Scrotum, Testicular, and Penile (MUT)
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
What divides the scrotum into two compartments?
A septum formed by the median raphe and dartos fascia.
Which muscle forms the scrotal wall and moves the testicles closer or farther from the body?
The cremaster muscle.
What are the two layers of the tunica vaginalis?
Parietal (outer) and visceral (inner) layers.
What is the space between the layers of the tunica vaginalis called?
Cavum vaginale.
What dense layer surrounds the testis and forms the mediastinum?
Tunica albuginea wraps around and form the mediastinum
what is in the spermatic cord?
pampiniform plexus, testicular artery, deferens ducts, nerves, lymphatics, and cremaster muscle
Where does sperm production begin?
In the seminiferous tubules (spermatogenesis).
Where do sperm travel after the seminiferous tubules?
To the straight tubules, then to the rete testis at the mediastinum.
What ducts carry sperm from the rete testis to the epididymis?
efferent duct
What is the function of the epididymis?
Sperm storage and maturation.
What is the function of the vas (deferent) duct?
Carries mature sperm from the epididymis up into the body toward the seminal vesicles.
list the order of sperm transportation:
Seminiferous tubules
Straight tubules
Rete testis
Efferent duct
Epididymis
vas deferens
seminal vesicle
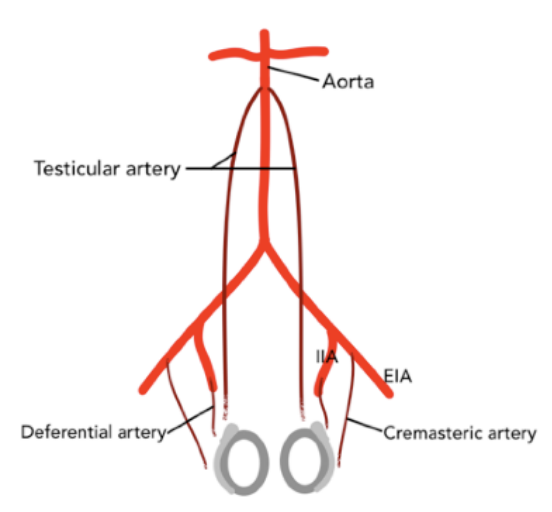
What is the main blood supply to the testes?
The testicular (gonadal) artery.
Where does the testicular (gonadal) artery originate?
Aorta
Which arteries supply the scrotal wall and ducts?
The cremasteric and deferential arteries.
Where do the cremasteric and deferential arteries originate from?
The iliac arteries.
What venous network drains blood from the testes?
The pampiniform plexus.
Where does the pampiniform plexus drain into?
The testicular (spermatic) veins.
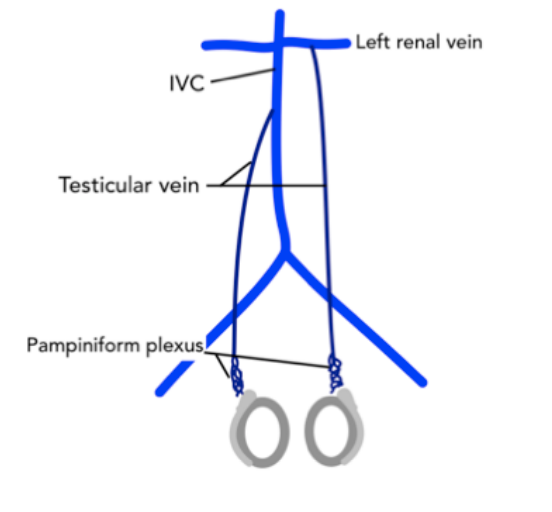
Where does the right testicular vein drain?
Into the inferior vena cava (IVC).
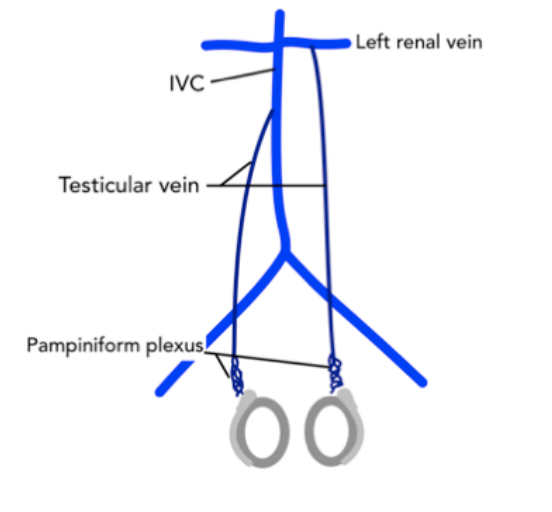
Where does the left testicular vein drain?
Into the left renal vein.
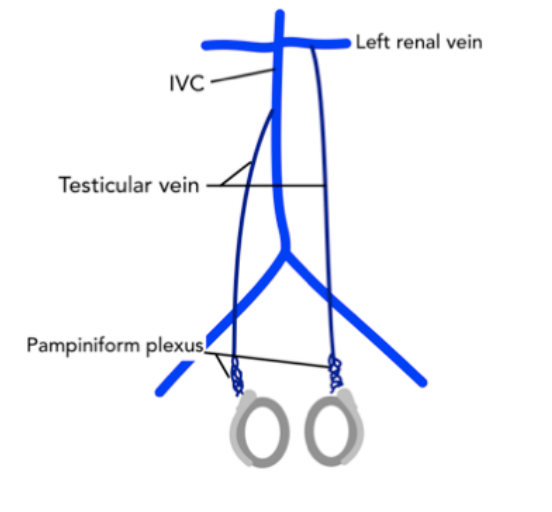
Which testicular vein is the longest?
The left testicular vein (longest pelvic vein).
what is the measurement of the epi?
usually 12mm
Excess fluid between the layers of the tunica vaginalis (in the cavum vaginale).
is a hydrocele usually intratesticular or extratesticular?
Extratesticular.
What causes a hydrocele?
It can be idiopathic or reactive (secondary to infection, trauma, or tumor).
What is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in prepubescent boys?
Appendix testis torsion.
What is the “blue dot” sign?
A visible blue spot on the scrotal skin indicating a torsed appendix testis.
What are the sonographic findings of appendix testis torsion?
Avascular extratesticular mass near the testicle with normal intratesticular flow and possible reactive hydrocele.
What is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in adolescents?
Testicular torsion (spermatic cord torsion).
What happens during testicular torsion?
The spermatic cord twists, cutting off the arterial blood supply to the testis.
When does testicular torsion most often occur?
During sleep.
what is Orchiopexy?
saving and fixing the testicle
After ___, not salvageable.
24 hours
Orchiectomy
removing the dead testicle
What is a bell-clapper deformity?
A congenital condition where the testis lacks posterior fixation, making it freely mobile and more prone to torsion (often bilateral).
What are common clinical symptoms of testicular torsion?
Acute scrotal pain, scrotal swelling, nausea, and vomiting.
What are the sonographic findings in testicular torsion?
Enlarged, hypoechoic or heterogeneous testis with decreased or absent intratesticular blood flow.
What is the most common cause of acute scrotal pain in adults?
epididymitis
How does epididymitis usually develop?
It typically starts as an external infection (like an STD) that travels down the ducts to the epididymis and may extend into the testicle.
Which STDs are most commonly associated with epididymitis?
Chlamydia and gonorrhea.
What is it called when infection spreads from the epididymis into the testicle?
Orchitis.
What are the clinical symptoms of epididymitis/orchitis?
Acute pain, fever, leukocytosis, swelling, and dysuria.
What are the sonographic findings of epididymitis?
Enlarged, hypoechoic epididymis with increased blood flow (hyperemia).
What are the sonographic findings when infection extends into the testicle (orchitis)?
Enlarged, hypoechoic, and hyperemic testicle with reactive hydrocele.
what is a pyocele?
complex hydrocele containing pus
What usually causes testicular trauma?
Blunt force or penetrating injury.
What complications can result from testicular trauma?
Intraparenchymal hemorrhage, hematoma, rupture, or fracture
What structure should be assessed for interruption in testicular trauma?
The tunica albuginea (to check for rupture).
What is a hematocele?
A complex or echogenic hydrocele containing blood.
What is cryptorchidism? and where is it located ?
Undescended testis. inguinal canal
What is the surgical correction for cryptorchidism?
orchiopexy
What is a major risk associated with cryptorchidism?
Increased risk of testicular cancer (seminoma).
What is the most common scrotal mass?
spermatocele
Where are spermatoceles most often located?
In the epididymal head.
Where can an epididymal cyst occur?
Anywhere along the epididymis.
Where are tunica albuginea cysts found?
Along the periphery of the testicle.
What is a varicocele?
Dilated veins (>2 mm) of the pampiniform plexus within the scrotum.
What is the most common cause of correctable male infertility?
Varicocele, due to overheating of sperm.
What maneuver increases visualization of varicocele flow on Doppler?
Valsalva maneuver or standing position.
What causes a primary varicocele? and what side is it usually?
Incompetent venous valves, usually on the left side bc left testicular vein is longer.
What causes a secondary varicocele?
Abdominal or pelvic pathology (e.g., renal or retroperitoneal mass), usually on the right side.
What should be investigated when a right-sided varicocele is found?
The renal and retroperitoneal regions for possible obstruction.
What is a scrotal pearl?
A mobile calcification within the tunica vaginalis, usually a remnant of a torsed appendage.
What type of hernia can extend into the scrotum?
Indirect inguinal hernia.
What happens to a hernia during Valsalva?
It pushes further into the scrotum.
What is tubular ectasia of the rete testis?
Dilated rete testis near the mediastinum; benign and often post-vasectomy.
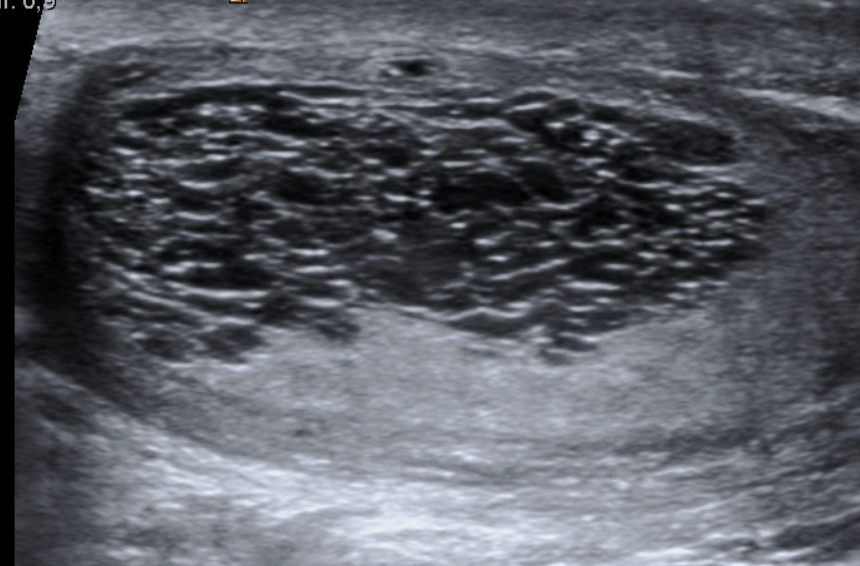
What is the sonographic look of an epidermoid cyst?
Onion” or whorled appearance.**
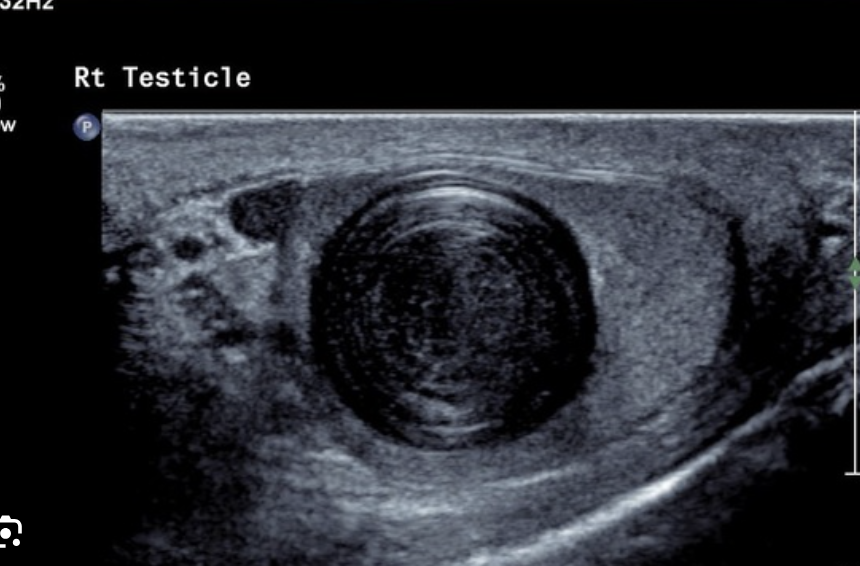
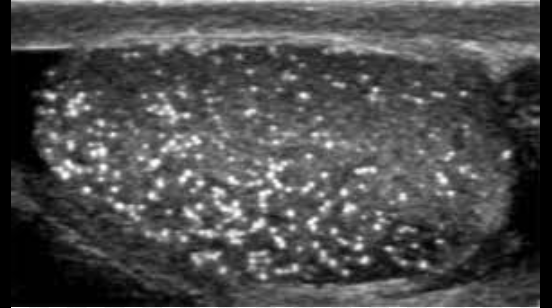
What is this?
Microlithiasis
What risk is associated with microlithiasis?
Increased risk of testicular cancer.
Which labs are elevated with testicular cancer?
hCG and/or AFP.
What is the most common testicular cancer?
seminoma
What are risk factors for seminoma?
Cryptorchidism and microlithiasis.
Sono appearance of seminoma?
Solid, hypoechoic or heterogeneous mass.
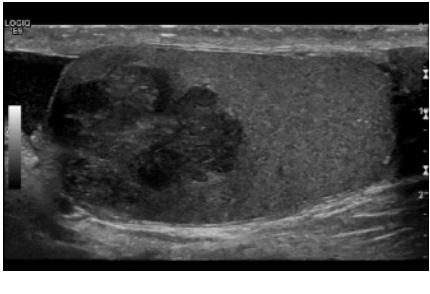
Which tumor shows elevated AFP only?
yolk sac tumor
Which tumor shows elevated hCG only?
Choriocarcinoma.
Which tumor shows both hCG and AFP elevation?
Embryonal cell carcinoma
Solid masses of testicle are most likely ____
malignant germ cell tumor
What covers the penis?
Buck fascia
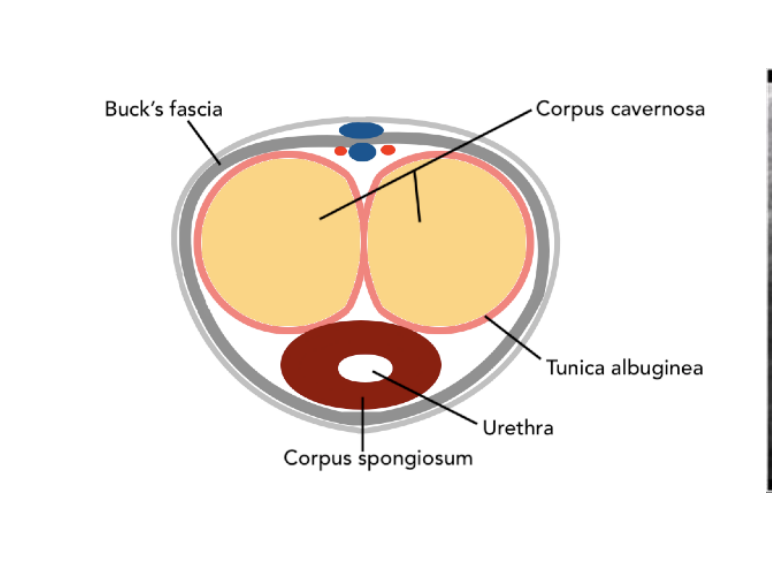
What covers the corpus cavernosa?
tunica albuginea
How many corpus cavernosa are there?
Two (dorsal side) (yellow arrows)
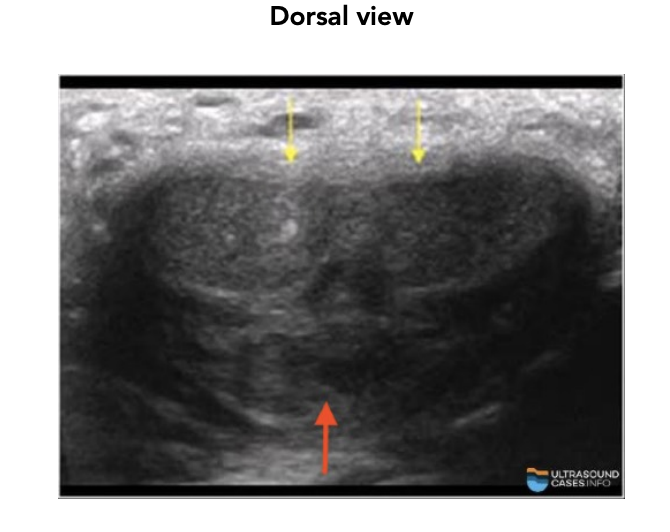
What does the corpus spongiosum contain?
urethra (red arrow)
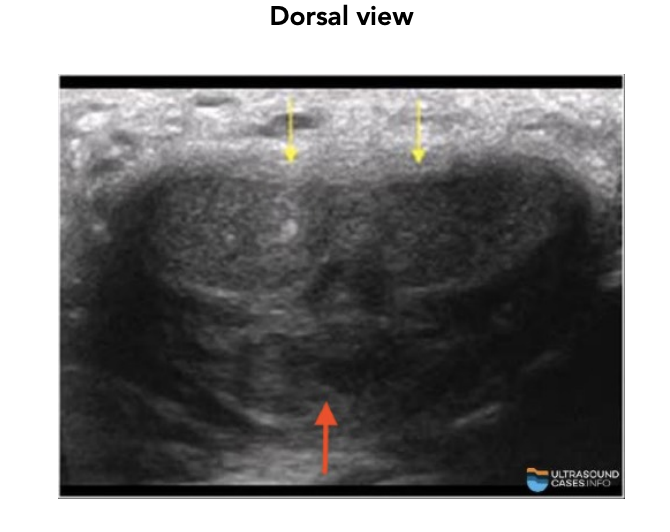
Where is the corpus spongiosum located?
ventral side
Main artery of the penis?
Internal pudendal artery
What is Peyronie disease? Main symptom?
Fibrous plaque/scar on tunica albuginea; Painful curved erection
What causes penile fracture?What to check on ultrasound? Possible finding?
Blunt trauma; Tunica albuginea tear; Hematoma in corpus cavernosum
What is vasculogenic impotence? Arterial cause? Venous cause?
Erectile Dysfunction from poor blood flow, , Arterial stenosis (low inflow), Venous leak (poor closure)
Is the prostate retroperitoneal or intraperitoneal?
retroperitoneal
What type of gland is the prostate?
Exocrine gland that helps make semen.
What does elevated PSA indicate?
Prostate abnormality (not specific for cancer).
What is the pathway of sperm starting from vas deferens?
Vas deferens → seminal vesicles → ejaculatory duct → prostate → urethra (verumontanum).
What do seminal vesicles secrete?
Fluid that contributes to semen.
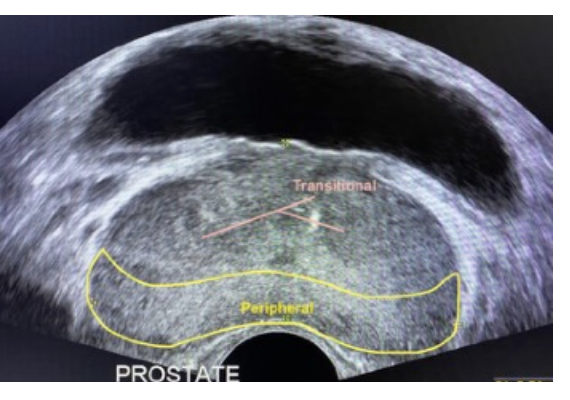
Which prostate zone is the largest?
Peripheral zone.
Where is the peripheral zone located?
Posterior and apical region of the prostate.
Which prostate zone is at the base (superior)?
Central zone.
Which prostate zone surrounds the urethra?
Transitional zone.
What is the anterior fibromuscular stroma?
The fibrous tissue covering the anterior prostate.
Where are seminal vesicles located sonographically?
Posterior to bladder and superior to prostate base.
Which part of the prostate is closest to the bladder?
Base.
What is the normal prostate volume?
Up to 30 mL (L × H × W × 0.52).
In the coronal plane, which prostate zone is closest to the transducer footprint?
Peripheral zone (also apical)