biology unit 2 plants - quiz 1 review
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Photosynthesis
A series of chemical reactions that converts energy from sunlight into chemical energy stored in molecules.
Photosynthesis equation (word and chemical)
carbon dioxide + water —> oxygen + glucose
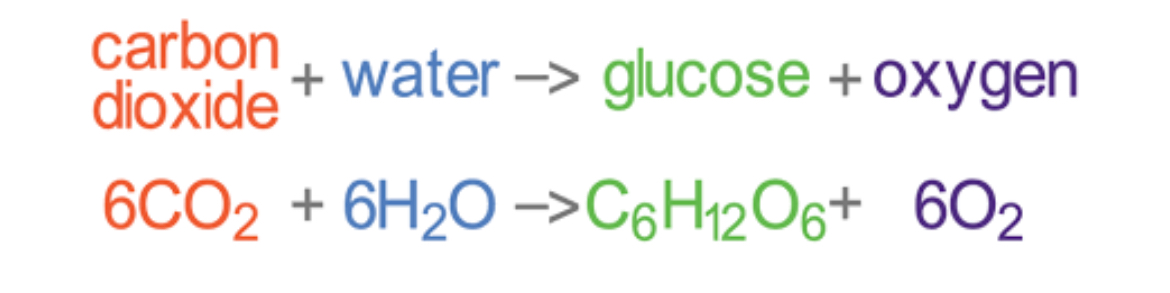
Cellulose
A large carbohydrate molecule that is the main component of cell walls in plants.
Vascular Plants
Plants that have specialized tissues (xylem and phloem), a shoot system and a root system.
Nonvascular Plants
Plants that do not have vascular tissue and obtain water and nutrients through osmosis and diffusion.
Xylem
Transports water and nutrients, contains lignin for strength, made of dead cells.
Phloem
Transports sugars and nutrients, made of living cells.
Angiosperms
Flowering plants with seeds enclosed in fruit, comprising about 90% of all plant species.
Gymnosperms
Plants with exposed seeds on the surface of cone scales; also known as 'naked seed' plants.
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
Diffusion
Net movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
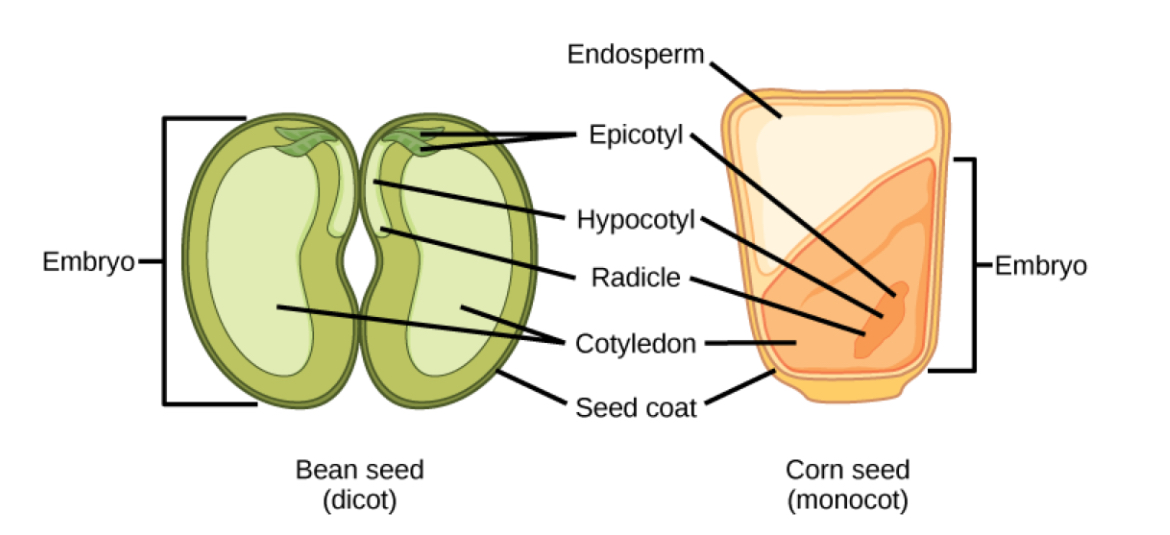
Monocots description
A type of angiosperm with one cotyledon in the seed, parallel leaf veins, scattered vascular bundles, flowers are in multiples of 3.
Examples: corn seed, rice, wheat
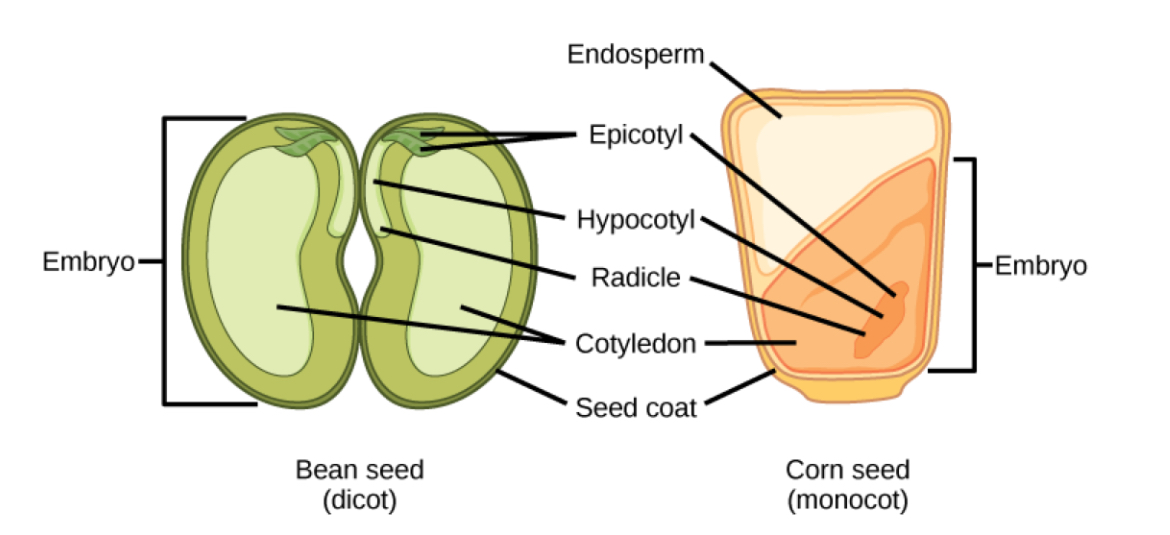
Dicots description
A type of angiosperm with two cotyledons in the seed, net pattern leaf veins, ring shaped vascular bundle, and flowers in multiples of 4 or 5
Examples: Bean seed, peas, sunflowers
Endosperm function
The part of a seed that provides food for the developing embryo.
Cotyledon function
A seed leaf for food storage and providing nutrients
Plant Cell Types
Includes parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma, each with specialized functions.
Plant cell: Parenchyma
Some have chloroplasts and some without chloroplasts
Storage, photosynthesis, gas exchange, protection, tissue repair and replacement
Plant cell: Collenchyma
Support surrounding tissues
Provide flexibility for plant
Tissue repair and replacement
Plant cell: Sclerenchyma
Support mature plant
Comparative Process of Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
Photosynthesis produces oxygen and glucose, which are used in cellular respiration to produce carbon dioxide and water.
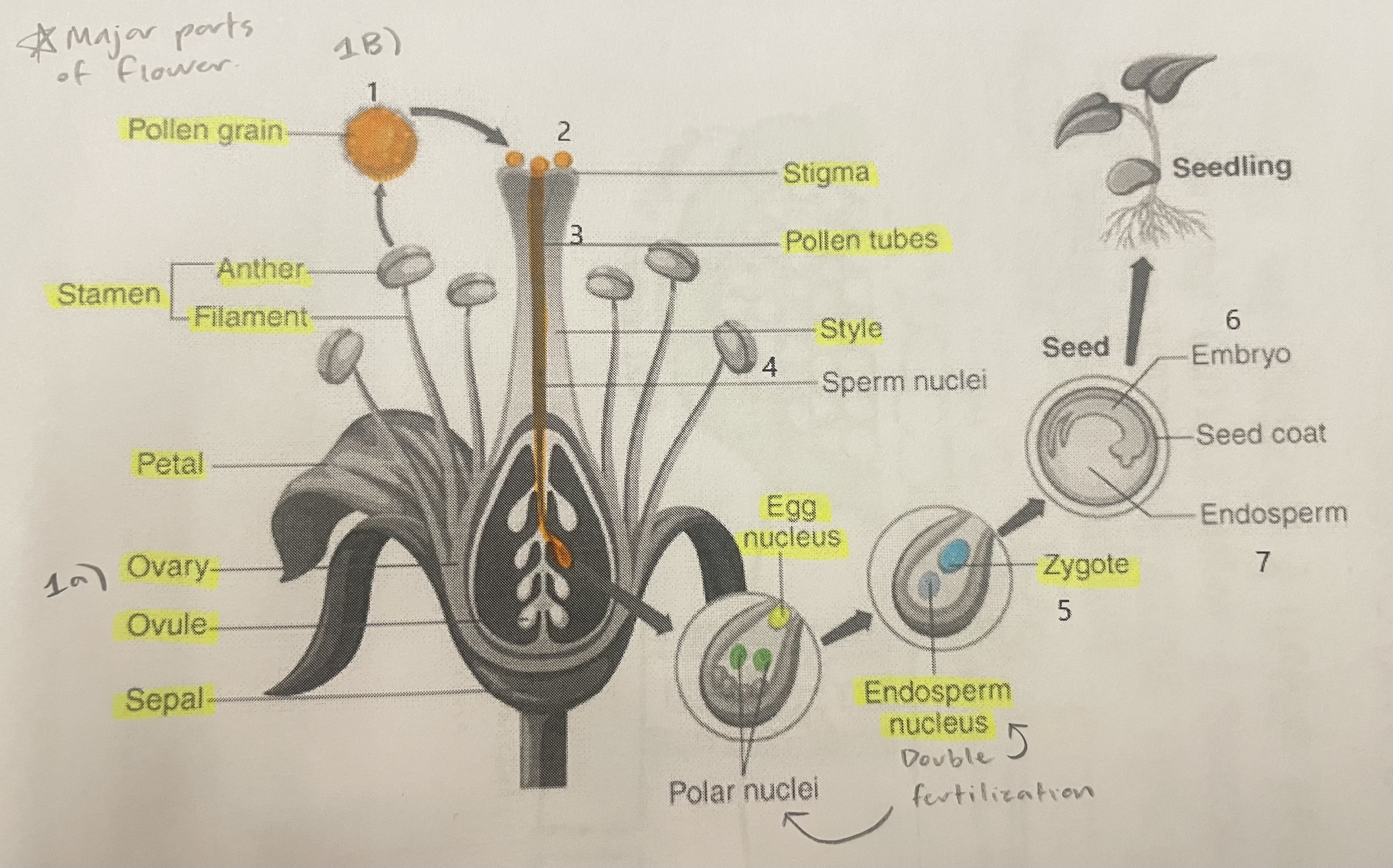
Pollen Grain
Carries male gametes or sperm, essential for fertilizing female ovules.
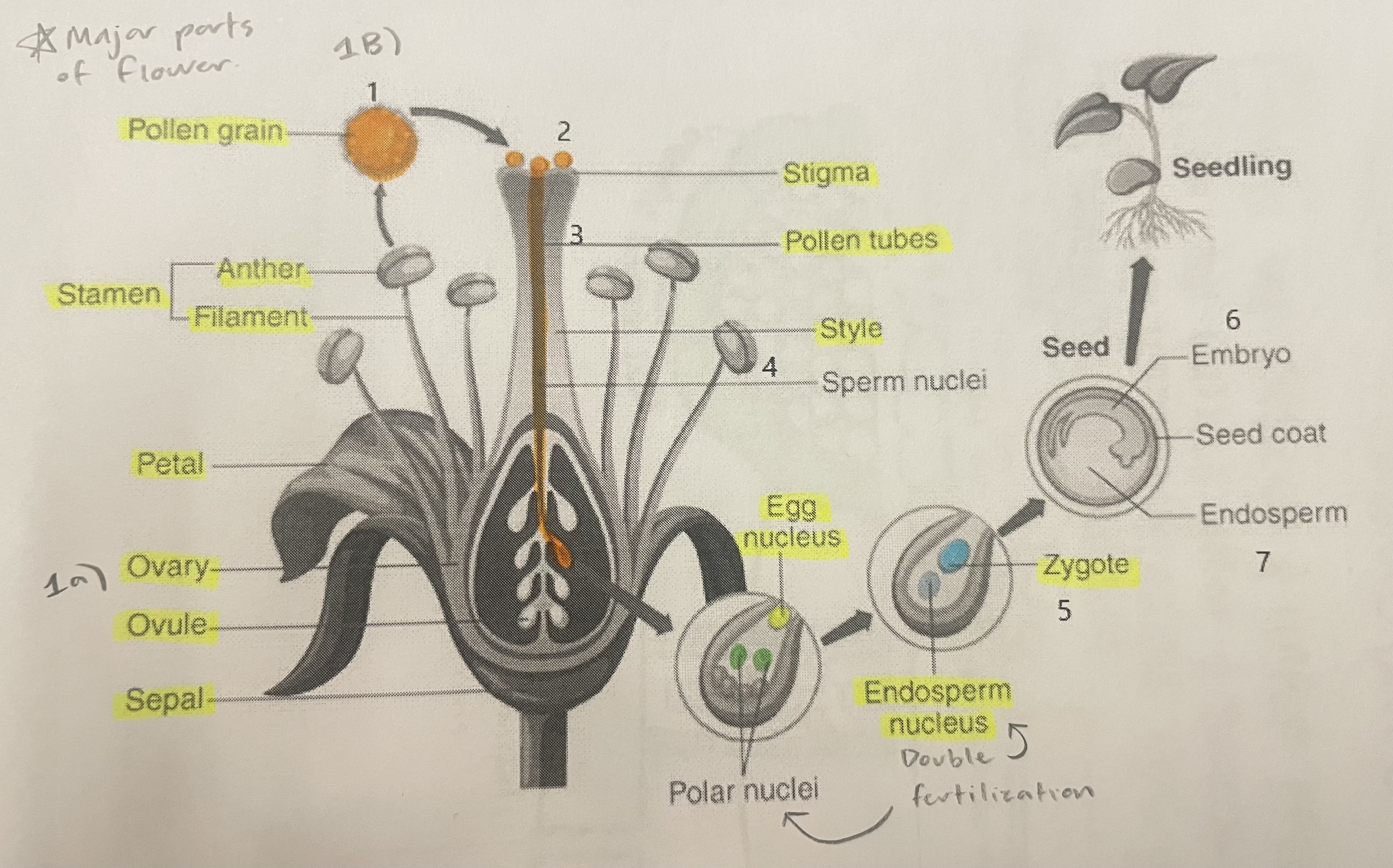
Stigma
Helps collect pollen.
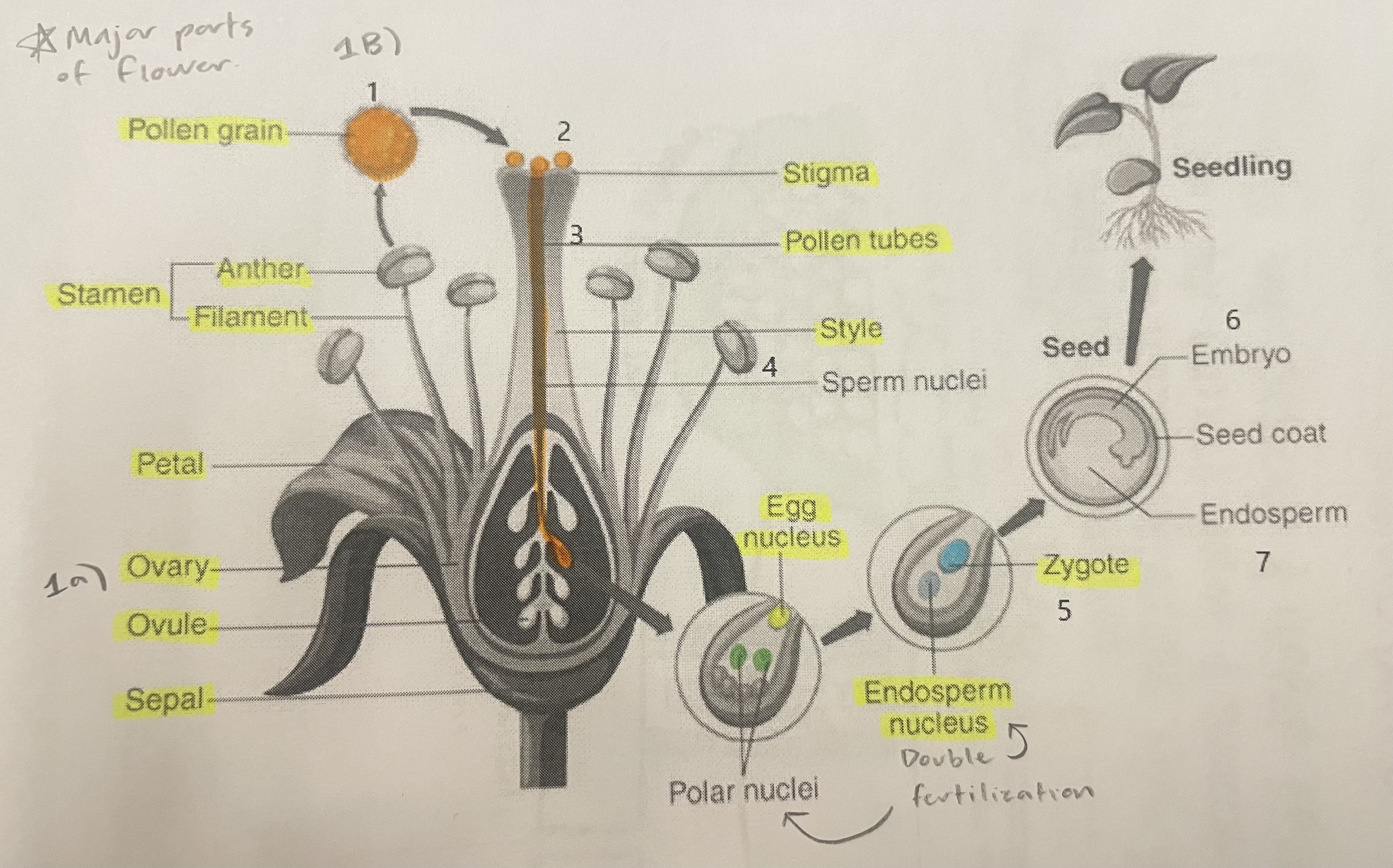
Pollen Tubes
Transports male gametes (sperm cells) from pollen grain to the ovule.
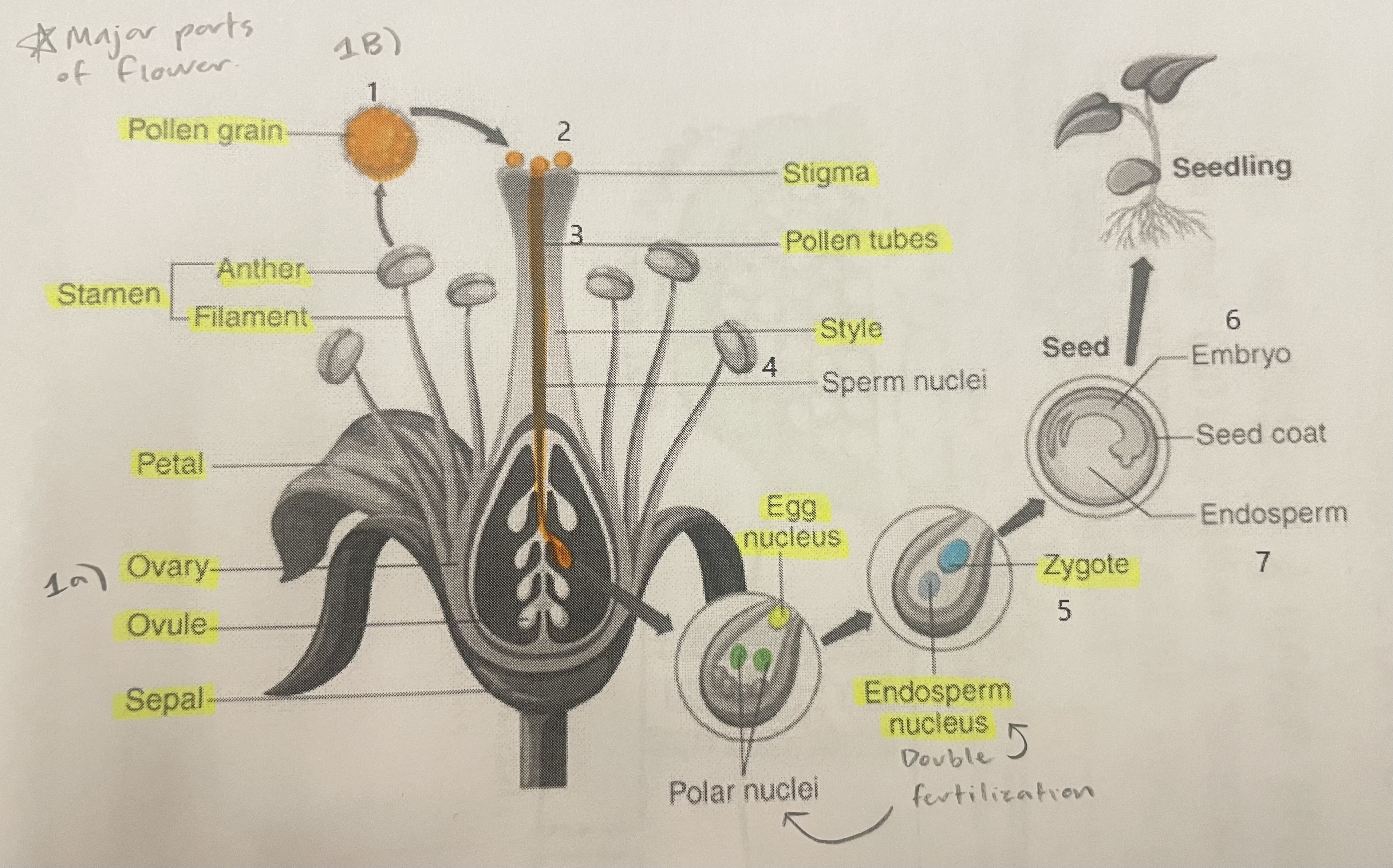
Stamen
The male reproductive part of the flower that produces pollen.
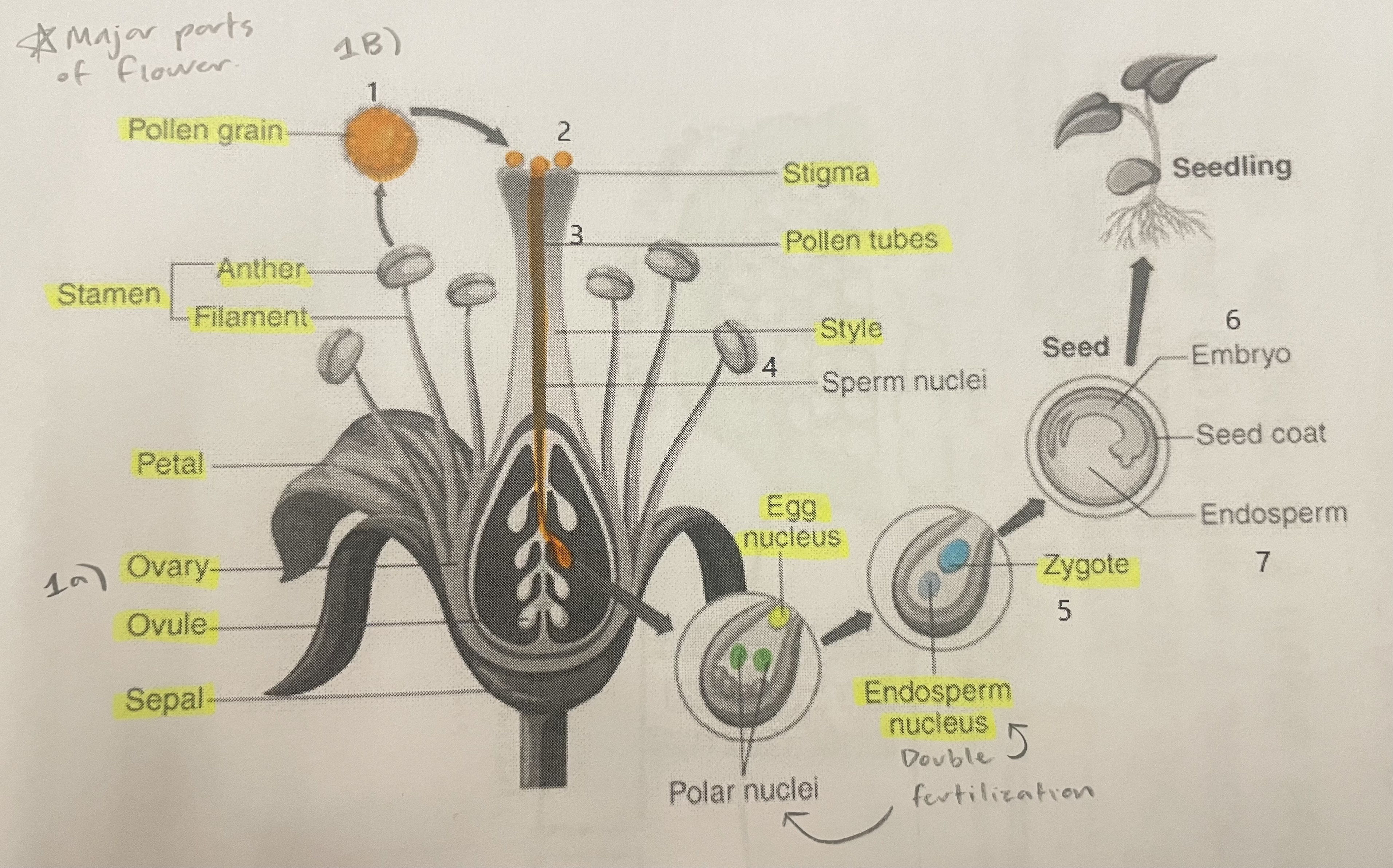
Anther
Produces and contains pollen.
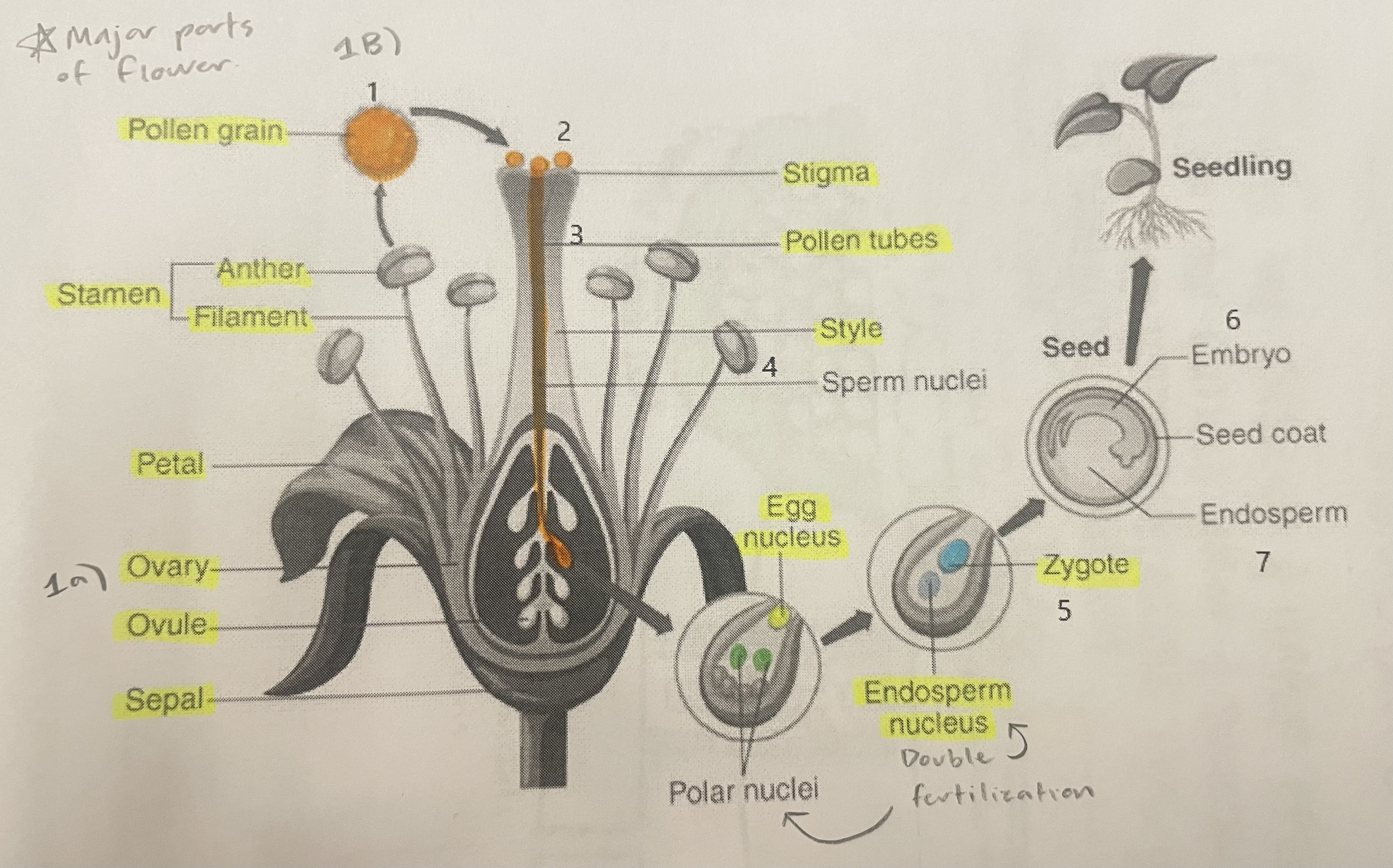
Filament
Holds the anther up.
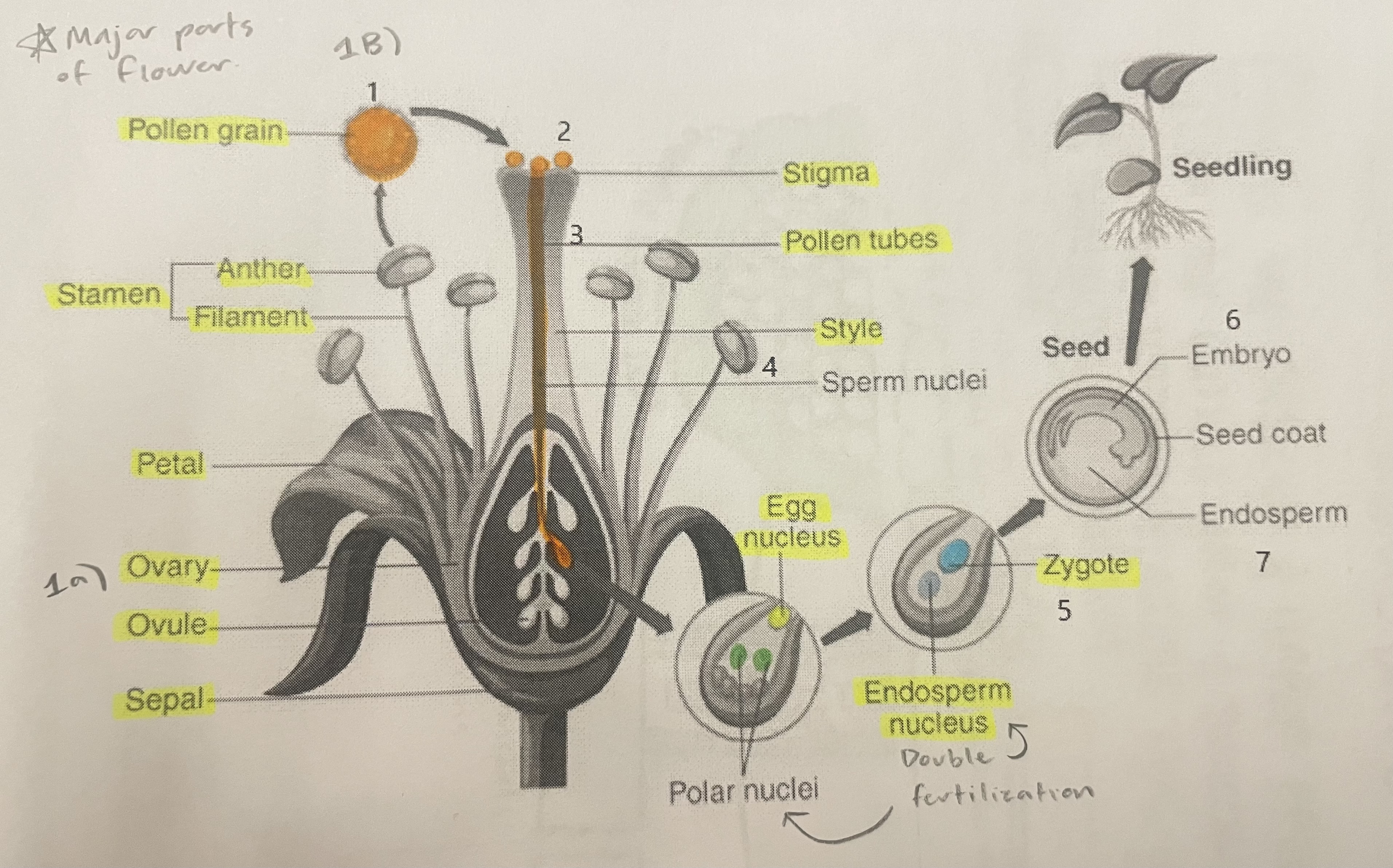
Petal
Attracts pollinators.
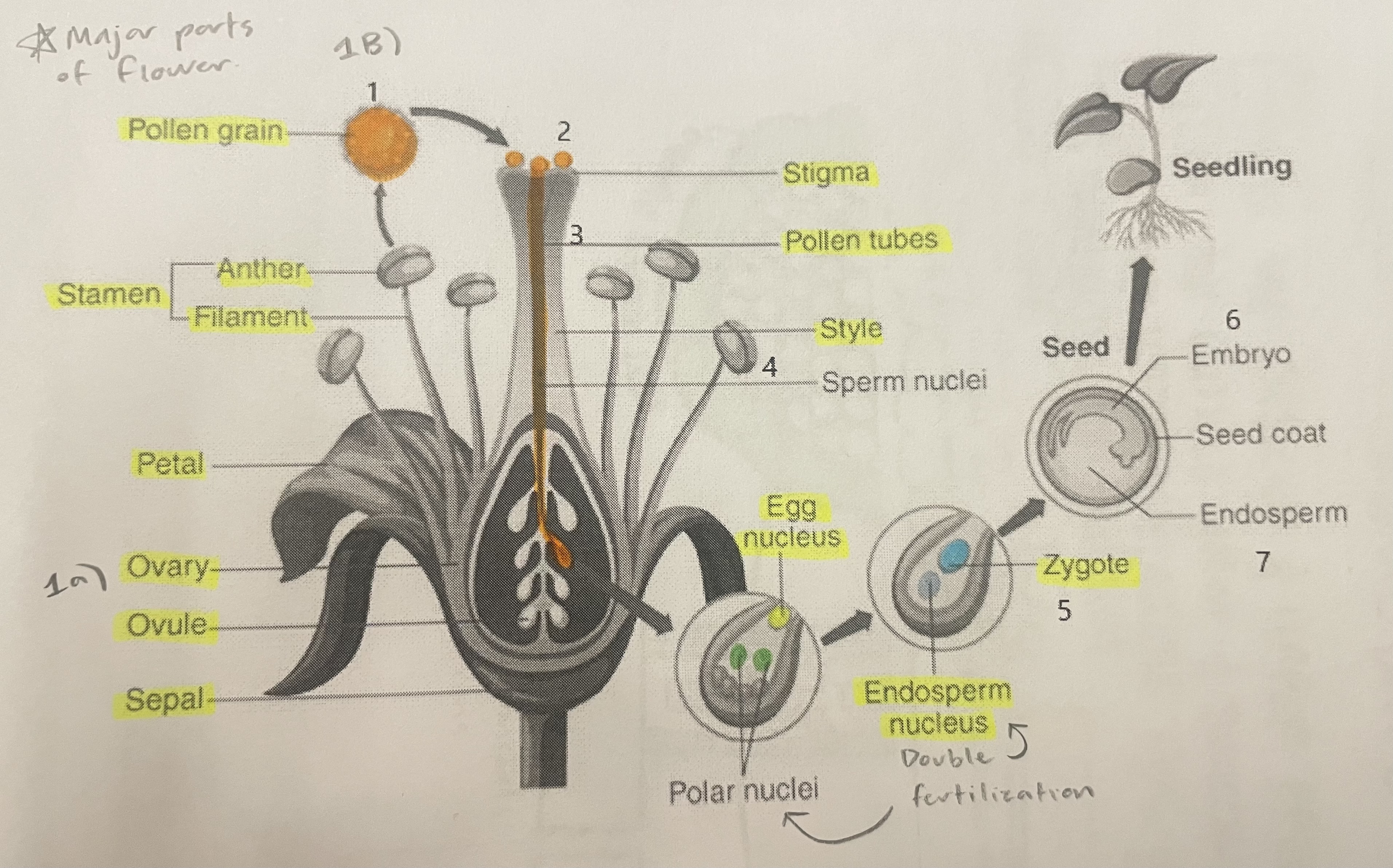
Ovary
Prepares the ovules for fertilization, protects developing zygotes.
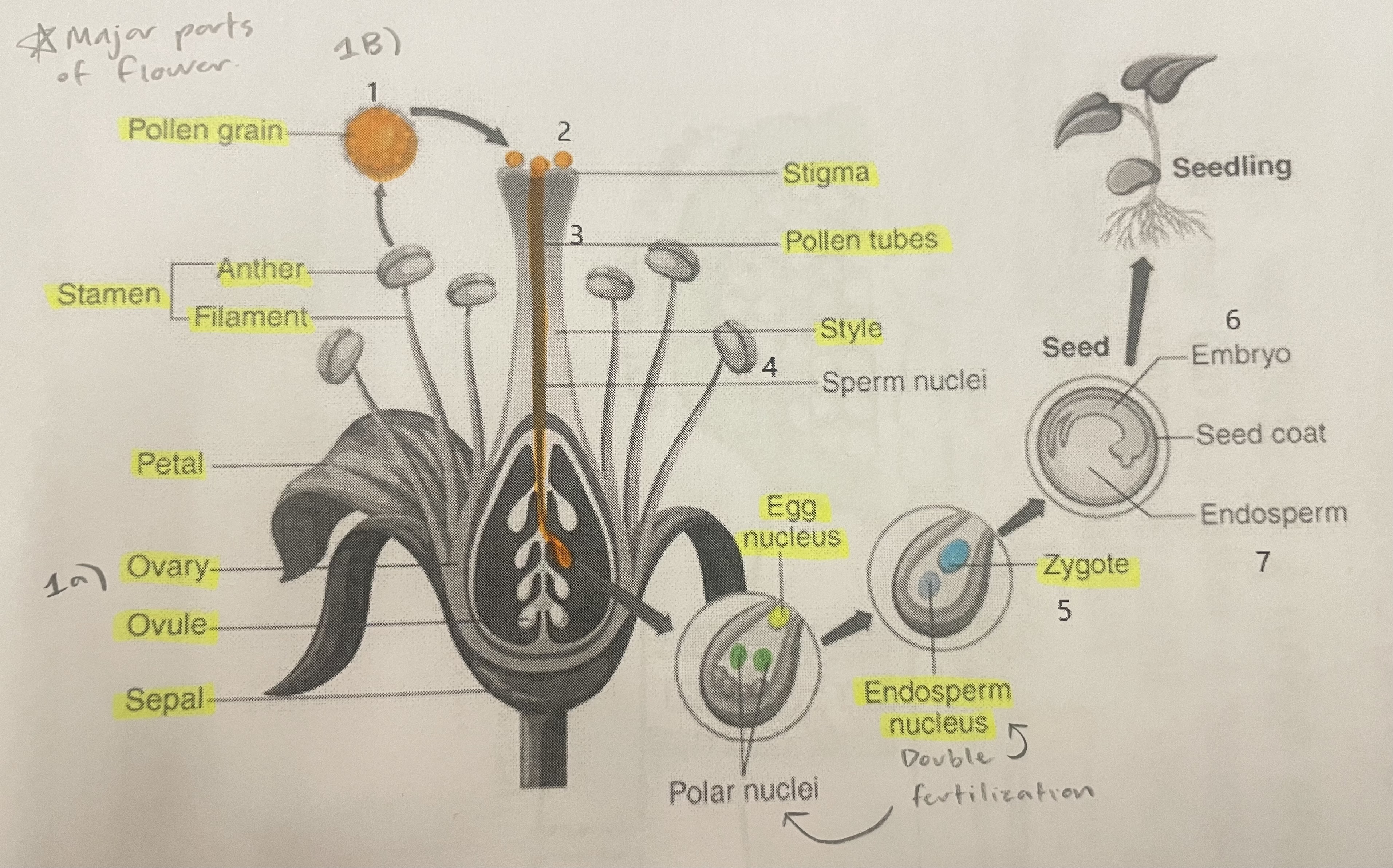
Ovule
Produces eggs.
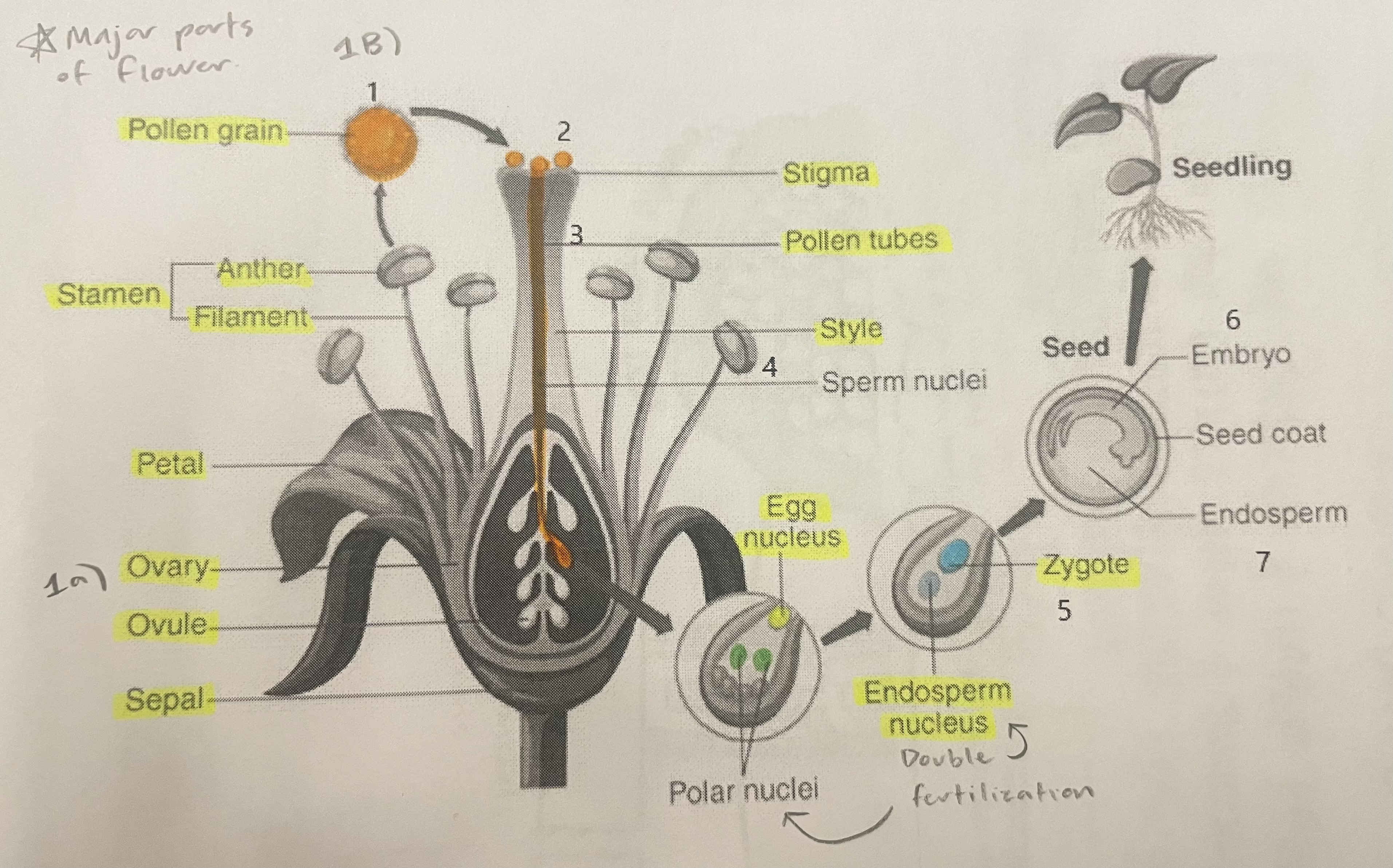
Sepal
Protects the bud.
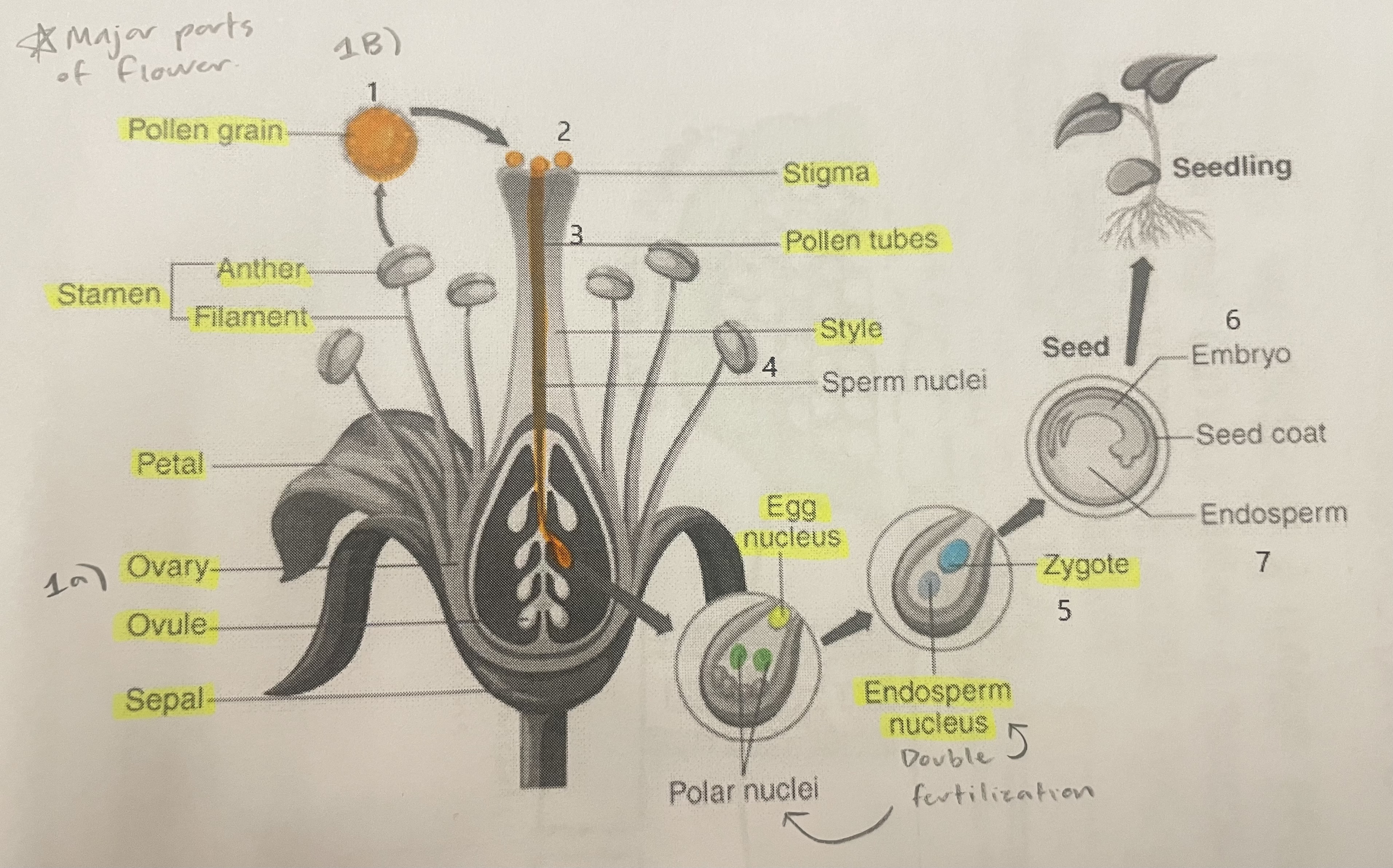
Style
Assists fertilization, contains the pollen tubes which transfer sperm to the egg.
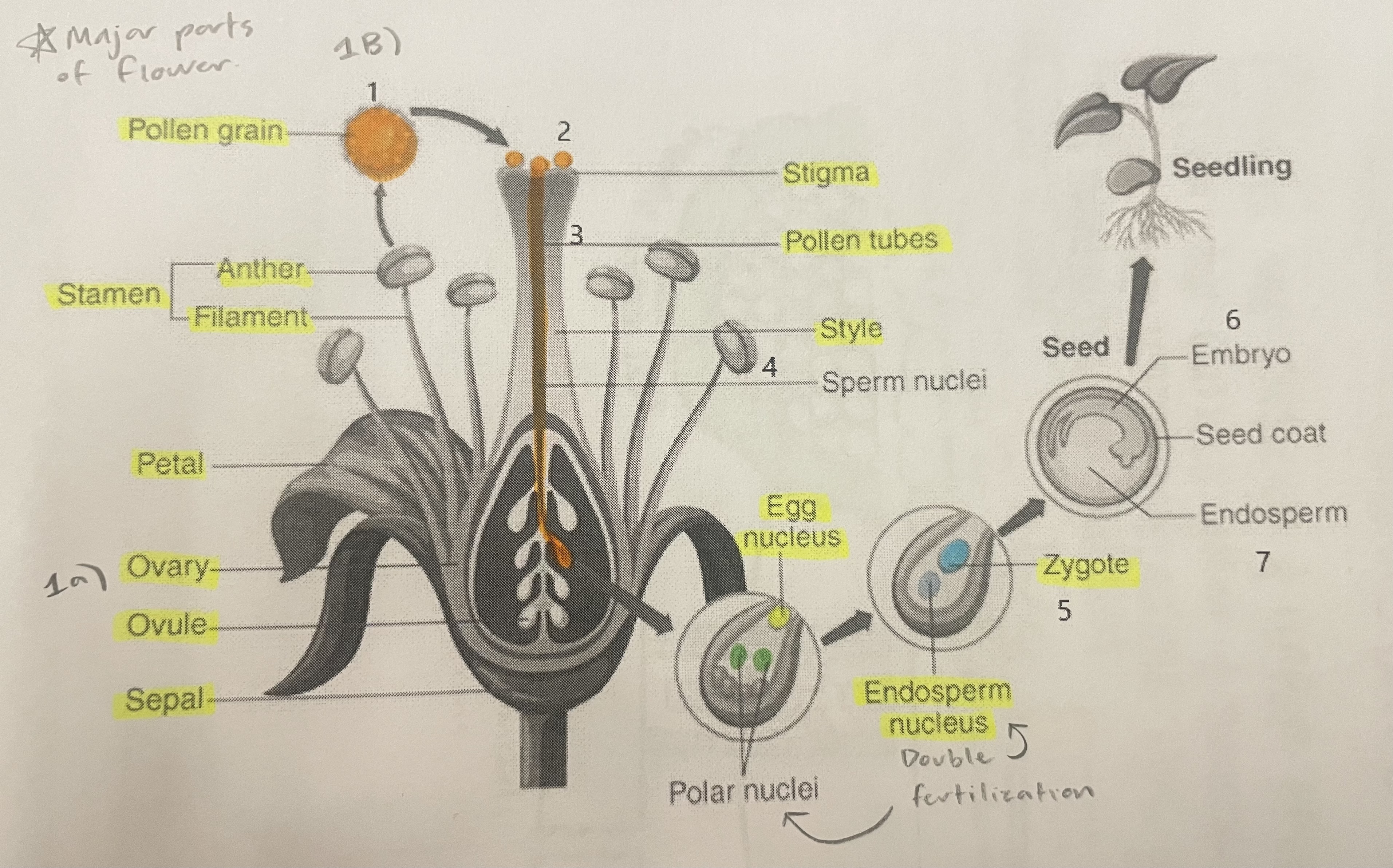
Egg Nucleus
Helps plant reproduce and grow new plants.
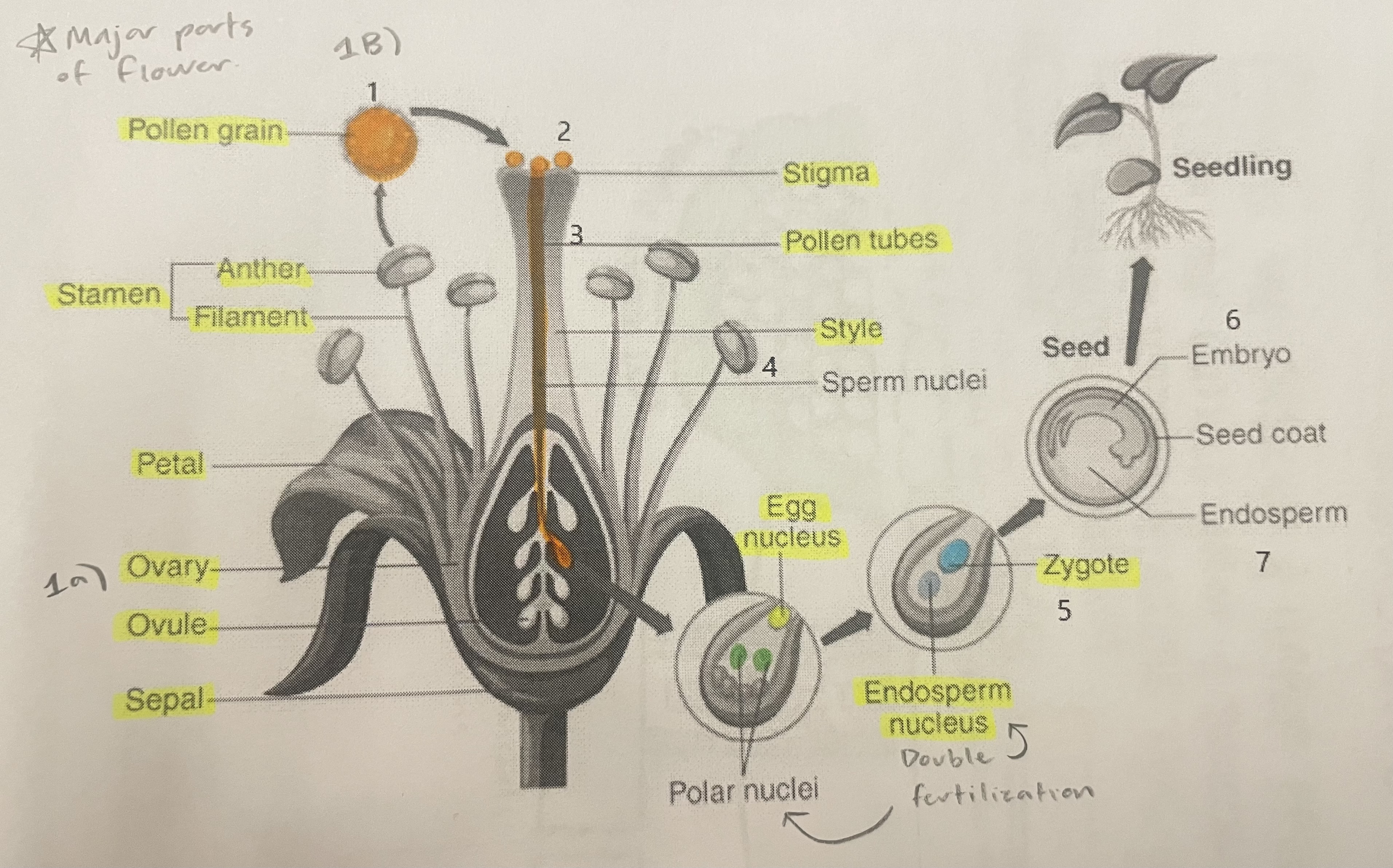
Endosperm Nucleus
Grows into the endosperm, which provides food for the developing seed.
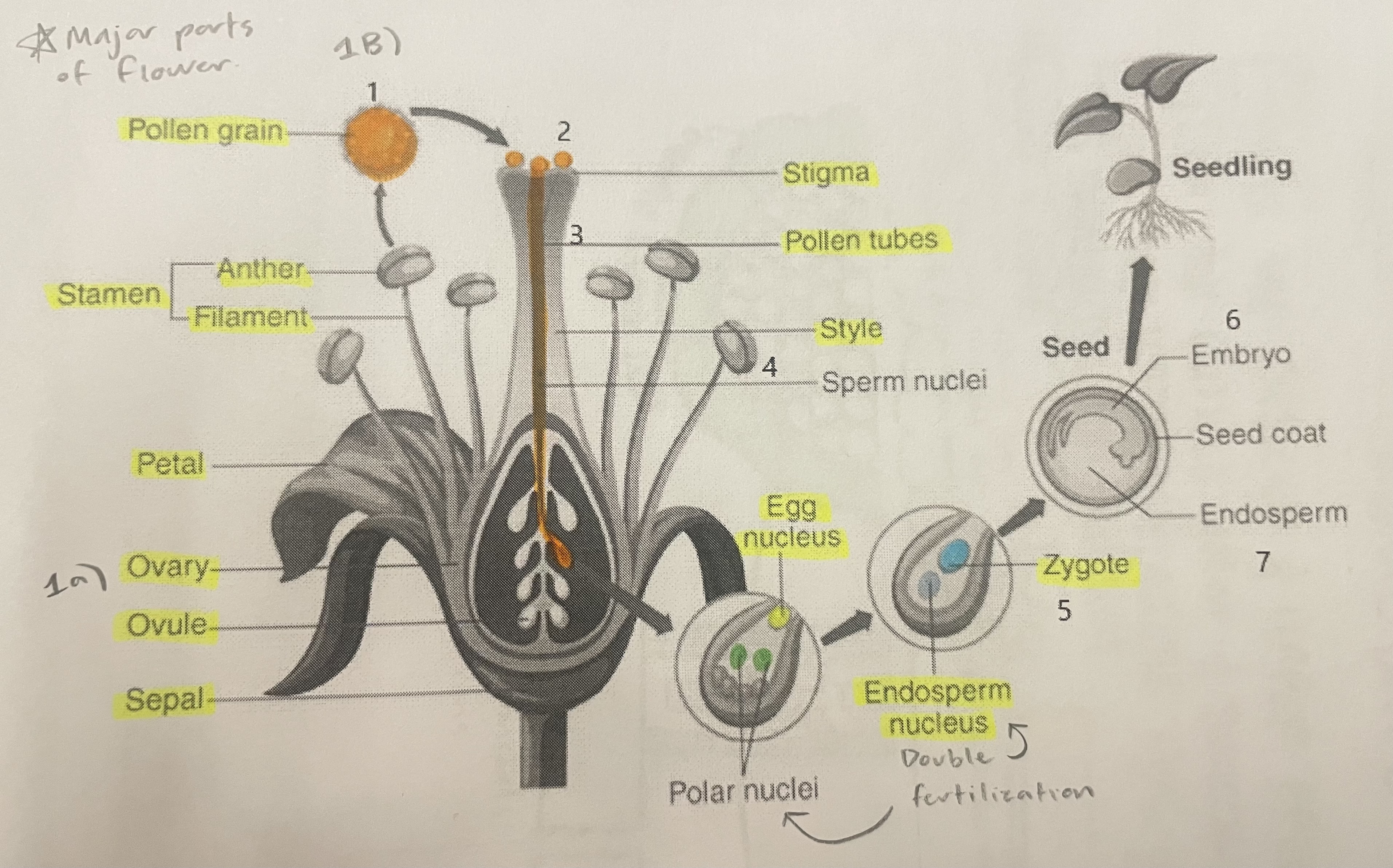
Zygote
Formed when the egg nucleus and sperm cell join during fertilization. Grows into a baby plant (embryo) inside the seed.
Bright Colors and Strong Scents
Attract insects for pollination.
Small Flowers
Adapted for wind pollination.
Fruits
Provide protection for seeds and promote seed dispersal.
Seed Dispersal by Animals
Seeds can be dispersed when animals consume fruits and excrete the undigested seeds.
Forceful Seed Ejection
Some fruits can eject their seeds forcefully.
Reproductive Success in Plants
Enhanced through flowers and fruits that promote pollination, along with effective vascular systems and leaves.
Flowers and Gametophytes
Flowers have male and female parts called gametophytes.
Male Gametes
Male gametes are found in pollen grains.
Female Gametes
Female gametes are found in ovules within the ovary.
Hilum
Small, whitish scar on the inner curve of the seed.
Micropyle
A tiny opening close to the hilum.
Testa
The brown covering of the bean.
Plumules
Two tiny leaf structures that become the plant’s first leaves.
Epicotyl
The embryonic stem located at the base of the plumules.
Hypocotyl
Will form the lower part of the stem below the epicotyl.
Radicle
Will form the root and is at the tip of the embryonic plant.
Endosperm (in Monocot)
Large area toward the broad end of the fruit.
Silk Scar
A small projection at the broad end of the kernel.
Dermal Tissue
The outermost covering of a plant's organs, providing protection and aiding in absorption.
Vascular Tissue
The transport system in plants that moves water, sugars, and nutrients throughout the plant.
Ground Tissue
Tissue that makes up much of the plant body, responsible for storage, photosynthesis, and support.
Self and Cross Pollination
Self pollination: Transfer of pollen from stamen (anther) to the stigma of the same flower or another flower on the same plant
Cross pollination: Transfer of pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of a flower on a different plant of the same species
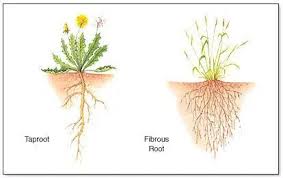
Fibrous vs Taproots
Fibrous (monocot): Bushy, made up of many small branching roots
Taproots (dicot): Small, has small root hairs
Perfect vs Imperfect Flowers
Perfect: Both reproductive parts (stamen and pistil)
Imperfect: Has either male or female parts, but NOT BOTH
Meristematic
Crucial for plant growth, supplies new cells to let roots grow longer
Epidermis
Acts as a protective barrier, regulates gas exchange, and helps with water retention
Pith
Important for nutrient storage and transport, providing structural support, and aiding in water and sugar distribution
Cambium
Primarily responsible for secondary growth, which is the increase in a plant's girth
Cork
Important for storing carbon dioxide, and supporting biodiversity
Cohesion-Tension Theory
Water sticks to itself because it’s sticky (cohesion)
When water leaves the leaf, it pulls the next drop up like a chain (tension)
This helps water move up the plant
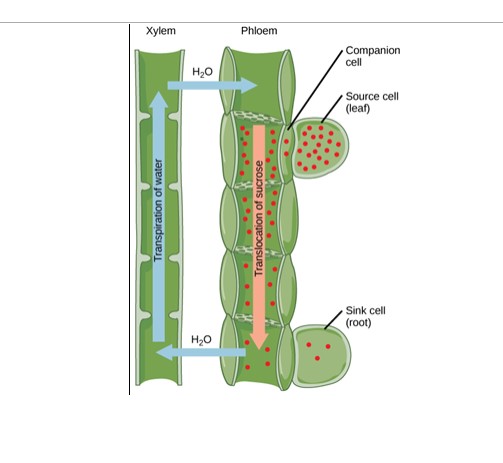
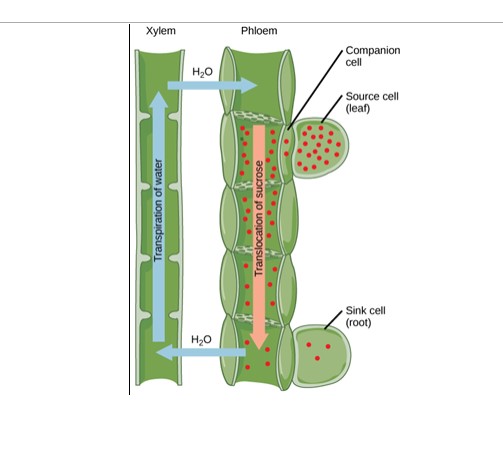
Translocation Process
The process of transporting sugars and other nutrients (assimilates) from where they are produced (sources) to where they are needed (sinks)
Pholem transports sugars
Leaves are “sources”
Roots/growing shoots are “sinks”
Plant Hormones, How they affect plant growth
Auxins: Helps plants grow taller and bend toward light
Gibberellins: Makes plants grow bigger (taller, bigger fruit)
Cytokinins: Helps with cell division and slows aging of plant
Ethylene: Makes fruit ripen
Abscisic acid: Slows things down, closes stomata helps during stress (like drought)
Tropism
How a plant grows in response to something
Positive: grows toward something
Negative: grows away from something
Phototropism (light)
Gravitropism (gravity)
Thigmotropism (touch)