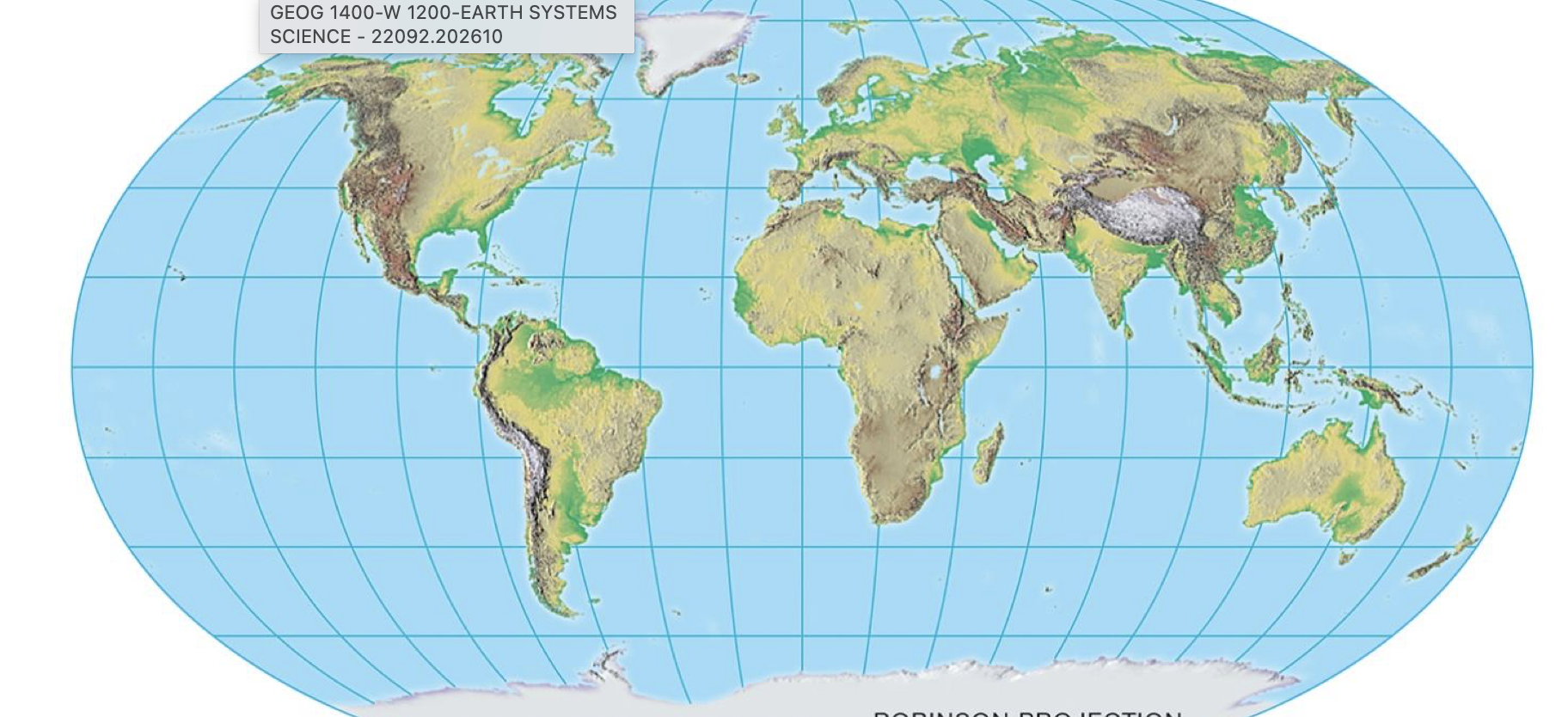
Robinson Projection
curved distortion towards the poles
relatively accurate for a projection
AKA compromised projection
Crenulation V
when a stream intersects a contour line
Remote Sensing
includes systems such as LiDAR and imagery
acquisition of data by using aircrafts or satellites orbiting earth
Useful for:
Land use and land coverage
Change in land use or coverage
Terrain analysis (elevation, slope, water run off)
Environmental monitoring (crop health, drought presence, vegetation health)
Geographic Information System (GIS)
information system that stores, analyzes, and can manipulate or present spatial data.
Includes the following components:
Size
Shape
Distance
Direction
Useful for:
Proximity (how far away are things from a particular feature)
Navigation (shortest path)
Overlay analysis
Electrical companies use GIS to keep up with their lines locations, status, and upkeep
The sun
powers earth’s seasons, climate, weather, erosion, and biological food webs
fusion reaction
H + H = He + energy (electromagnetic radiation)
The electromagnetic radiation is coming through space and bombarding the earth’s system
How does the sun heat the earth?
Short Wave
High energy waves
ex: XRays UltraViolet Rays
Long Waves
Low energy waves
ex: Radio Waves, TV Waves
47 Percent
______ of energy on earth from the sun presents as visible spectrum waves.
47 percent
________ of energy on earth from the sun presents as thermal energy
8 percent
_______ of energy on earth from the sun presents as Gamma, XRays, or UltraViolet
• Rotation
• Revolution
• Tilt
• Axial parallelism
• Sphericity
The amount of solar radiation received by a certain location on earth is affected by _______________.
Tilt
• Axial parallelism
• Sphericity
Seasons are due to _______________.
Rotation
The earth’s full turn on its’ axis in a 24 hour period
Counterclockwise
We rotate _________
Revolution
The earth’s journey on its path around the sun which takes a total of 365.25 days.
perihelion
_________ is when the earth is 5 million km closer to the sun
Season
Variation in climate patterns and temperature during different parts of the year
influenced by insolation (incoming solar radiation)
Vertical rays
direct, concentrated rays of radiation
Oblique rays
diffused rays of radiation
23.5
Tilt of the earth’s axis is ________ degrees
Axis Parallelism
the earth’s axis remains at a constant 23.5 degrees during its entire revolution around the sun
Equinox
when the sun is directly above the equator and all latitudes receive an equal 12 hours of sunlight.
Solstice
when the sun is directly above one of the tropic latitudes
brings the longest and shortest days for its respective hemispheres
June solstice
Sun is directly over the Tropic of Cancer
longest day of the year for the northern hemisphere
24 hours of sun above the arctic circle
June 20-22
December Solstice
Sun is directly over the Tropic of Capricorn
longest day of the year in the southern hemisphere
24 hours of sun below the antarctic circle
December 20-23
March Equinox
March 19-21
September Equinox
September 22-24
Declination
the degree of latitude of the sun’s location in relation to the equator
Zero Degrees
what is the declination of the sun during equinoxes?
Atmosphere
A blanket of gasses that envelops the earth and is held there by gravity
It goes well up beyond the clouds
It protects us from space
It contains oxygen that allows us to breathe and live on earth
Nitrogen, then oxygen
the atmosphere is mainly ________
Decreases
Atmospheric pressure __________ as you move away from the earth’s surface due to the difference in air density
Sydney
Who is the best fiancée ever
below
50 % of atmospheric pressure is ________ 18,000 ft.