Neuroscience 320 Lab - University of Delaware
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
With Professor Dr. Roth
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
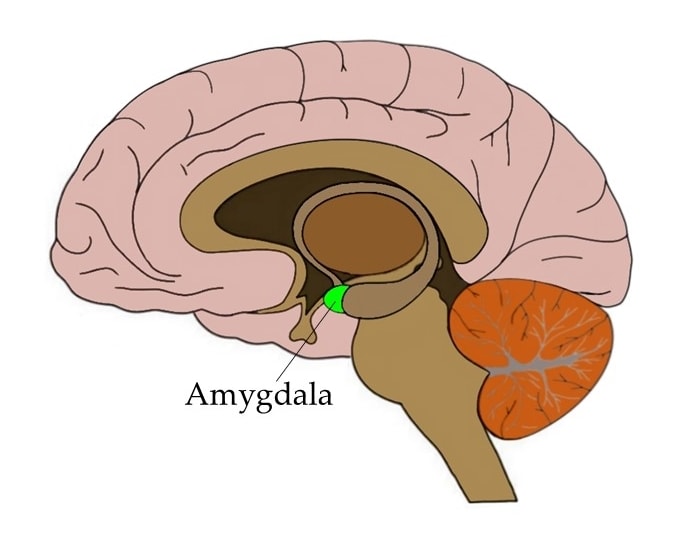
Amygdala
-almond-shaped structure located deep within the temporal lobe of the brain
-primarily responsible for processing emotions, particularly fear and anxiety, plays a key role in triggering the "fight or flight" response by identifying potential threats
-part of the limbic system and consists of multiple nuclei, with the basolateral, central, and medial nuclei being the most prominent, each contributing to different aspects of emotional processing and memory formation
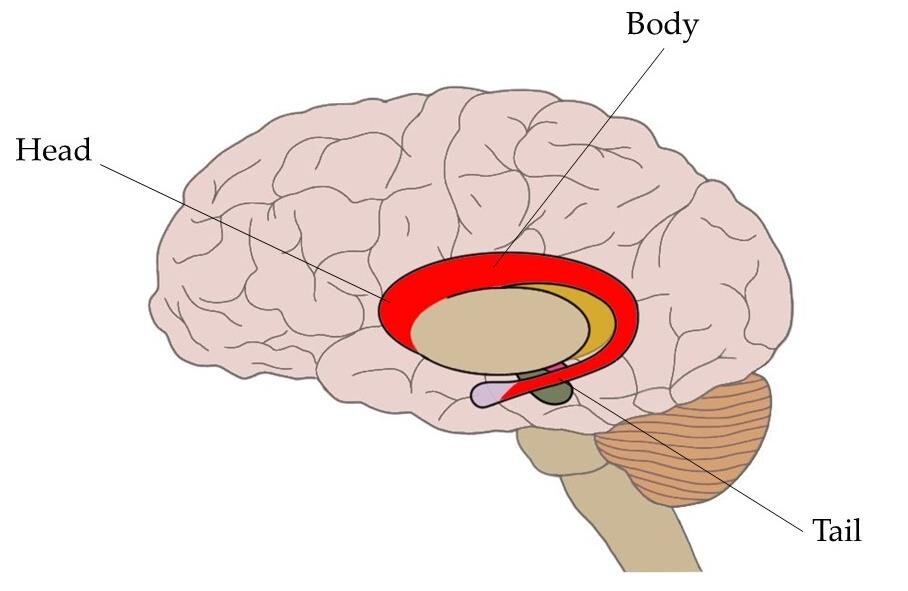
Caudate Nucleus
-C-shaped structure deep within the brain, consisting of a large head, a body, and a thin tail, and is part of the basal ganglia
-primary functions include controlling voluntary movement, processing sensory information related to spatial orientation, and playing a role in cognitive functions like learning, memory, and reward processing
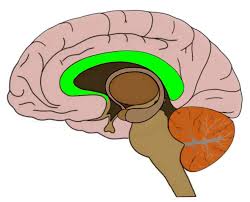
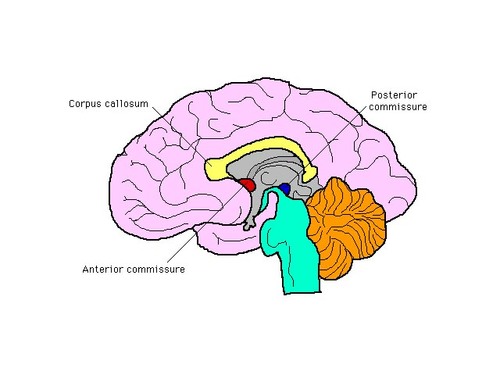
Corpus Callosum
-thick band of nerve fibers located deep within the brain, acting as the primary communication pathway between the left and right cerebral hemispheres, allowing them to exchange information by transferring signals across the midline of the brain
-it is essentially a "bridge" connecting the two sides, composed of white matter and consisting of several distinct parts including the rostrum, genu, body, and splenium
Anterior Commissure
-white matter tract in the brain that acts as a connection between the two temporal lobes of the cerebral hemispheres
-primarily responsible for transmitting olfactory information (smell), but also plays a role in visual, auditory, and taste perception by connecting various brain regions like the amygdala and temporal lobes, contributing to functions like memory, emotion, and behavior
-smaller bundle of fibers compared to the larger corpus callosum
Posterior Commissure
-small band of white matter fibers located in the brain, crossing the midline on the dorsal aspect of the cerebral aqueduct
-primarily functions as a crucial part of the pathway for the pupillary light reflex, connecting the pretectal nuclei of the two hemispheres to enable coordinated pupil constriction in response to light stimulation in either eye
-considered part of the epithalamus and is situated near the pineal gland
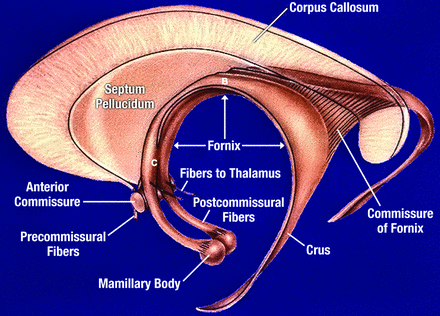
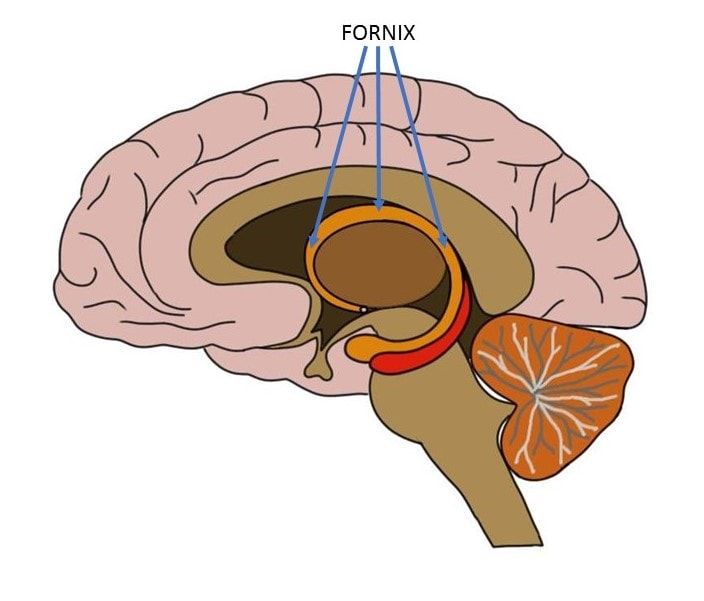
Fornix
-C-shaped bundle of white matter nerve fibers in the brain, acting as the primary output tract of the hippocampus and considered a key part of the limbic system
-primary function is to connect various limbic structures, playing a critical role in cognitive function, particularly in the formation and retrieval of episodic memories
-damage to the fornix can lead to significant memory loss, especially regarding recall of past events
Globus Pallidus
-subcortical brain structure, part of the basal ganglia
-primarily responsible for regulating conscious and voluntary movements by sending inhibitory signals to the thalamus, effectively controlling the initiation and execution of motor functions
-divided into two segments: the external globus pallidus (GPe) which acts as a relay for information, and the internal globus pallidus (GPi) which is the primary output nucleus sending signals to the thalamus
Hippocampus
Hypothalamus
Insular Cortex
Putamen
Red Nucleus
Substantia Nigra
Thalamus
Cerebellum: Arbor Vitae
Cerebellum: Folia
Cerebellum: Peduncles
Nucleus Accumbens
Medial Geniculate Nucleus
Laterl Geniculate Nucleus
Optic Radiations
Ventricles