Unit 6: Blood Defence and Movement
1/47
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
composition of blood
plasma
buffy coat (leukocytes/white blood cells for immune system, platelets for clotting)
red blood cells/erythrocytes (carry oxygen)
separated through centrifugion
artery
blood away from heart, often oxygenated
thick walls thin lumen
withstand high pressure
vein
blood to heart, often deoxygenated
thin walls thick lumen
transport at lower pressure
capillary
thin walls of endothelial cells
diffuse oxygen, nutrients, co2, nitrogen into organs through gas exchange
process through heart
vena cava → right atrium → right ventricle → pulmonary artery → lungs and capillaries → pulmonary vein → left atrium → left ventricle → aorta → body → vena cava…
sinoatrial node (SA)
sends out electrical impulses rhythmically that stimulate heart (atrial) contractions as a pacemaker. located in the right atrium.
atrioventricular node (AV)
tells ventricles to contract following direction from the SA.
myogenic contractions
originate in the muscle itself and are not necessarily controlled by the brain.
process of blood circulation
atrial systole- shock and blood goes through atria
ventricular systole- shock and blood goes through ventricles
diastole- both relax and blood slowly fills back in for the next beat
this is why two beats. blood circulation relies on a flow from high pressure to low pressure
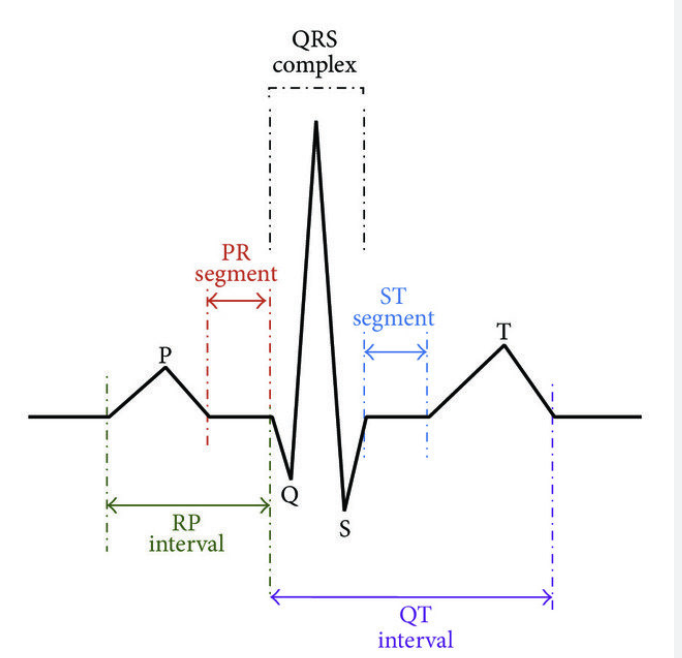
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
measures electric activity of systole and diastole to identify problems eg heart attacks
p-wave atrial
qrs complex ventricular
t-wave diastole
process of blood clotting
cut- collagen exposed → clotting factors → platelets activated → release more clotting factors which trigger prothrombin→ prothrombin triggers thrombin → thrombin triggers fibrinogen → fibrinogen turns into fibrin → fibrin clots cut using mesh → attracts more platelets into clot → external scab
heart attacks
blockage in coronary artery. risks:
high blood pressure
fat forming plaque deposits on arteries, constricting them
William Harvey
Scientist who formulated the current understanding of the blood system.
closed system
no use of “animal spirits”
blood is oxygenated in the lungs, not in the heart itself
blood is not made in the liver
Pathogens
Infectious transmitters of disease. The four types are:
Bacteria- eg salmonella
Virus- eg influenza
Fungus- eg yeast infection
Protist- malaria
Non-specific response
Protective measures in the body that fight against general infection. This includes the first and second line of defence.
Specific response
Protective measures in the body that are specialised to fight against a certain pathogen. These are created upon exposure to the pathogen.
First line of defence
Physical barriers such as the skin, mucous, hair, liquids with enzymes to dissolve pathogens (eg saliva). The “castle moat”. Weak points are orifices or openings.
Second line of defence
Destroy any invading pathogens before they can cause harm to the body system. Body only attacks pathogens (marked with antigens), and not itself (marked with MHC self markers). Involves neutrophils, macrophages, t-helper lymphocytes.
Neutrophils
Second line: first to infection site. Engulf pathogen and then self destruct. Dead ones form pus.
Macrophages
Second line: fight chronic infections through endocytosis (to absorb and destroy pathogens). Capture a sample of the pathogen’s antigen to show to the third line of defence.
Side effects of fighting illness
A fever happens as blood rushes to the site to bring the defence white blood cells. This transports heat to the area- but this heat may denature proteins and cause issues for the body.
Third line of defence
Creates a specific defence against a certain pathogen to a) eradicate it or b) know how to fight it if it appears again. Cells fall into two categories: effector and memory.
Involves helper t lymphocytes, b lymphocytes, and cytotoxic (killer) t lymphocytes.
Helper t lymphocytes
Third line: when a macrophage presents an antigen of a particular pathogen to them, they activate, and also activate specific B lymphocytes for that pathogen.
B lymphocytes
Third line: once activated by helper t lymphocytes, they clone into either:
plasma effector cells- start working on specific antibodies for that pathogen
memory B cells- store a bit of the antibody for later in case the pathogen comes back
cytotoxic (killer) T cells
Third line: Activate to protect a specific body system against a specific pathogen when marked by an antibody. Effector cells.
Antibodies
Third line: these do not themselves kill the pathogen: they just tag the pathogen’s antigens (like stamping a luggage tag) to draw attention to them. The killer T cells see the tags and know which cells to kill and which to leave alone.
HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
retrovirus: contains mRNA and turns itself back into DNA using reverse transcriptase
targets and destroys helper t cells- link between immune system 2nd and 3rd line of defence
may progress into AIDS: Acquired ImmunoDeficiency Syndrome
Not likely to die of AIDS, but of a secondary infection that you cannot fight
passed through fluids
Florey and Chain
Scientists responsible for the discovery of the antibiotic medicine Penicillin in the 1930s, and its testing and rollout in the 1940s.
1930s observed penicillium bacteria caused sterilisation of a contaminated agar plate
1940s injected 4 rats with penicillin and left 4 without, and then infected all with bacteria. 4 without died = antibacterial medicine.
1941 Albert Alexander’s self tests were successful
1943 fast rollout of drug due to WWII- questions how rigorous the testing process was
Drug testing processes of today
preclinical trials- drugs simulated on computer models to see effect on DNA/ proteins
Animal testing (not for cosmetics, cigarettes)
Human clinical trials
test side effects on small group
test efficacy on small group with disease
with placebo on global scale to test strength
post-approval research trials (eg long term effects)
Antibiotics
Anti bacteria. Bacteria = prokaryote. People = eukaryote. Therefore target prokaryotic processes eg: anaerobic respiration, breaking down cell boundary to “pop” it, binary fission (replication), circular chromosomes.
bacteriostatic- stops bacteria
bactericidal- kills bacteria
NOTE: antibiotics don’t work on viruses.
Antibiotic resistance
human takes antibiotics when not needed → good bacteria dies → some bacteria survive due to mutation → bacteria asexually reproduce and plasmids with mutation are cloned → resistant gene is transferred from harmless to pathogenic bacteria → pathogenic bacteria is resistant to antibiotics
Multi Resistant Organisms (bacteria) MROs
resistant to multiple strains of antibiotics. Increased amount of invasive surgeries = more need to sterilise equipment = more exposure to multiple antibiotics.
Example: methicillin-resistant staphyloccus aureus (golden staph)
Releasing glucose for blood sugar levels
glucose needed for ATP (for cell respiration). Too much = hypertonicity, too little = hypotonicity. Regulated by insulin and glucagon.
Insulin
released from beta cells in pancreas. decreases blood glucose concentration.
→ this may involve glycogenesis- glucose into glycogen synthesis in liver.
Glucagon
released from alpha cells in pancreas. increases blood glucose concentration.
→ this may involve glycogenolysis- glycogen into glucose release by liver and adipose (fat) tissue.
Type 1 Diabetes
Genetically body kills beta pancreas cells = no insulin naturally produced. May need insulin shots to keep blood sugar at appropriate level.
Type 2 Diabetes
Acquired across lifetime, generally as a result of lifestyle and diet. Target cells in the liver don’t receive insulin properly, leading to no regulation of blood sugar.
Thyroxin
Produced by thyroid gland. Targets most cells, mainly liver, muscle and brain. Controls metabolic rate/rate of protein synthesis. Needs iodine.
Leptin
Produced by adipose (fat) tissue. Targets hypothalamus in brain. Tells brain that fat cells and by extension we are full and to stop eating (inhibitor). Hungry → no hormone. Full → hormone.
Discovery of Leptin
Surgically fusing the blood of obese and healthy mice:
healthy blood → obese mouse with leptin deficiency (genetic) = lost weight
healthy blood → obese mouse with faulty receptor (genetic) = stayed obese
extra leptin → healthy mouse = emaciated
In humans, most obesity is caused to a faulty leptin receptor. Therefore, simply adding more leptin won’t affect appetite, and in fact causes skin conditions.
Melatonin
Retina ganglion cells sense it is dark → suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) in hypothalamus → pineal gland. Targets several tissues including kidneys. induces drowsiness, sleep, decrease in body temperature, reduction of energy production. Maintains circadian rhythm.
Sex determination
Y Chromosome → carries SRY gene → codes for DNA binding protein called testis determining factor (TDF) → causes development of embryonic gonads (testes) → testosterone produced; male embryo.
In all cases UNLESS the Y chromosome is present, ovaries form and embryo is female.
Testosterone
Pregnancy: Produced in male gonads (testes) of the embryo from week 8 until genetalia develop at week 15.
Puberty: levels increase stimulating sperm production, secondary sex characteristics:
libido
growth of larynx/voice drops
body hair
muscle mass increase
external genetalia development
Estrogen
Pregnancy: ovaries of the mother/placenta secrete estrogen and progesterone → female genetalia develop
Puberty: ovaries secrete both hormones, secondary sex characteristics:
breast development,
hips widen/fat deposition
body hair
external genetalia develop
menstruation
Menstrual cycle: Follicular phase
Follicular Stimulating Hormone (FSH) rises and stimulates follicle in ovary to mature 2 eggs.
Estrogen from follicle increases → eventually reaches high enough level and FSH starts to decrease.
Endometrium thickens.
Menstrual cycle: Ovulation
Eggs are released from follicle.
Leutenising Hormone (LH) peaks, increases estrogen and FSH.
Egg waits in uterus to be fertilised.
Menstrual cycle: Luteal Phase
Corpus luteum (broken down follicle) eventually breaks down and is reabsorbed.
FSH and LH fall, estrogen fall due to inhibition from progesterone.
Thick endometrium waiting for fertilisation- but egg doesn’t embed.
Menstrual cycle: Menstruation
Unfertilised egg and endometrium (uterus lining) are shed. Triggered by a dip in all four hormones: estrogen, progesterone, LH, FSH.
→ the pill prevents the dip from happening = no period.