head and neck anatomy ch 4-6 exam
1/133
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
134 Terms
muscular system
system that includes skeletal muscle tissue
muscle
body tissue that shortens under neural control, causing soft tissue and bony structures to move
origin
end of muscle attached to least movable structure
insertion
end of the muscle attached to more moveable structure
action
movement accomplished by a muscle when muscle fibers contract
cervical muscles
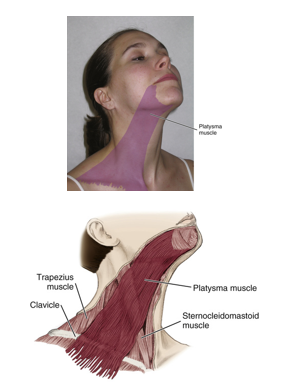
sternocleidomastoid
trapezius
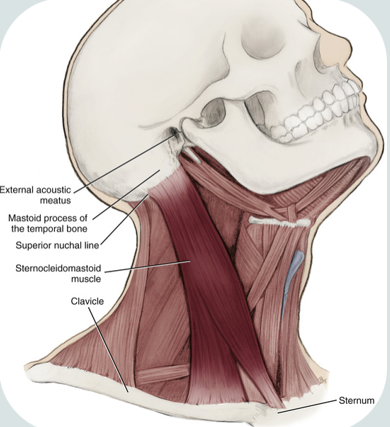
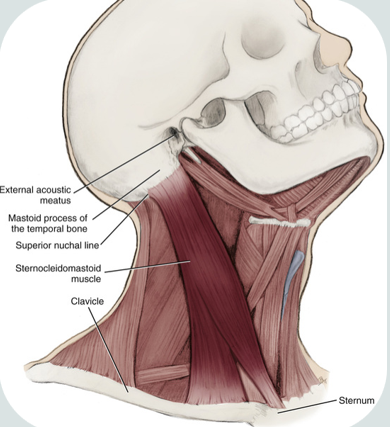
sternocleidomastoid
paired
one of the largest and most superficial cervical muscle
origin : medial part of clavicle, sternum’s superior and lateral surfaces
insertion : mastoid process of temporal bone and anterior portion of the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone
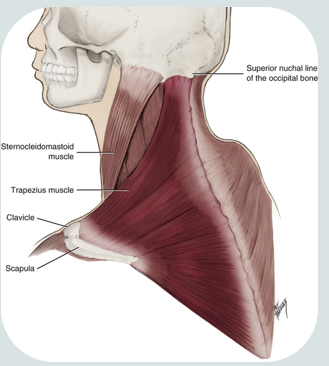
trapezius muscle
paired
superficial to both the lateral and posterior surfaces of the neck
broad, flat triangular muscle
responsible for shoulder movements
origin: external occipital protuberance
insertion: lateral third of clavicle
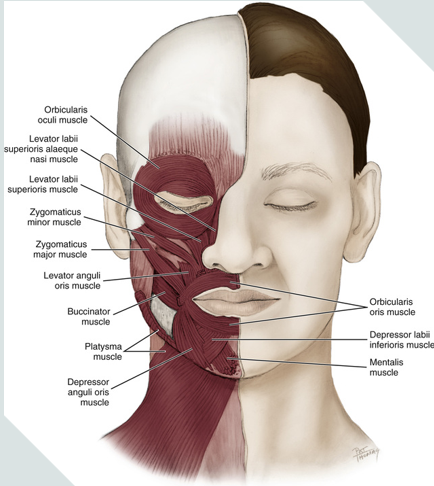
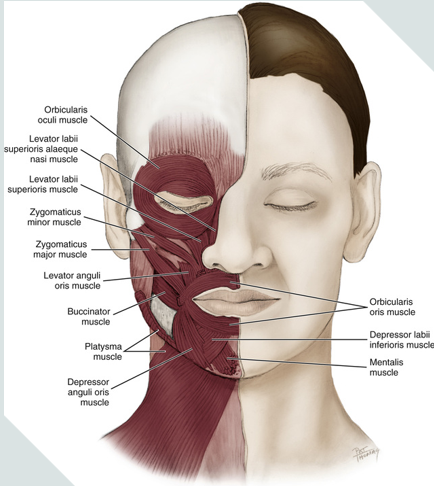
muscles of facial expression
epicranial
frontalis
occipital belly
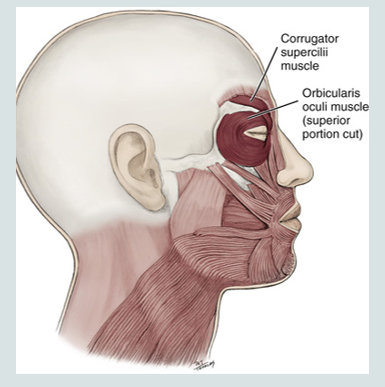
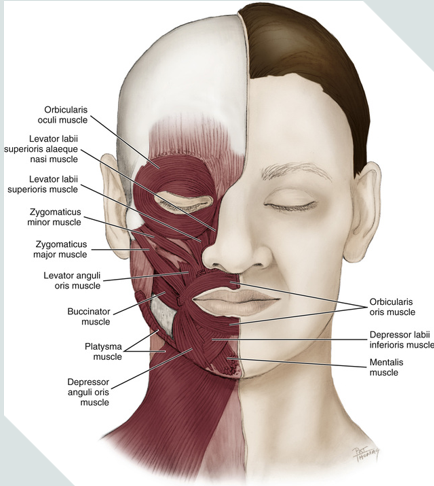
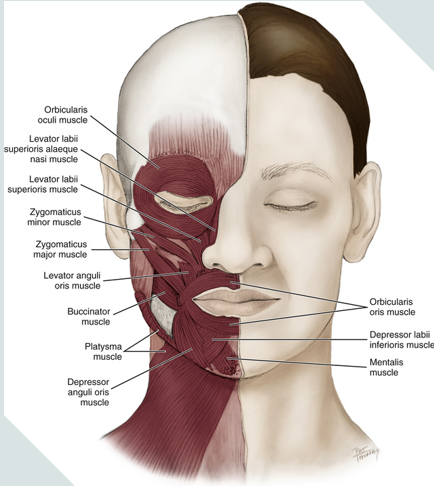
orbicularis oculi
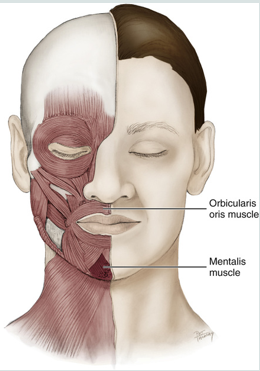
orbicularis oris
depressor anguli oris
mentalis
platysma
risorius
buccinator
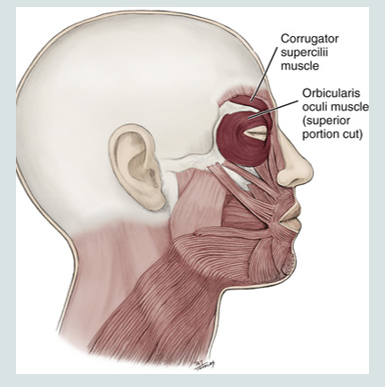
corrugator supercilli
zygomaticus minor
zygomaticus major
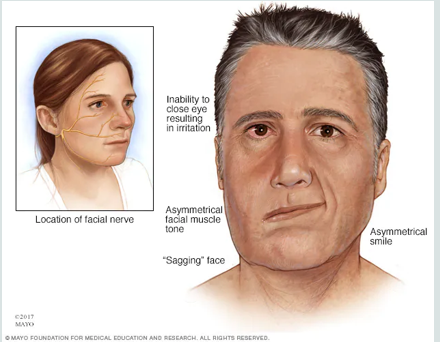
bells palsy
causes paralysis or weakness in one side of the face
frontalis facial movement
raises the eyebrows
epicranial facial movement
surprise
depressor anguli oris facial expression
pulls corners of the mouth down (frowning)
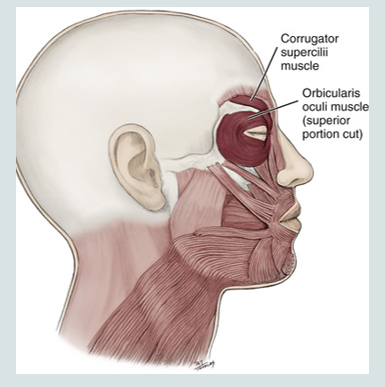
orbicularis oculi facial expression
closing eyelid and squinting
opening and closing the eye
zygomaticus major facial expression
smiling (draws corners of the mouth up)
orbicularis oris facial expression
puckers lips
closing and pursing of lips
pouting or grimacing
mentalis facial expression
pouting
raising chin and protruding lower lip
platysma facial expression
tenses the neck and responsible for grimacing
raising neck skin
risorius facial expressions
grimacing
stretching lips
corrugator supercilli facial expression
furrows eyebrows
(not silly)
frowning
zygomaticus minor facial expression
raising upper lip to assist in smiling
zygomaticus major, levator anguli oris, risorius facial expressions
all of these contract when smiling
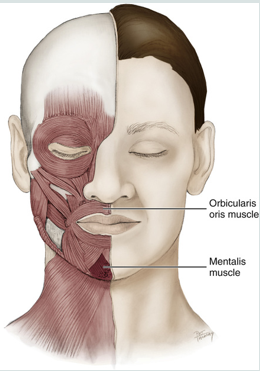
orbicularis oris
oris = mouth
encircles the mouth
muscle of facial expression
orbicularis oculi
oculi = eye
encircles the eyes
levator labii superioris facial expression
raising upper lip
levator labii superioris alaeque nasi facial expression
raising upper lip and dilating nares with sneer
depressor labii inferioris facial expression
lowering lower lip
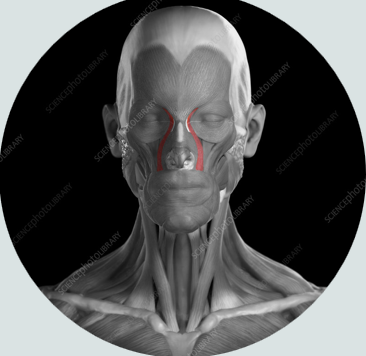
corrugator supercilli muscle
is a muscle of facial expression
moves the eyebrow down and inward toward the nose and inner eye
involved in frowning
“dont be silly”
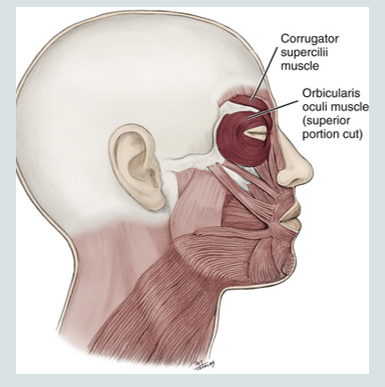
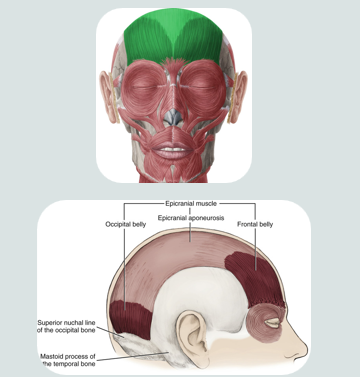
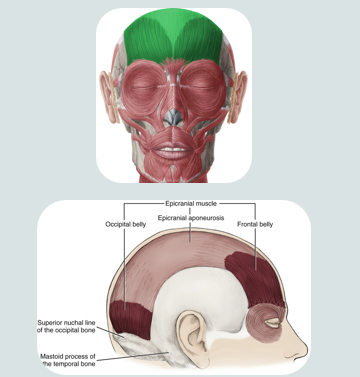
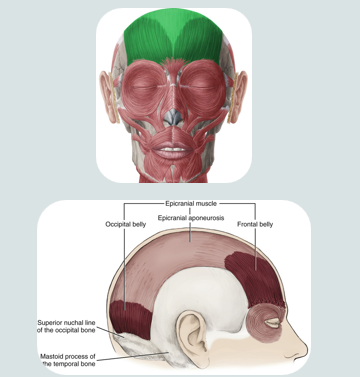
epicranial muscle
a muscle of facial expression
used when making a “surprised face”
this muscle covers part of the skull
consists of two bellys that are separated by a large spread out scalpal tendon
occipital
fontal
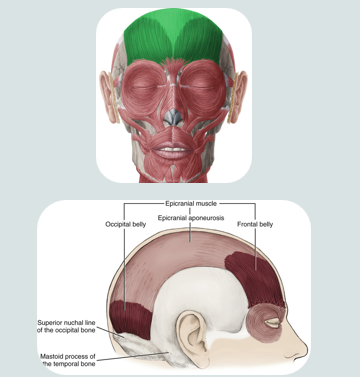
ocipitalis muscle of epicranial muscle
retracts the scalp
located on the occipital lobe
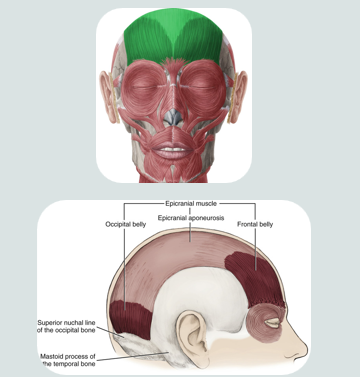
frontalis muscle of epicranial muscle
elevates eyebrows and wrinkles forehead
insertion: into skin of eyebrow and root of nose
mentalis muscle
a muscle of facial expression
works to protrude the lower lip (pouting)
raises the skin of the chin
it is the only elevator of the lower lip and chin
provides vertical support for the lower lip
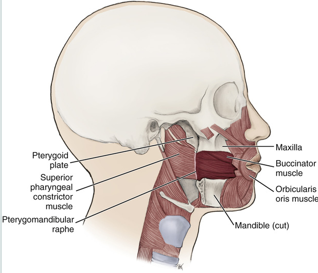
buccinator facial expression
compresses the cheeks during chewing
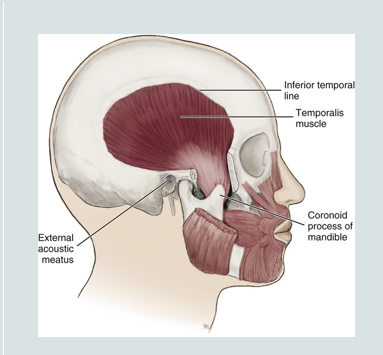
temporalis muscle
a fan shaped muscle
main function is to move the mandible
originates from the temporal fossa and inserts at the coronoid process of the mandible
its fibers pass deep to zygomatic arch to attach to mandible
muscles of mastication
masseter
temporalis
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
responsible for chewing
innervated by the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve
motor fibers that contract these muscle travel in the trigeminal nerve
MONSTOR TRUCKS MAKE LOUDNESS
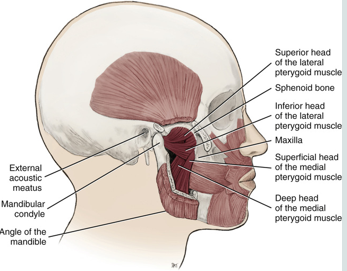
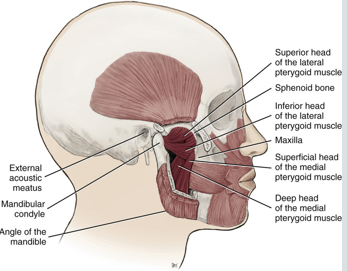
lateral pterygoid muscle
a muscle of mastication
lies superior to the medial pterygoid muscle
a thick and short triangular shaped muscle located in the infratemporal fossa of the skull
superior and inferior heads
causes the power stroke ( moving side to side)
bilateral contraction:
mainly protrusion of mandible with mandible forward
slight depression of mandible during opening of jaws
unilateral contraction
lateral deviation of mandible, shift mandible to contralateral side
trismus
patient cannot open their mouth due to dysfunction in lateral pterygoid muscle
medial pterygoid muscle
attaches to the mandible and to the medial surface of the lateral pterygoid plate
bilateral contraction
elevation of mandible during closing of jaws
aids in elevating the mandible while closing the jaw, protruding the mandible, and mastication
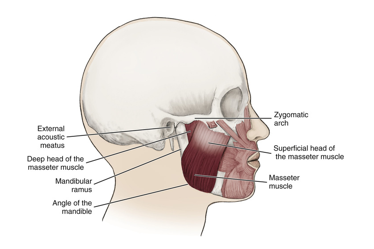
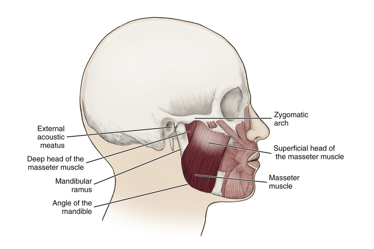
masseter muscle
a muscle of mastication
attaches to the zygomatic arch
when contracted it elevates the mandible
most superficial and is the strongest muscle of mastication
bilateral contraction:
elevation of mandible during closing of jaw
bruxism
bilateral enlargement of the masseter muscle from trauma (grinding)
grinding of teeth
alters facial dimensions
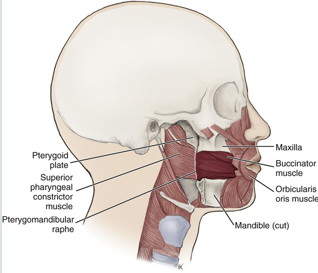
buccinator muscle
keeps food under molars during chewing
compresses cheeks inward during use
assists the tongue in keeping bolus of food in the center of mouth
hyoid
the only bone in the body that does not attach to another bone
small, u-shaped located in the anterior midline of the neck
geniohyoid
stylohyoid
omohyoid
all attach directly to the hyoid bone
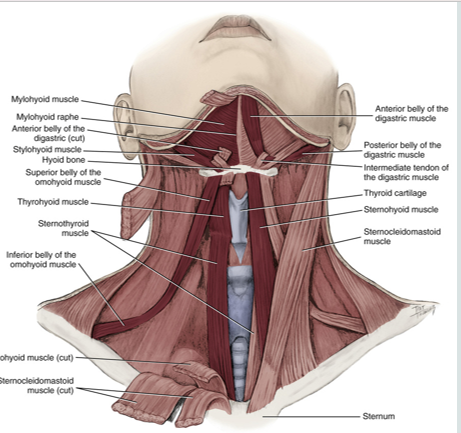
suprahyoid muscles
purpose is to elevate the hyoid bone
digastric
mylohyoid
stylohyoid
geniohyoid
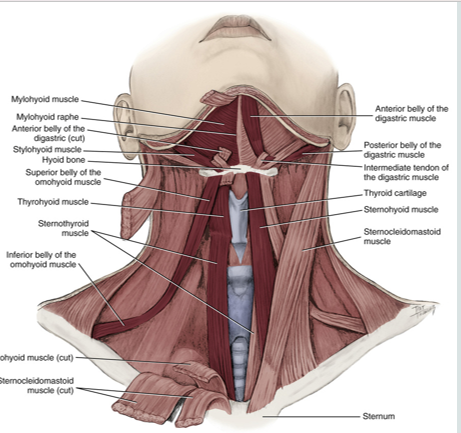
infrahyoid muscles
acts to depress the hyoid bone
group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck
omohyoid
sternohyoid
sternothyroid
thyrohyoid
recieve motor fibers from the cervical spinal serves
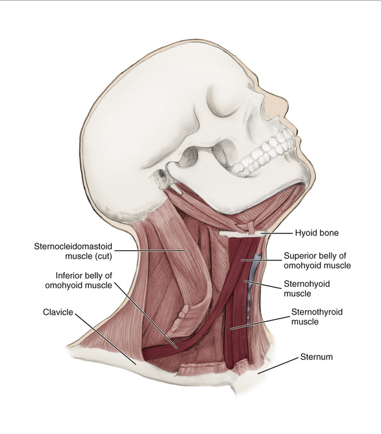
omohyoid
an infrahyoid muscle
has 2 bellies that are connected by a tendon
originates from the scapula and inserts on the hyoid bone
depresses hyoid bone
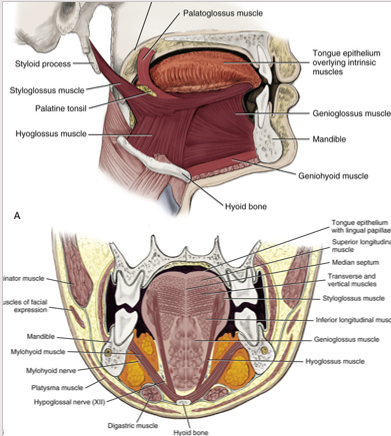
extrinsic tongue muscles
hypoglossus
genioglossus
styloglossus
palatoglossus
used when changing positions of the tongue
receive motor innervation from the hypoglossal nerve
involves with protrusion, retraction, depression, and elevation of the tongue
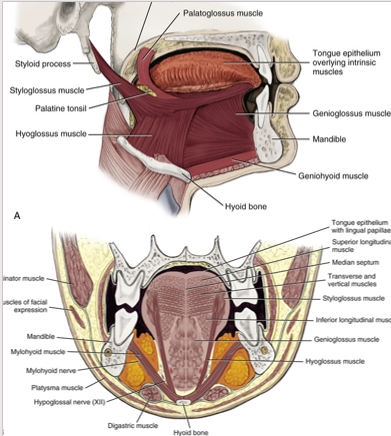
intrinsic tongue muscles
superior longitudinal
inferior longitudinal
transverse muscles
vertical muscles
receive motor innervation from hypoglossal nerve
act to change the shape of the tongue
also move the tongue while suspending and anchoring the tongue to bony structures
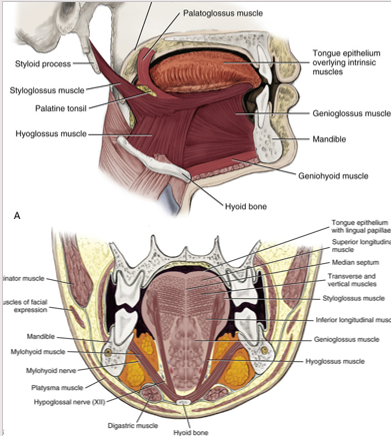
hypoglossus muscle
extrinsic tongue muscle
involved with depression and retraction of tongue
originates along the whole length of the hyoid bone and inserts into the side of the tongue
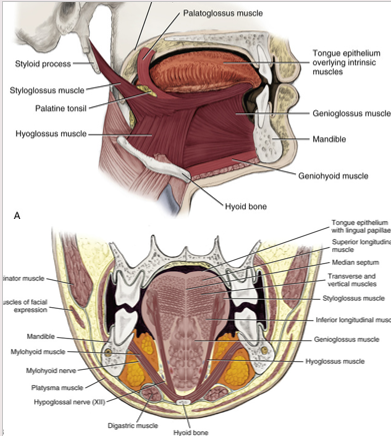
genioglossus muscle
protrudes the tongue anteriorly and deviates the tongue to the opposite side
attaches to the inferior surface of the tongue and the mandible
aids in swallowing
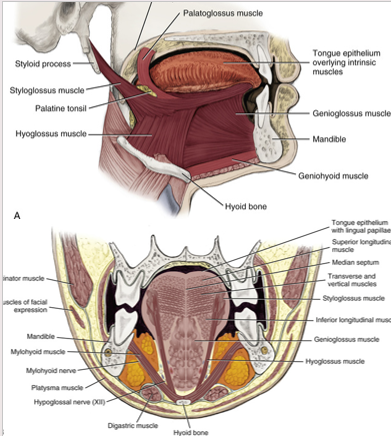
styloglossus
lips lateral edges and retracts the tongue
attaches the styloid process to the tongue
retracts and elevates the tongue
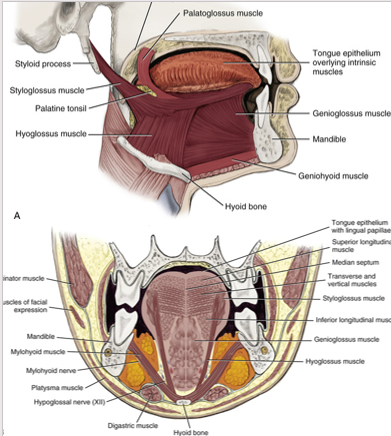
palatoglossus
extrinsic muscle of the tongue
elevates the posterior portion of the tongue and depresses the soft palate towards the tongue
creates the anterior faucial pillar in oral cavity
involved in both speech and swallowing
originates int he palatine aponeurosis
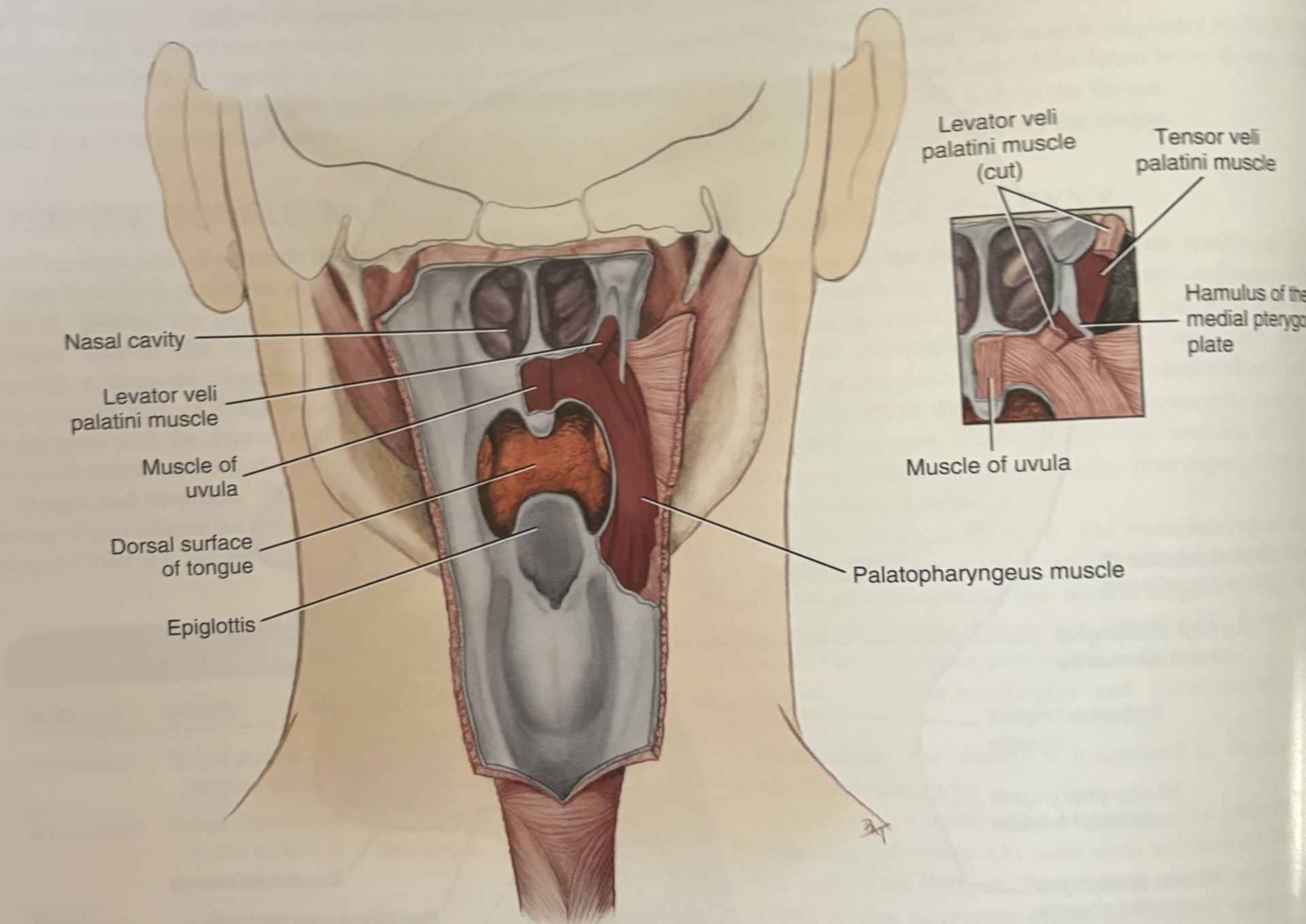
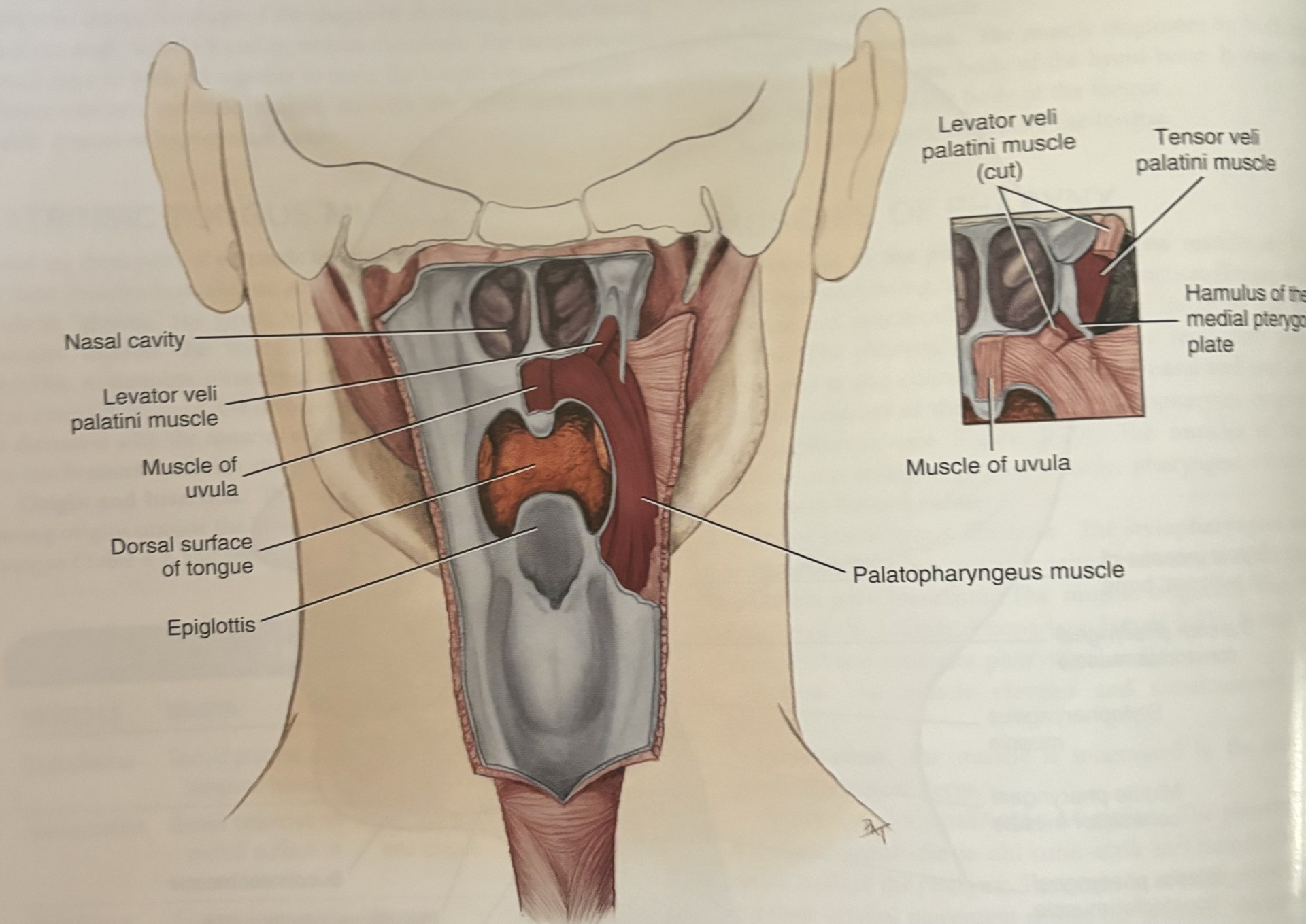
soft palate
closes off the nasopharynx from the oropharynx during swallowing
essential in breathing, swallowing, and speech
palatoglossus
palatopharyngeus
levator veli palatini
tensorveli palatini
uvula
muscles of soft palate
palatoglossus
palatopharyngeus
levator veli palatini
tensorveli palatini
uvula
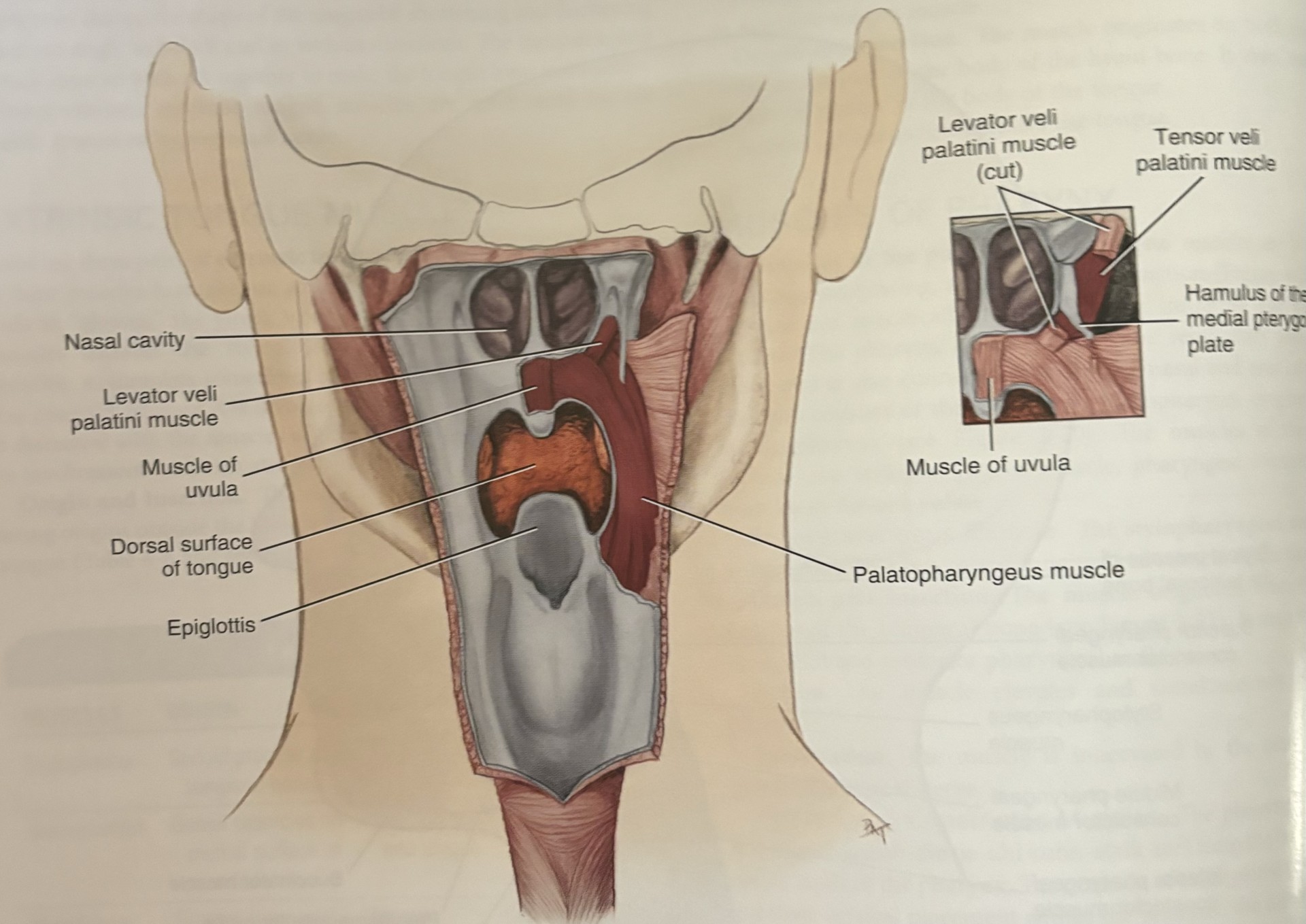
tensor veli palatini
goes across the pterygoid hamulus to attach to the soft palate
tenses the soft palate and assists the levator veli palatini in elevating the palate
this prevents entry of food into nasopharynx during swallowing
only one not laterally connecting the soft palate to the tongue
muscles of pharynx
involved in speaking, swallowing, and middle ear function
nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx
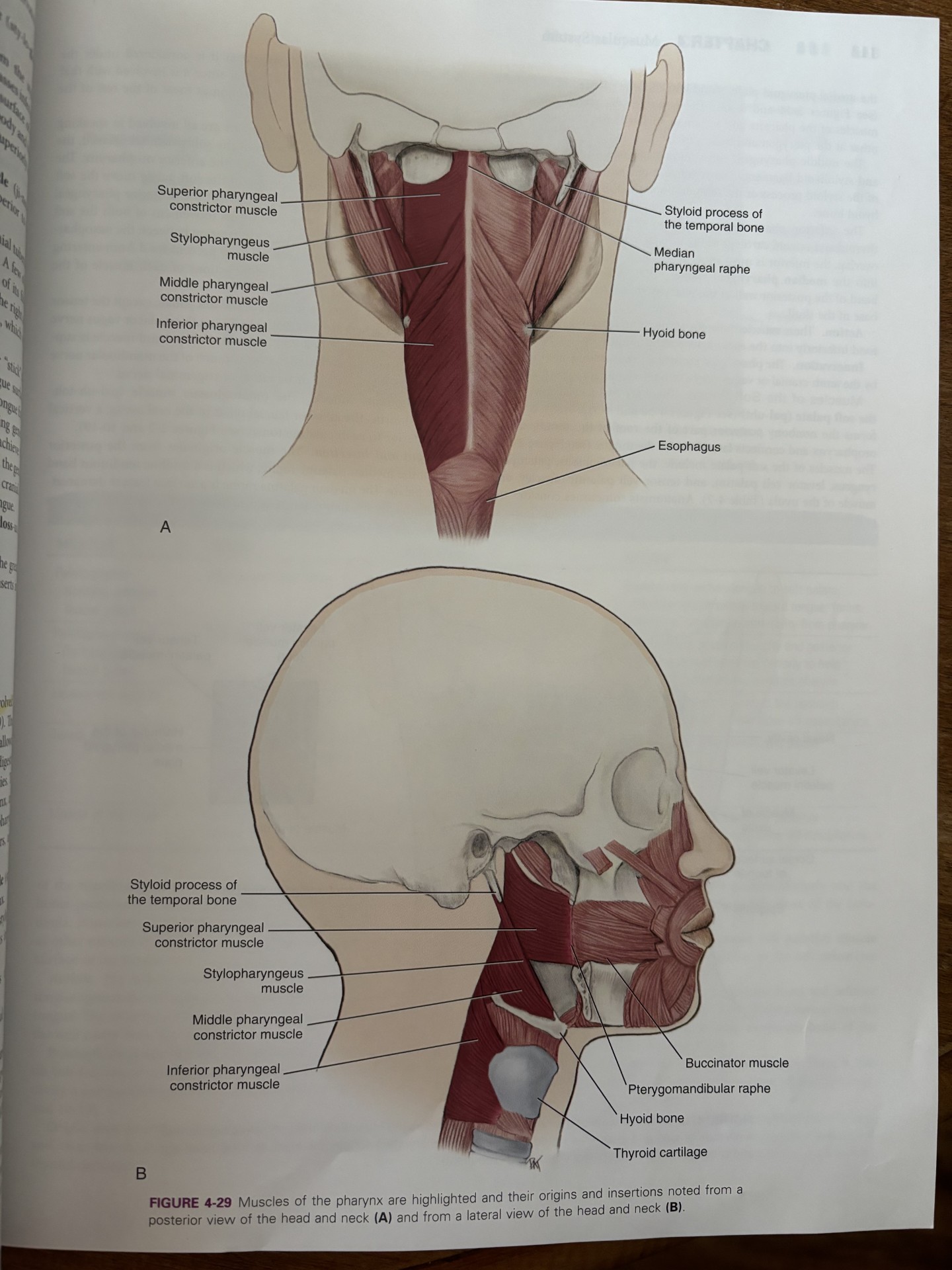
stylopharyngeus muscle
pharyngeal constrictors
muscles of soft palate
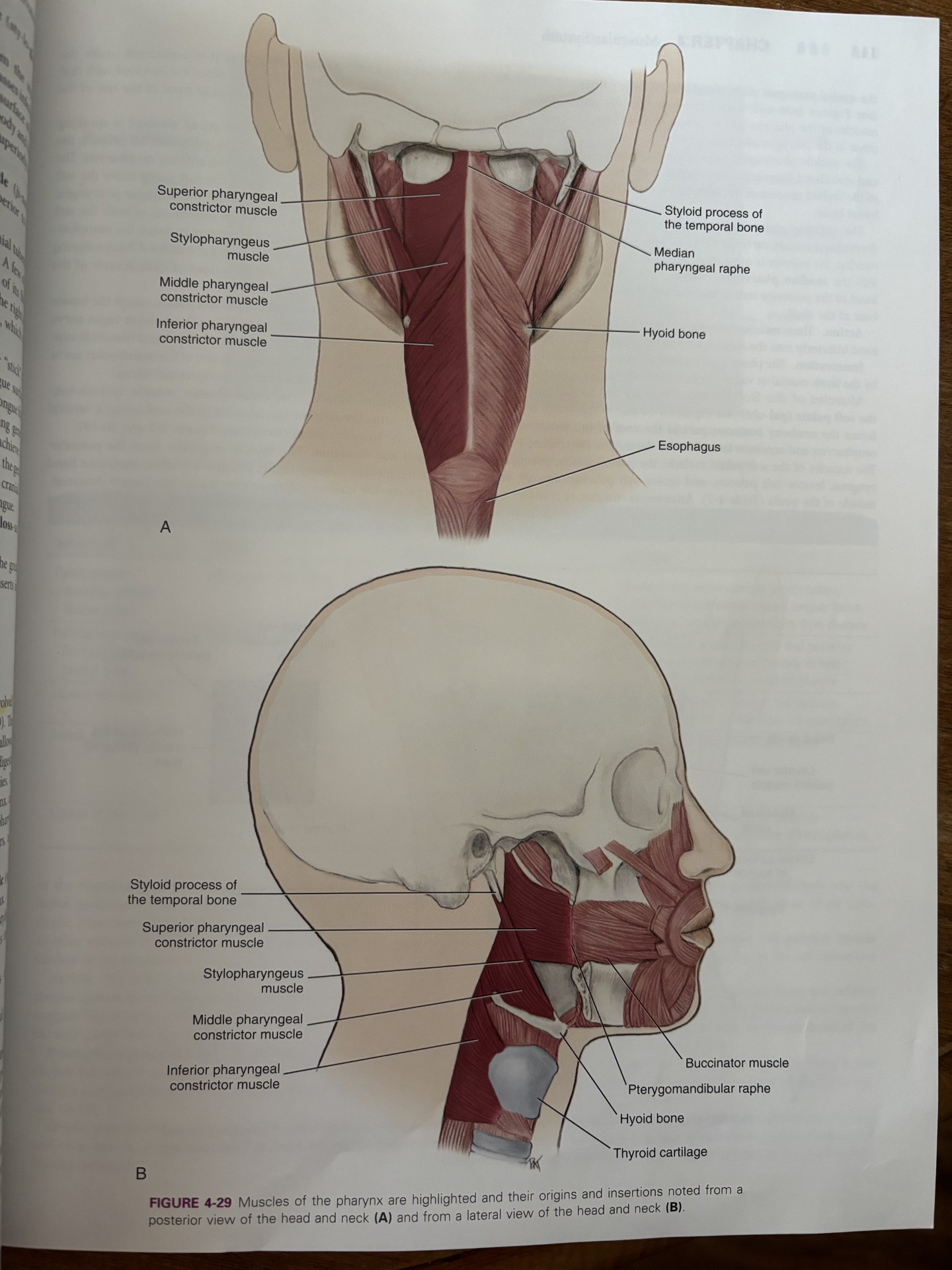
superior constrictor of the pharynx
construction of the upper part of the pharynx
originates from the hamulus of the pterygoid plate, mandible, and pterygomandibular raphe
facilitates in swallowing by pushing the ball of food inferiorly towards esophagus
attaches to pterygomandibular raphe
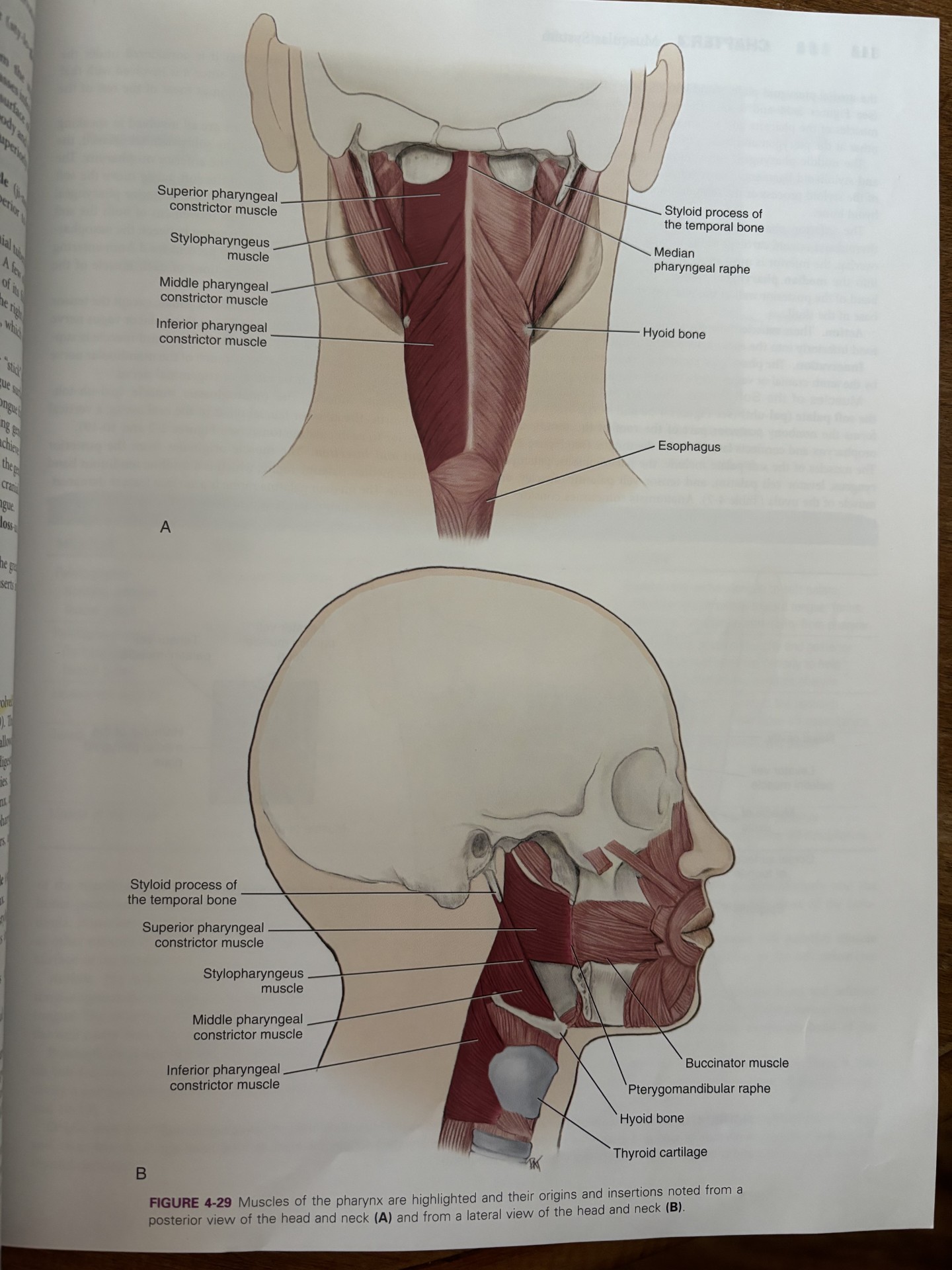
middle constrictor of the pharynx
attaches to hyoid bone
pharyngeal constrictor muscles receive motor innervation from vagus nerve
originates on hyoid bone and stylohyoid ligament
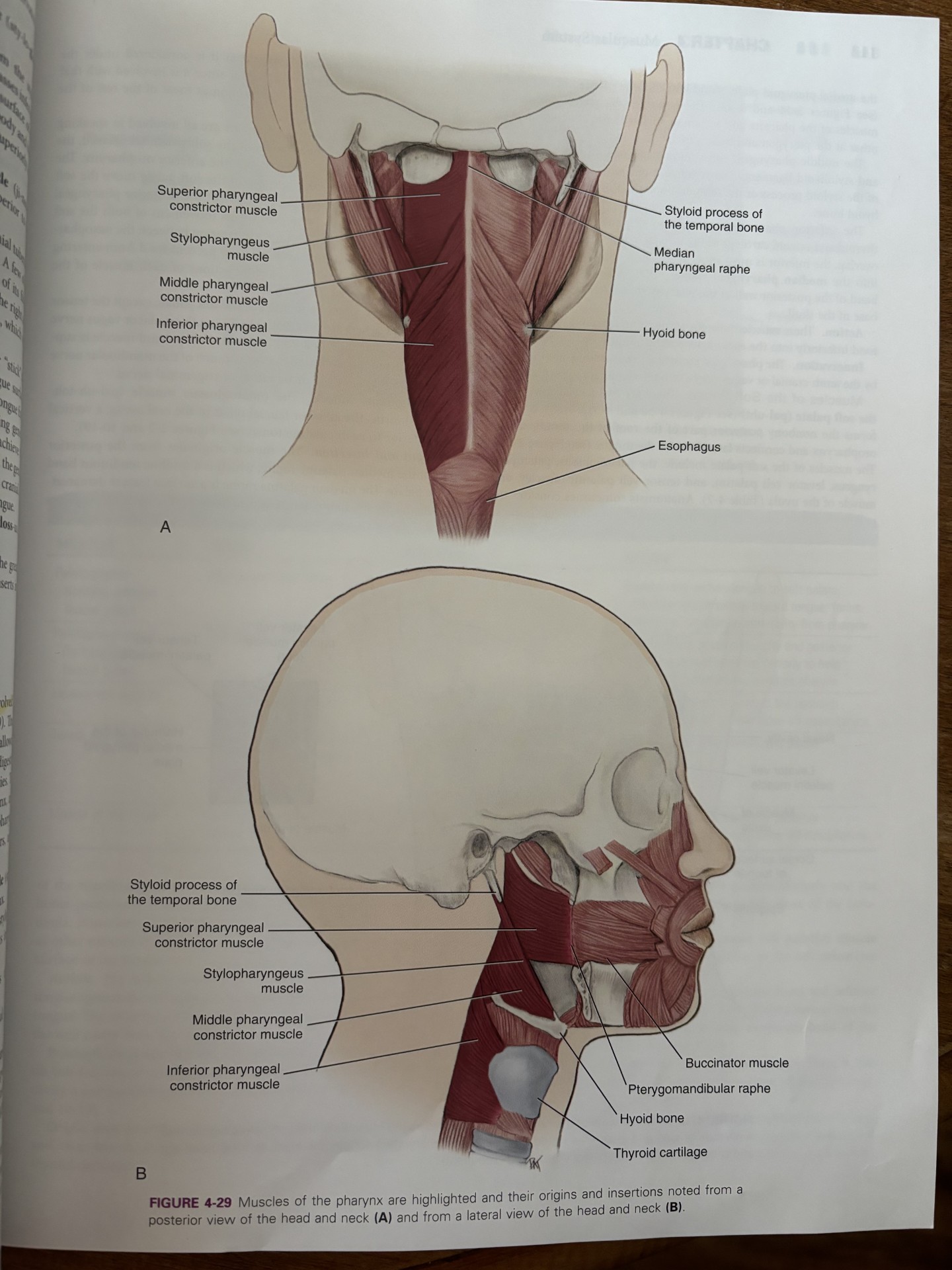
inferior constrictor of pharynx
aids in swallowing by constricting the wall of the pharynx during swallowing
attaches the thyroid and cricoid cartilages
pharyngeal constrictor muscles receive motor innervation from the vagus nerve
all the constrictor muscles insert into the median pharyngeal raphe
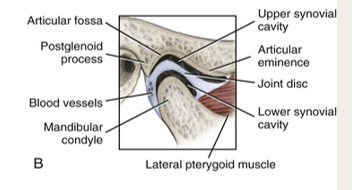
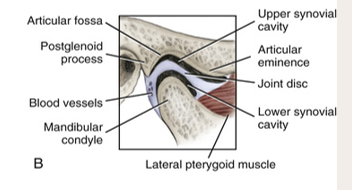
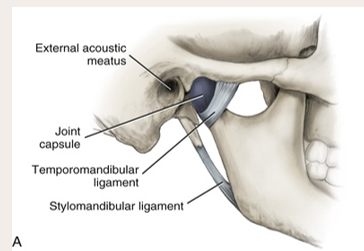
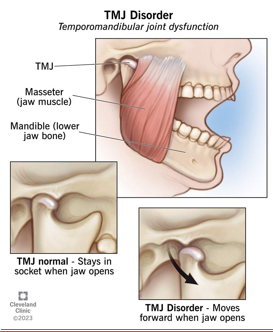
temporomandibular joint
formed by and articulation between the mandibular condyle and the temporal bones
the muscles involved are attached to the cranium and the mandible
allows for the mandible to be elevated and depressed
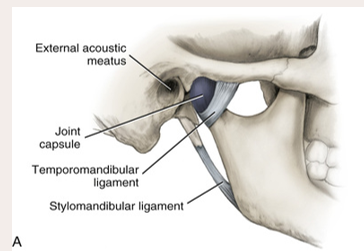
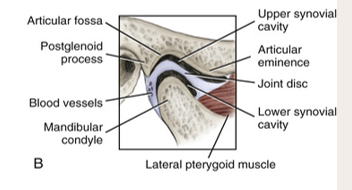
Joint capsule covers the
area, completely encloses the TMJ
disc separates the
bones
A ligament
is a band of fibrous tissue that connects bones.
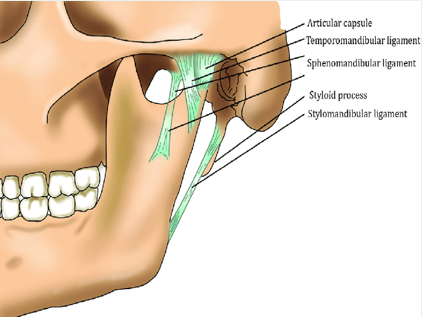
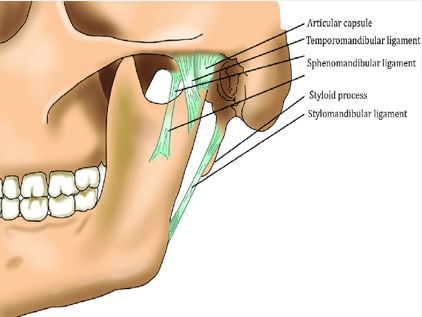
The 3 paired ligaments of the TMJ
1. Temporomandibular (major)
2. stylomandibular (minor)
3. sphenomandibular (minor)
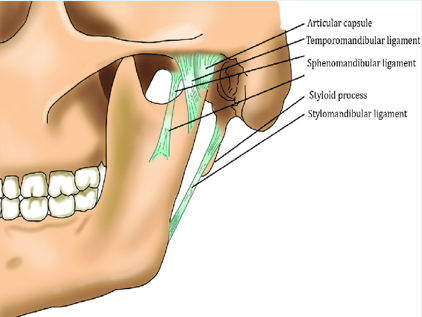
Temporomandibular
The major ligament is the __. This prevents excessive retraction or moving backward of the mandible.
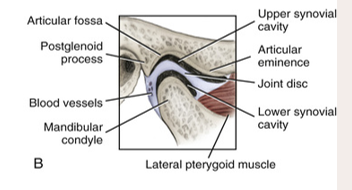
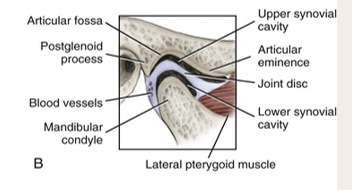
the __ movement mainly occurs in the upper synovial cavity.
gliding
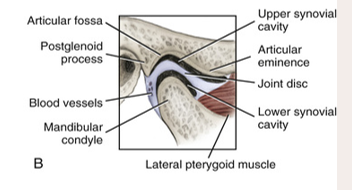
the __ movement mainly occurs in the lower synovial cavity.
rotation
is a physiologic rest of the mandible. 2mm to 4mm of space between opposing arches
Freeway space
Subluxation
is the dislocation of both joints
occurs when the head of each condyle moves too far anteriorly on the articular eminence.
TMD
temporomandibular disorder
joint tenderness, neck/shoulder pain from tension, chronic headaches
articular disc
a fibrous structure in the TMJ that functions to separate and provide cushion between the temporal bone and the mandibular condyle
powerstroke of mandible
moving the jaw from side to side → rotational movement
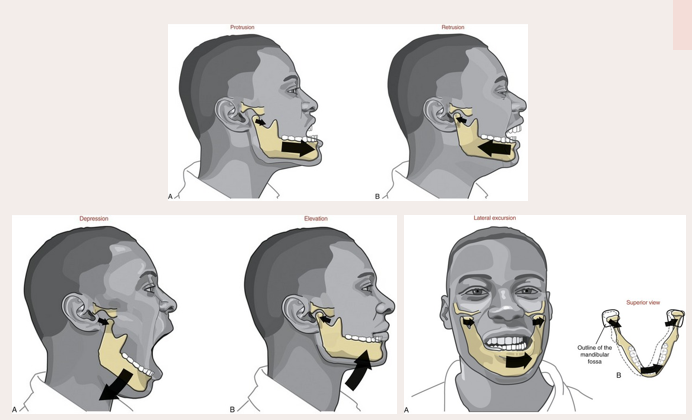
retraction of mandible
contraction of the posterior fibers of the temporalis muscle
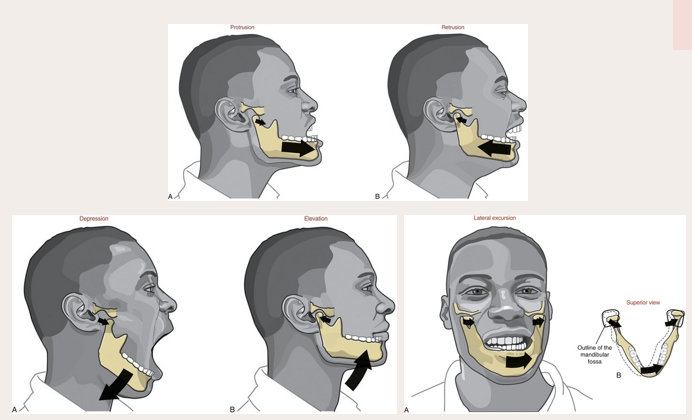
gliding movement of the TMJ
condyle and the disc of the articular eminence move the jaw forward and backward
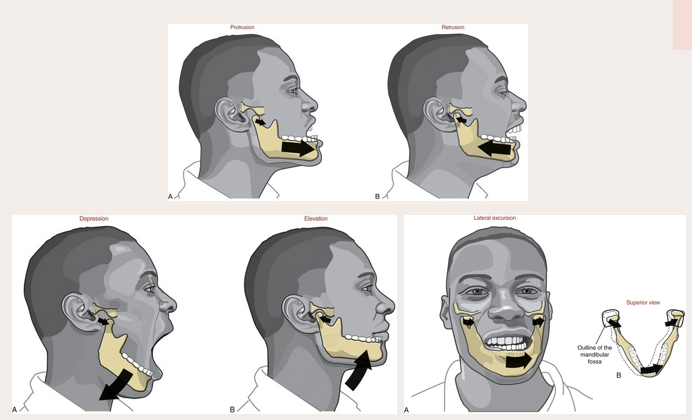
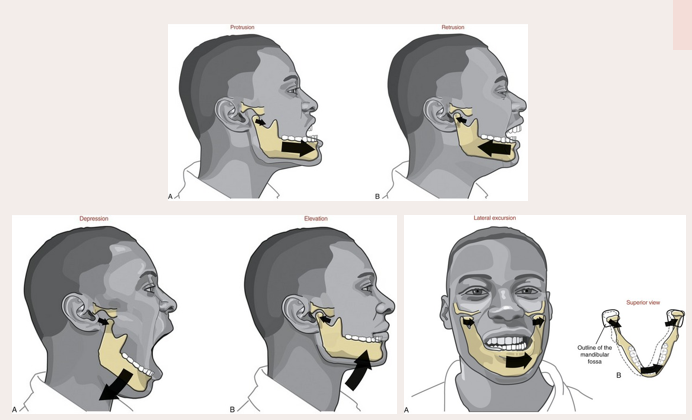
sideways movement of mandible
independent contraction of lateral pterygoid on one side and independent contraction of posterior fibers of temporalis on the other side
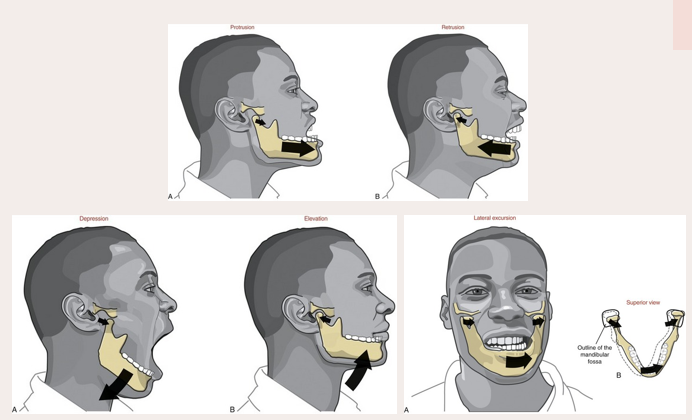
depression of mandible
achieved by contraction of the anterior suprahyoid muscles following stabilization of the hypoid bone by posterior suprahyoid muscles and the infrahyoid muscles
sphenomandibular ligament
not strictly considered part of the TMJ but is located on the medial side of the mandible
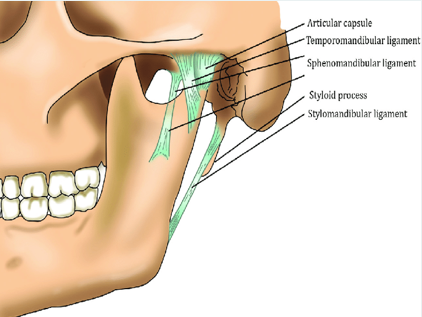
stylomandibular ligament
minor
runs from the styloid process of the temporal bone to the angle of the mandible
taut when the mandible is protruded
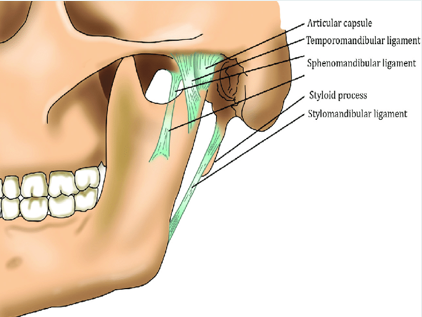
temporomandibular ligament
located on the lateral side of each joint and forms the lateral part of the joint capsule
base is attached to the zygomatic process and lateral to the articular eminence
apex of ligament is fixed to the lateral side of the neck and mandible
synovial cavity
upper: gliding
lower: rotation
vascular system of the head and neck..
consists of an arterial blood supply
a capillary network
venous drainage
anastomosis/anastomoses
communication of blood vessels with other blood vessels
arterial plaque
substance lining arteries mainly consisting of cholesterol
arteriole
smaller artery branching off artery and connecting with capillary
artery
carry blood away from the heart
strong, muscular blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body
handle a large amount of force and pressure from your blood flow but dont carry a large volume of blood
atherosclerosis
narrowing and blockage of arteries by fatty arterial plaque
bacteremia
bacteria traveling within vascular system
capillary
smaller blood vessel branching off an arteriole to supply blood directly to tissue
transport blood, nutrients, and oxygen to cells in your organs and body systems
smallest blood vessels in vascular system
carotid pulse
reliable pulse palpated from common carotid artery
embolus/emboli
foreign material such as a thrombus traveling in blood to block vessel
hematoma
bruise resulting when a blood vessel is injured and a small amount of blood escapes into the underlying tissue then clots
hemorrhage
larges amounts of blood escaping into surrounding tissue without clotting
when blood vessel is seriously injured
thombus/thrombi
forming on inner blood vessel wall
vascular plexus
large network of blood vessels, usually veins
vein
blood vessel traveling to the heart carrying blood
carry oxygen-poor blood
hold most of the blood in the body
venous sinus
blood-filled space between two layers of tissue
venule
smaller vein draining capillaries and then joins larger veins
blood vessels
channels that carry blood throughout body
form a closed loop: begins and ends at heart
body composed of about 60,000 miles of blood vessels
able to carry cancer at a faster rate than lymphatic vessels
arterial blood supply
major arteries that supply the head and neck
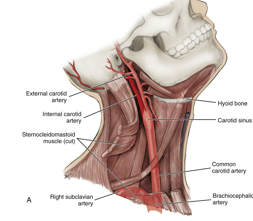
common carotid artery
subclavian arteries
different origins depending on the side of the body
unique for head and neck arteries because most are symmetrical
common carotid artery
left side of the body: originate directly from aorta
right side of body: branch off brachiocephalic artery
branchless and travels along neck in lateral position to trachea and larynx
travels in carotid sheath deep to SCM
internal and external
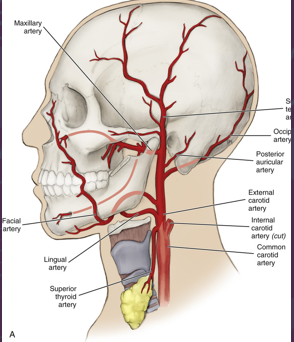
subclavian artery
left side of body: originate directly from aorta
right side of body: branch off brachiocephalic artery