Membrane Transport: Active vs. Passive Transport
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
Active Transport
Moving particles against their gradient requires input of external energy.
Passive Transport
Moving particles down/with gradient from high to low concentration; no additional energy input needed.
Thermodynamic Coupling
Coupling a thermodynamically favorable process with a thermodynamically unfavorable process to drive transport.
Channel Proteins
Proteins that don't appreciably bind solute; a single shape change allows many ions to pass; always passive transport.
Carrier Proteins
Proteins that bind solute and undergo allosteric change to deliver a small number of molecules across the membrane; can be passive or active transport.
Primary Active Transport
Active transport that directly uses energy from ATP hydrolysis to move substances against their gradient.
ATP Hydrolysis Reaction
ATP + H2O → ADP + phosphate; the reaction releases energy used for active transport.
Energy for Active Transport
Comes from coupling the movement of a substance against its gradient to the hydrolysis of ATP.
Gradient
The difference in concentration of a substance across a membrane, which can be used as a source of energy in passive transport.
Transporters
Proteins that facilitate the movement of substances across a membrane, can be classified as pumps or channels.
Shape Change in Proteins
The conformational change in proteins that occurs during transport, allowing the movement of substances across membranes.
Energy Input for Active Transport
Requires external energy, typically from ATP, to move substances from low to high concentration.
Concentration Gradient
The process of particles moving through a solution or gas from an area with a higher number of particles to an area with a lower number of particles.
Allosteric Change
A change in the shape of a protein that occurs when it binds to a substrate, allowing it to perform its function.
Pumps
Primary active transporters that couple energy from ATP hydrolysis to move substances against their gradient.
Energy in Passive Transport
Is derived from the gradient itself, allowing substances to move from high to low concentration without additional energy.
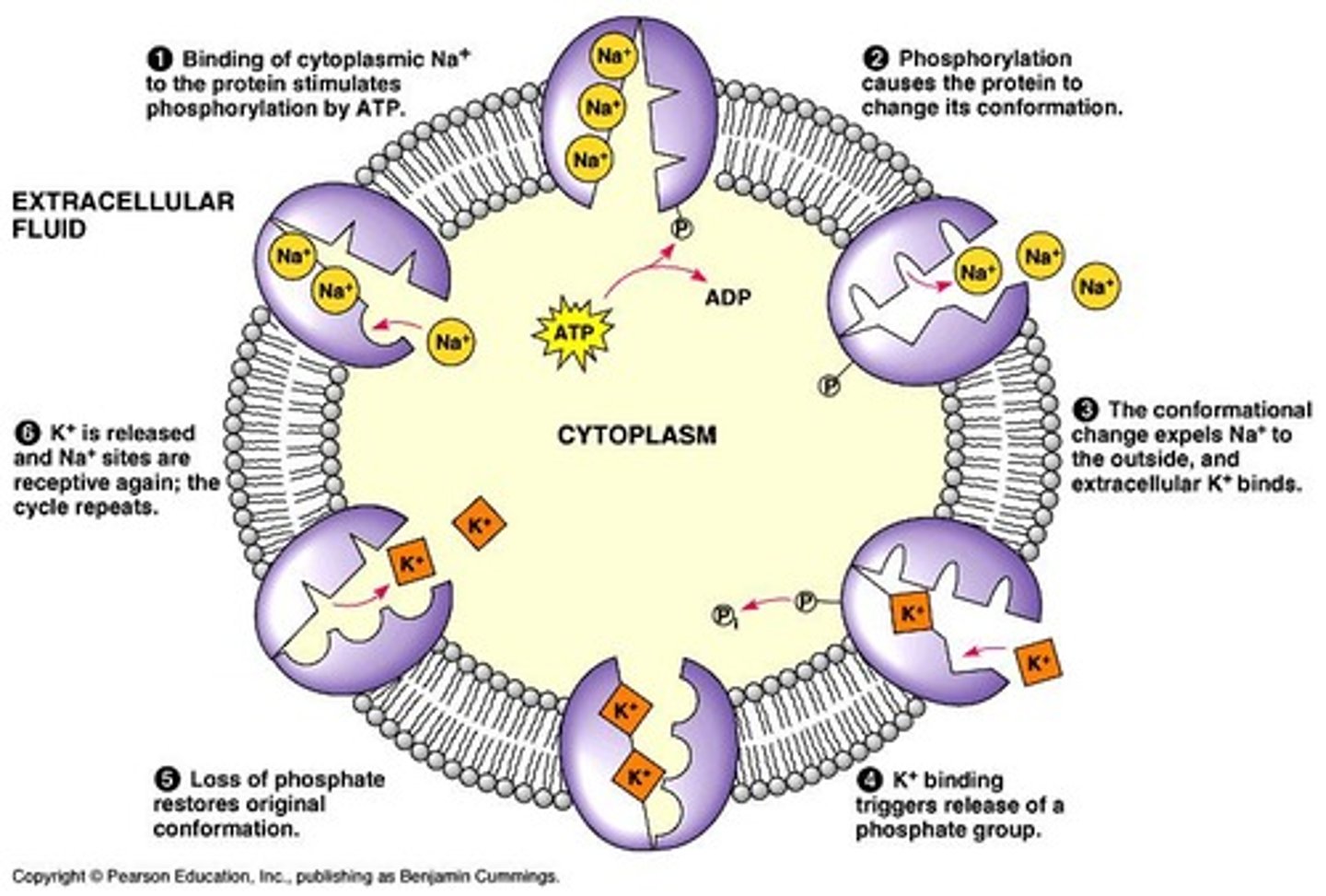
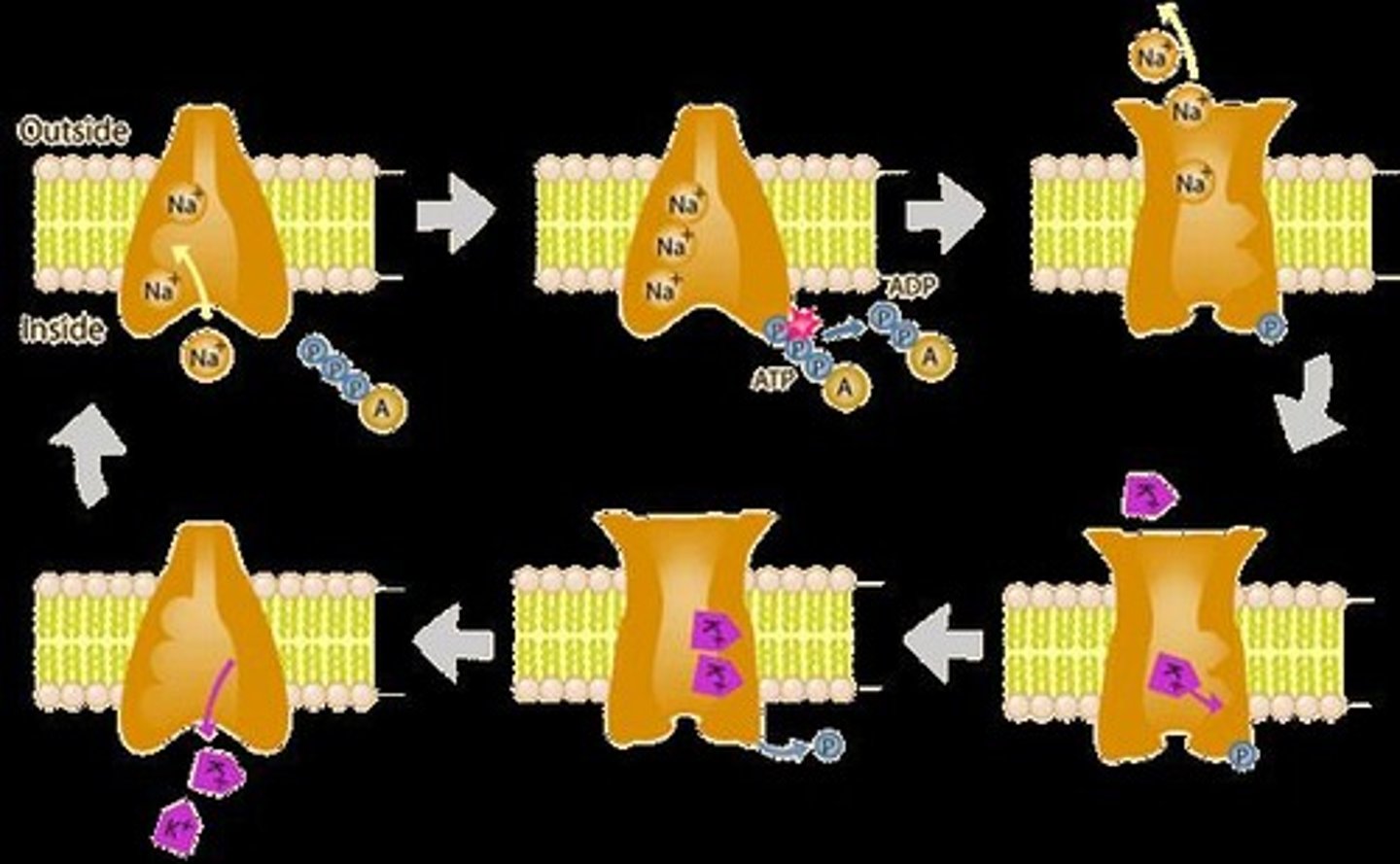
Sodium-Potassium Pump
An example of a primary active transport mechanism that moves sodium out of and potassium into cells against their concentration gradients.
External Energy Source
Energy required for active transport, which can come from ATP or other energy sources.
Hydrolysis of ATP
The process of breaking down ATP to release energy, which is used in active transport.
Transport Mechanisms
Different methods by which substances are moved across cell membranes, including passive and active transport.
Energy Transfer
The process of transferring energy from ATP to transport proteins to facilitate active transport.
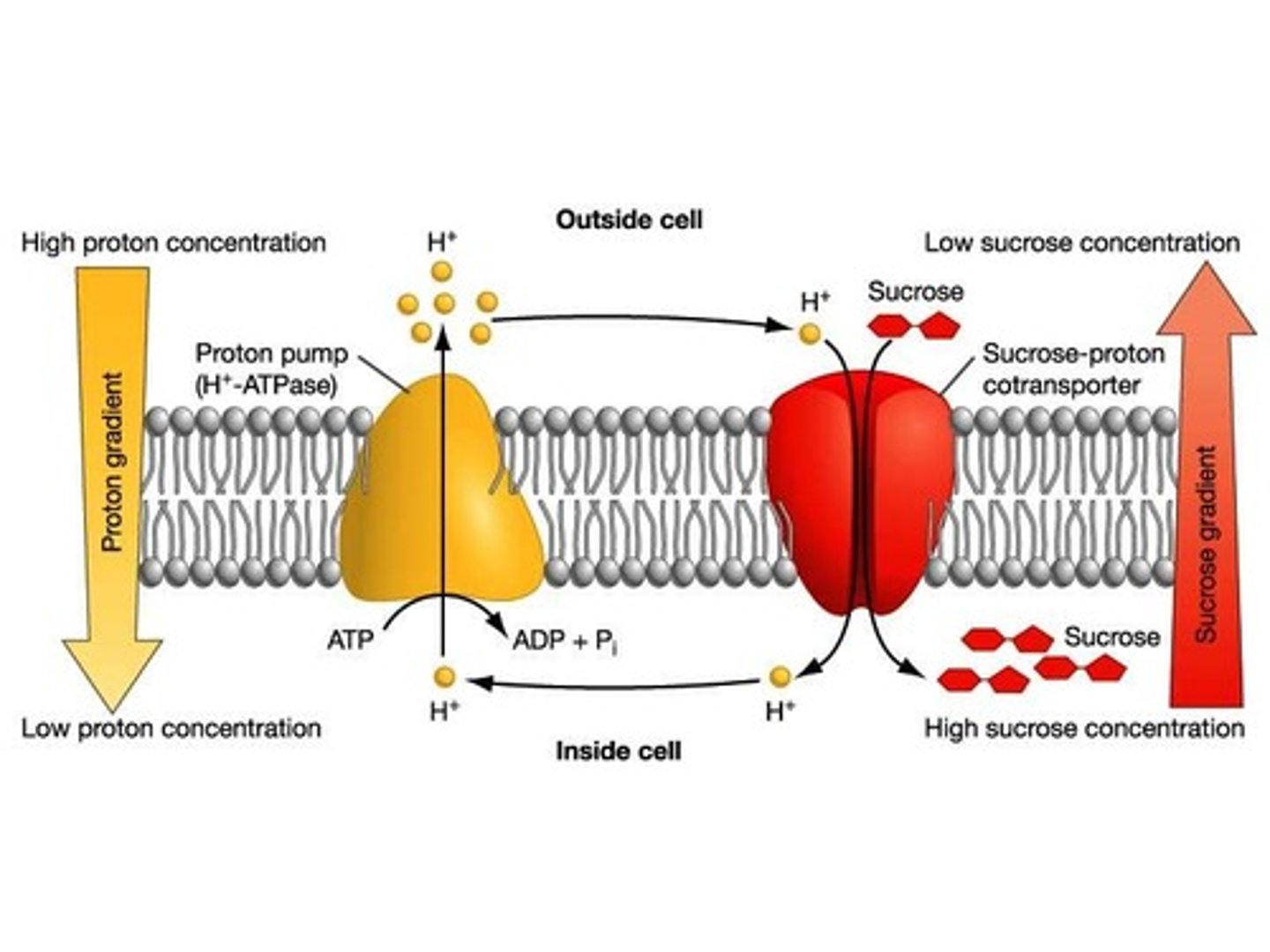
Secondary active transport
Energy to move S against gradient comes indirectly, from harnessing energy of another gradient (here of X).
Primary Active Transport
The Na+ / K+ Pump establishes and maintains gradients that contribute to osmotic balance and the resting electrical potential.
Na+ / K+ Pump
Moves 3 Na+ out and 2 K+ in, both against their gradients.
Na+ gradient
Established by primary active transport (Na+/K+ pump) and provides energy for secondary active transport.
Na+ / glucose co-transporter
Exploits the Na+ gradient; both Na+ and glucose must bind for the transporter to change conformation and transport.
Passive transport
Facilitates movement down solute's gradient; not pumps.
Affinity
Strength of binding of Na+ and K+ changes through the cycle of transport.
Allosteric change
Shape changes that occur during the cycle of transport.
Conformational changes
Allow 'process proteins' (enzymes, transporters, signaling molecules etc.) to perform their jobs.
ATP
Role is to provide energy for active transport mechanisms.
ATP hydrolysis
Process that releases energy for cellular activities.
Membrane transport proteins
Include carrier proteins, channel proteins, and pumps (ATPase transport proteins).
Carrier protein
Facilitates the transport of specific substances across a membrane.
Channel protein
Forms pores in the membrane to allow specific ions or molecules to pass through.
Pump (ATPase transport protein)
Uses ATP to transport substances against their concentration gradient.
Uniporter
Transports a single type of molecule across the membrane.
Symporter
Transports two different molecules in the same direction across the membrane.
Antiporter
Transports two different molecules in opposite directions across the membrane.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
Energy currency of the cell, used in various biochemical processes.
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
Product of ATP hydrolysis, can be converted back to ATP.
Phosphate group
Part of ATP that is released during hydrolysis to provide energy.