5.4/5.5 Sum and Difference Formulas and Reduction Formulas and Lots OF FORMULAS
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
VERY IMPORTANT AND REVIEW
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Proof for sum and difference formulas
Videos
What you can do with these formulas
You can use identities to rewrite
trigonometric expressions and you can rewrite a trigonometric
expression in a form that helps you solve the problem
SUM AND DIFFERENCE FORMULAS
Note: To derive others, manipulate algebraically using these numbered formulas.
Sin (M+N)
sin(m + n) = sin m cos n + cos m sin n
SIN (M-N)
sin(m − n) = sin m cos n − cos m sin n
cos is an even function so sin(m)cos(-n) + cosm sin(-n) get sin m cos n -cos m sin n
COS (M + N)
cos m cos n − sin m sin n
COS (M − N)
cos m cos n + sin m sin n
cos is an even function and sin is an odd function so cosmcos(-n) - sinmsin(-n) is cos m cos n + sin m sin n
TAN(M+N)
(tan m + tan n)/(1 − tan m tan n)
TAN(M-N)
(tan m − tan n)/(1 + tan m tan n)
Notes Example problems and what you can prove
Prove using the Sum and difference formulas
Sin(pie/2-x)=cosx
Cos(pie/2-x)=sinx
Sin(pie-x)
Sin(pie+x)
cos(pie-x)
cos(pie+x)
tan(pie-x)
tan(pie+x)
Solve
cos75
sin(pie/12)
sin15
Sin42cos12- cos42sin12
Cos(theta-3pie/2)
Tan(theta+3pie)
Good one solve
cos(arctan1+arccosx) use triangle to solve
MAIN EXAMPLE OF USING SUM AND DIFFERENCE. SOLVING AND EQUATION
Find all solutions of sin(x+pie/4)+sin(x-pie/4) = -1 in the interval [0,2pie)
use the sin sum formulas to get
sinxcospie/4+cosxsinpie/4 + sinxcospie/4 - cosxsinpie/4 =-1
and can cross out the 2nd and 4th terms and get
2sinxcospie/4=-1. and know from unit circle value that cospie/4 is root2/2.
so 2(sinx)(root2/2)=-1
and divide both sides by 2 to get (sinx)(root2/2)=-1/2 and then multiply by root2/2 to get
sinx=-root2/2.
and know by using unit circle x=5pie/4 and x=7pie/4. and then check

Sum and difference HW
Page 423
Part 1 do Exs. 1-21 (odds), 31-36,

Sum and difference HW
Page 424
Part 2 do 37-63 (odds), 69-72.

5.5 ALL THE OTHER TRIG FORMULAS
Overview of section
In this section you will study the 4 other categories of Trig identities
Products of Trig functions such as sinmcosn
functions of multiple angles such as sin km and cos kn
squares of trigonometric functions such as sin²x
involves functions of half-angles such as sin(x/2)
PRODUCT- TO- SUM
Formulas (labeled a-d) for future derivation
Derivations (Add/Subtract sum equations for all 4):
easily verified using the sum and difference formulas discussed in the preceding section.
Product-to-sum formulas are used in calculus to evaluate integrals involving the products of sines and cosines of two different angles.
PRODUCT- TO- SUM example problems
Rewrite the product cos 5x sin 4x as a sum or difference.

(A) sin M cos N
and derivation
1/2 [sin(M + N) + sin(M − N)]
For formula A you do sum equation 1 + sum equation 2 =
Add sin(M + N) + sin(M − N) = 2 sin M cos N
(B) cos M sin N
and derivation
1/2 [sin(M + N) − sin(M − N)]
For Formula B you do sum equation 1- sum equation 2 =
Sin(m+n)-sin(m-n)= 2 cosM sinN
(C) cos M cos N
and derivation
1/2 [cos(M + N) + cos(M − N)]
For Formula C you do sum equation 3 + sum equation 4 =
Cos(m+n)+cos(m-n)= 2cosM cosN
D) sin M sin N
and derivation
1/2 [cos(M − N) − cos(M + N)]
For formula D you do sum equation 4 - sum equation 3
Cos(m-n)-cos(m+n) = 2sinM sinN
SUM-TO-PRODUCT RULES (WITH x & y)
Derivation for all have to Derivations (let x = M + N and y = M − N): so m=(x+y)/2 and n=(x-y)/2
Occasionally, it is useful to reverse the procedure and write a sum of trigonometric functions as a product. This can be accomplished with the following sum-to-product formulas.
sin x + sin y
and derivation
2 sin(x+y/ 2)cos(x-y/ 2)
SO now you just plug those values into the Product to sum formulas
so if I plug into formula A in you get Sin(x+y)/2 cos (x-y)/2 = 1/2(sin(x)+sin(y) which simplifies to get your formula
sin x - sin y
and derivation
2 cos(x+y/ 2)sin(x-y/ 2)
Derivations (let x = M + N and y = M − N): so m=(x+y)/2 and n=(x-y)/2
SO now you just plug those values into the Product to sum formulas
So if I plug into formula B you get cos(x+y/2)sin(x-y/2)=1/2(sinx-siny) which simplifies to get your formula
cos x + cos y
and derivation
2cos(x+y/ 2)cos(x-y/ 2)
Derivations (let x = M + N and y = M − N): so m=(x+y)/2 and n=(x-y)/2
SO now you just plug those values into the Product to sum formulas
So If I plug into formula C you get cos(x+y/2)cos(x-y/2)=1/2(cosx+cosy)
cos y - cos x
and derivation
2sin(x+y/ 2)sin(x-y/ 2)
Derivations (let x = M + N and y = M − N): so m=(x+y)/2 and n=(x-y)/2
SO now you just plug those values into the Product to sum formulas
So If I plug into formula D you get sin(x+y/2)sin(x-y/2)=1/2(cosy-cosx)
SUM-TO-PRODUCT RULES example problem
cos 195 degreees + cos 105 degrees

SUM-TO-PRODUCT RULES example problem Verifying TRIG WITH IT
IMPORTANT EXAMPLE
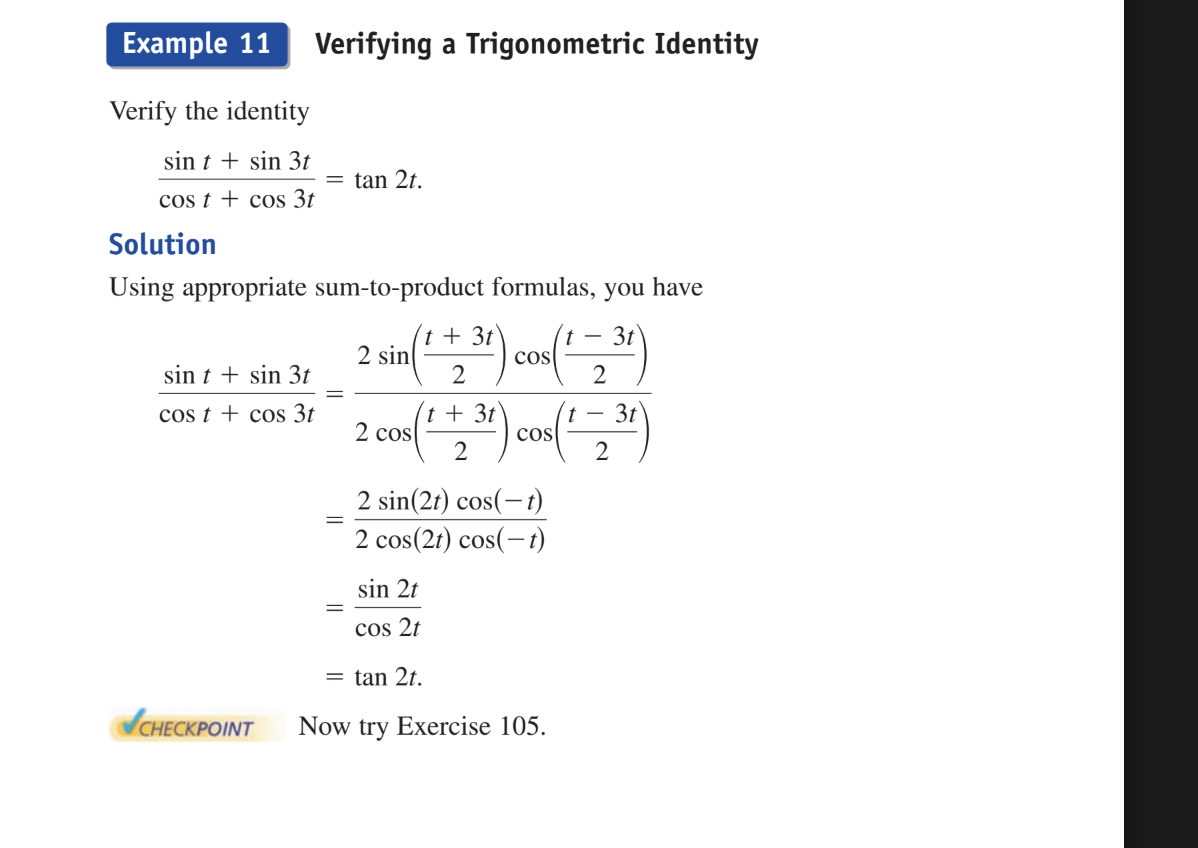
verify the identity
(sint+sin3t)/(cost+cos3t) = tan 2t
Use Sum-to-product formulas to get (2sin((t+3t)/2) cos((t-3t)/2))/(2cos((t+3t)/2)cos((t-3t)/2))
and simplifies to 2sin(2t)cos(-t)/2cos(2t)cos(-t). and you can cross out the 2 and the cos(-t) to get
sin(2t)/cos(2t) which is tan(2t)
SUM-TO-PRODUCT RULES example problem SOLVING EQUATION WITH IT
IMPORTANT EXAMPLE
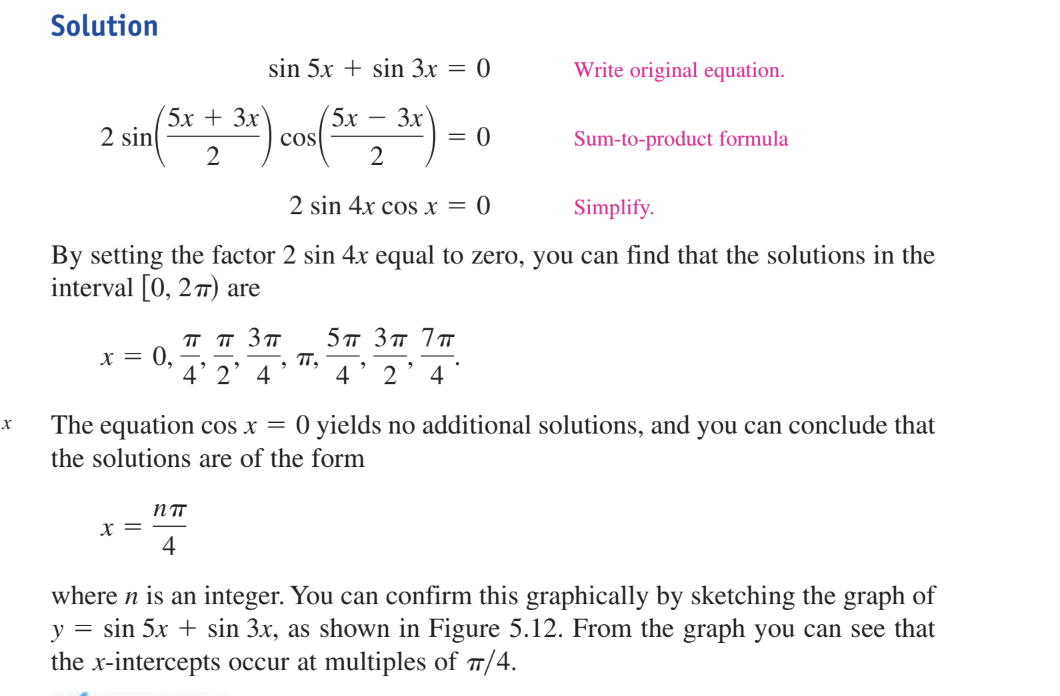
solve sin 5x +sin 3x = 0
use sum to product rule to get 2sin((5x+3x)/2)cos((5x-3x)/2)=0
equals 2sin4xcosx=0
and then divide by 2 to get sin4xcosx=0
so sin4x=0 and cosx=0
x=npie/4 . and x=pie/2+ npie
Multiple angle/ Double angle identities
all derivations by using sum and difference formulas and like this trigfunction(x+x)=and then do it.
You should learn the double-angle formulas because they are used often in trigonometry and calculus. For proofs of the formulas, see Proofs in Mathematics on page 425.
sin(2x)
and derivation
2 sin x cos x
to derive these formulas you just do the sum formula for each
For Sin 2x= Sin(x+x) and then you do the sum formula for sin and get 2(sinxcosx)
cos(2x)
and derivation
THIS FORMULA SUPER IMPORTANT BECAUSE IT IS BASE OF POWER REDUCTION IDENTITIES. The power reduction identities are derived by rearranging specific forms of the double-angle formula to solve for the squared term
cos² x − sin² x
Which could also be 2cos^2 x -1 because -sin^2 x is also -1+cos^2 x
Could also be 1-2sin^2 x because cos^2 x is also 1-sin^2 x
To derive these formulas you just do the sum formula for each
For Cos 2x= Cos(x+x) and then you do the sum formula for cos and get cos^2 x - sin^2 x
Tan(2x)
and derivation
2 tan x / (1 − tan² x)
To derive these formulas you just do the sum formula for each
For Tan 2x= Tan(x+x) and then you do the sum formula for Tan and get (2tanx)/(1-tan^2 x)
Multiple angle/ Double angle identities Example solving an equation
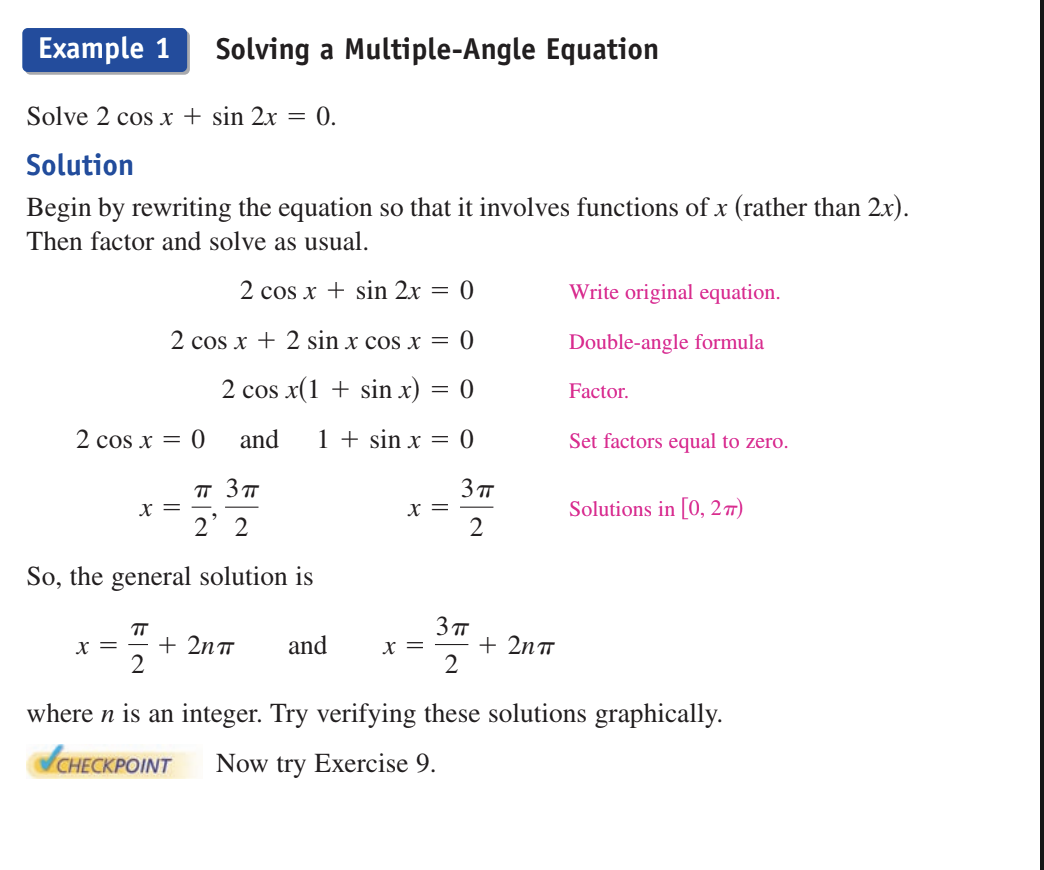
SUPER IMPORTANT EXAMPLE
solve
2cosx + sin2x = 0
Use the sin double angle formula
2cosx+2 sin x cos x = 0
factor
2cosx(1+sinx)=0
2cosx=0 1+sinx=0
cosx=0. sinx=-1
x= pie/2, 3pie/2 and x= 3pie/2
General solution
x=pie/2 +2pien. x=3pie/2 + 2pie n
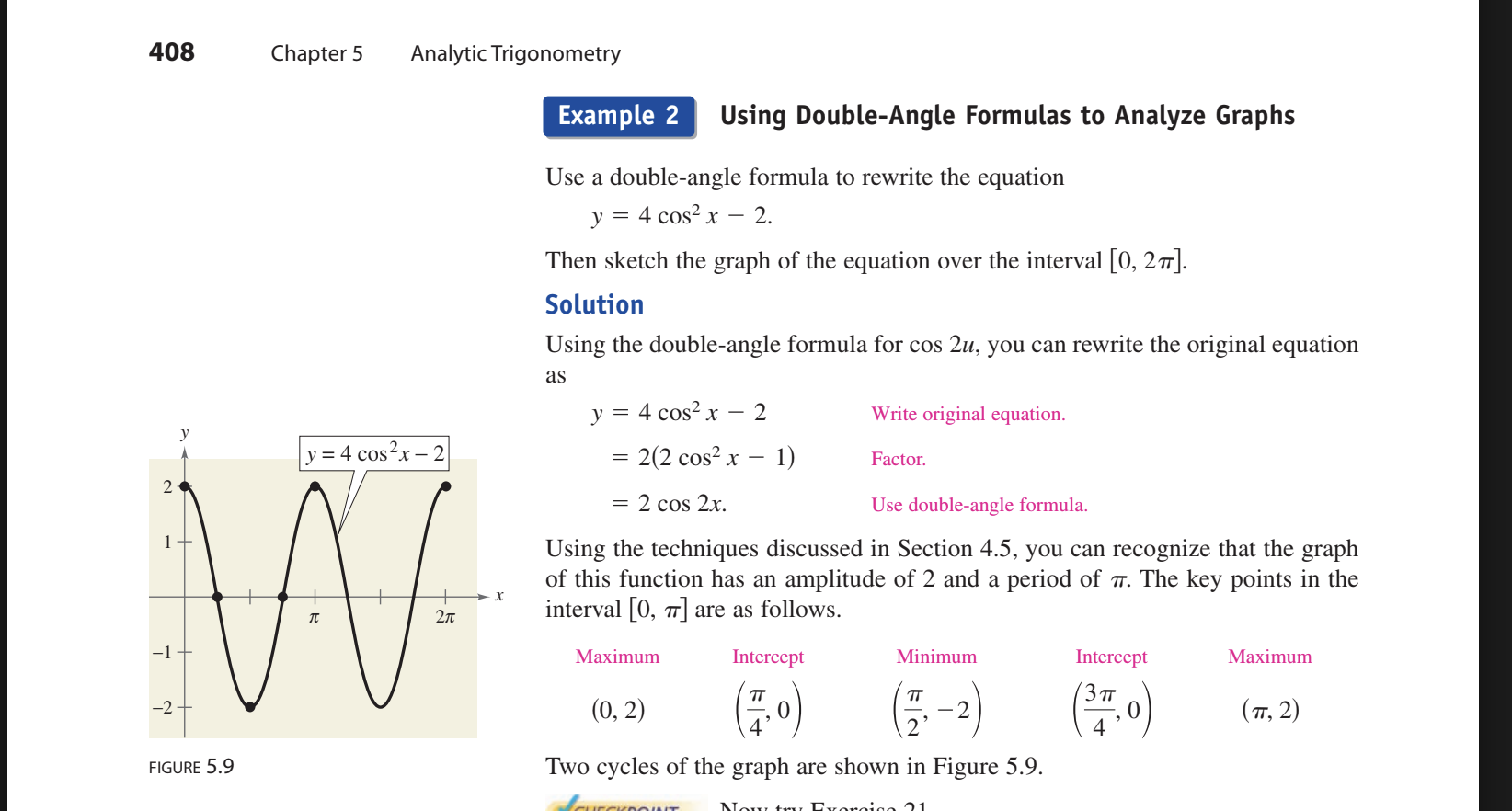
Multiple angle/ Double angle identities Example USING to analyze graphs
SUPER IMPORTANT EXAMPLE
Use a double-angle formula to rewrite the equation
y=4cos²x-2
Then sketch the graph of the equation over the interval [0,2pie)
y=4cos²x-2
y=2(2cos²x-1)
then using the double angle formulas you get
y=2(cos2x)
Then you can graph this
Amplititude 2 and period pie and then just graph it.
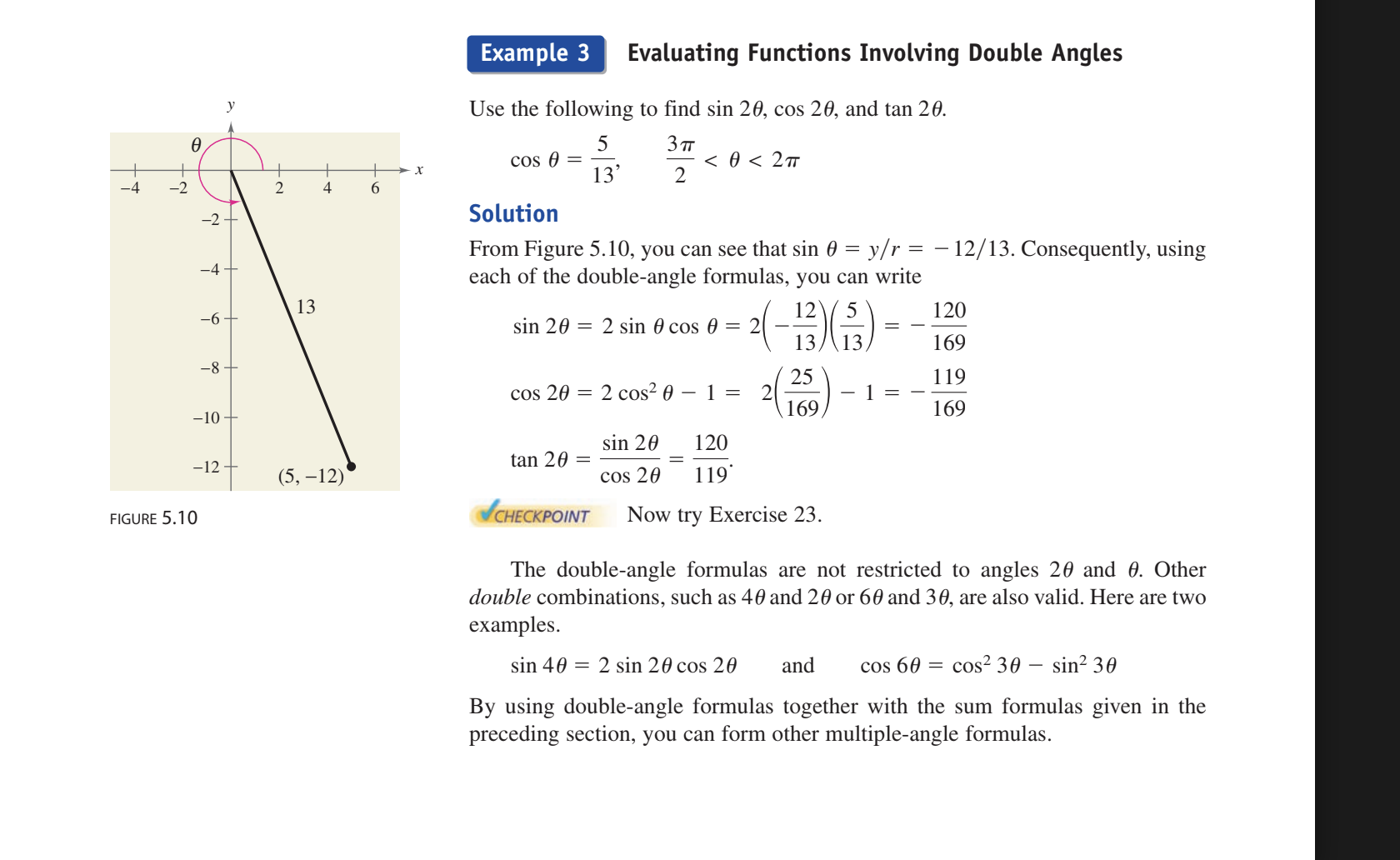
Multiple angle/ Double angle identities Example Evaluating Functions Involving Double Angles
Use the following to find sin(2theta), cos(2theta), and tan(2theta)
cos(theta)= 5/13, 3pie/2<theta<2pie
so know that it is in the 4th quadrant and sin would be -12/13
and then you can use those values to get them
Sin(2theta)= 2sinxcosx= 2(-12/13)( 5/13) = -120/169
Cos(2theta)=cos²x-sin²x= (5/13)²-(-12/13)²= (-119/169)
Tan(2theta)= sin2x/cos2x= -120/169/-119/169= 120/119
Power Reduction Identitites
Derivation using the cos double angle formulas
These allow you to go from a squared trig to a non squared term and the other way around
These formulas are derived by the double angle formula for COS. The Two forms of cos(2x) allow solving for sin² θ or cos² θ; choose the form depending on which variable you need to isolate.
The double-angle formulas can be used to obtain the following power-reducing formulas. Example 5 shows a typical power reduction that is used in calculus.
sin² x
and derivation
(1 − cos(2x)) / 2
To get the sin formula you use the Cos 2x double angle formula cos2x=1-2sin^2 x that has the sin^2 x and then you just solve for sin^2 x and get Sin^2 x = (1-cos2x)/2
cos² x
and derivation
(1 + cos(2x)) / 2
To get the cos formula you use the Cos 2x double angle formula Cos2x=2cos^2 x -1 because it has the cos^2 x and then you just solve for Cos^ 2 x and get cos^2 x = (1+cos2x)/2
tan² x
and derivation
(1 − cos(2x))/ (1 + cos(2x))
To get the tan formula you use the 2 sin^2 x and cos ^2 x formulas and the identity that tan^2 x = Sin^2 x / Cos^2 x so then you plug in the formulas to get ( (1-cos2x)/2 )/ ((1+cos 2x)/2) and then get the Tan formula
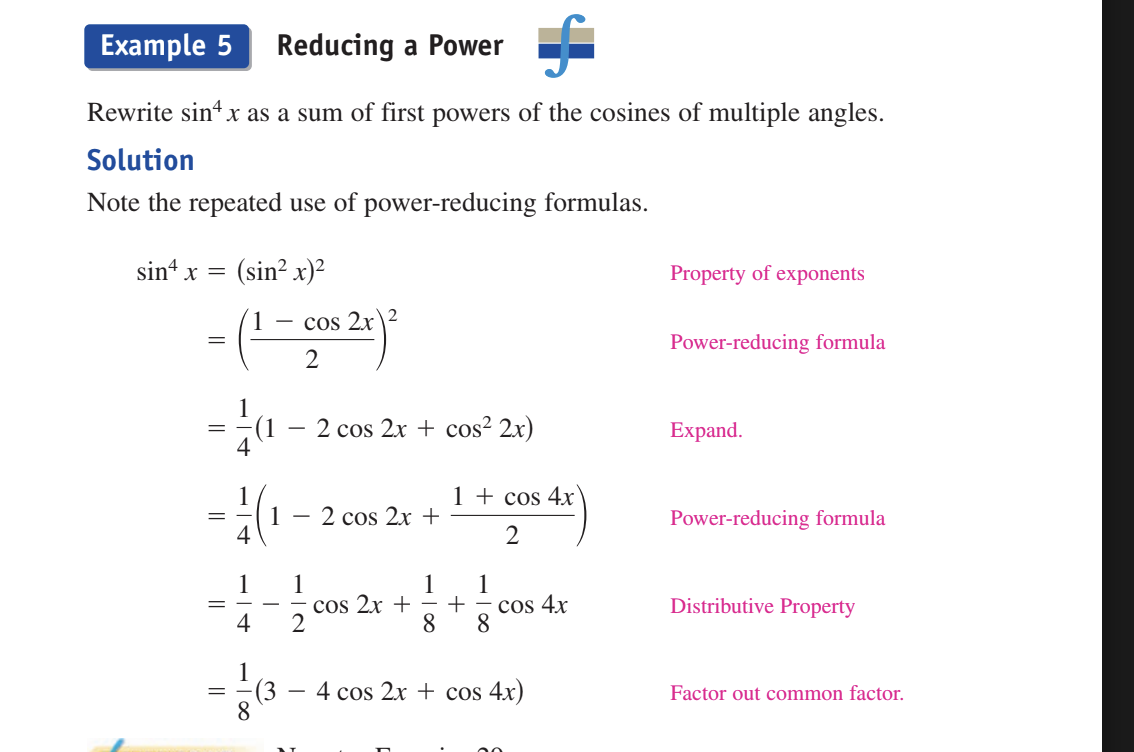
Power Reduction Identitites example
IMPORTANT
rewrite sin^4 x as a sum of first powers of the cosines of multiple angles.
sin^4 x = (sin²x)2
use power reduction formula to get ((1-cos2x)/2)²
can expand this and get 1/4(1-2cos2x+cos²2x)
use power reduction formula again and get 1/4(1-2cos2x+((1+cos4x)/2)
and then distribute to get 1/4-1/2cos2x+1/8+1/8 cos 4x
and then factor out the common factor
and get 1/8(3 - 4cos2x+cos4x)
Half angle formulas
The signs of sin(u/2) and cos(u/2) depend on the quadrant in which u/2 lies.
DERIVED BY USING POWER REDUCTION FORMULAS
You can derive some useful alternative forms of the power-reducing formulas by replacing with The results are called half-angle formulas.
sin(x/2)
and derivation
±√((1-cosx)/2)
For sin(x/2) you use the reduction formula for sin which is sin^2 x = (1 − cos(2x)) / 2 and then just plug x as x/2 and then get sin ^2 (x/2) = (1-cos(x))/2) and then you solve for sin (x/2) by square rooting both sides
cos(x/2)
and derivation
±√((1 + cos x)/2)
For cos(x/2) you use the reduction formula for cos which is cos² x = (1 + cos(2x)) / 2 and then plug in x as (x/2) so get cox ^2 (x/2) = (1+cos(x))/2) and then you solve for cos(x/2) by square rooting both sides
tan(x/2)
And derivation
sinx/(1+cosx) or (1-cosx)/(sinx)
For tan(x/2) you use the sin/cos identitiy and do the sin half angle formula over the cos half angle formula and then get it.
Half angle formulas example problem
Good example
find the exact value of sin 165
165 s half of 33 and so
sin(330/2)=plus minus (root (1-cosx)/2) Sin positive in quadrant 2 so positive
Sin 165=+(root (1-cos330)/2)= root(1-root3/2)/2) and that give (root (2-root3)/4) and then can pull the 4 out of the root and get ½ (root(2-root3))
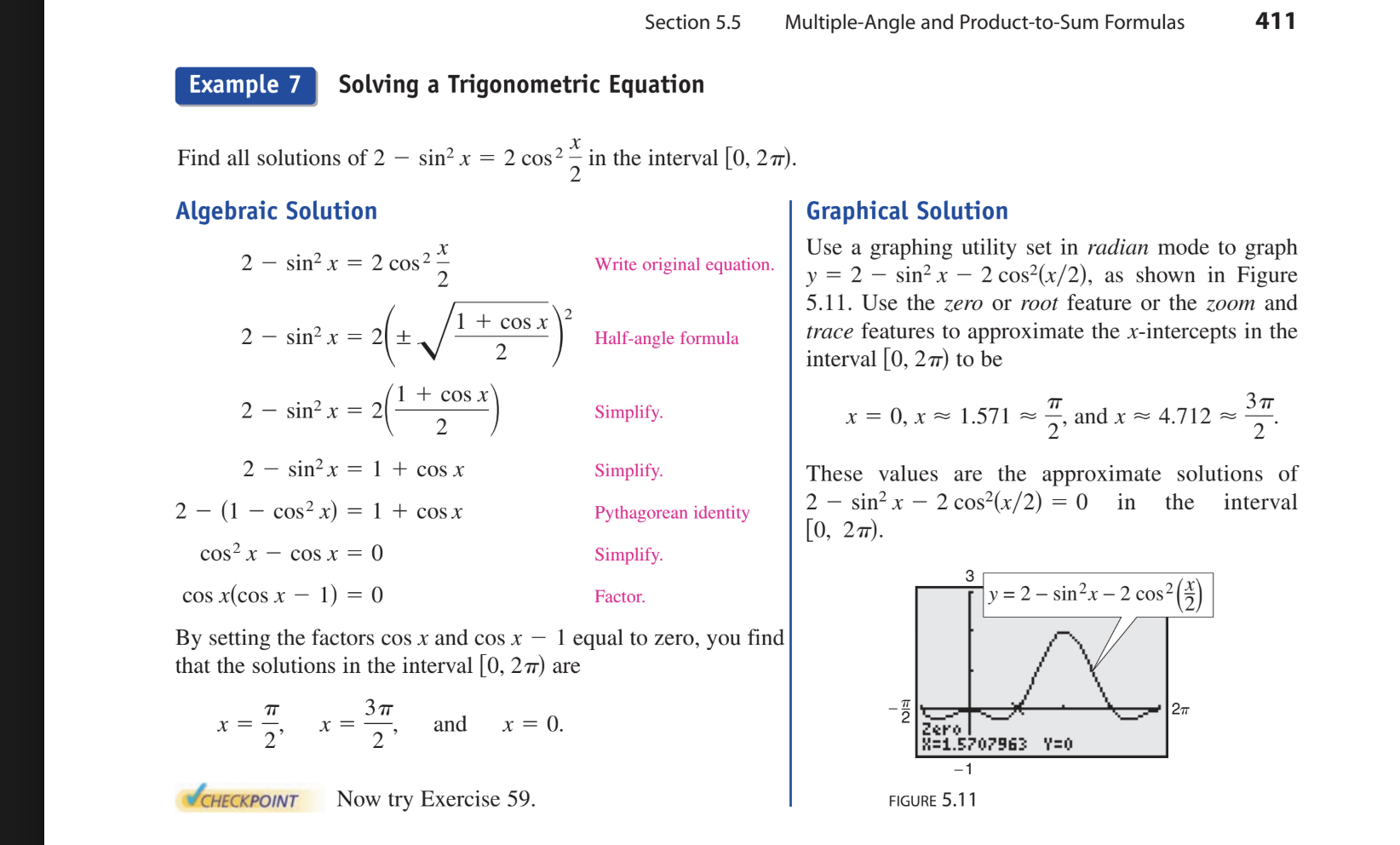
Half angle formulas example problem solving TRIG EQUATION
SUPER IMPORTANT
find all the solutions of 2-sin²x = 2cos² x/2 in the interval [0,2pie)
Use half angle formula to get 2-sin²x=2(plus minus root(1+cosx)/2)
can simplify by using the square root get 2-sin²x=2(1+cosx)/2
and that simplifies to
2-sin²x=1+cosx
and then you can use the pythagorean identity to get
2-(1-cos²x)=1+cosx
and 1+cos²x=1+cosx. and isolte on one side to get
cos²x-cosx=0 factor to get
cos(cosx-1)=0.
and x=pie/2, 3pie/2 and x=0
HW part 1 9-33 odds
HW part 2 41-81 odds 87, 89

HW part 3 95-109 odds
CHAPTER 5 REVIEW IS GOOD Part 1 to 54

CHAPTER 5 REVIEW IS GOOD Part 2 to 54-101

CHAPTER 5 REVIEW IS GOOD Part 3 to 101-118