networks
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
- Operating System - File structures: partitioning and formatting - Cables: ethernet vs fibre, key terms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
what is the topology of a network
the way a network is laid out
what is a star network
all devices and computers are managed from a central point, the switch
what does the switch do
manages all the traffic on the network
diagram of star network
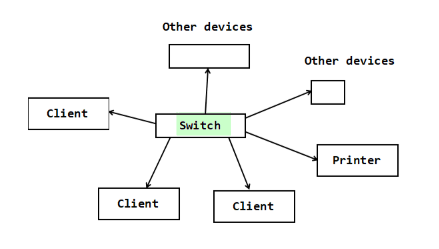
what is a client and what do they do
the terminals where users log in
clients retrieve documents and software from the server
any device which connects to and uses the server/eq;
what is a printer
a shared resource, managed by a server
The star network can link to a server through a router.
diagram:
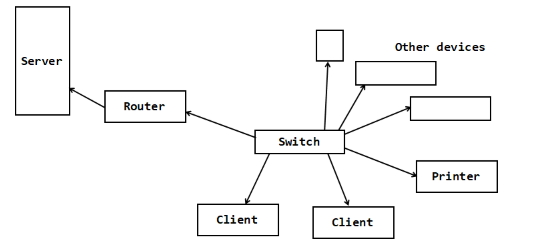
define server
a computer which has been set up to hold resources centrally, such as the documents of user profilewha
what do profiles enable users to do
log in to any client on the network and access your personal resources, which are all stored centrally on the sever
examples of servers:
insert server after each word:
database, file, mail, print, web, game, app
what does a router do
connects different networks together simultaneously
what is a terminal
A point at which data enters or leaves a network
advantages vs disadvantages of a star network
advantages:
very reliable - if one cable/device fails the others will keep working
high-performing (no data collisions)
disadvantages:
expensive to install
extra hardware required (e.g. hubs, switches) which adds to cost
if a hub or switch fails, all the devices connected to it will have no network connection
what is an Edge router
The outermost connection point between an internal network and an external network is known as an edge router
what is a node + what can they do x3 small
any connection point in a network (can recognise, process and forward data transmissions)
what is client-side processing
Processing of transmissions and received data conducted on a client is client-side processing
what is server-side processing
Processing of transmissions and received data on a server is server-side processing
what is the user profile
A user profile is a set of information pertaining to one user.
e.g. file permissions, security settings (password), available services
how does data on a network move, in p______s
in packets
each packet is sent individually and then reassembled into the original file at the receiving end
what 3 parts are is the data packet made up of
headers, the payload (data being transmitted) and a trailer.
what is the header and what happens to it when it reaches the receiver
header identifies the source and the destination of the data packet. The header is stripped off the packet when it reaches the receiver.
what is the trailer and what may in contain
if _____ fails, what must happen
trailer uses a few bits to indicate the end of the packet, and it may contain verification. If the verification fails the data packet may need to be retransmitted.
what does an IP address mean for a device on a network.
what form does it take
the digital addresses of devices on a network.
internet protocol
They take the form of 4 denary numbers between 0 and 255, separated by dots. IP addresses are the LOCATION of a device on a network
Servers usually have ___ IP addresses so that…
what else could be given an IP address
STATIC IP addresses
so that devices always know where to find them
(also other resources that always need to be found, like shared printers, could also be given static IP addresses)
what is a MAC address
how is it formed
who is it assigned by
the unique identifiers of a device on a network. They are a group of 6 pairs of hexadecimal digits, separated by colons or dashes
assigned by a manufacturer when the device is first produced
media access control
define protocols
A protocol is a set of rules for communication between two devices.
what is the primary use of a port number
to transfer the data between a computer network and an application.
a port is a ____ address assigned for ___ ______ in the computer system that receives data from the network
LOGIAL address assigned for EACH APPLICATION
what does OSI model stand for, what does it describe
Open Systems Interconnection
describes how data is transmitted from one device to another. (could be public or private or internet).
what are the 5 OSI layers?
1 - Physical
2 - Data link
3 - Network
4 - Transport
5 - Application
what is Layer 1 responsible for
physical:
Physical transmission hardware - cables (like CAT-6/ethernet) and ports
what does Layer 2 do
Matches sending/receiving addresses using MAC addresses & Ethernet protocol
a protocol on Layer 2: Prevents data collisions by ensuring only one packet can arrive at an address at a time
…
Ethernet is a network protocol that controls how data is transmitted over a Local Area Network (LAN). Ethernet defines when to transmit, transmission speeds and media.
….
what does Layer 3 do
Uses IP to route data packets between networks via routers
describe specifically how it works with the route tables and stuff (probs unofficial)
Routers hold tables of IP addresses
use them to send data packets to the right address.
If table does not hold the required address, they pass the data packet to another router.
generally 64 attempts before the data packet is discarded.
TimeToLive (TTL) variable keeps track of the number of attempts and is decremented by one every time the data packet is passed to another router.
what is layer 4
what does TCP stand for
transport layer:
where data is broken down into packets
Transmission Control Protocol
what's Layer 5's purpose?
what is it for web vs email
Application layer
Handles application-specific protocols like HTTP (web) and SMTP (email)