Design and CAD Final First Part Cards
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Process
A rational progression of actions
Developing
Involves evaluating, iterating, and refining
Satisfactory
Not perfect or ideal; a compromise
Idea
Requires thinking, creativity, and imagination
Specific
Success depends on meeting defined requirements
What is the most important step of the engineeing process?
Problem definition
What is the order of the design process?
Problem definition → Ideation → Concept development → Prototyping → Testing → Evaluation
What are the subsections of the design process?
Ethics, Feasibility, Impact
What are the sub-subsections of the design process?
Technical, People, Commercial, Organizational
What should be in a design specification?
What is required, what is desired, and what are the constrains.
What are stakeholders
A stakeholder is a party with a vested interest in an enterprise.
A planetary gear with a fixed gear has what input and output?
Input: Sun Gear - Output: Ring Gear
A planetary gear with a fixed gear has what input and output?
Input: Sun gear - Output: Carrier
The problem definition stage of the design process often includes?
Identifying a potential problem to solve
Validating the problem to ensure it is worth solving
Defining the specifics of the problem
The design problem and solution parameters are defined in a design…
Specification
What are the gear ratio equations?

What is the torque equation?
T = L X W
Relationship of the torque of a motor to a weight hung on it.

Force to torque and pitch radius relation/equation

Pitch equation

Module is 2x the pitch, true or false?
False, it is the inverse of pitch (1/P)
Planetary gear equations

What was the first known technical drawing?
Statue of Gudea
Who was the advocate of orthographic drawings?
Marcus Vitruvius Pollio “De Architectura”
Who invented Cartesian coordinates?
Renee Descartes
What was the main reason dimensioned drawings were standardized?
Interchangable parts, also led to quality measuring tools
What was the first true CAD software
"Sketchpad”
What is the US Standard also called
3rd Angle Projection (British is 1st angle projection)
The generic design solution features
Energy, Material, and Information into and out of the system

What is the goal of the ideation process?
To generate lots of different ideas
What is ideal for brainstorm
5-15 people with a leader
Diverse backgrounds
Equals
Focus on one function only
Write down or sketch all ideas
Quantity is the goal
Not judging/criticism
30-45 mins max per session
What is design fixation?
Focusing too much on your first ideaA v
A view on a plane parallel to an inclined surface that shows its true size and shape is called a ____ view.
Auxiliary view
Are hidden lines generally included on auxiliary views?
No, unless needed for clarity
For an auxiliary view, can a centerline continue between adjacent views?
Yes, to indicate alignment
How do you see interior details of an object that cannot be seen from the outside?
A section view

What view is this?
A section view

What are these
Cross-hatching styles
Stiffness, Strength, Hardness, Toughness, Endurance limit, Wear-resistance, Coefficient of friction are all examples of…
Mechanical material properties
Conductivity, Diffusivity, Heat Capacity, Coefficient of Expansion are all examples of…
Thermal material properties
Resistivity and Permittivity are examples of…
Electrical material properties
Remanence and Saturation Magnetization are examples of…
Magnetic material properties
Refractive index and Absorptivity are examples of…
Optical material properties
Corrosion resistance, Toxicity, Degradability are examples of…
Chemical properties

What is this
Uniaxial tension
When does a uniaxial tension graph become linear?
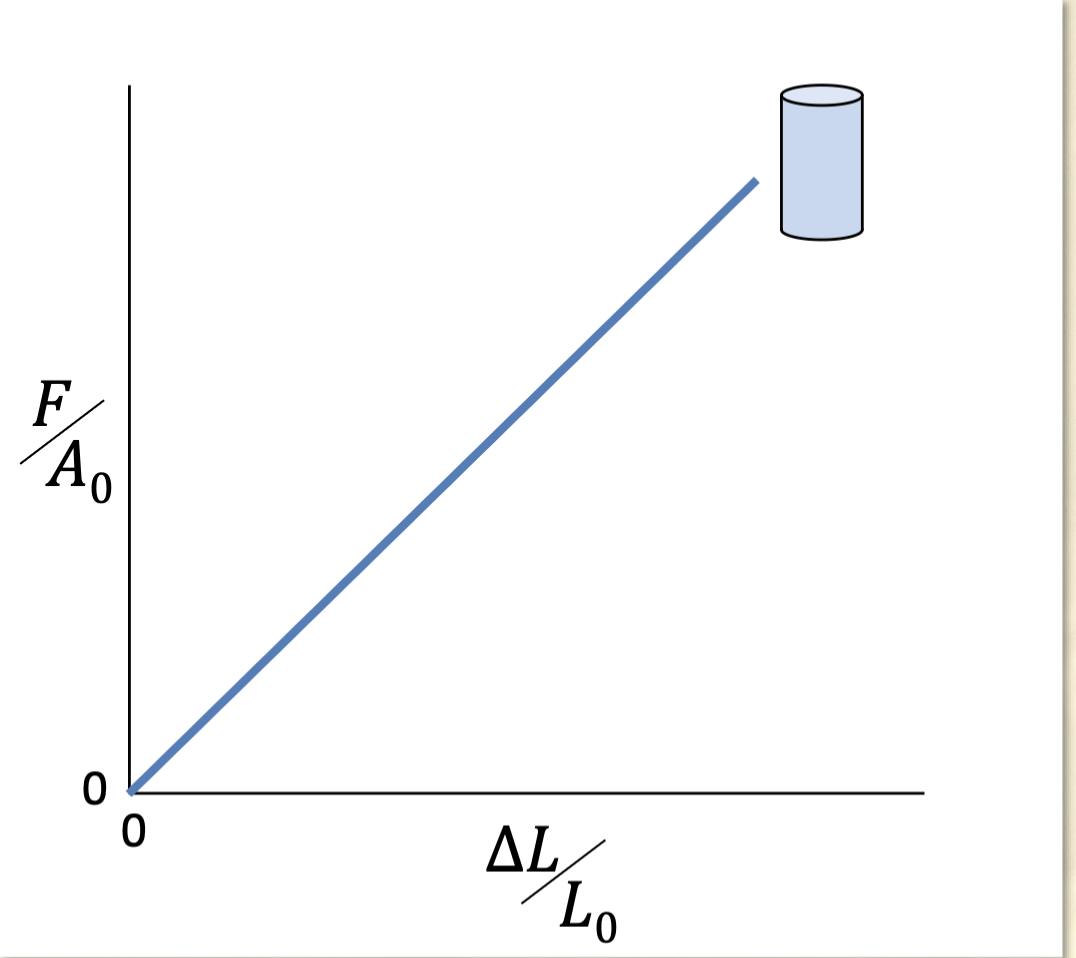
What are the stress and strain equations

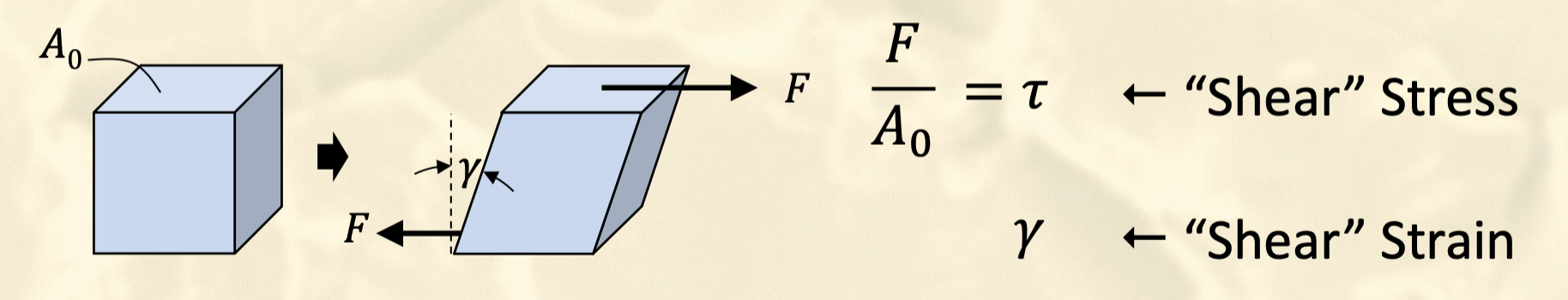
What is shear, and what are its stress and strain equations
Stiffness
Resistance to elastic deformation. Relates stress & strain.
Structural stiffness
Resistance to elastic deformation. Relates load and displacement.
Spring stiffness
Structural stiffness of a spring
Strength
Resistance to the onset of plastic deformation
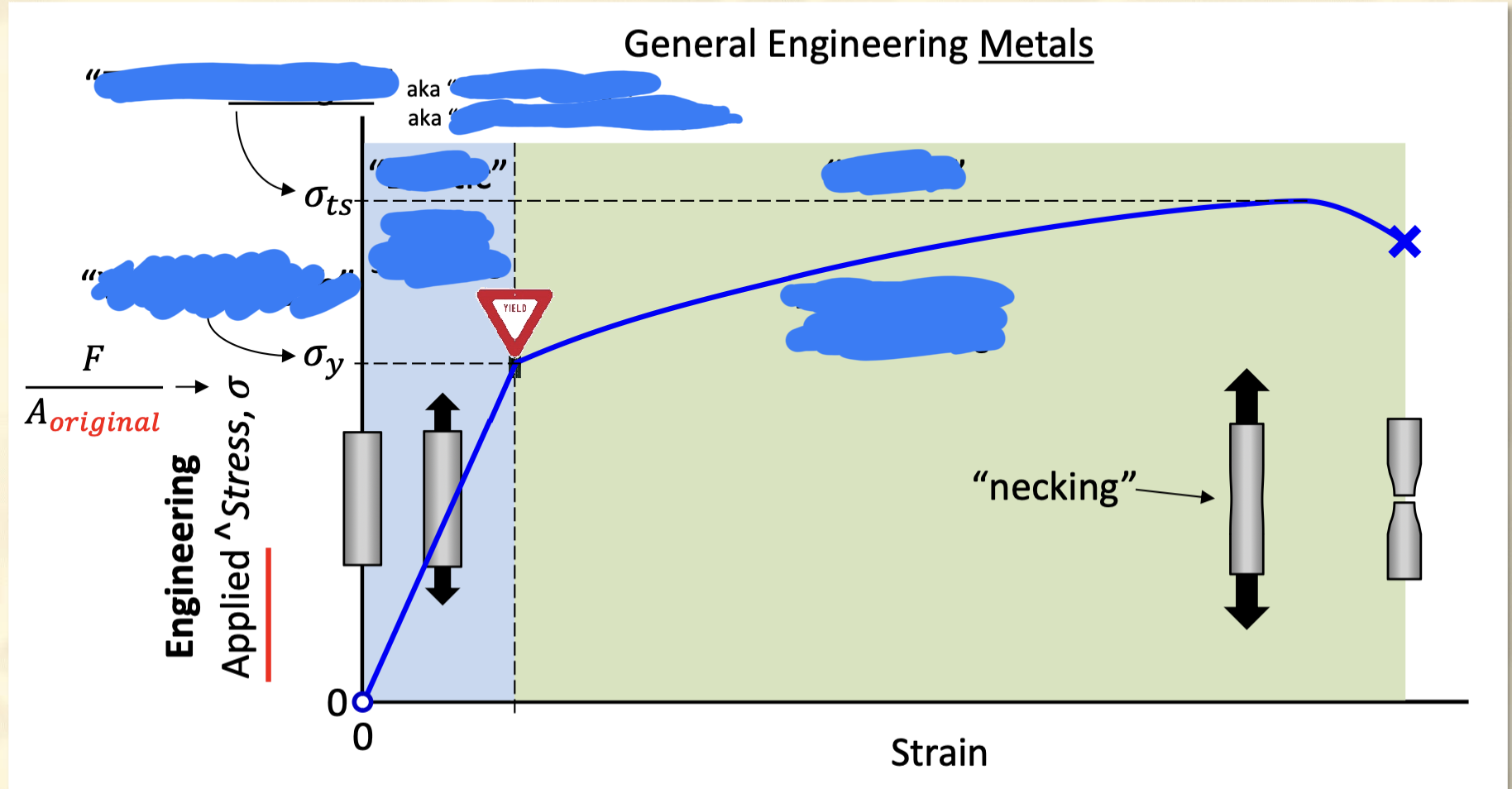
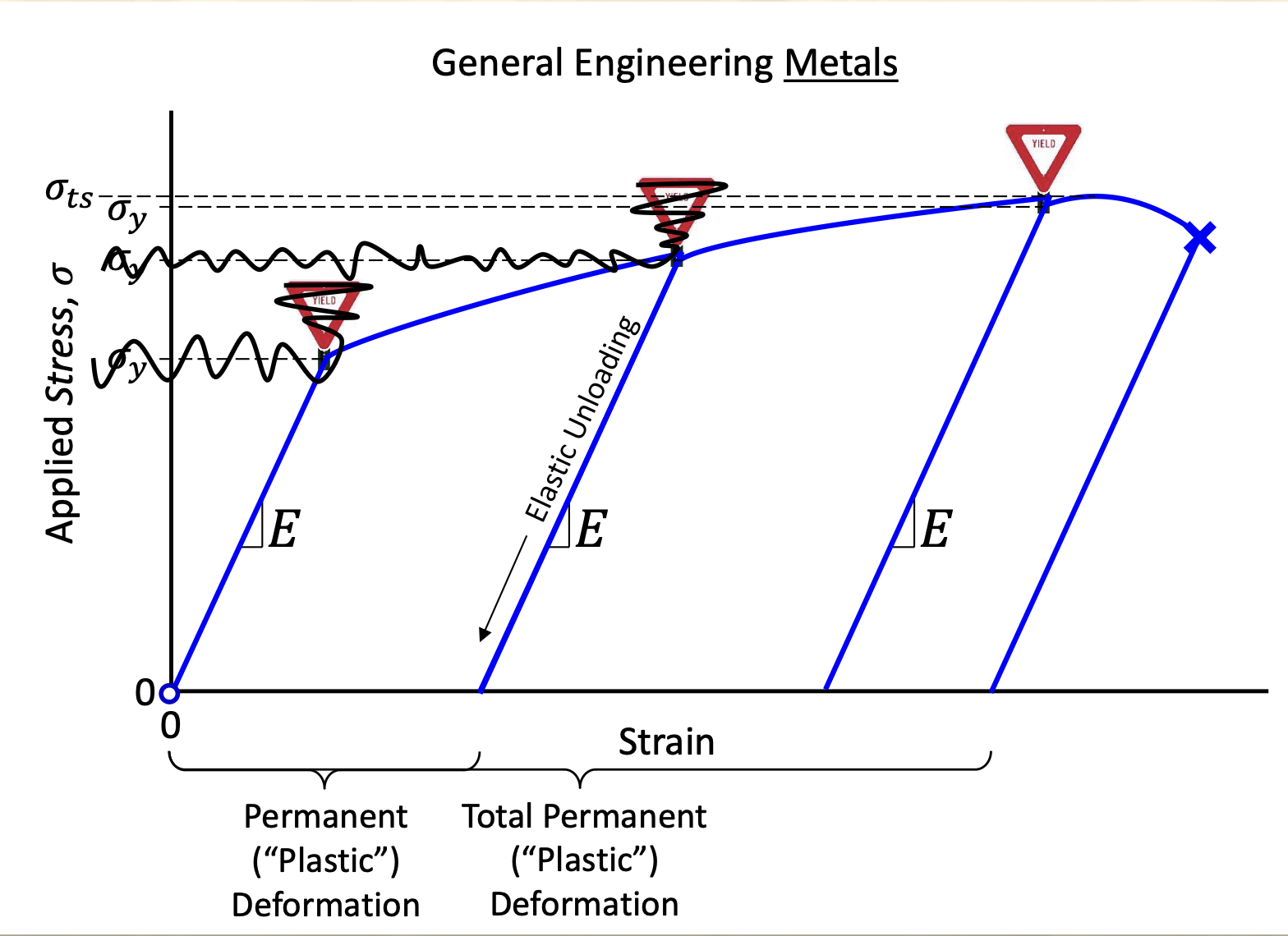
Material strength graph, locate points of interest and what they are.
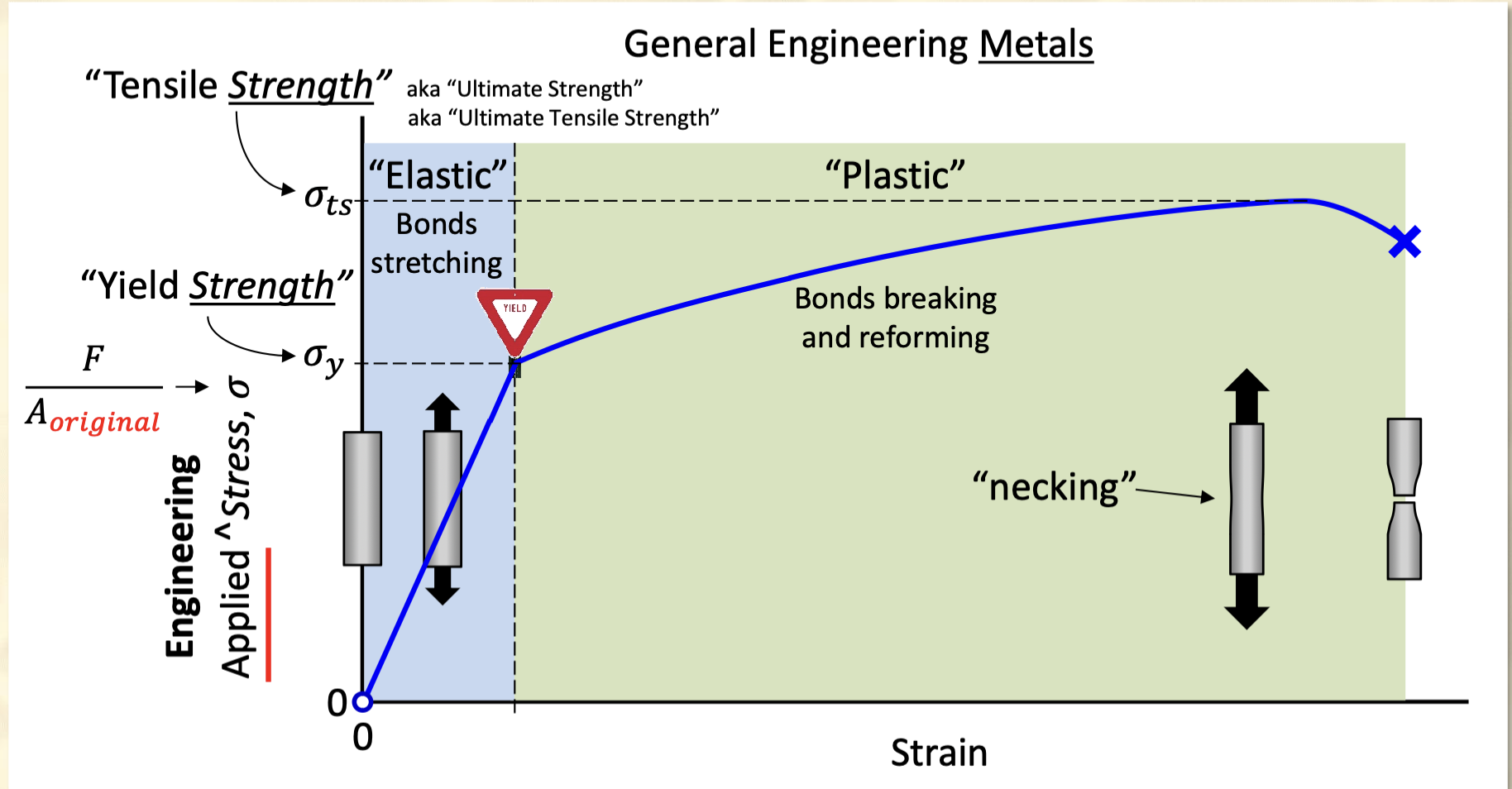
You can strengthen or “work-harden” a material by putting stress on it past the yield strength, true or false?
True
What is hardness (and an example of something that demonstrates it)
Resistance to local plastic deformation, typically on the surface (example would be a gear or shaft)
How do you test hardness?
With an indenter
Is hardness a direct measure of strength?
No, but strength can be estimated from hardness
Toughness
Resistance to fracture
Fracture
Propagation of a crack in the material
If the fracture toughness exceeds the stress intensity factor, a crack propagates. True or false?
False, its the other way around
Brittle
Once a crack starts to grow,
It continues to grow with very little plastic
deformation (yielding)
Ductile
Material around crack tip yields and inhibits additional crack growth
Fatigue
Progressive and localized damage due to
cyclic loading
Endurance limit

When does friction and wear happen?
When real contact area is less than surface area
Abrasive wear
Material at the tips of a harder material breaks off the tips of a softer material, creating wear particles.
Adhesive wear
Material at the tips of one surface bonds to the other surface and is torn off.
- Crystalline with metallic bonds
• Stiff – high 𝐸
• Tough – high 𝐾𝐼𝐶
• Ductile
• Wide range of strengths depending on
composition and processing
• Thermally and electrically conductive
• Reactive – low corrosion resistance
• Mostly used as alloys
Are the characteristics of what
Metals
• Crystalline with ionic and/or covalent bonds
• Stiff – high 𝐸
• Hard
• Abrasion resistant
• Brittle – low 𝐾𝐼𝐶
• Good high temperature strength
• Good corrosion resistance
• Should avoid loading in tension
Are the characteristics of what
Ceramics
-Non-crystalline with ionic and/or covalent bonds
• Hard
• Brittle – low 𝐾𝐼𝐶
• Corrosion resistant
• Electrically insulating
• Transparent (mostly)
Are the characteristics of what
Glasses
-Long chain molecules with covalent and secondary bonds
• Properties are highly sensitive to temperature
• High strength per unit weight (𝜎𝑦/𝜌)
• Light weight – low 𝜌
• Easily shaped
• Low stiffness – low 𝐸
Are the characteristics of what
Polymers
• Long chain cross-linked molecules
• Able to retain initial shape after being stretched significantly
• Non-linear elastic stress-strain behavior
• Relatively strong and tough
Are the characteristics of
Elastomers
• Properties dependent on a combination of materials
• Difficult to shape and join
• Expensive
Are the characteristics of
Hybrids
What are dimensions used to indicate
Size and location
Welding
Components joined by locally
melting the work pieces together
with a filler metal
“TIG” – Tungsten Inert Gas welding
“MIG” – Metal Inert Gas welding
Lugs and brazing
Components joined by melting a filler metal which then flows into the gaps between the work pieces through capillary action