Imaging in Neuroanatomy
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANHB2217
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
What is neuroimaging and is it quantitative or qualitative
A way to study the structure (and even function!) of the brain in a non-invasive way.
A quantitative technique
Neuroradiology
Quantitative/qualitative
A medical specialty that focuses on recognizing brain lesions, vascular disease, strokes, tumors
Largely qualitative
Structural vs functional imaging
Structural imaging: used to quantify brain structure • ex. Voxel-based morphometry which uses a computation approach to measure differences in brain tissue
Functional imaging: which is used to study brain function • ex. Functional magnetic resonance imaging
Computed tomography (CT)
Risk, what it is used for, characteristics of CT scan
Aka computed axial tomography (CAT) CT uses x-rays to quickly view brain injuries Ex. Bone fractures, tumors, internal bleeding
Cheap
Risks: exposes a person to radiation, potential reaction to dyes
Very white bone, less distinct image, air is dark black
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Uses what, risks and characterizes of the image it produces
Uses magnetic fields and radio fields to produce high quality 2D or 3D images of the brain
Many types of MRI to look at different structures in more detail
Expensive
Risks: uses powerful magnets and are incredibly loud producing noise up to 120 dB
More distinct, CSF black, grey tissue
Types of MRI
T1-weighted: enhances fatty tissue
T2-weighted: enhances water
FLAIR: nulls the effect of fluid on images, useful for identifying areas of demyelination
Diffusion: maps white matter tractography
Cerebral angiogram
Provides images of the blood vessels around the brain
Risks: contrast allergy, renal insufficiency, and coagulation disorders
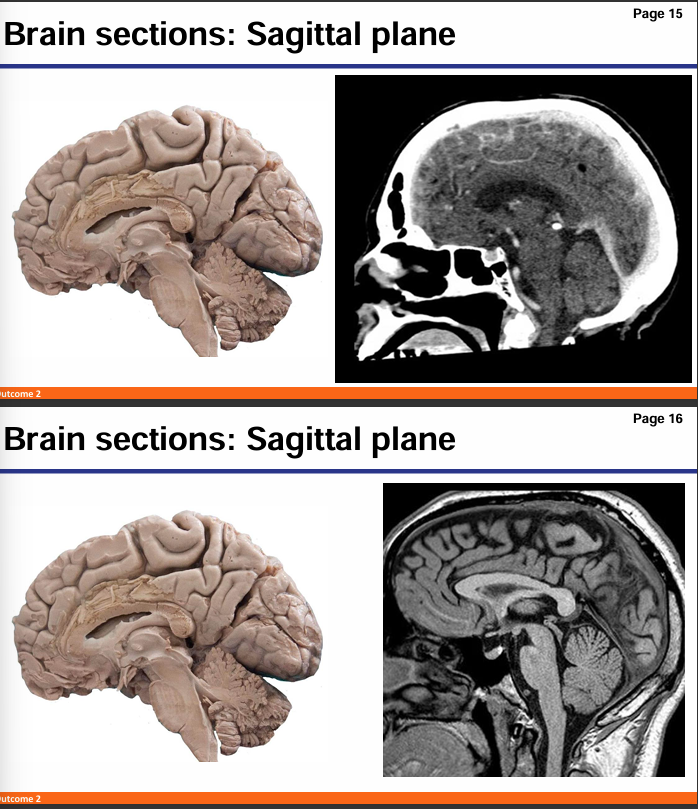
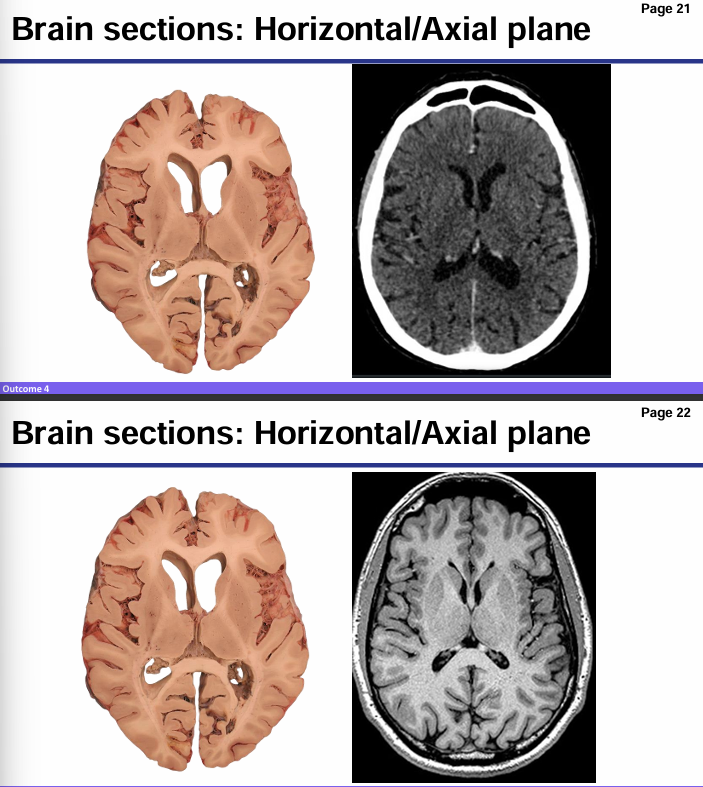
Which is MRI and which is CT
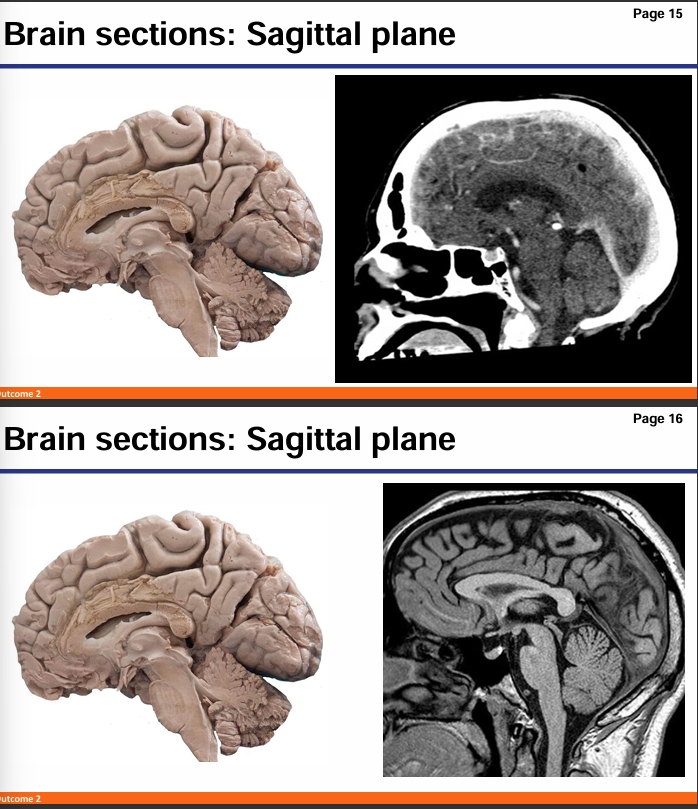
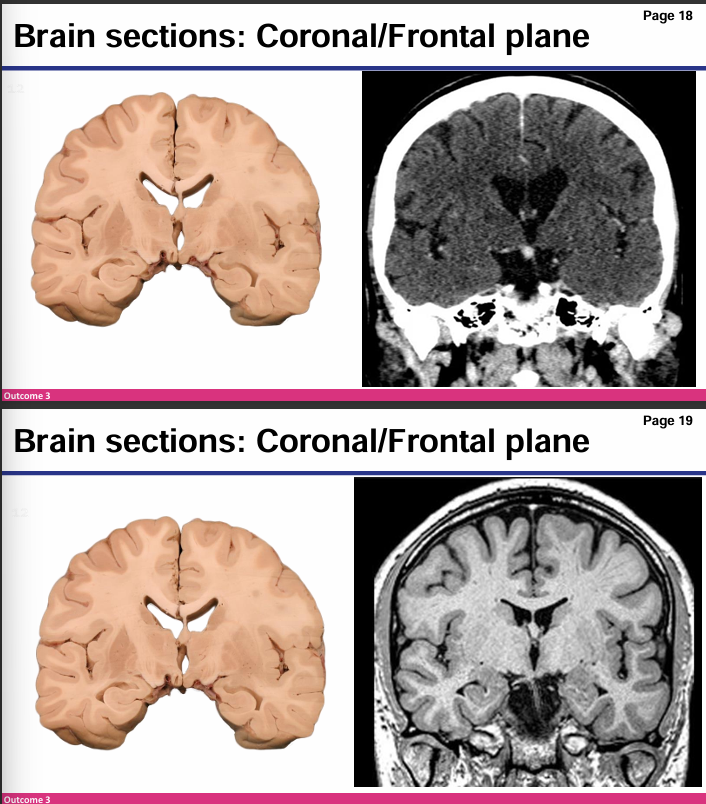
Which is MRI and which is CT
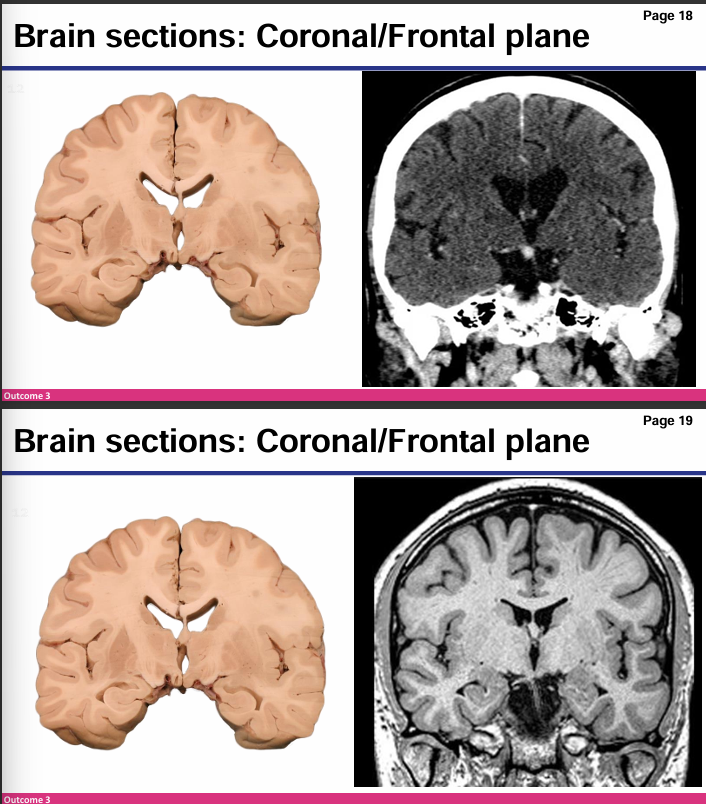
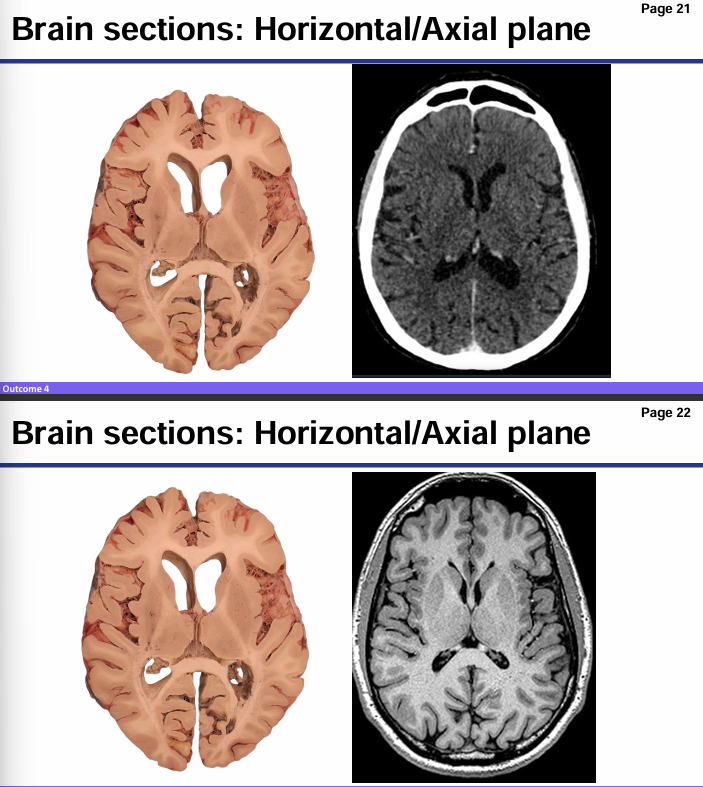
Which is MRI and which is CT