MEDCHEM 16 - phospholipids, non-glycerides and complex lipids
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:58 AM on 3/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards

lipiiiiids lipiiiiids
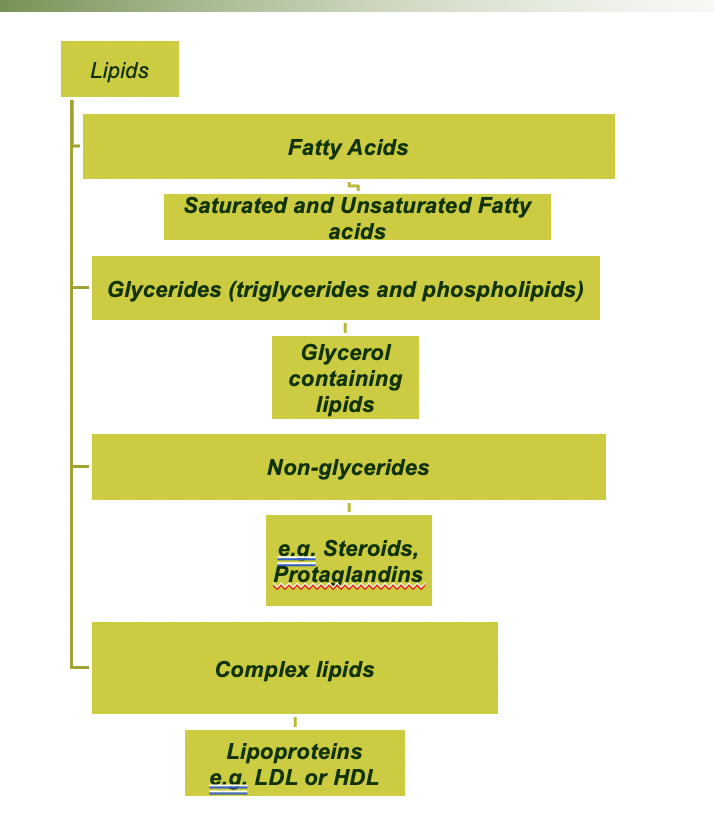
lipids:
* fatty acids (sat & unseat)
* glycerides (triglycerides and phospholipids)
* glycerol containing lipids
* non-glycerides
* complex lipids
* lipoproteins (LDL, HDL)
* fatty acids (sat & unseat)
* glycerides (triglycerides and phospholipids)
* glycerol containing lipids
* non-glycerides
* complex lipids
* lipoproteins (LDL, HDL)
2
New cards
Lipids and disease:
* Hyperlipidemia
* Arteriosclerosis
* treatment of Hyperlipidemia
* Hyperlipidemia
* Arteriosclerosis
* treatment of Hyperlipidemia
**Hyperlipidemia** - condition associated w %%elevation of dif forms of lipids in bloodstream%%
* this condition is the most important risk factor for artherosclerosis (the major cause of cardiovascular disease) (atherosclerosis also leading cause of death for male/female worldwide
\
**treatment** - can have dietary treatment then drug treatment (eg. statins) *dietary treatment of hyperlipidemia is a necessary foundation for drug treatment*\*
* this condition is the most important risk factor for artherosclerosis (the major cause of cardiovascular disease) (atherosclerosis also leading cause of death for male/female worldwide
\
**treatment** - can have dietary treatment then drug treatment (eg. statins) *dietary treatment of hyperlipidemia is a necessary foundation for drug treatment*\*
3
New cards
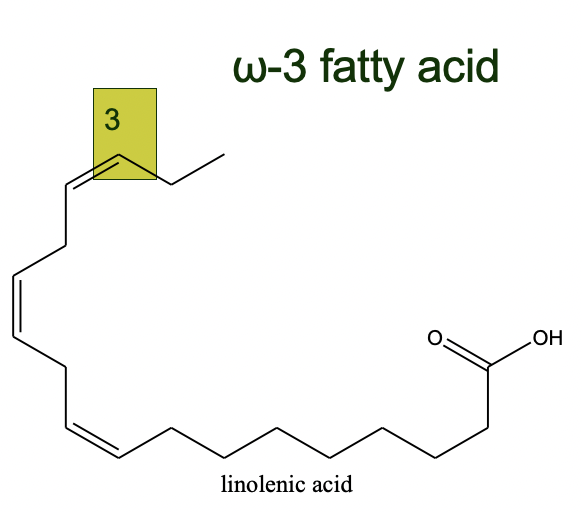
omega-3 fatty acids
_
diet and health
_
diet and health
* present in high concentration in **fish oils**
* can reduce risk to atherosclerosis and heart disease
* w-3 fatty acids **inhibit platelet function** which contributes to ==blood clots that can cause heart attacks==
* e.g. %%linolenic acid%%
_
studies of increased incidence of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease associated w diets high in **sat fats and trans fats**
* can reduce risk to atherosclerosis and heart disease
* w-3 fatty acids **inhibit platelet function** which contributes to ==blood clots that can cause heart attacks==
* e.g. %%linolenic acid%%
_
studies of increased incidence of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease associated w diets high in **sat fats and trans fats**
4
New cards
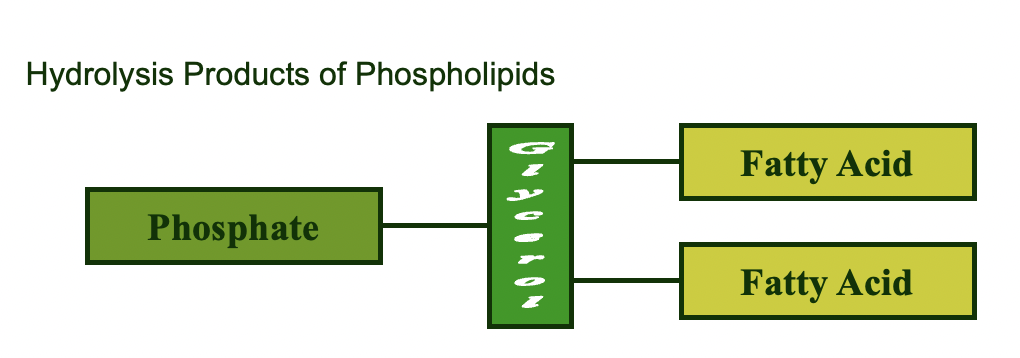
phospholipids
Upon hydrolysis *phospholipids* will yield:
* (2) Fatty Acids
* An alcohol (glycerol)
* One additional compound (phosphate)
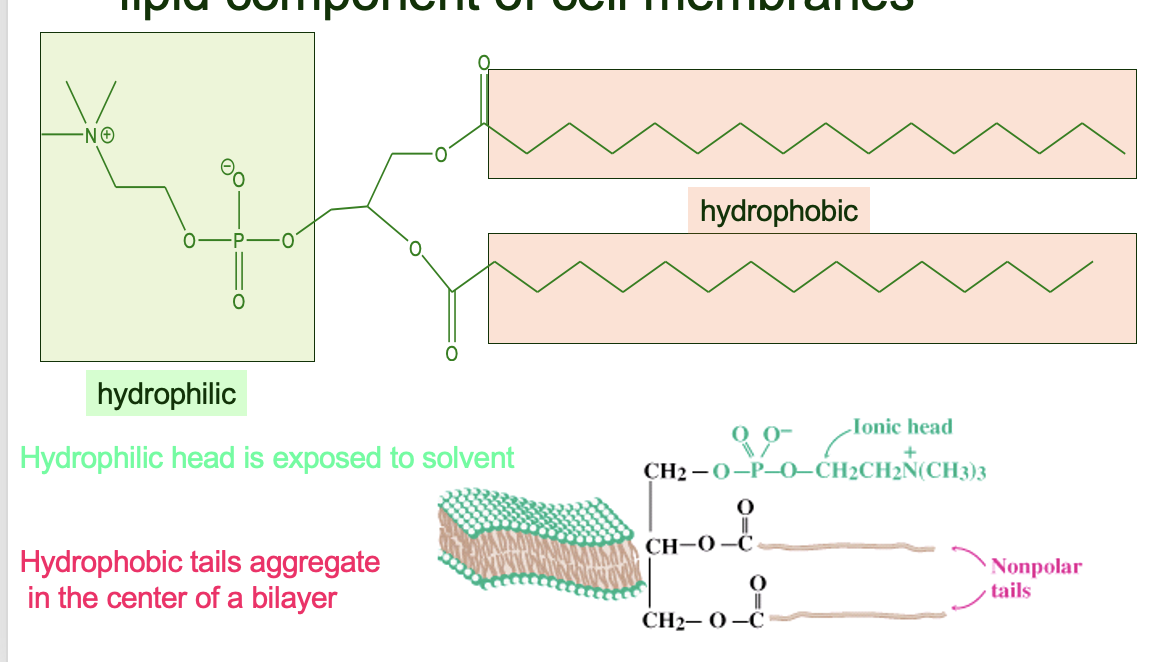
phosphoglucerides comprise the major lipid component of cell membranes
\
yaya hydrophilic head exposed to solvent, hydrophobic tails aggregate in the centre of a bilayer
* (2) Fatty Acids
* An alcohol (glycerol)
* One additional compound (phosphate)
phosphoglucerides comprise the major lipid component of cell membranes
\
yaya hydrophilic head exposed to solvent, hydrophobic tails aggregate in the centre of a bilayer
5
New cards
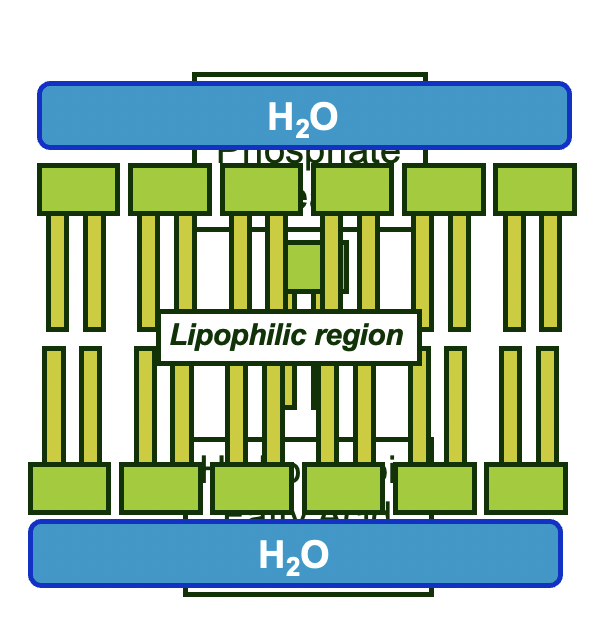
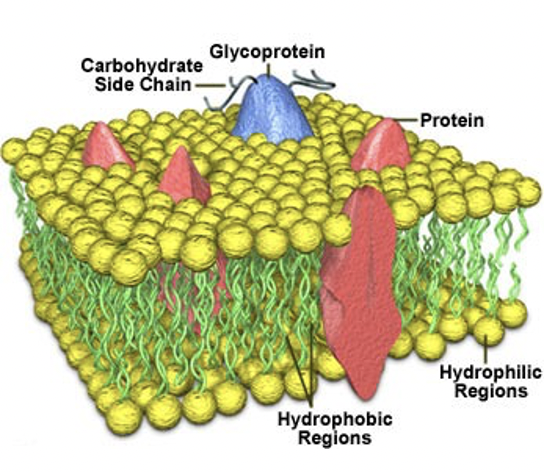
phospholipid bilayer
* Molecules will orientate to exclude water from the lipophilic fatty acid tails
* The structure of phospholipids gives them good membrane forming properties
* Allow formation of cell and individual compartments in biological systems
* Allow control of chemical environment
* Allow selective transport of particular cellularcomponents
* Allow cell recognition
* Contain receptors for specific signal compounds
* The structure of phospholipids gives them good membrane forming properties
* Allow formation of cell and individual compartments in biological systems
* Allow control of chemical environment
* Allow selective transport of particular cellularcomponents
* Allow cell recognition
* Contain receptors for specific signal compounds
6
New cards
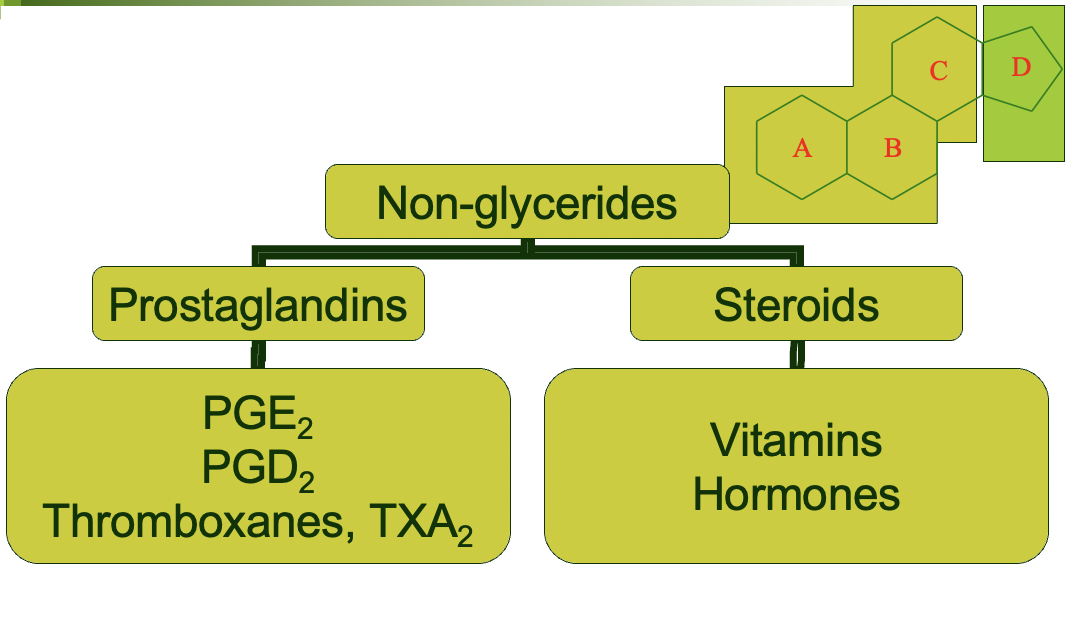
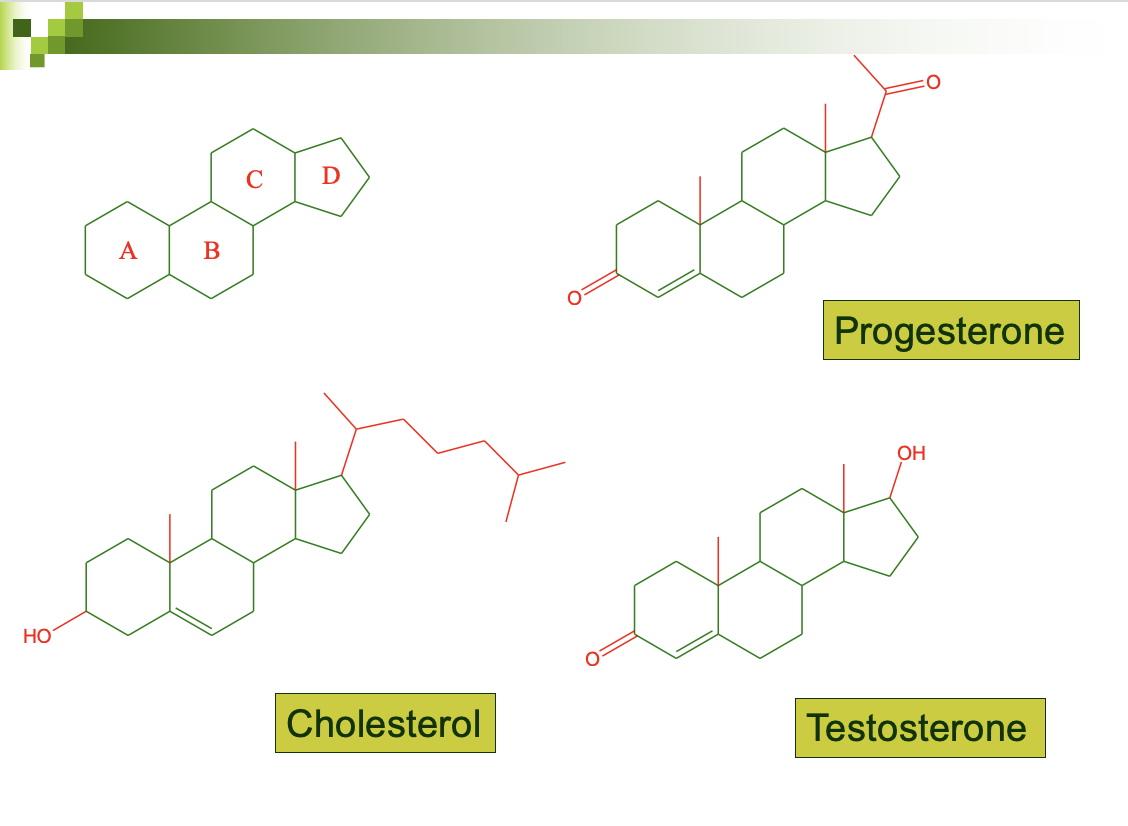
*Non-glycerides* - **steroids**
all steroids have the same basic structure, contains 4 rings
* 3 **cyclohexanes** and 1 **cyclopentane**
* variations occur in the substituents at particular sites giving rise to dif compounds:
* cholesterol
* progesterone - main female sex hormone (has 1 ketone)
* testosterone - male sex hormone (has 1 alcohol)
both derived from cholesterol (recognize that its a steroid)
* 3 **cyclohexanes** and 1 **cyclopentane**
* variations occur in the substituents at particular sites giving rise to dif compounds:
* cholesterol
* progesterone - main female sex hormone (has 1 ketone)
* testosterone - male sex hormone (has 1 alcohol)
both derived from cholesterol (recognize that its a steroid)
7
New cards
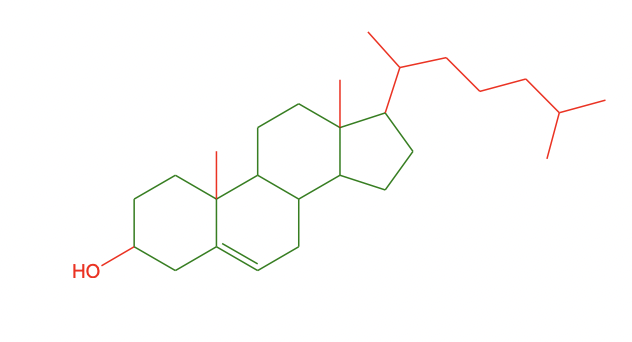
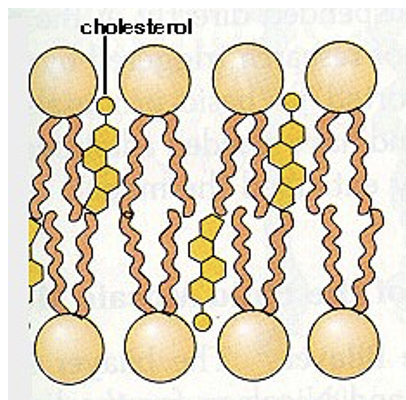
cholesterol
cholesterol in membranes
cholesterol in membranes
component of all cell membranes
* synthetic precursor of steroid hormones
* precursor of bile acids and salts
\
plasma membranes can have around 1 cholesterol per phospholipid, they maintain the osmotic pressure u find in the cell
* ¨They immobilize the first few hydrocarbon groups of the phospholipid molecules. This makes the lipid bilayer less deformable and decreases its permeability to small water-soluble molecules.
* ¨Without cholesterol (such as in a bacterium) a cell would need a cell wall.
* synthetic precursor of steroid hormones
* precursor of bile acids and salts
\
plasma membranes can have around 1 cholesterol per phospholipid, they maintain the osmotic pressure u find in the cell
* ¨They immobilize the first few hydrocarbon groups of the phospholipid molecules. This makes the lipid bilayer less deformable and decreases its permeability to small water-soluble molecules.
* ¨Without cholesterol (such as in a bacterium) a cell would need a cell wall.
8
New cards
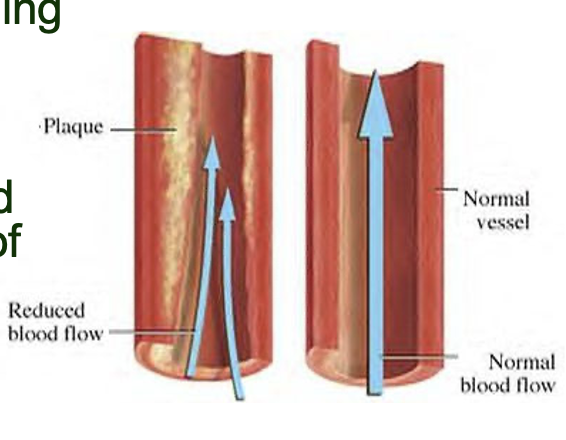
artherosclerosis
\
cholesterol in atherosclerosis
\
cholesterol in atherosclerosis
* the hardening and/or thickening of major arteries
* high fat diet, smoking, diabetes and high BP increase artherosclerosis risk
* the condition can lead to **thrombosis**, stroke and restricted movement of limbs which can result in gangrene
Lipids in excess in blood leads to atherosclerosis (a form of arteriosclerosis, a blockage of blood vessels, in this case a blockage w lipids)
\
* Deposition of cholesterol from *LDL* on the walls of arteries
* Gradual build up of fat and other deposits such as calcium to form plaque
* Plaque restricts flow of blood through arteries
* Rupture can cause blood clot
* Rupture of plaque in major artery or heart can cause heart attack
* Rupture of plaque in brain can cause stroke
%%Issue is when the plaque breaks down bc that stimulates platelets which will block and clot the blood vessels, cholesterol merely initiates the process of blockage, doesn’t do it itself%%
* high fat diet, smoking, diabetes and high BP increase artherosclerosis risk
* the condition can lead to **thrombosis**, stroke and restricted movement of limbs which can result in gangrene
Lipids in excess in blood leads to atherosclerosis (a form of arteriosclerosis, a blockage of blood vessels, in this case a blockage w lipids)
\
* Deposition of cholesterol from *LDL* on the walls of arteries
* Gradual build up of fat and other deposits such as calcium to form plaque
* Plaque restricts flow of blood through arteries
* Rupture can cause blood clot
* Rupture of plaque in major artery or heart can cause heart attack
* Rupture of plaque in brain can cause stroke
%%Issue is when the plaque breaks down bc that stimulates platelets which will block and clot the blood vessels, cholesterol merely initiates the process of blockage, doesn’t do it itself%%
9
New cards
transportation of cholesterol
Cholesterol is insoluble in water, but must be moved from tissue of origin (liver) to tissues in which it is stored or consumed. in the bloodstream its transported in the form of complex lipids
* LDL - Low Density Lipoproteins (bad cholesterol)
* HDL - High Density Lipoproteins (good cholesterol)
U should have a max level of LDL that u don’t go over bc it can lead to atherosclerosis cholesterol only leaks from LDL, not HDL
\
**Complex lipids**: combination of lipids and proteins produce soluble particles
**Proteins**: are called apolipoproteins when they are not in complex with lipids (“apo” designates protein in its lipid-free form)
**Different apolipoproteins in LDL and HDL**:
%%apolipoprotein A (ApoA) in HDL%%
%%apolipoprotein B (ApoB) in LDL%%
Need to wrap ur lipids in smthn that will make them soluble in water in blood. This soluble protein packet engulfs urlipids, its called an apolipoprotein
* LDL - Low Density Lipoproteins (bad cholesterol)
* HDL - High Density Lipoproteins (good cholesterol)
U should have a max level of LDL that u don’t go over bc it can lead to atherosclerosis cholesterol only leaks from LDL, not HDL
\
**Complex lipids**: combination of lipids and proteins produce soluble particles
**Proteins**: are called apolipoproteins when they are not in complex with lipids (“apo” designates protein in its lipid-free form)
**Different apolipoproteins in LDL and HDL**:
%%apolipoprotein A (ApoA) in HDL%%
%%apolipoprotein B (ApoB) in LDL%%
Need to wrap ur lipids in smthn that will make them soluble in water in blood. This soluble protein packet engulfs urlipids, its called an apolipoprotein
10
New cards
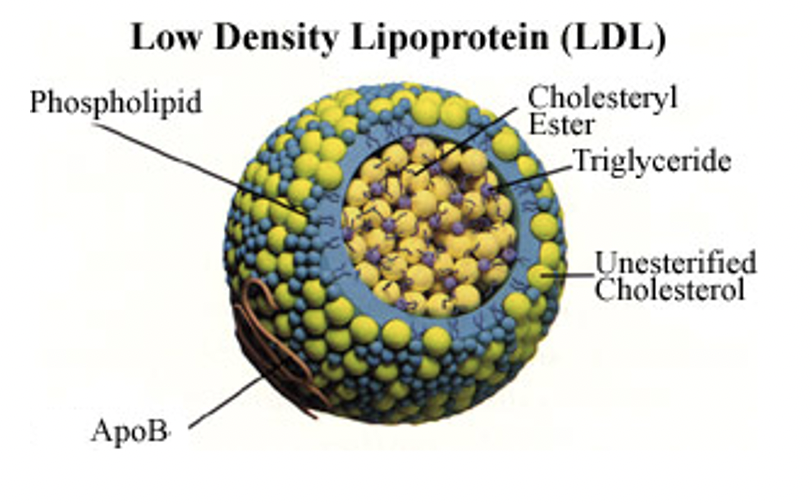
lipoprotein
**low density lipoproteins**
**low density lipoproteins**
Complexes of:
* Specific carrier protein (apolipoprotein)
* Phospholipids
* Triglycerides
* Cholesterol
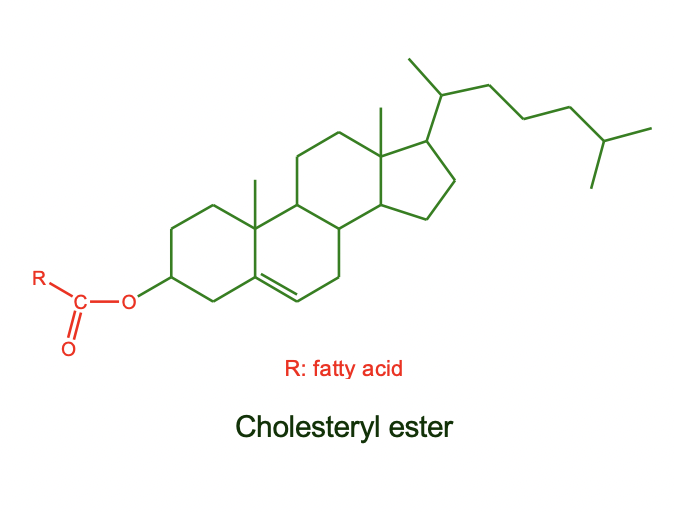
* Cholesteryl esters
? Can esterify it w a fatty acid
Chain of a fatty acid ?
_
**LDL:** very __rich__ in cholesterol & cholesteryl esters
* Specific carrier protein (apolipoprotein)
* Phospholipids
* Triglycerides
* Cholesterol
* Cholesteryl esters
? Can esterify it w a fatty acid
Chain of a fatty acid ?
_
**LDL:** very __rich__ in cholesterol & cholesteryl esters
11
New cards
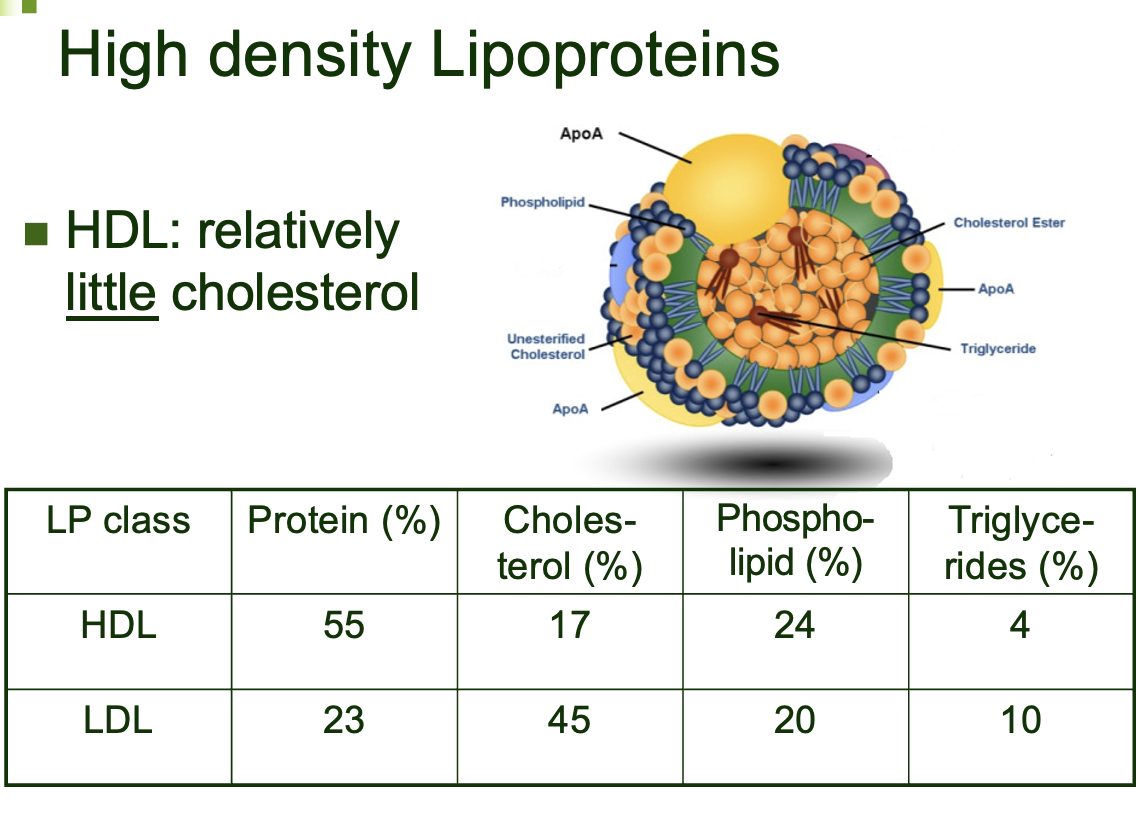
High density lipoproteins
HDL: relatively **little** cholesterol
Main components of HDL r proteins and LDL is cholesterol
\
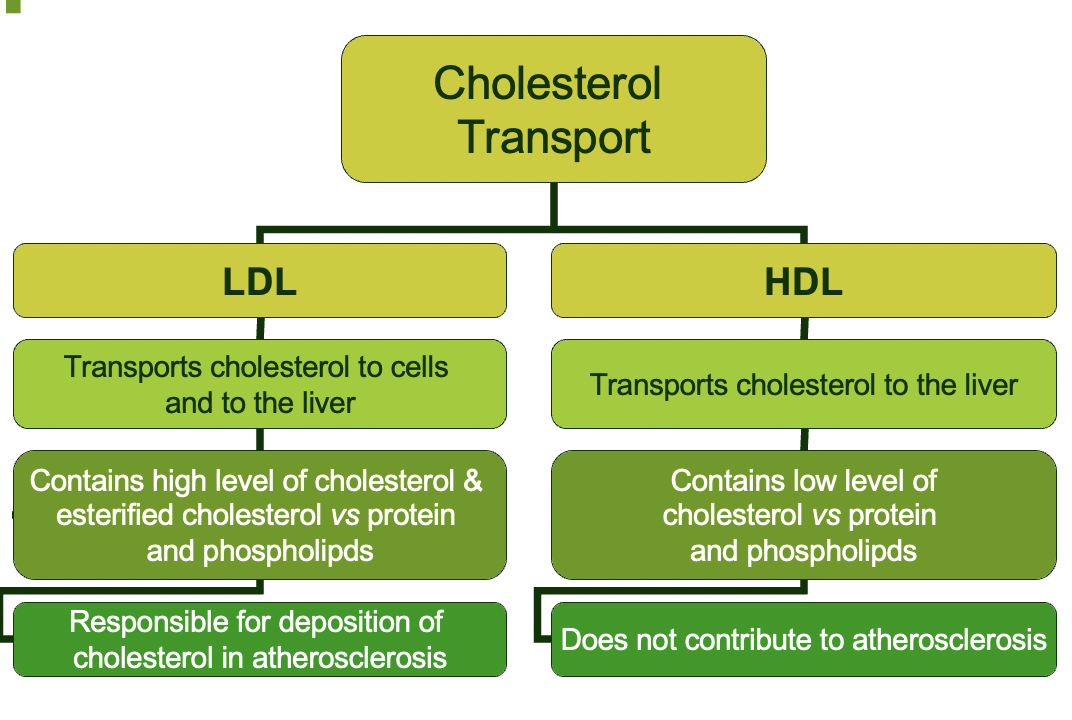
cholesterol transport summary
LDL:
* transports cholesterol to cells and to the liver
* contains high level of cholesterol & esterified cholesterol vs protein and phospholipids
* responsible for deposition of cholesterol in atherosclerosis
HDL:
* transports cholesterol to liver
* contains low level of cholesterol vs protein and phospholipdis
* does not contribute to atherosclerosis
Main components of HDL r proteins and LDL is cholesterol
\
cholesterol transport summary
LDL:
* transports cholesterol to cells and to the liver
* contains high level of cholesterol & esterified cholesterol vs protein and phospholipids
* responsible for deposition of cholesterol in atherosclerosis
HDL:
* transports cholesterol to liver
* contains low level of cholesterol vs protein and phospholipdis
* does not contribute to atherosclerosis