Chemistry of Life, Water, and Macromolecules
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Bonding, macromolecules, water, A.A, Isomers
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
What are Covalent bonds?
atoms share electrons, strong, form the backbone of biological molecules, C-C, C-H bonds in fatty acids
What are Ionic bonds?
one atom transfers an electron to another ~ charged ions attract (Na+ and Cl- in table salt)
What are Hydrogen bonds?
H bonds between H2O molecules or between DNA base pairs.
Importance of Bonding?
Determine structure and therefore function of macromolecules and explain H2O behaviour.
What is Nonpolar colavlent bonding?
electrons are shared equally (C-H, O=O)
What is Polar covalent bonding?
electrons are shared unequally, creating dipoles with slightly negative/positive ends (O-H, O is more ΔEN, hogs electrons), asymmetrical molecules
Why is Water special?
Polar + forms H bonds.
Cohesion; water sticks to itself (surface tension, H2O droplets)
Adhesion; sticks to other surfaces (water climbs up plant xylem)
HSH; resists temp. changes, stabilizes climate and body temp.
HHV; sweating cools you when H2O evaporates
Density annomaly; Ice is less dense then liquid, ice floats, insulating lakes (if ice denser, lakes would freeze solid from bottom up, killing most aquatic life)
What are the 4 main macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, Nucleic acids
Describe Carbohydrates
Functions: quick energy (glucose), energy storage (starch in plants glycogen in animals).
structural support (cellulose in plant cell walls, chitin in fungi/insects).
What are Glycosidic linkages?
Starch- branched chain of glucose (plant energy storage)
Cellulose- straight chains, humans cannot digest β-glycosidic bonds.
Glycogen- Highly branched glucose storage in animals (liver/muscles)
Describe Lipids
Not polymers. Long-term energy storage (fats), cell membrane (phospholipids), Hormones (estrogen), Insulation + protection. 3 main types; fats (triglycerides), phospholipids, steroids.
Describe the 3 Main types of Lipids
Fats (triglycerides); Glycerol + 3 fatty acids (hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail), saturated (no double bonds ~ butter), unsaturated (double bonds ~ oil)
Phospholipids; cell membrane, amphipathic (hydrophillic head + hydrophobic tail), form bilayers
Steroids; 4 fused carbon rings (chloesterol, estrogen)
Describe Proteins
Enzymes, structural component, transport, signalling, immune functions. Monomer amino acids (20), only differ in R group (determines polarity, charge, hydrophobic/philic, where they appear, bonds)
Describe Non-polar amino acids
Hydrophobic, avoid water, cluster inside proteins, or in membrane interiors. Mostly hydrocarbons, R groups only contain C, H, sometimes S. Very little O or N in side chain, aromatic rings, no obvious polar groups. Stabilize shape with Van der Waals forces, appear in membrane-spanning regions.
Describe Polar amino acids
Hydrophilic, form H-bonds with H2O, side chain contains O or N, polar functional groups. OH groups, amide groups (CONH2), S-H cytesine could be considered polar + hydrophobic, forms disulfide bonds). Located on protein surface, participate in H-bonds, imp. in enzyme active sites, Serine & threonine are phosphorylated for cell signalling.
Describe Charged Amino Acids
Hydrophilic + charged at pH, most hydrophilic since they carry full charge. Form ionic bonds (salt bridges), imp. in enzyme activity and substrate binding, often cluster in active sites, stablize teritiary structure, pKa close to physiological pH.
~Acidic, -charge at pH 7, have Carboxylate COO- groups
~Basic, +charge at pH 7, have extra amine NH, accept protons
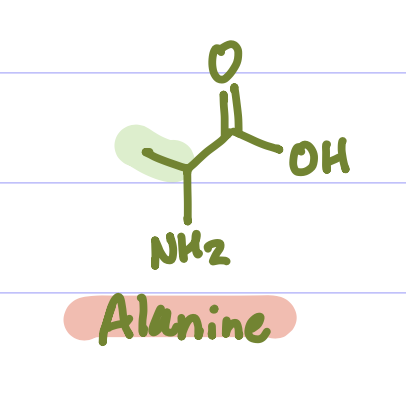
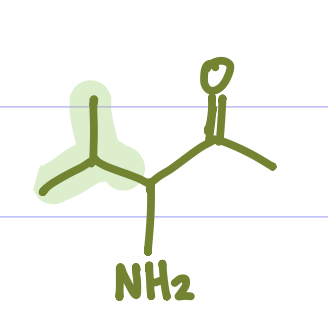
What are the Hydrophobic Amino Acids?
Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine, Proline, Phenylalanine, Tryptophan, Cysteine, Methionine. (Grandma Always Visits Landon’s Intensely Proud Penis To Cuck Matthew)
What Amino Acids are -Charged?
Aspartic and Glutamic acid
What Amino Acids are +Charged?
Lysine, Arginine, Histidine
Describe Nucleic Acids
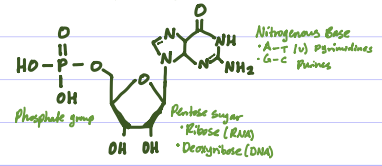
Store, transmit, and express genetic information, directing cellular activities, esp. in protein synthesis. Long chains of nucleotides, each made of a sugar, (ribose for RNA, deoxyribose for DNA), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base A~T, U (pyrimidines), G~C (purines). DNA stable double helix for long-term storage, RNA versatile messenger, template, and catalyst for protein synthesis.
What is the Structure of a Nucleotide?
Phosphate group, ribose sugar, nitrogenous base
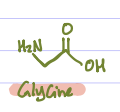
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
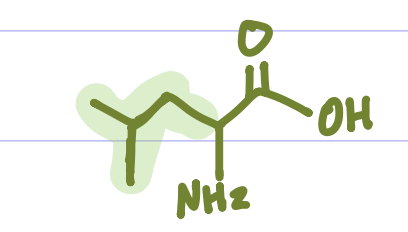
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
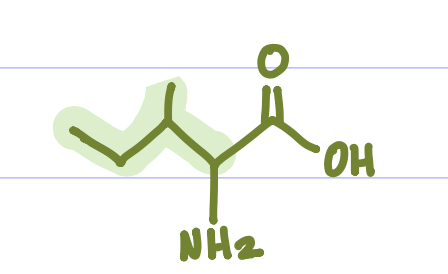
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
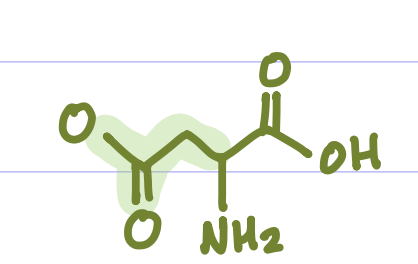
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic, -charge
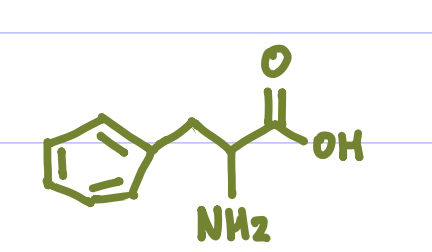
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
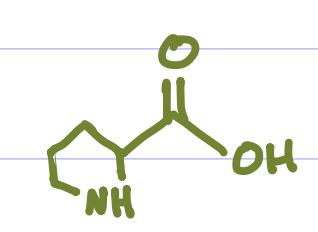
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
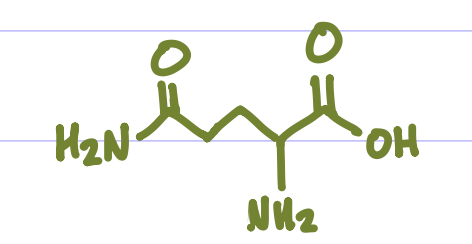
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic
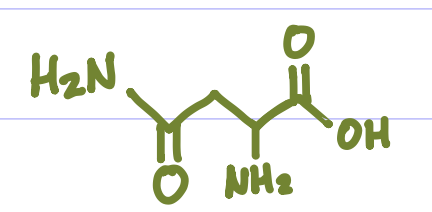
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic
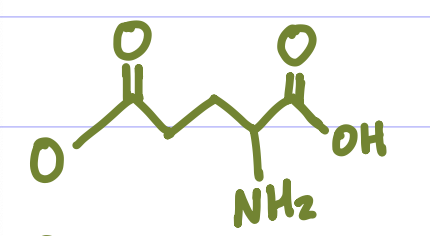
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic, -charge
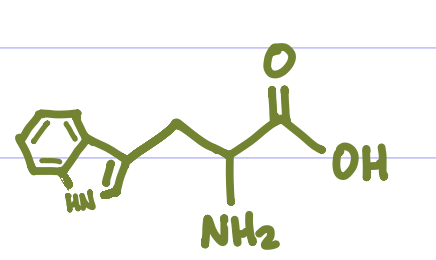
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophilic
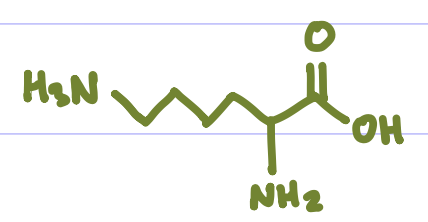
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic, +charged
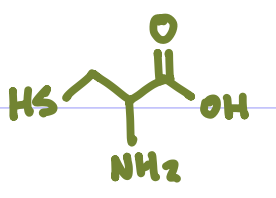
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
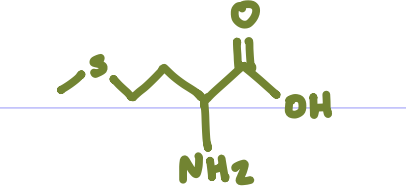
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Non-polar, hydrophobic
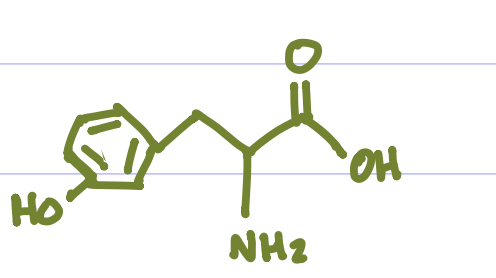
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic
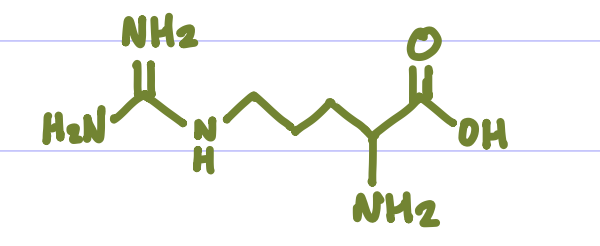
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic, +charge
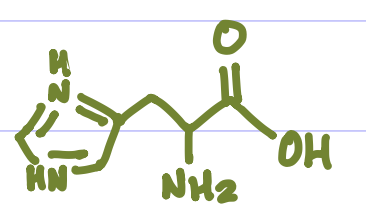
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, Hydrophilic, +charge
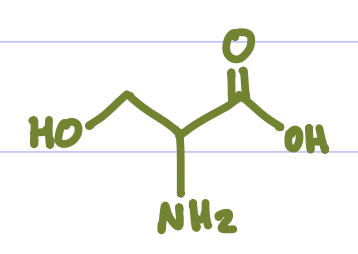
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
polar, hydrophilic
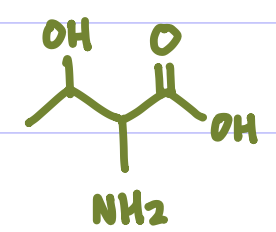
Is this Amino Acid Polar or Non-polar?
Polar, hydrophilic
Describe Isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formula, different structures.
Structural isomers- Atoms connected in different orders (butane vs. isobutane, diff. shape, BP)
Cis/Trans isomers- geometric, same convalent arrangement, diff positions around double bond.
Enantiomers- mirror image isomer, many enzymes and receptors stereospecific, only bind one enantiomer
~Thalidomide: one enantiomer effective sedative, other teratogenic.
What do amino acid sequences represent?
Primary structure (folding~function)
Compare and Contrast Covalent bonds, Ionic bonds, and Hydrogen Bonds
Covalent Bonds: e- shared, very strong, single/double/triple, determines macromolecule backbones, specific molecular shapes. (ex. peptide bonds between a.a. phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides in DNA)
Ionic Bonds: one atom donates e- , ions attract, H2O environments, weaken because H2O surrounds ions, reduces attraction, stabilizes protein structures, helps substrates bind. (ex. salt bridges between a.a and basic a.a.
Hydrogen Bonds: Weak attraction between partially negative and partially positive atom on other molecule, weak individually, strong collectively, create unique H2O properties, DNA Base pairing (A-T 2, G-C 3), protein secondary structure (α-helicase and β-sheets)
Describe the Difference between Polar Covalent bonds and Non-polar Covalent bonds
Polar Covalent- unequal sharing of electrons, slight positive pulls closer, permanent dipoles, O-H in H2O, O hogs electron, H loses density becomes slightly positive.
Non-polar Covalent- equal sharing of electrons, no dipoles, often between identical or similar ΔEN, determine hydrophobic/philic, protein folding + membrane structure.
How do Polar Covalent bonds in H2O cause H-bonding?
O highly ΔEN, pulls shared electron towards itself
Results on partially -O, and partially +H
Partially +H from one H2O attracted to partially -O of another
This attraction = H-bond
ΔEN?
0-0.04 NPC ~ 0.04-1.7 PC ~ 1.7+ Ionic
What are the Levels of Protein Structure
Primary ~ structure of protein is unique a.a sequence
Secondary ~ structure are coils and folds within polypeptide chain
Tertiary ~ structure determined by interactions among various side chains (R groups)
Quaternary ~ structure is wen a protein consists of multiple poly peptide chains
Explain why Ice is less denser than Water
Liquid H20, H-bonds constantly break/reform, molecules come close tg, increasing density. Ice forms 4 stable H-bonds in tetra. lattice, creates fixed open structure molecules re further apart decreasing density. If ice denser, lakes would freeze solid from bottom killing most aquatic life, Earth’s climate would fail.
How do the Properties of Water support life?
Cohesion; H2O molecules stick together, create surface tension, water transport in plants (xylem)
Adhesion; sticks to other surfaces, water climbs up plant cell walls via capillary action
HSH; absorbs +energy before heating, stabilizes ocean/body temp., buffers organisms from rapid temp. changes
HSV; evaporation removes heat, sweating cools organisms, prevents overheating
Excellent Solvent; dissolves ions and polar molecules, metabolism dependent on dissolved solutes, blood transports nutrients and waste
Ice Floats; insulates lakes, allows life to persist under ice
How does Water Moderate Temp.?
HSH, heat energy goes into breaking H-bonds, temp. changes slow, ocean regulate climate, blood/H2O regulates temp. evaporative cooling, sweating removes heat as hottest molecules escape.
How do CO2 Emissions cause Ocean Acidification?

Why does Ocean Acidification threaten marine life?
Shell building organisms (corals, oysters, plankton) need carbonate ions to make calcium carbonate shells/skeletons. Acidification depletes carbonated, hindering shell building, weakens reef structure, collapses ecosystems. Food chain collapse, plankton with CaCO3 shells decline, affects fish, marine mammals, ocean economy. Physiological effects, low pH can disrupt enzyme function, interfere with gas exchange in fish, alter sensory behaviour.
Where do trees get their mass?
CO2 in the air
Why are unknown isomers dangerous in pharamceuticals?
Biological receptors are stereospecific, 1 may bind properly + help, another may bind incorrectly + harm. Ex. Thalidomide, R-enantiomer ~ sedative S-enantiomer ~ teratogenic
How do Changes in Protein Structure affect Protein Function?
Primary structure = sequence of a.a., if one changes H-bonding changes causing interactions to shift, ionic interactions alter. Folding changes, shape changes, function changes.
What are Chaperonins?
Proteins that promote proper folding of other proteins