Lec Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:00 AM on 2/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
1
New cards
hormones
* Messenger of the endocrine system
* Secreted by exocytosis
* Produced in minute amounts by a collection of specialized epithelial cells
* Secreted directly into blood or extracellular fluid
* Acts on specific tissues of the body called target tissues
* Most are protein based or steroids
* Secreted by exocytosis
* Produced in minute amounts by a collection of specialized epithelial cells
* Secreted directly into blood or extracellular fluid
* Acts on specific tissues of the body called target tissues
* Most are protein based or steroids
2
New cards
protein derived hormone
water soluble
receptors typically membrane bound
receptors typically membrane bound
3
New cards
steroid derived hormone
fat soluble
can cross cell membrane
receptors typically in cytosol or nucleus
can cross cell membrane
receptors typically in cytosol or nucleus
4
New cards
nervous system vs endocrine system
the nervous system uses electrical impulses to send messages through neurons while endocrine glands use hormones to send messages to the target cells through the bloodstream
5
New cards
membrane bound receptors
protein derived hormones bind to them
\n Activation of 2nd messengers
\n Response time: fast
\n Activation of 2nd messengers
\n Response time: fast
6
New cards
intracellular receptors
steroid hormones bind to them \n
Response time: slower than membrane bound \n
activate gene expression by binding to steroid receptors, proteins in the cytoplasm that, when activated, act as factors that initiate transcription
Response time: slower than membrane bound \n
activate gene expression by binding to steroid receptors, proteins in the cytoplasm that, when activated, act as factors that initiate transcription
7
New cards
prolactin
abbrev: PRL
location: anterior pituitary
structure: protein
target: mammary glands
response: causes milk production
conditions: secreted at the end of pregnancy; excess production can be a sign of breast cancer in men
location: anterior pituitary
structure: protein
target: mammary glands
response: causes milk production
conditions: secreted at the end of pregnancy; excess production can be a sign of breast cancer in men
8
New cards
growth hormone
abbrev: GH
location: anterior pituitary
structure: protein
target: mainly muscle and connective tissues
response: a. a. uptake for protein & glycogen synthesis, growth in tissues, stimulates muscle and bone growth
conditions: (decreased amounts) pituitary dwarfism, and pituitary giants (gigantism) and acromegaly (abnormal amounts)
location: anterior pituitary
structure: protein
target: mainly muscle and connective tissues
response: a. a. uptake for protein & glycogen synthesis, growth in tissues, stimulates muscle and bone growth
conditions: (decreased amounts) pituitary dwarfism, and pituitary giants (gigantism) and acromegaly (abnormal amounts)
9
New cards
thyroid stimulating hormone
abbrev: TSH
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: thyroids gland
response: increase thyroid hormone production
conditions: hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: thyroids gland
response: increase thyroid hormone production
conditions: hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
10
New cards
adrenocorticotropic hormone
abbrev: ACTH
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: adrenal cortex
response: increased hormone secretion from the adrenal cortex (especially glucocorticoids)
conditions: cushings
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: adrenal cortex
response: increased hormone secretion from the adrenal cortex (especially glucocorticoids)
conditions: cushings
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
11
New cards
follicle stimulating hormone
abbrev: FSH
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: follicles in ovaries, seminiferous tubules (males)
response: follicle maturation and estrogen secretion in ovaries, and sperm cell production in testes
conditions: infertility, menstrual difficulties in women, low sex drive in men, and early or delayed puberty in children
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: follicles in ovaries, seminiferous tubules (males)
response: follicle maturation and estrogen secretion in ovaries, and sperm cell production in testes
conditions: infertility, menstrual difficulties in women, low sex drive in men, and early or delayed puberty in children
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
12
New cards
androgens
location: adrenal cortex
* Female: testosterone
* Male: progesterone
structure: steroid
target: many tissues
response: some secondary sex characteristics in females
conditions: persistent acne, hirsutism, androgenic alopecia
* Female: testosterone
* Male: progesterone
structure: steroid
target: many tissues
response: some secondary sex characteristics in females
conditions: persistent acne, hirsutism, androgenic alopecia
13
New cards
epinephrine and norepinephrine
Epi - 80%; Nor- 20%
location: adrenal medulla
structure: protein
target: heart, blood vessels, liver, fat cells
response: fight or flight response
conditions: hypertension, depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
location: adrenal medulla
structure: protein
target: heart, blood vessels, liver, fat cells
response: fight or flight response
conditions: hypertension, depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
14
New cards
glucagon
location: pancreas
structure: protein
target: liver
response: associated with sympathetic response to low levels of glucose in the blood. Stimulates breakdown of glycogen stores in usable glucose
conditions: hypoglycemia, diabetes, acute or chronic pancreatitis
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
structure: protein
target: liver
response: associated with sympathetic response to low levels of glucose in the blood. Stimulates breakdown of glycogen stores in usable glucose
conditions: hypoglycemia, diabetes, acute or chronic pancreatitis
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
15
New cards
testosterone
location: testes
structure: steroid
target: most body tissues
response: secondary sex characteristics, libido, sperm production
conditions: hypogonadism
structure: steroid
target: most body tissues
response: secondary sex characteristics, libido, sperm production
conditions: hypogonadism
16
New cards
tropic hormones
\n TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH
17
New cards
tropic hormone function
target other endocrine glands
18
New cards
luteinizing hormone
abbrev: LH
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: ovaries and testes
response: ovulation and progesterone production in ovaries, testosterone synthesis, and support for sperm cell production in testes
conditions: abnormal development, sexual dysfunction, and infertility
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
location: anterior pituitary (tropic)
structure: protein
target: ovaries and testes
response: ovulation and progesterone production in ovaries, testosterone synthesis, and support for sperm cell production in testes
conditions: abnormal development, sexual dysfunction, and infertility
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
19
New cards
antiduretic hormone
abbrev: ADH
location: posterior pituitary
structure: protein
target: nephrons on kidney
response: causes the nephrons to reabsorb water instead of losing it as urine
conditions: copious urination can lead to diabetes insipidus; can be inhibited by alcohol
\
DAG (Directed acyclic graphs) IP3 Second messenger system
location: posterior pituitary
structure: protein
target: nephrons on kidney
response: causes the nephrons to reabsorb water instead of losing it as urine
conditions: copious urination can lead to diabetes insipidus; can be inhibited by alcohol
\
DAG (Directed acyclic graphs) IP3 Second messenger system
20
New cards
oxytocin
location: posterior pituitary
structure: protein
target: uterus and mammary glands
response: causes uterine contraction during birth and milk ejection, high during ejaculation and orgasm
conditions: autism, schizophrenia, mood and anxiety disorders
\
DAG (Directed acyclic graphs) IP3 Second messenger system
structure: protein
target: uterus and mammary glands
response: causes uterine contraction during birth and milk ejection, high during ejaculation and orgasm
conditions: autism, schizophrenia, mood and anxiety disorders
\
DAG (Directed acyclic graphs) IP3 Second messenger system
21
New cards
thyroid hormone
abbrev: TH
location: thyroid
structure: protein
target: most cells in the body
response: increases metabolism, essential for growth
conditions: low TH (hypothyroidism) can lead to cold, weight gain, and fatigue, can be treated w/ steroids, associated with high TSH levels; high TH (hyperthyroidism) loss of weight, high energy, and increased ocular pressure, and can sometimes die from heart issues, treatment is to remove or kill portions of thyroid, associated with low TSH levels
location: thyroid
structure: protein
target: most cells in the body
response: increases metabolism, essential for growth
conditions: low TH (hypothyroidism) can lead to cold, weight gain, and fatigue, can be treated w/ steroids, associated with high TSH levels; high TH (hyperthyroidism) loss of weight, high energy, and increased ocular pressure, and can sometimes die from heart issues, treatment is to remove or kill portions of thyroid, associated with low TSH levels
22
New cards
calcitonin
location: thyroid
structure: protein
target: bone
response: decreases Ca2+ by decreasing osteoclast activity
conditions: medullary thyroid cancer, brittle bones
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
structure: protein
target: bone
response: decreases Ca2+ by decreasing osteoclast activity
conditions: medullary thyroid cancer, brittle bones
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
23
New cards
parathyroid hormone
abbrev: PTH
location: parathyroid
structure: protein
target: bones, kidneys, small intestine
response: raise levels of blood calcium by breaking down bone, causes reabsorption of calcium by kidney, and causes intestines to absorb more calcium and vitamin D
conditions: is sometimes removed when thyroid is removed
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
location: parathyroid
structure: protein
target: bones, kidneys, small intestine
response: raise levels of blood calcium by breaking down bone, causes reabsorption of calcium by kidney, and causes intestines to absorb more calcium and vitamin D
conditions: is sometimes removed when thyroid is removed
\
act via cAMP mechanisms
24
New cards
aldosterone
location: adrenal cortex
structure: steroid
target: nephrons of the kidney – sodium ion resorption
response: controls nephron tubule permeability and reabsorbs salts based on need, thus water will follow the salt back in by osmosis
conditions: Hyperaldosteronism
structure: steroid
target: nephrons of the kidney – sodium ion resorption
response: controls nephron tubule permeability and reabsorbs salts based on need, thus water will follow the salt back in by osmosis
conditions: Hyperaldosteronism
25
New cards
cortisol
location: adrenal cortex
structure: steroid
target: most tissues in the body
response: increase fat and protein breakdown, inhibit immune inflammatory response
conditions: cushings
structure: steroid
target: most tissues in the body
response: increase fat and protein breakdown, inhibit immune inflammatory response
conditions: cushings
26
New cards
insulin
location: pancreas
structure: protein
target: especially liver, skeletal muscle, fat tissue
response: increases intake of glucose by cells
conditions: diabetes mellitus, obesity, cardiovascular disease
\
Usually, part of the parasympathetic response after a meal when a lot of glucose is present in the blood
structure: protein
target: especially liver, skeletal muscle, fat tissue
response: increases intake of glucose by cells
conditions: diabetes mellitus, obesity, cardiovascular disease
\
Usually, part of the parasympathetic response after a meal when a lot of glucose is present in the blood
27
New cards
estrogen and progesterone
location: ovaries
structure: steroid
target: most body tissues
response: secondary sex characteristics, menstrual cycle
conditions: menstrual problems, menopause, premature menopause
structure: steroid
target: most body tissues
response: secondary sex characteristics, menstrual cycle
conditions: menstrual problems, menopause, premature menopause
28
New cards
islet vs acinar cells
**islet**
produces hormones (e.g., insulin and glucagon)
endocrine (secrete hormones or other products directly into the blood)
\
**acinar**
produce digestive enzymes
exocrine (secrete their products through ducts opening onto an epithelium)
produces hormones (e.g., insulin and glucagon)
endocrine (secrete hormones or other products directly into the blood)
\
**acinar**
produce digestive enzymes
exocrine (secrete their products through ducts opening onto an epithelium)
29
New cards
up regulation
the number of receptors increases in response to rising hormone levels, making the cell more sensitive to the hormone and allowing for more cellular activity
\
ex. increase in uterine oxytocin receptors in the third trimester of pregnancy, promoting the contraction of the smooth muscle of the uterus
\
ex. increase in uterine oxytocin receptors in the third trimester of pregnancy, promoting the contraction of the smooth muscle of the uterus
30
New cards
down regulation
the number of receptors decreases in response to rising hormone levels allowing for decreased cellular activity
\
ex. insulin receptors may be down regulated in type 2 diabetes
\
ex. insulin receptors may be down regulated in type 2 diabetes
31
New cards
affinity
the extent or fraction to which a drug binds to receptors at any given drug concentration or the firmness with which the drug binds to the receptor
32
New cards
pineal gland
* Sits right above corpora quadrigemina
* Secretes melatonin
* Secretes melatonin
33
New cards
pituitary gland
* Connected to hypothalamus
* In sella turcica of sphenoid bone
* In sella turcica of sphenoid bone
34
New cards
thyroid gland
two lobes are connected by a bridge
located in neck
located in neck
35
New cards
parathyroid
* Connected to thyroid
* 4 of them
* 4 of them
36
New cards
thymus
* Located in the chest cavity
* Extremely important at birth and young infants
* Takes over for immunity
* Can be as large as from the heart to thyroid gland
* By adulthood it deteriorates
* Extremely important at birth and young infants
* Takes over for immunity
* Can be as large as from the heart to thyroid gland
* By adulthood it deteriorates
37
New cards
heart
* Not technically an endocrine organ
* Secretes hormone to regulate BP
* Secretes hormone to regulate BP
38
New cards
stomach and intestine lining
* Secretes hormones that help metabolism and digestion
* Not considered endocrine
* Not considered endocrine
39
New cards
adrenal glands
Located on top of the kidneys
40
New cards
pancreas
* Mix of endocrine and exocrine gland
* Endocrine: insulin, glucagon
* Exocrine: more digestive related
* Epithelial glands
* Endocrine: insulin, glucagon
* Exocrine: more digestive related
* Epithelial glands
41
New cards
ovary
* Mix of endocrine and exocrine gland
* Epithelial glands
* Exocrine: ova
* Endocrine: estrogen and progesterone
* Epithelial glands
* Exocrine: ova
* Endocrine: estrogen and progesterone
42
New cards
testes
* Mix of endocrine and exocrine gland
* Epithelial glands
* Exocrine: spermatozoa
* Endocrine: testosterone
* Epithelial glands
* Exocrine: spermatozoa
* Endocrine: testosterone
43
New cards
eicosanoids
* Derived from cell membranes (arachidonic acid)
* Leukotrienes and prostaglandins
* Also called paracrine substances
* Not considered true hormones by some
* Leukotrienes and prostaglandins
* Also called paracrine substances
* Not considered true hormones by some
44
New cards
cell response
* Opening or closing of ion channels.
* Stimulate enzyme synthesis within cells.
* Activates or deactivates enzymes within the cell.
* Can cause phosphorylation of enzymes within the cell.
* mRNA synthesis and direct gene activation.
* Can influence or affect mitosis.
* Stimulate enzyme synthesis within cells.
* Activates or deactivates enzymes within the cell.
* Can cause phosphorylation of enzymes within the cell.
* mRNA synthesis and direct gene activation.
* Can influence or affect mitosis.
45
New cards
permissiveness
* One hormone cannot exert its full effects unless another hormone is present
* Congenital hypothyroidism
* Congenital hypothyroidism
46
New cards
synergism
* When two or more hormones affect a target cell and their effects are amplified
* Ex. After you eat blood sugar begins to drop so body secretes glucagon and epinephrine to cause liver to break down glycogen and raise blood sugar levels
* Ex. After you eat blood sugar begins to drop so body secretes glucagon and epinephrine to cause liver to break down glycogen and raise blood sugar levels
47
New cards
antagonism
* When one hormone opposes the action of another
* Ex. High blood sugar – insulin; low blood sugar – glucagon
* PTH vs calcitonin
* Ex. High blood sugar – insulin; low blood sugar – glucagon
* PTH vs calcitonin
48
New cards
humoral regulation
* Insulin and glucagon
* Aldosterone and potassium
* Aldosterone and potassium
49
New cards
neural regulation
* Posterior pituitary
* Hypothalamus
* Activation of adrenal medulla
* Hypothalamus
* Activation of adrenal medulla
50
New cards
hormonal regulation
Anterior pituitary (tropic hormones)
51
New cards
primary hypothyroidism
TH decrease → TRH and TSH increase
52
New cards
secondary hypothyroidism
TH decreases and TSH decreases → TRH increases
53
New cards
tertiary hypothyroidism
TH, TSH, TRH decrease
54
New cards
primary hyperthyroidism
TH increases → TSH and TRH decreases
55
New cards
secondary hyperthyroidism
TRH decreases → TH and TSH increase
56
New cards
tertiary hyperthyroidism
TH, TSH, and TRH increase
57
New cards
Cushing’s (primary hypercortisolism)
Cortisol high → ACTH low
58
New cards
secondary hypercortisolism
cortisol high → ACTH high
59
New cards
addison’s disease ( primary adrenal insufficiency)
Cortisol low → ACTH high
60
New cards
secondary adrenal insufficiency (hypopituitarism)
Cortisol low → ACTH low
61
New cards
plasma
about 55% blood volume
about 92% H2O 8% proteins, gases, nutrients
about 92% H2O 8% proteins, gases, nutrients
62
New cards
formed elements of blood
45%
RBCs
WBCs
Platelets
RBCs
WBCs
Platelets
63
New cards
plasma proteins
Albumin (60%)
* Maintains osmotic pressure in capillaries, carries other molecules through the blood
\
Globulin (36%)
* Transport binding proteins and some types of antibodies
\
Fibrinogen (4%)
* Important for blood clotting
* Maintains osmotic pressure in capillaries, carries other molecules through the blood
\
Globulin (36%)
* Transport binding proteins and some types of antibodies
\
Fibrinogen (4%)
* Important for blood clotting
64
New cards
erythrocytes
RBCs
45% of blood by volume
4-6million/ μL
They do not have a nucleus
Short life span 120 days (about 4 months) max
Small biconcave discs
They can bend to pass through capillaries
Larger surface area to capture oxygen and CO2
45% of blood by volume
4-6million/ μL
They do not have a nucleus
Short life span 120 days (about 4 months) max
Small biconcave discs
They can bend to pass through capillaries
Larger surface area to capture oxygen and CO2
65
New cards
too few RBCs
tissue hypoxia
66
New cards
too many RBCs
viscous blood
67
New cards
hemoglobin
Oxygen carrier
Each erythrocyte has enough hemoglobin to carry 1 billion molecules of oxygen
Has 4 atoms of iron to bind to oxygen
* Women 12-16 g/dL
* Men 13-18 g/dL
Each erythrocyte has enough hemoglobin to carry 1 billion molecules of oxygen
Has 4 atoms of iron to bind to oxygen
* Women 12-16 g/dL
* Men 13-18 g/dL
68
New cards
hematopoiesis
Takes place in red bone marrow
Production is stimulated by erythropoietin (EPO)
Production is stimulated by erythropoietin (EPO)
69
New cards
platelets
150k-400k/ μL
Fragments of megakaryocytes
Short lived (abt 10 days)
Help with clotting
Fragments of megakaryocytes
Short lived (abt 10 days)
Help with clotting
70
New cards
leukocytes
WBCs
**N**ever **L**et **M**onkeys **E**at **B**ananas (most to least abundant)
Less than 1% of blood
Are true cells
Includes different subtypes
* Neutrophils
* Basophils
* Lymphocytes (B and T cells)
* Monocytes (macrophages)
**N**ever **L**et **M**onkeys **E**at **B**ananas (most to least abundant)
Less than 1% of blood
Are true cells
Includes different subtypes
* Neutrophils
* Basophils
* Lymphocytes (B and T cells)
* Monocytes (macrophages)
71
New cards
leukopoiesis
WBC production
Hormones and other stressors can stimulate their production in bone marrow
Hormones and other stressors can stimulate their production in bone marrow
72
New cards
leukopenia
insufficient amount of WBCs
Autoimmune disease
Severe stress
Cancer treatment
Bone marrow deficiency
Autoimmune disease
Severe stress
Cancer treatment
Bone marrow deficiency
73
New cards
leukocytosis
Too many WBCs
Infections (especially bacterial)
Inflammatory disease
Leukemia
Mono
Infections (especially bacterial)
Inflammatory disease
Leukemia
Mono
74
New cards
neutrophils
Most abundant WBC
Band cell stage – immature version of neutrophil
50-70%
Nucleus has between 3-5 lobes
Clinical significance
* Increase in number during acute bacterial infections such as appendicitis
* Most bacteria are extracellular pathogens
* Increased number = neutrophilia
* Decreased number = neutropenia
Band cell stage – immature version of neutrophil
50-70%
Nucleus has between 3-5 lobes
Clinical significance
* Increase in number during acute bacterial infections such as appendicitis
* Most bacteria are extracellular pathogens
* Increased number = neutrophilia
* Decreased number = neutropenia
75
New cards
eosinophils
1-4% of WBC
Nucleus often bi-lobed or figure 8 shape
Cytoplasm dyes red in presences of dye eosin
Clinical significance
* Increased eosinophils may indicate allergic conditions or parasitic infections (trichinosis)
* eosinophilic esophagitis
Nucleus often bi-lobed or figure 8 shape
Cytoplasm dyes red in presences of dye eosin
Clinical significance
* Increased eosinophils may indicate allergic conditions or parasitic infections (trichinosis)
* eosinophilic esophagitis
76
New cards
basophils
< 1% of WBC
Large U or S shaped nucleus stains blue in presences of basic dyes
Can release histamine and heparin
Clinical significance
* Release histamine to promote inflammation and heparin to prevent clotting
* Very important for immune response
77
New cards
lymphocytes
20-30% of WBC
Smallest WBC
Nucleus is spherical
Clinical significance
* Increased amounts seen with almost all general immune system responses
* T-cells – contact killing, generally attack viruses
* B-cells – often more active against bacteria, antibody production
Smallest WBC
Nucleus is spherical
Clinical significance
* Increased amounts seen with almost all general immune system responses
* T-cells – contact killing, generally attack viruses
* B-cells – often more active against bacteria, antibody production
78
New cards
monocytes
3-8% of WBC
Largest of WBC
Nucleus generally kidney shaped
When they leave blood, they are macrophages
Clinical significance
* Voracious phagocyte that acts in long-term cleanup of chronic infections (mononucleosis, tuberculosis)
* Increased amounts during viral infections and chronic infections
**Add or Remove Flashcards**
Largest of WBC
Nucleus generally kidney shaped
When they leave blood, they are macrophages
Clinical significance
* Voracious phagocyte that acts in long-term cleanup of chronic infections (mononucleosis, tuberculosis)
* Increased amounts during viral infections and chronic infections
**Add or Remove Flashcards**
79
New cards
hemostasis
1) Constriction of the blood vessel
2) Formation of a temporary “platelet plug."
3) Activation of the coagulation cascade
4) Formation of “fibrin plug” or the final clot
2) Formation of a temporary “platelet plug."
3) Activation of the coagulation cascade
4) Formation of “fibrin plug” or the final clot
80
New cards
reticulocyte
* often found in hypoxic situations
* Immature RBCs
* Immature RBCs
81
New cards
hazards of cross matching blood types
agglutination which can cause:
\
red blood cell destruction
renal failure
shock
death
\
red blood cell destruction
renal failure
shock
death
82
New cards
vascular spasm
narrowing of the arteries caused by a persistent contraction of the blood vessels
83
New cards
platelet plug formation
Major stimulus is when platelets are exposed to underlying connective tissue
\
the process where a platelet plug forms to prevent further loss of blood from a damaged vessel
\
the process where a platelet plug forms to prevent further loss of blood from a damaged vessel
84
New cards
coagulation
adhesion and aggregation of platelets, as well as deposition and maturation of fibrin.
85
New cards
clot retraction
Actomyosin proteins pull edges of cut together
\
increases clot density and decreases clot size
\
increases clot density and decreases clot size
86
New cards
fibrinolysis
* Fibrin mesh that trapped RBCs needs to be dissolved once vessel is healed
* If not dissolved it can get stuck somewhere and cause a clot (pulmonary embolism – blood clot stuck in lungs)
* If not dissolved it can get stuck somewhere and cause a clot (pulmonary embolism – blood clot stuck in lungs)
87
New cards
RBC counts
* Women 4.2-5.4 million/µL
* Men 4.6-6.2 million/µL
* Men 4.6-6.2 million/µL
88
New cards
WBC counts
5000 - 10000 cells/μL
89
New cards
hematocrit
aka PCV (packed cell volume) percentage of blood that is cells (usually RBCs)
* Women 37-48%
* Men 45%-52%
\
referred to as H&H in clinical settings (hematocrit and hemoglobin)
\
clinical significance
\
Anemia: a reduction of the delivery of O2 to tissues caused either by having too few RBCs or not enough hemoglobin in the circulating blood. \n
Polycythemia - is an abnormally high density of RBC, can lead to overexertion of the heart and vessel clogging
* Women 37-48%
* Men 45%-52%
\
referred to as H&H in clinical settings (hematocrit and hemoglobin)
\
clinical significance
\
Anemia: a reduction of the delivery of O2 to tissues caused either by having too few RBCs or not enough hemoglobin in the circulating blood. \n
Polycythemia - is an abnormally high density of RBC, can lead to overexertion of the heart and vessel clogging
90
New cards
differential WBC count
measures the percentages of each type of leukocyte present
\
Neutrophils: 50-70% \n –Basophils: 0.5-1.0% \n –Eosinophils: 1-4% \n –Lymphocytes: 20-30% \n –Monocytes: 3-8%
\
Neutrophils: 50-70% \n –Basophils: 0.5-1.0% \n –Eosinophils: 1-4% \n –Lymphocytes: 20-30% \n –Monocytes: 3-8%
91
New cards
blood functions
Distribution – oxygen delivery, waste transport, hormones \n
Regulation – body temp, pH, fluid volume \n
Protection – preventing blood loss, immune functions
Regulation – body temp, pH, fluid volume \n
Protection – preventing blood loss, immune functions
92
New cards
oxygen rich
bright red blood
93
New cards
oxygen poor
dark red blood
94
New cards
average amount of blood in people
5-6L in adult males
4-5L in adult females
4-5L in adult females
95
New cards
danger of Rh factor
If Rh- mother
* Develops Rh+ fetus (75-80%)
* Few complications during first pregnancy
* Mom develops antibodies against Rh+ because mom and baby blood mix at birth
* During second pregnancy usually Rh+ again
* Rh antibodies can cross the placenta and interact with Rh+ fetus and agglutinate fetus blood (stroke, embolism, renal failure)
* Can lead to death of baby and mom
* Shots of Rhogam block body reacting to Rh factor
* Develops Rh+ fetus (75-80%)
* Few complications during first pregnancy
* Mom develops antibodies against Rh+ because mom and baby blood mix at birth
* During second pregnancy usually Rh+ again
* Rh antibodies can cross the placenta and interact with Rh+ fetus and agglutinate fetus blood (stroke, embolism, renal failure)
* Can lead to death of baby and mom
* Shots of Rhogam block body reacting to Rh factor
96
New cards
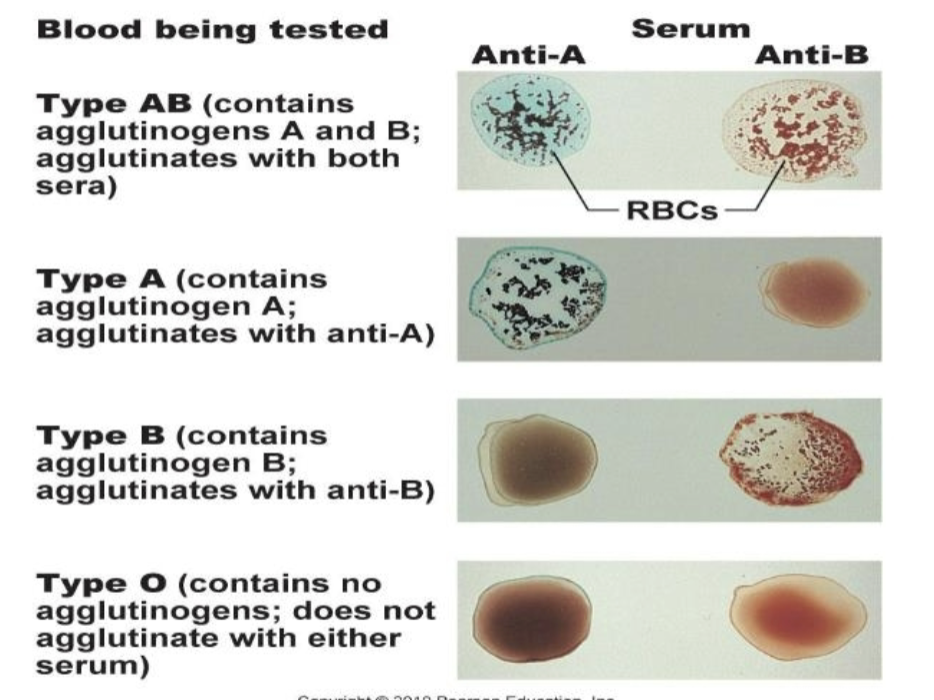
blood typing
Serological testing
* Antibody–antigen reaction
* Shows up as clotting
* Antibody–antigen reaction
* Shows up as clotting
97
New cards
thromboembolytic disorders
* Clotting in undamaged vessels
* Thrombus is a clot in a vessel
* Embolus is a clot that has broken free
* TPA (thromboplastin activator) breaks up clots and doctors use it to treat clots in strokes
* Thrombus is a clot in a vessel
* Embolus is a clot that has broken free
* TPA (thromboplastin activator) breaks up clots and doctors use it to treat clots in strokes
98
New cards
bleeding disorders
Thrombocytopenia
* Scarcity of thrombocytes
\
Hemophilia
* Blanket term for wide variety of bleeding disorders
* Most are genetic
* Related to lack of various clotting factors
* Scarcity of thrombocytes
\
Hemophilia
* Blanket term for wide variety of bleeding disorders
* Most are genetic
* Related to lack of various clotting factors
99
New cards
systemic circuit
blood pumped out to body (all tissues)
\
left ventricle through arteries into capillaries in tissues
\
left ventricle through arteries into capillaries in tissues
100
New cards
pulmonary circuit
shunts de-oxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be re-saturated with oxygen before being dispersed into the systemic circulation