Muscle Overall Study Guide (copy)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Last updated 5:16 AM on 12/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Skeletal Tissue
Tissue with voluntary movement; majority of the muscle in the body; striated
2
New cards
Smooth Tissue
Lines hallow organs; involuntary; not striated
3
New cards
Cardiac Tissue
In the heart; involuntary; striated
4
New cards
Muscle Fiber
single muscle cell; help control physical forces within the body
5
New cards
Myofibril
Functional units of a muscle; made up of think and thin myofilaments which give striated look
6
New cards
Myosin Filament
Protein molecule in muscle, Thick filament
7
New cards
Actin Filament
Protein muscle in muscle; thin; slide along with myosin filaments; has attatchment sites for myosin
8
New cards
Myofilament
Threads of myofibril
9
New cards
Contractile Proteins
Actin and Myosin
10
New cards
Sarcolemma
plasma membrane; fine transparent sheath enveloping skeletal muscles
11
New cards
Sarcomere
Contractile unit of muscle; repeated over and over along a myofibril
12
New cards
Skeletal muscle cells into muscle: Smallest to Largest
Muscle fiber/cell (contained by sarcolemma), Endomysium, Fascicle (multiple muscle fibers held together by perimysium), Muscle (multiple fascicles held together by epimysium)
13
New cards
Muscle
multiple fascicles held together by epimysium
14
New cards
Fascicle
multiple muscle fibers held together by perimysium
15
New cards
Perimysium
Sheath of connective tissue surrounding bundle of muscle fibers
16
New cards
Epimysium
Sheath of fibrous elastic tissue surrounding a muscle
17
New cards
Neuromuscular Junction
The axon terminal and sarcolemma are separated by a space called the synaptic cleft; Neurotransmitter acetylcholine is released into the synaptic cleft via exocytosis and it diffuses across the synaptic cleft via exocytosis and it diffuses across synaptic cleft and triggers muscle contraction
18
New cards
Sliding Filament Theory
muscles need ATP and calcium ions to contract; myosin "heads" walk along the actin filament, shortening the muscle; contraction can last for as long as there are adequate ATP and CA+ stores
19
New cards
Muscles attach at two points
Bone or connective tissue
20
New cards
Origin
Stationary; immovable (or less movable) bone during movement
21
New cards
Insertion
More movable bone; muscle contracts across diarthrotic fibers (fibers shorten); Insertion towards the origin; Type of movement depends on joint type/shape and placement of the muscle
22
New cards
Agonist
Prime Mover; produces a movement
23
New cards
Antagonist
Opposes or reverses a movement; can also be prime movers
24
New cards
Bicep muscle of the arm
Agonist of flexion at elbow; motion is antagonized by the triceps
25
New cards
Triceps
prime mover of extension at the elbow
26
New cards
Synergist
Aid action of agonist by assisting or stabilizing; stabilizing is necessary when a muscle crosses two or more joints (ex. making a fist)
27
New cards
Fixator
Specialized synergist; immobilizes origin so all tension is on insertion; muscle that holds scapula in place during arm motions
28
New cards
Rectus
parallel (usually w/ midline)
29
New cards
Transverse
right angle midline
30
New cards
Oblique
Angled
31
New cards
Biceps
2 origins
32
New cards
Tricep
3 origins
33
New cards
Quadricep
4 places of origin
34
New cards
Adductor
muscles located on inner thigh; bring legs toward center of your body; motion of bringing legs inward is "adduction"
35
New cards
Flexor
Muscle whose contraction bends a limb or other part of the body; muscle that decreases the angle between bones
36
New cards
Extensor
Muscle whose contraction extends or straightens a limb or other part of the body
37
New cards
Phalanges
bones found in fingers and toes; has no muscle
38
New cards
Brain
Largest and most complex part of nervous system; sensation, perception, movement, thinking
39
New cards
Frontal Lobe
Executive functioning, multitasking
40
New cards
Temporal Lobe
Auditory Processing
41
New cards
Parietal Lobe
Interprets pain/touch; identifies objects; understands spoken language
42
New cards
Occipital Lobe
Vision
43
New cards
Grey matter
Center of Spinal Cord; Superficial layer; a.k.a cerebral cortex; cell bodies of cerebral neurons; unmyelinated region
44
New cards
White Matter
Outer area of Spinal Cord; Myelinated Axons
45
New cards
Gyri (Gyrus)
Fold
46
New cards
Sulci (Sulcus)
Depression
47
New cards
Fissure
Deep sulcus
48
New cards
Brainstem
Connects brain and spinal chord; the area where the majority of cranial nerves attach
3 Parts: Midbrain, Pons, Medulla
3 Parts: Midbrain, Pons, Medulla
49
New cards
Communication between CNS and PNS
Brain -> Brainstem -> Spinal Chord -> PNS
50
New cards
Midbrain
Vision, hearing
51
New cards
Pons
Regulation; where cerebellum connects
52
New cards
Medulla
Conscious thought and involuntary control (breathing, heard, blood, vessels, digestion); exits through foramen magnum
53
New cards
Cerebellum
located under occipital lobe; responsible for coordination, posture, balance, motor skills; associated w/ physical movement, and unconscious coordination and equilibrium
54
New cards
Arbor Vitae
branching white matter in the cerebellum
55
New cards
Diencephalon
Region of brain that contains Epithalamus, thalamus, and hypothalamus
56
New cards
Pineal Gland
Body's internal clock; in the Epithalamus; circadian rhythm; secretes melatonin
57
New cards
Thalamus
Relay station and processing center for incoming sensory information (not smell); outgoing motor information
58
New cards
Hypothalamus
Autonomic functions; hormone production; homeostasis
59
New cards
Cerebral Spinal Fluid (CSF)
surrounds CNS; brain and spinal cord; provides support, cushioning and protection; contains and transports nutrients, waste, and chemical messengers; flows through ventricles; flows into a subarachnoid space
60
New cards
Chloroid Plexus
network of blood vessels in each ventricle of the brain; derived from pia meter and produces CSF
61
New cards
Meninges
3 layers of connective tissue that protect brain and spinal chord; Dura mater, Arachnoid Mater, and Pia Mater
62
New cards
Dura Mater
most superficial layer of of tissue around brain and spinal chord; attached to inner surface of thee skull
63
New cards
Arachnoid Mater
second superficial layer of of tissue around brain and spinal chord; weblike connective tissue
64
New cards
Pia Mater
third superficial layer of of tissue around brain and spinal chord; delicate, highly vascular, attaches to surface of the brain
65
New cards
Meningitis
inflammation of meninges
66
New cards
Nervous System
Integrates and coordinates; monitors and processes internal and external environment; homeostasis
67
New cards
Central Nervous System
Brain and Spinal Cord; primarily interprets incoming sensory info and issues response/instructions
68
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
Nervous system elements other than CNS; sensory, cranial nerves, spinal nerves
69
New cards
Neuroglia
supports and protects neurons; astrocyte, ependymal cell, oligodendrocyte, shwann cell
70
New cards
Astrocyte
glial cell; IN CNS; most abundant; gives support and nutrients to neuron; controls chemical environment through the mopping up of leaked K+; blood brain barrier
71
New cards
Ependymal
glial cell IN CNS; aids in circulation of CFS and production
72
New cards
Oligrodendrocytes
glial cell in CNS; produces myelin sheath in CNS
73
New cards
Myelination
increases transmission speed of nerve impulse
74
New cards
Schwann Cells
most long nerve fibers that are covered w/ fatty myelin; nerves in the PNS are heavily myelinated by Schwann cells; wrap tightly around the axon; not continuous (gaps exist between cells)
75
New cards
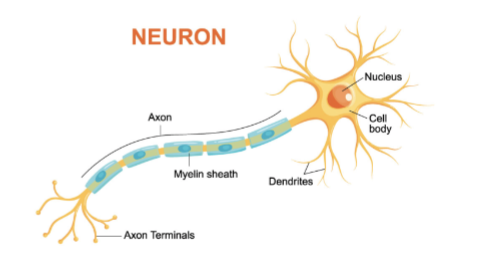
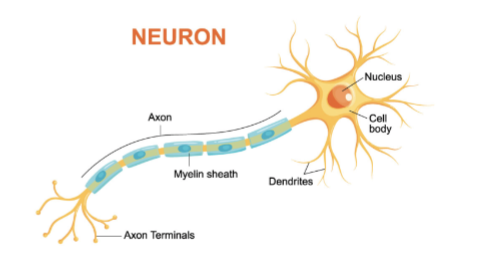
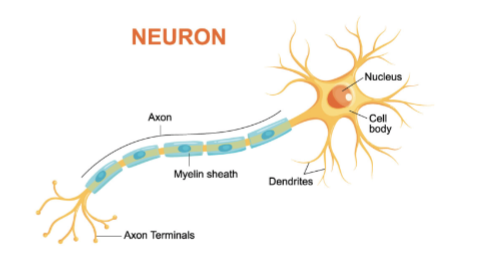
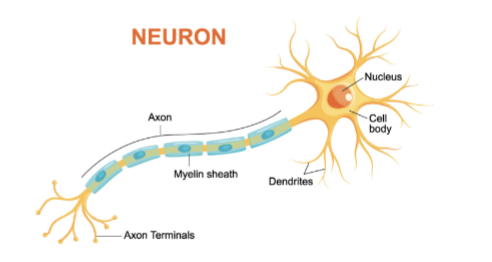
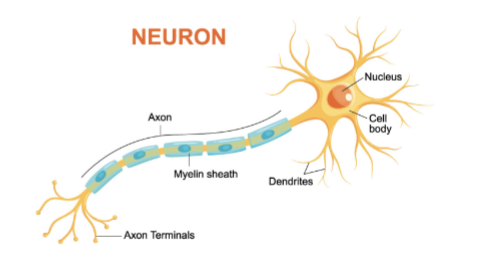
Neuron
tissues of nervous system; made up of cell body, axon, axon terminal, synaptic cleft, dendrite
76
New cards
(pseudo) Unipolar Neuron
one short process that divides; often conducts impulses toward CNS
77
New cards
Bipolar Neuron
2 processes; rare-sight, smell, hearing
78
New cards
Multipolar Neuron
multiple dendrites; 1 axon; brain, spinal chord, neurons that carry messages away from CNS; MOST COMMON
79
New cards
myelin
insulating layer or sheath that forms around nerves; makes up myelin sheath
80
New cards
Cell body
nucleus and cytoplasm
81
New cards
Dendrite
receptive region of a neuron
82
New cards
Axon
Impulse generating and conductive region
83
New cards
Axon Terminal
End of Axon; transmitting portion of neuron; transmits information via neurotransmitters
84
New cards
Synaptic Cleft
Junction between axon terminal and next cell; where neurotransmitters are released
85
New cards
Neuron Information Flow
Dendrite -> Cell Body -> Axon -> Axon Terminal -> Synapse; a neuron can synapse with another neuron, muscle, or gland
86
New cards
Action Potential
this is how nerves send signals
87
New cards
Sensory/Afferent Neuron
carry impulses from organs, skin, skeletal muscles, special senses to TOWARD CNS; endings have specialized receptors that are stimulated by specific changes in environment; typically unipolar
88
New cards
Motor/Efferent Neuron
carry Impulses AWAY FROM CNS to the organs, muscles, and glads; typically multipolar
89
New cards
Somatic
voluntary
90
New cards
autonomic
involuntary
91
New cards
Autonomic Nervous System
controls many INVOLUNTARY functions (ex. digestion, urination, heart rate)
92
New cards
Parasympathetic
"rest and digest"; digestive function increases; heart rate decreases; bronchi constrict; pupils constrict; promotes emptying of bladder; stimulates saliva
93
New cards
Sympathetic
"fight or flight"; digestive function slows; heart rate increases; bronchi relax; pupils dilate; inhibits emptying of bladder; inhibits saliva
94
New cards
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
Records electrical activity of the brain; brain waves are always present - even hen unconscious; can be used to locate specific areas of concern; diagnostic tool for seizures
95
New cards
Grey Matter
96
New cards
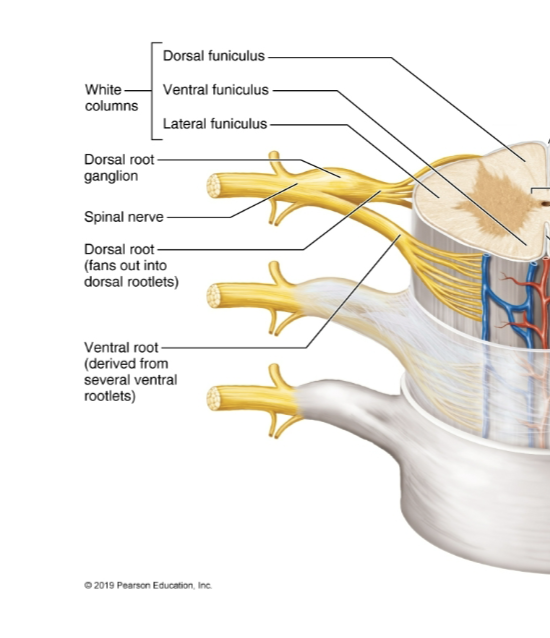
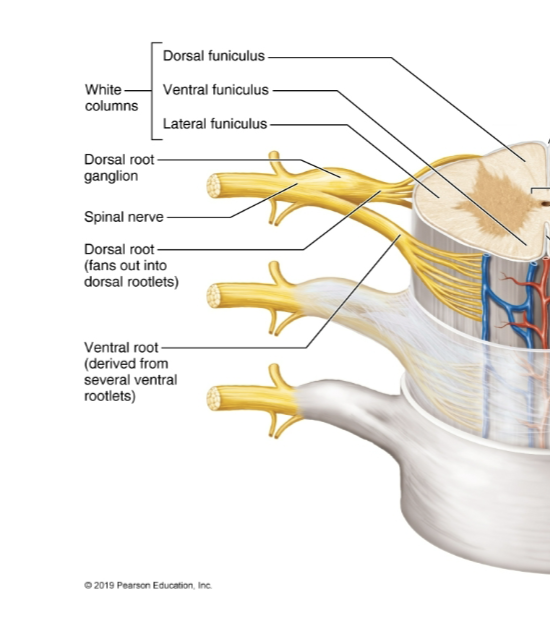
Central Canal
Continuous w/ the ventricles of the brain; located in spinal cord; has CSF
97
New cards
Dorsal Root/Root Ganglion
Contains sensory neurons
98
New cards
Ventral Root
Motor Neurons
99
New cards
Spinal Nerve
Fusion of dorsal and ventral roots; mixed nerve (contains both sensory and motor fibers)
100
New cards
Epidural Space
Space between the spinal dura mater and the periosteum of the vertebral column; pain medicine and anesthesia is injected into this space along the spine