Key Definitions - Circ Motion, SHM, g-fields, E-Fields
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Amplitude
The maximum displacement from the equilibrium position
Angular displacement
The angle in radians, about a fixed axis, that a rotating object has travelled through.
Capacitance
The charge stored per unit potential difference
Centripetal acceleration
Acceleration towards the centre of a curved or circular path.
Centripetal force
A force causing an object to move in a circle, acting towards the centre of the circle
Coulomb's Law
The force between two point charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
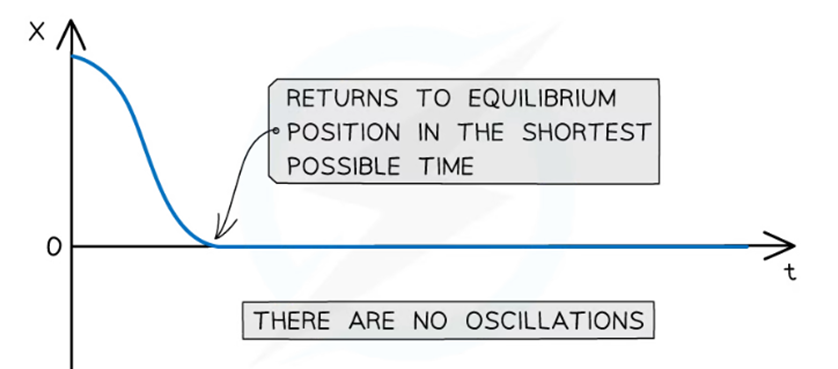
Critically damped
When the resistive forces on a system are just enough to prevent oscillation and the object returns to equilibrium in the minimum possible time
Damping
The removal of energy from an oscillating system.
Dielectric
A material which is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field.
Dielectric constant
The factor by which the electric field between two charges is decreased by the presence of the dielectric, relative to a vacuum
Electric field
An area around a charged object/particle where other charged objects/particles would experience a force.
Electric Field Strength
The force per unit charge on a positive test charge placed in the field at that point. A vector quantity.
Electric potential
The work done per unit charge in bringing a small positive test charge from infinity to a specific point in an electric field.
Electric potential difference
The work done per unit charge moving the charge between two points.
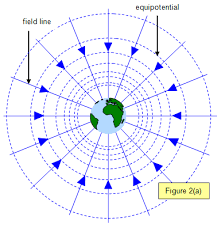
Equipotential surface
All points on an equipotential surface have the same gravitational potential. No work is done against the field or by the field when an object is moved along this surface.
Equipotential lines
All of the points in a gravitational field where the gravitational potential is the same value
Forced oscillation
An oscillation imposed upon a body or system by an external energy source
Free oscillation
An oscillation in which a body or system oscillates at its natural frequency
Geostationary Satellite
A satellite that has the same orbital period(24h) and direction as the earth and orbits on the equatorial plane, and thus remains over the same point on the Earth’s surface. It is used for communications (e.g. TV).
Gravitational Field Strength
The attractive force per kg acting on an object with mass at a specific point in that field
Gravitational potential
The work done per kg moving an object from infinity to a specific point in a gravitational field
Gravitational potential difference
The work done per kg moving an object from one point to another point in the same gravitational field
Gravitational potential energy
The total work done moving an object from infinity to a specific point in a gravitational field (gravitational potential x mass of object in field)
Gravitational Field
A region of space where an object with mass experiences an attractive force
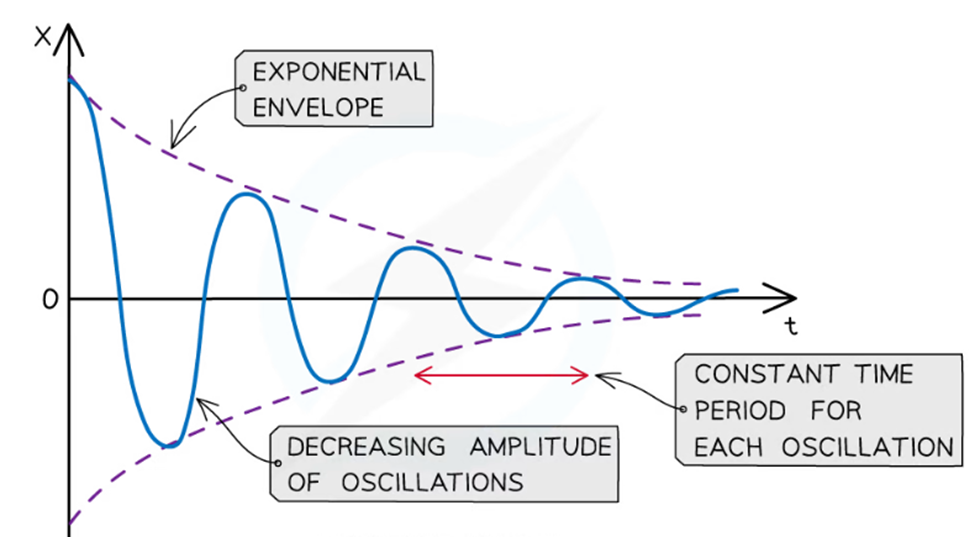
Light Damping
A type of damping in which the amplitude of oscillations decreases gradually over time without completely stopping the motion.
Mechanical Oscillation
A periodic conversion of energy such as from potential energy to kinetic energy to potential energy.
Newton's law of universal gravitation
The attractive force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them
Neutral point
A point between two or more objects with mass where the overall force due to gravity is 0
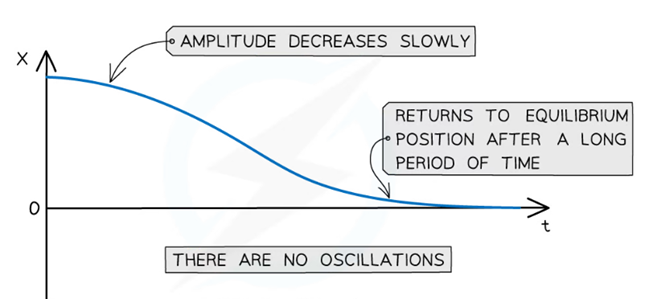
Over Damping
Occurs when the damping force is greater than the restoring force, resulting in a slow return to equilibrium without oscillation. This leads to a system that slowly approaches equilibrium.
Polar satellite
A satellite whose orbit takes it over each pole. It is used for weather monitoring and military surveillance. They are closer to the Earth’s surface and so travel faster than geostationary satellites.
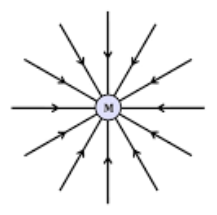
Radial field
A field where the field lines converge on a single point or diverge from a single point.
Resonance
Large amplitude vibrations caused when the driving frequency matches the natural frequency of a system
Resonant frequency
The natural frequency at which an object or system oscillates
Simple harmonic motion
The periodic motion in which the restoring force (and thus acceleration) is proportional to the displacement and acts in the opposite direction
Synchronous orbit
An orbit where the orbiting object’s orbital period and direction is the same as the rotational period and direction of the body it orbits.
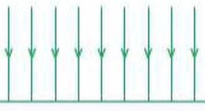
Uniform field
A field where the field lines are parallel and the field strength is constant