Ochem II Reagents
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
recall with definition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
halogenation on benzene
X2/FeX3
sulfonation on benzene
SO3/H2SO4
how do you reverse sulfonation/nitration?
H3O+/H2O
nitration
HNO3/HCl
FC alkylation
R-X/AlX3
FC acylation
RCOX/AlX3
reduce aldehydes/ketones to alkanes
wolffe kishner (H2NNH2 KOH) or clemmenson reduction (ZnHg HCl)
NO2 —> NH2
H2/ Pd/C
NH2 —> NO2
F3COOOH
NH2 —> N2+
HONO (HCl, NaONO)
N2+ —> Cl, Br, CN
CuCl, CuBr, CuCN
N2+ —> I
KI
N2+ —> F
HBF4
N2+ —> OH
H2O/acid
N2+ —> H/D
H3PO2/D3PO2
oxidation of aromatic alkanes (need one H available)
KMnO4
oxidation of alcohols
CrO3/H2O (ketones/carboxylic acids)
CrO3/dry pyridine (for ketones/aldehydes)
PCC (aldehydes)
Swern oxidation: 1. DMSO, (COCl)2 2. Et3N (aldehydes)
oxidative cleavage of vicinol diols
HIO4
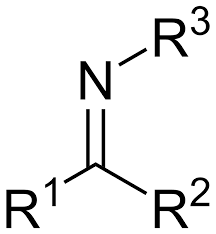
imine
R2CO + R-NH2, acid
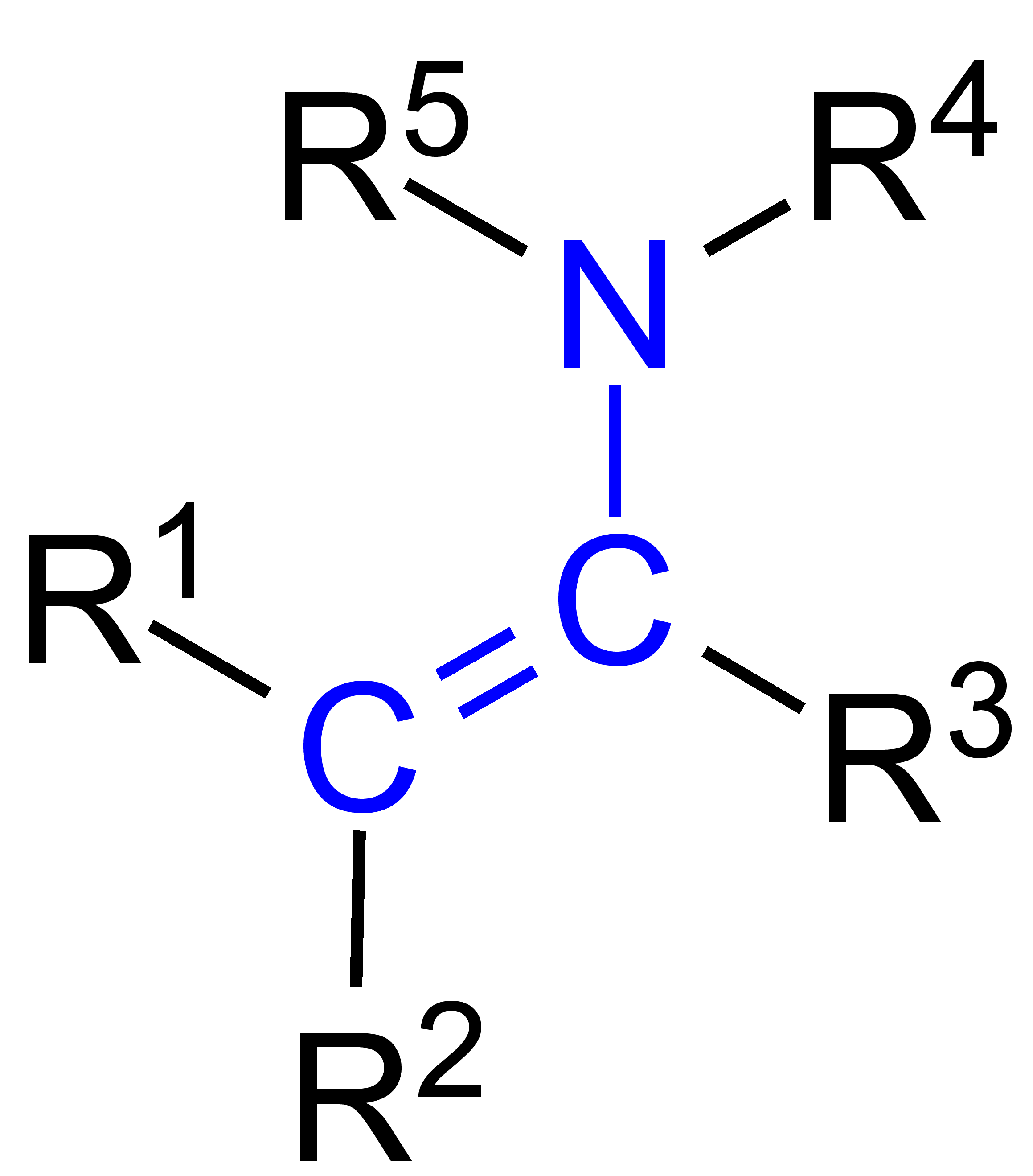
enamine
R2CO + R2-NH, acid
adding R groups to ketones
R-Li, R-MgX
H2O
reduction of C=O
LiAlH4/NaBH4 (*NaBH4 cannot be used to reduce carboxylic acids)
H2O
or meerwein-ponndorf-verley-oppenaner equilibration (for aldehydes and ketones)
making C=C bonds
Wittig reaction:
R2C=O + ylide (Ph3P=CR2) —> R2C=CR2
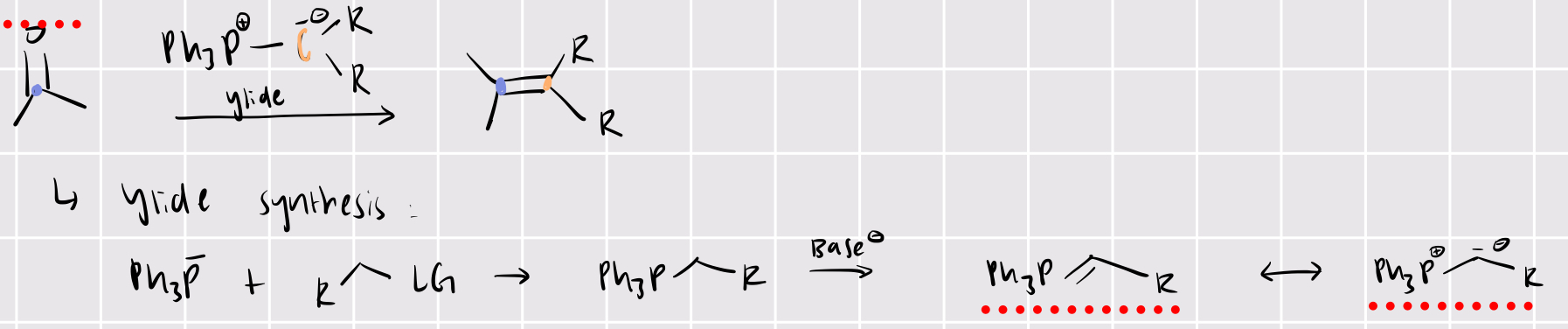
making carboxylic acids from CO2
R-Li/R-Mg-X + CO2
acid
b-keto carboxylic acid —> ketone
decarboxylation (heat)
alkene —> carboxylic acid
ozonelysis
O3
H2O2
making ester
fischer esterification: carboxylic acid + ROH/acid
SN2: 1. carboxylic acid + base 2. R-I
carboxylic acid + H2CN2 (diazomethane)
bayer-villager
carboxylic acid —> acyl chloride
SOCl2
carboxylic acid —> amide
DCC
R-NH2 or R2NH
2 carboxylic acid —> anhydride
300 C
adding R groups to carboxylic acids
R-Li (2 eq. for one addition)
H3O+
you make geminal diols, so you can use acid/base to reverse it into ketone with new R group
alcohols —> alkyl bromide/chloride
PBr3/SOCl2
alkyl halide —> carbon nucleophiles
2 Li+ or Mg
ester —> aldehyde
DIBAL-H / -78 C
acyl chloride —> amide
HNR2
anhydride —> amide
R2NH
R-I —> R-CN (nitrile)
KCN (SN2)
acyl chloride/ester/amide/nitrile —> carboxylic acid
NaOH or H3O+/H2O
(*if you use base, you have to adjust pH in the end with acid or else you have carboxylate ion)
RR’CO —> RCOOR’
bayer-villager: ketone + peroxy acid —> ester
rearrangement!
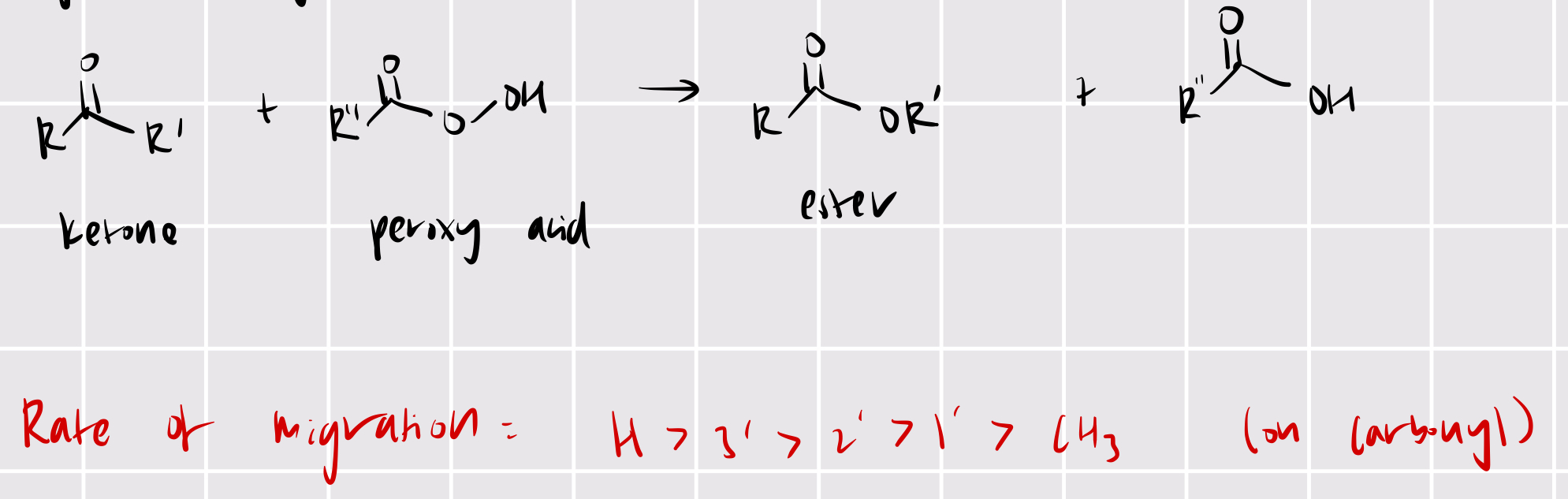
RCOR’ —> R‘CONHR
beckmann rearrangement
ketone + NH2OH/H3O+ —> oxime + acid/H2O —> amide
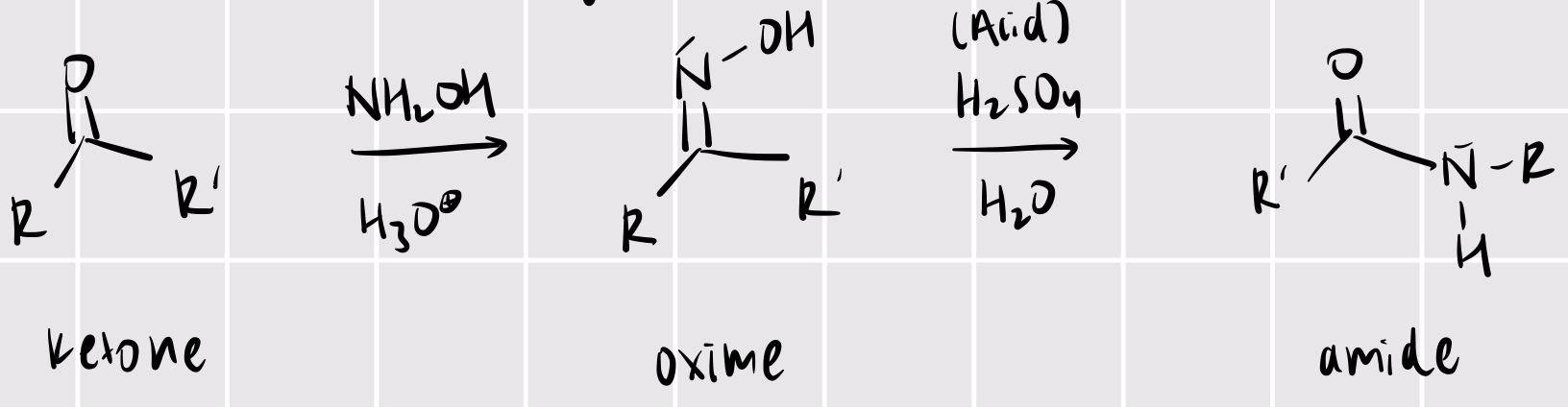
acyl chloride —> carboxylic acid (with one more carbon added)
wolffe rearrangement
acyl chloride + CH2N2 (diazomethane) —> ketene + H2O —> one more carbon added
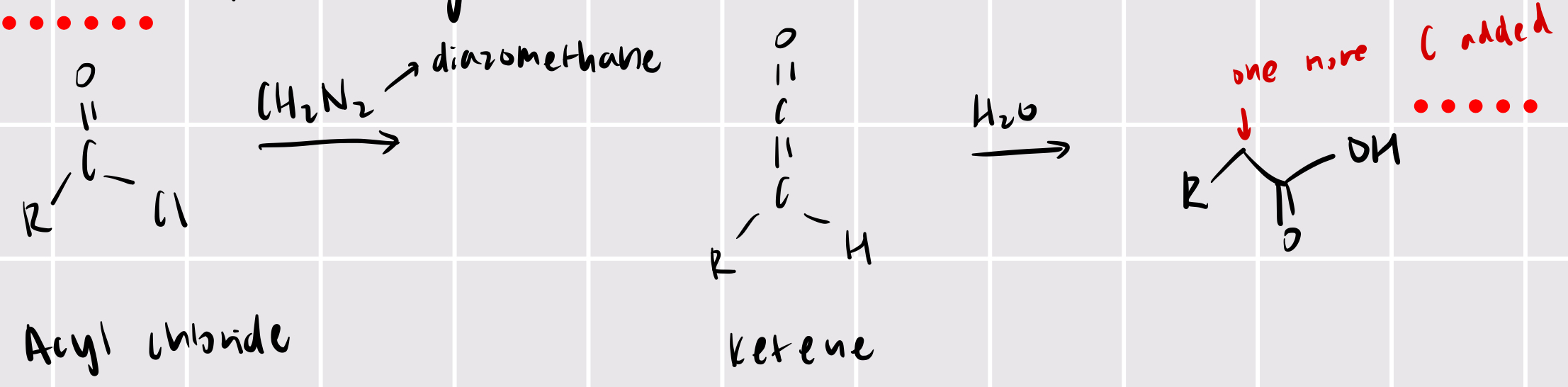
add one more carbon to carboxylic acid
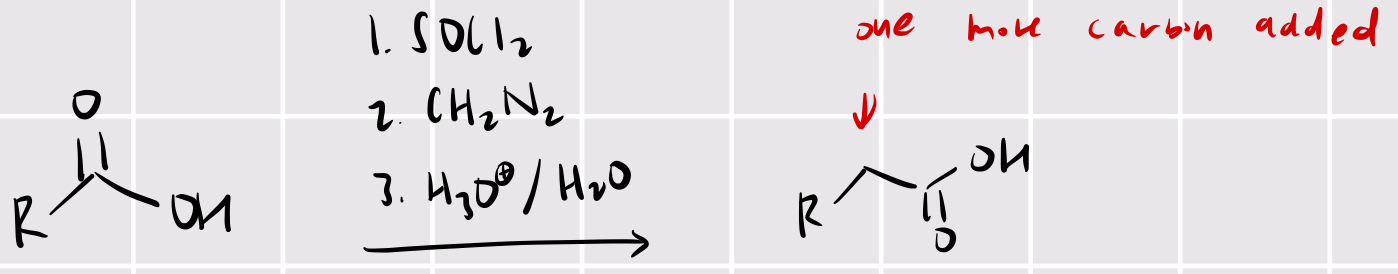
arndt-einstert rearrangement (basically wolffe but we convert carboxylic acid to acyl chloride first)
SOCl2 2. CH2N2 3. H3O+/H2O
acyl chloride —> isocyanate
curtius rearrangement
NaN3
heat or hv
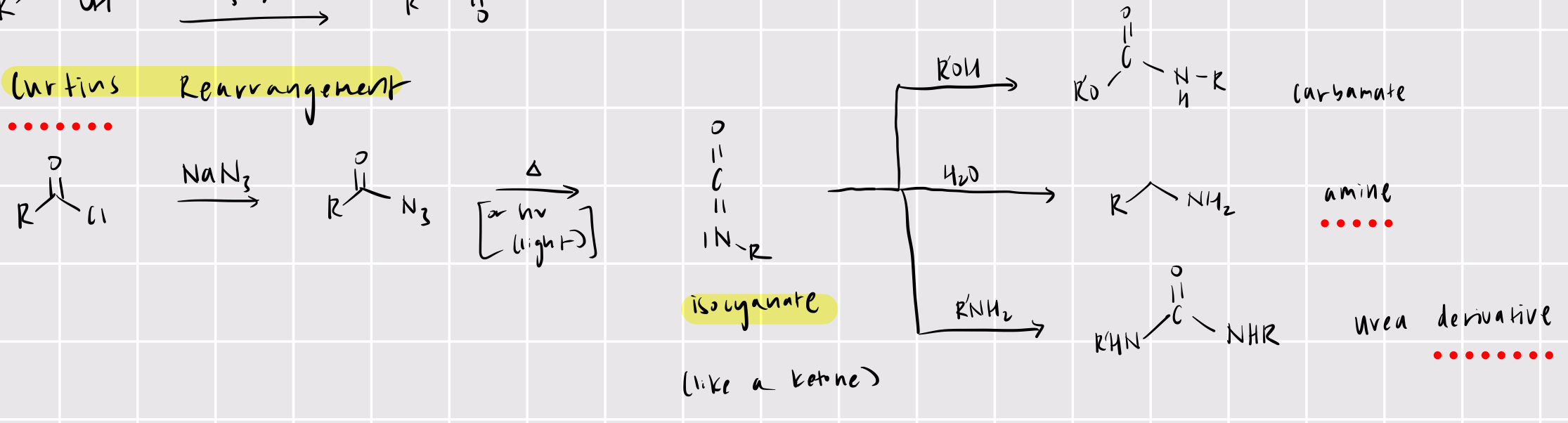
isocyanate —> products
carbamate (use ROH)
amine (use H2O)
urea derivative (RNH2)
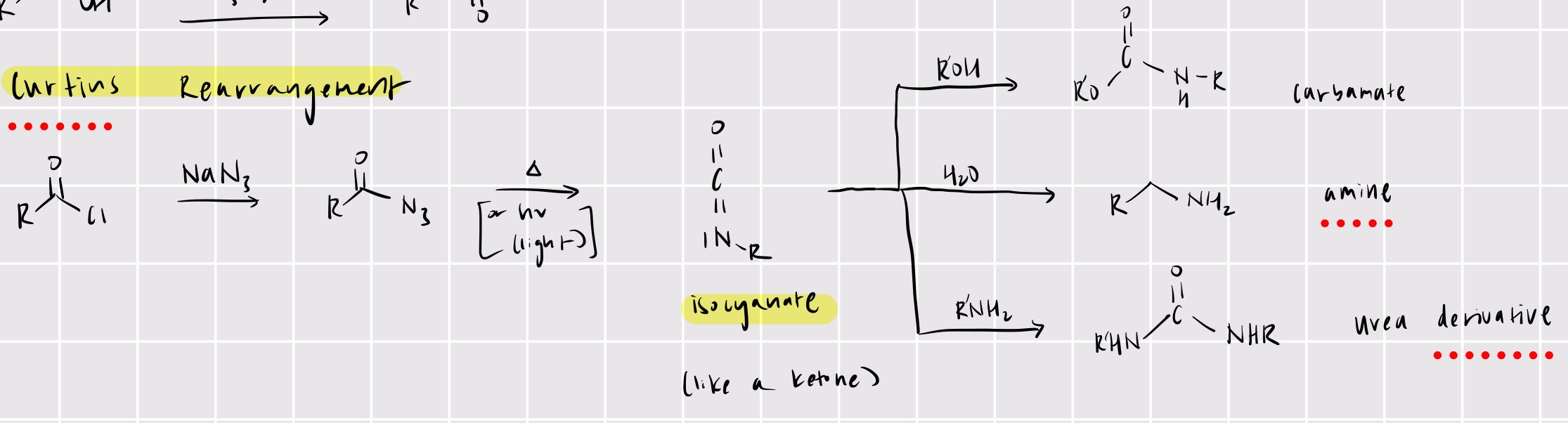
primary amide —> amine (with one less carbon)
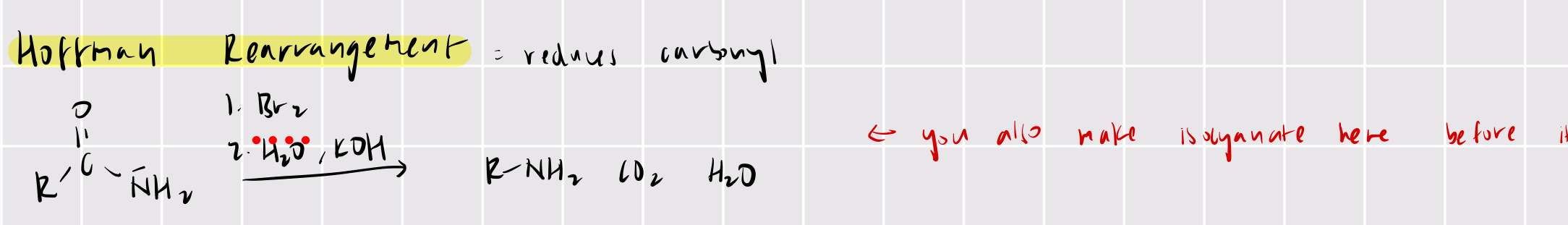
hoffman rearrangement
Br2
H2O/KOH
halogenation at a-position
X2/acid or X2/base (overreacts!)
no F!
keto-enol tautomerization
acid/base
methyl ketone —> carboxylate ion
haloform/iodoform reaction
I2/NaOH, H2O
making a-B unsaturated ketone
aldol condensation
NaOH/H2O
NaOH/H2O + heat
or
H3O+/H2O
alkylation at a-position
LDA (irreversible!)
R-I (SN2)
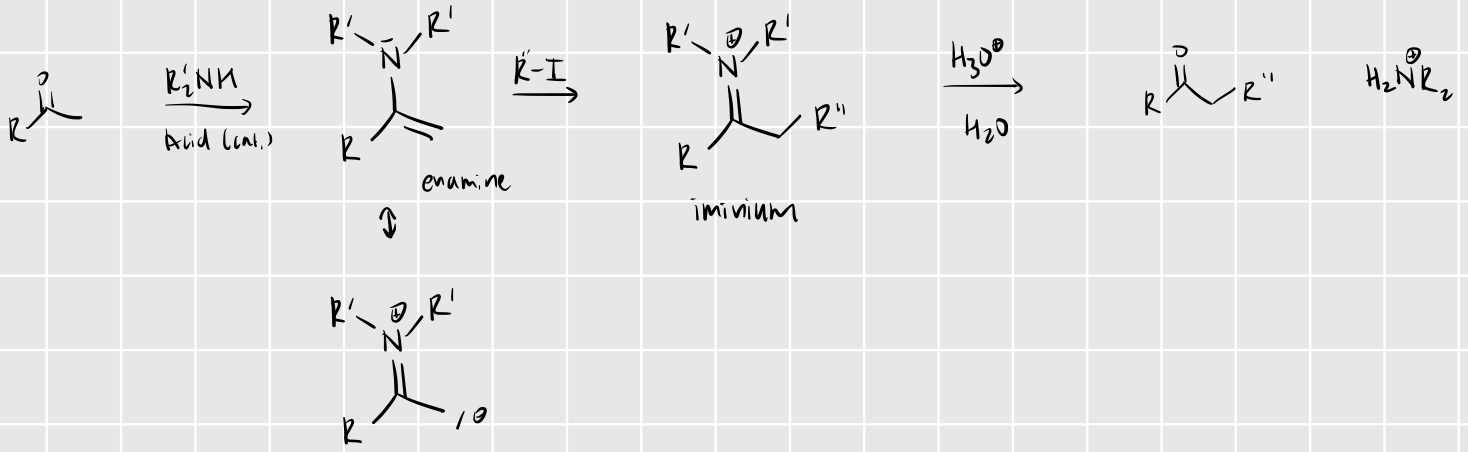
enamine —> iminimum —> alkylated ketone/aldehyde (with one more carbon added)
dean-stork alkylation
enamine + R-I —> iminium + acid —> alkylated ketone/aldehyde with one more carbon added
1,5 dicarbonyl
michael addition
ketone + a-B unsaturated ketone (prefers 1,4 addition) in NaOH/H2O
a-B unsaturated ketone selectivity
+ R-Li/R-MgX prefers 1,2 addition
+ R2CuLi prefers 1,4 addition (R adds once!)
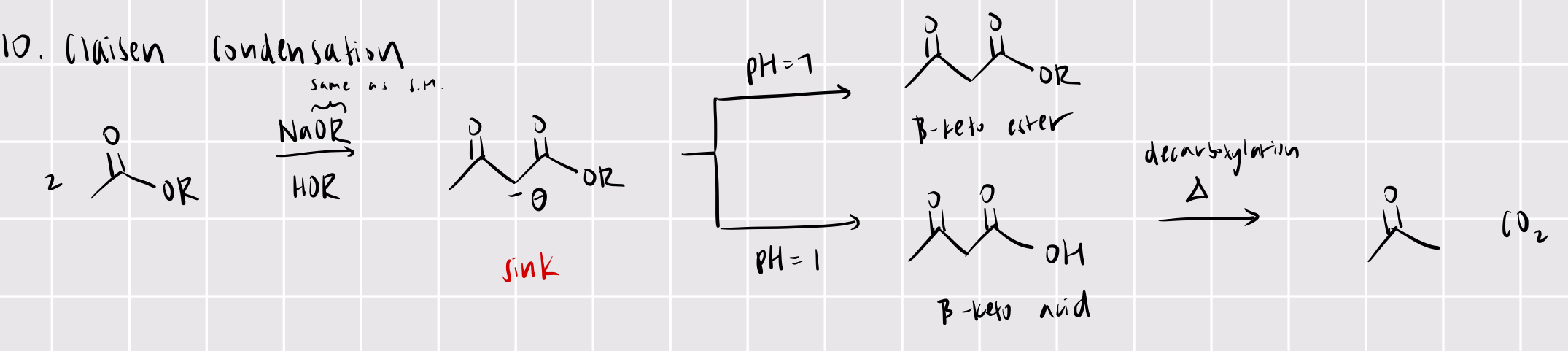
ester —> b-keto ester
claisen condensation *very useful for synthesis!
NaOR/HOR
adjust pH levels (bc a-H very acidic!) — pH = 7 makes ester, pH = 1 makes b-keto acid
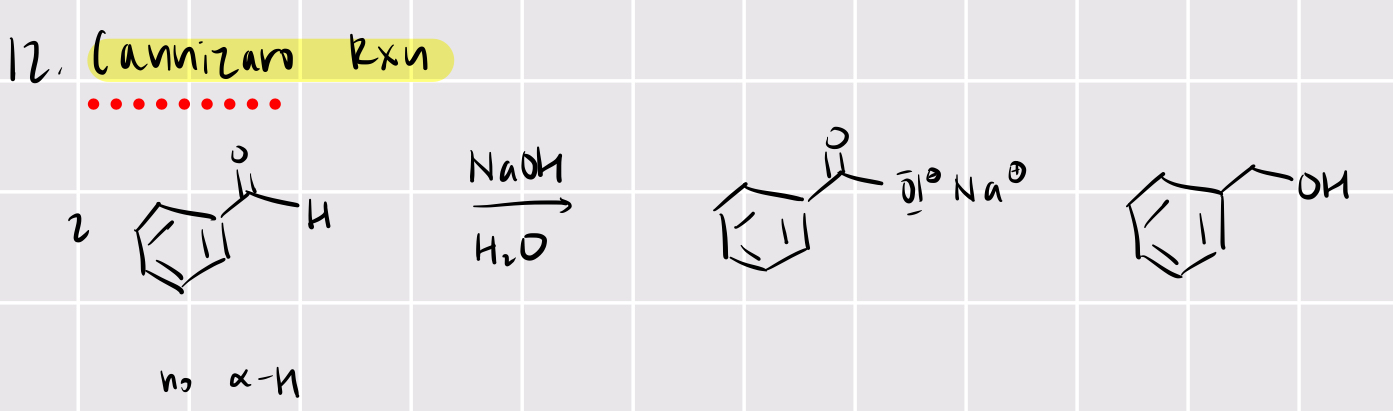
cannizaro reaction
base catalyzed (NaOH): 2 benzaldehyde —> benzoic acid ion + benzoic alcohol
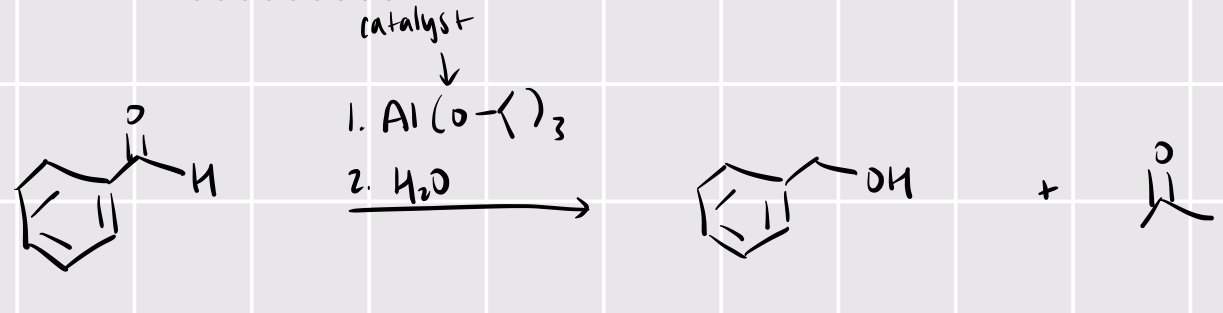
meerwein-ponndorf-verley-oppenaner equilibration
R2CO + 1. Al(OCH(CH3)2)3 2. H2O —> R2OH
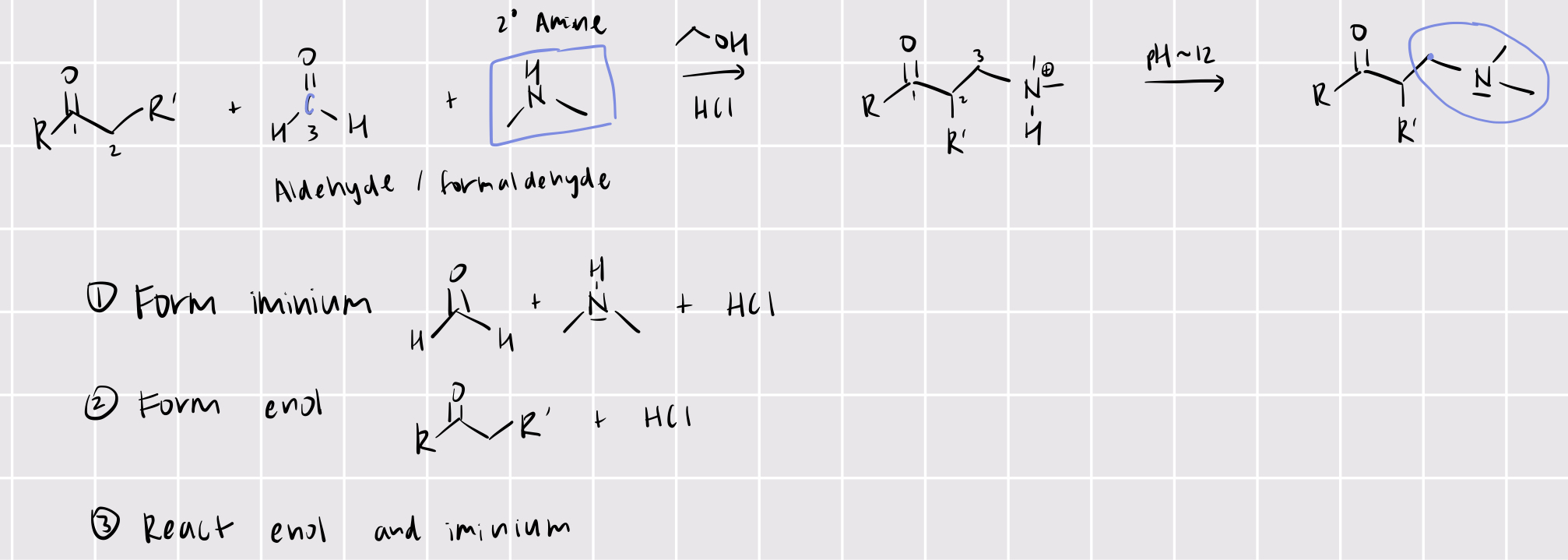
mannich reaction
swern oxidation
1. DMSO, (COCl)2 2. Et3N (aldehydes)
zipper reaction
NaNH2
H2O
making terminal alkynes with 100% yield
removing a protecting group
acid
base
removing blocking groups (SO3H and tertbutyl)
acid
LiAlH4 reduction on esters, carboxylic acids, amides, and nitriles
esters and carboxylic acids —> alcohol
amides and nitrile —> amine
reduce alkyne
H2, Lindlar catalyst