BIOS 114 Final Practicum F24'
1/219
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Organismal Bio Lab: Final study guide for practicum 2 . Terms and definitions, also with pictures to locate
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
220 Terms
Anterior
Refers to the front or head end of an organism.
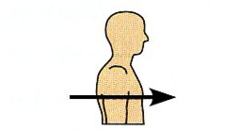
What is this orientation
Anterior
Posterior
Refers to the back or tail end of an organism.
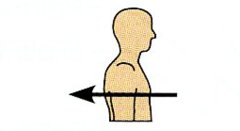
What orientation is this
Posterior
Superior
Refers to the upper side or back of an organism.
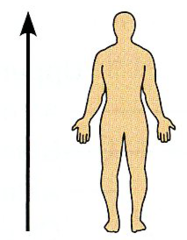
What orientation is this
Superior
Inferior
Refers to the lower side or belly of an organism.
What orientation is this?
Inferior
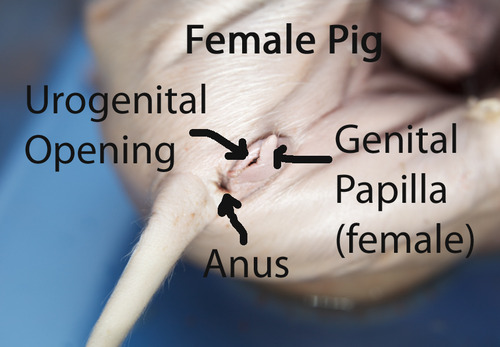
Genital Papilla
A structure found on female fetal pigs, important for reproductive anatomy.
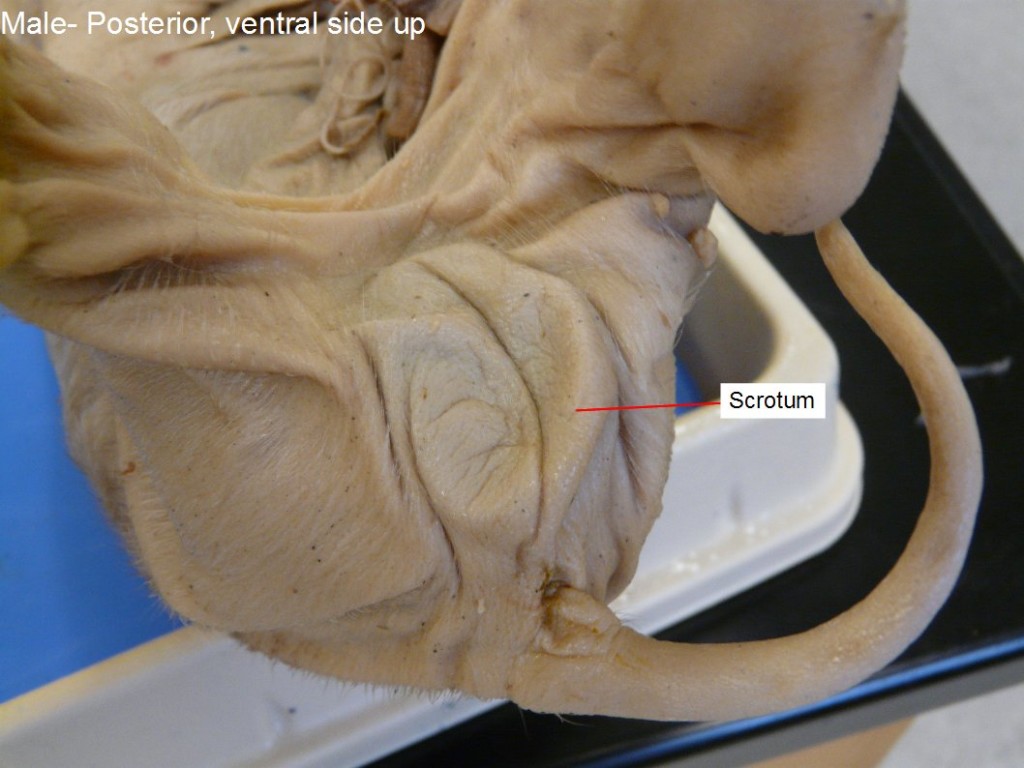
Scrotal Sac
A structure found on male fetal pigs that houses the testes.
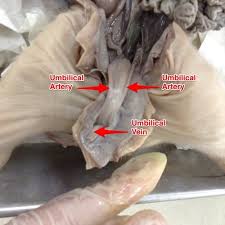
Umbilical Cord
Connects a developing fetus to the placenta
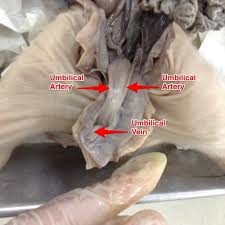
Umbilical Arteries
Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta.
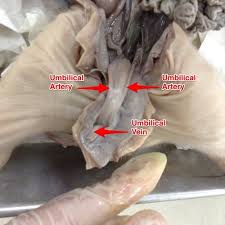
Umbilical Vein
Blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta to the fetus.
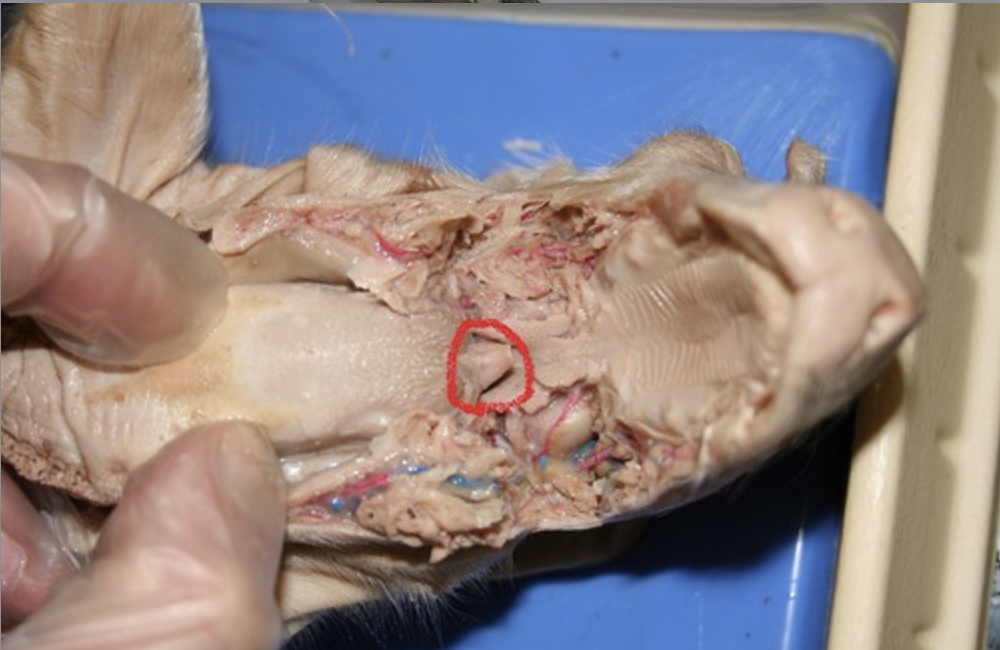
Epiglottis
A flap of tissue that covers the trachea during swallowing to prevent food from entering the airway.
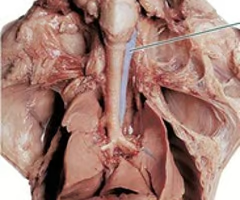
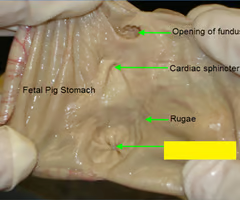
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the throat (pharynx) with the stomach.
Hard Palate
The bony front part of the roof of the mouth, separating the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
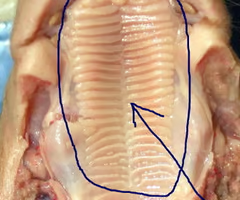
Soft Palate
The soft back part of the roof of the mouth that is muscular and plays a role in swallowing and speech.
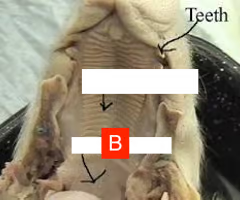
Nasal Pharynx
The upper part of the pharynx located behind the nasal cavity.
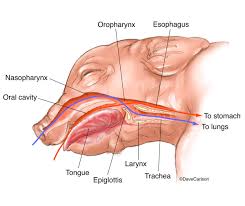
Oral Pharynx
The part of the pharynx located behind the mouth, involved in both respiratory and digestive functions.
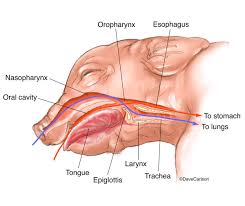
Trachea
The windpipe; a tube that connects the larynx to the lungs and allows the passage of air.
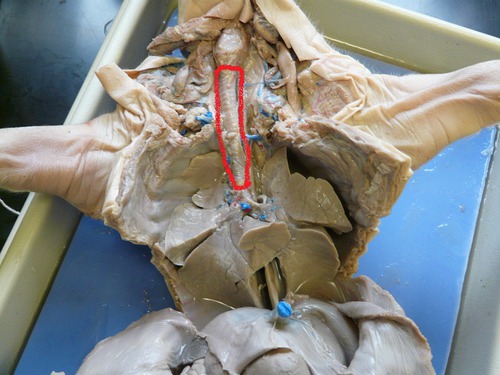
Lungs
The organs of respiration that allow for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Bronchi
The main air passages from the trachea to the lungs that branch into smaller bronchioles.
Heart
The muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.

Larynx
The voice box; a structure in the throat that produces sound and protects the trachea during swallowing.
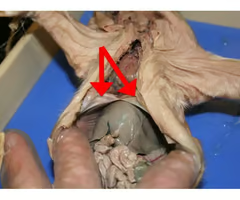
Diaphragm
A dome-shaped muscle that plays a major role in breathing by contracting and relaxing to change the volume of the thoracic cavity.
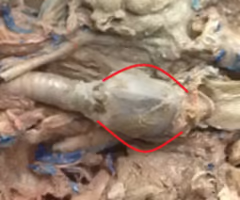
Thymus
An organ of the immune system located in the upper chest that is important for the maturation of T cells.
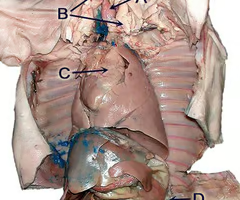
Thyroid
A gland in the neck that produces hormones regulating metabolism and growth.
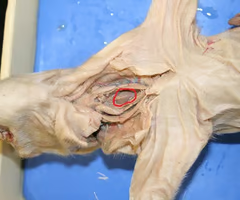
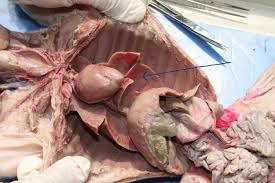
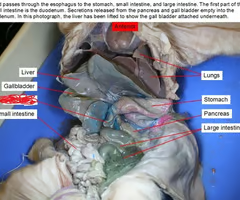
Liver
The largest internal organ, involved in metabolism, detoxification, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.
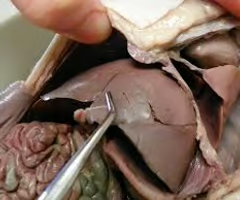
Gallbladder
A small organ that stores bile produced by the liver
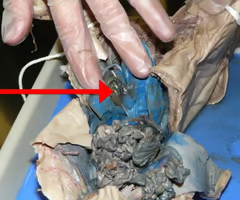
Pyloric Sphincter
The muscular valve that controls the flow of partially digested food from the stomach to the small intestine.
Spleen
An organ involved in filtering blood, recycling iron, and supporting the immune system.
Kidneys
Organs that filter blood to produce urine, regulating blood pressure, electrolyte balance, and red blood cell production.
Duodenum
The first section of the small intestine, where the majority of chemical digestion occurs.
Pancreas
An organ that produces digestive enzymes and hormones

Jejunum-ileum (Small Intestines)
The sections of the small intestine that absorb nutrients from digested food.
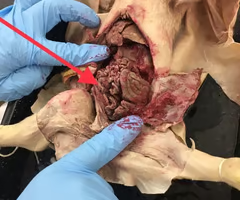
Cecum
The first part of the large intestine, connecting the ileum of the small intestine to the colon.
Colon (Large Intestines)
The part of the digestive system responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes
Bladder
An organ that stores urine before it is excreted from the body.
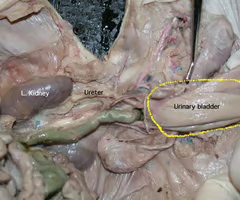
Ureters
Tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
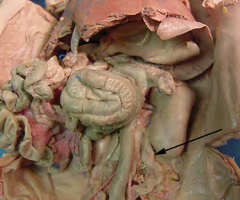
Urethra
The tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.

Mesenteries
Folds of tissue that attach the intestines to the abdominal wall and support blood vessels and nerves to the intestines.
Erythrocyte
A red blood cell that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body tissues and carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs.
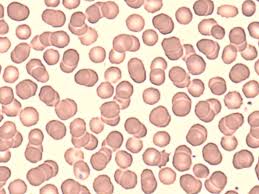
Thrombocyte
A platelet; a cell fragment that plays an essential role in blood clotting.
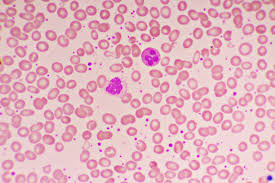
Leukocyte
A white blood cell that is part of the immune system and helps the body fight infections.
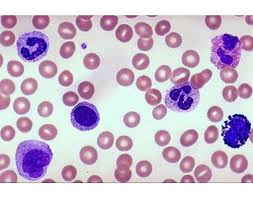
blood groups
A, B, and Rh factors.
blood types
A+, A-, B+, B-, AB+, AB-, O+, and O-.
O-
Universal Donor
AB+
universal recipient
Anti-B antibodies
Type A
Anti-A antibodies
Type B
No antibodies
Type AB
Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies
Type O
Anterior Vena Cava
collects blood from upper part of body to return to heart
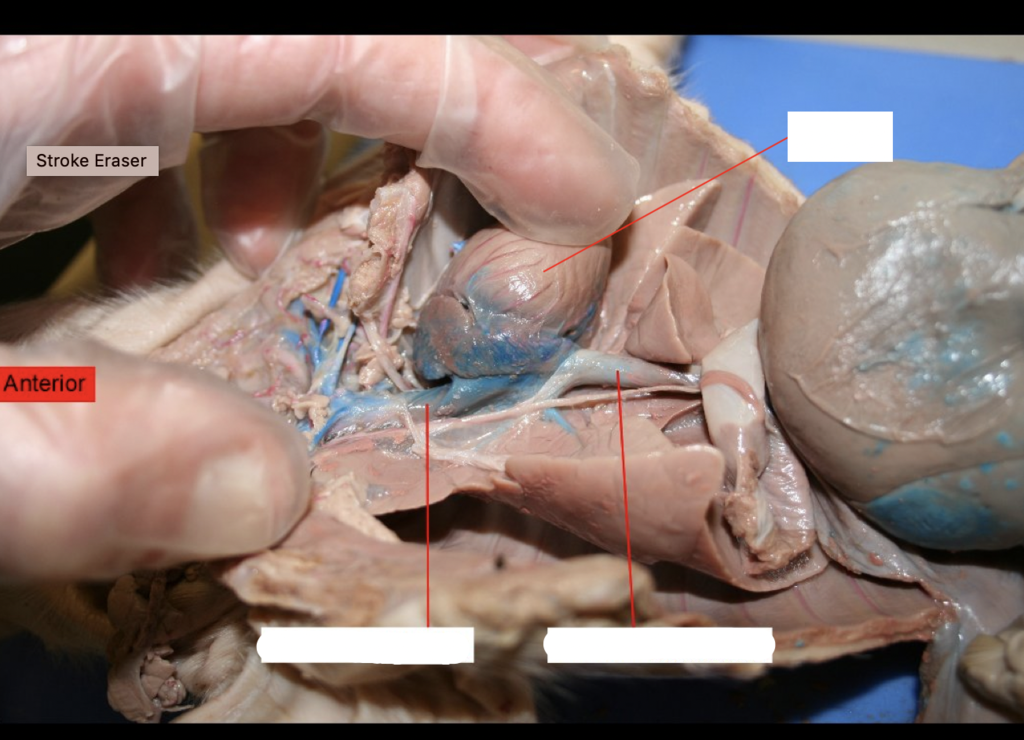
posterior vena cava
drains deoxygenated blood from the posterior body to the right atrium
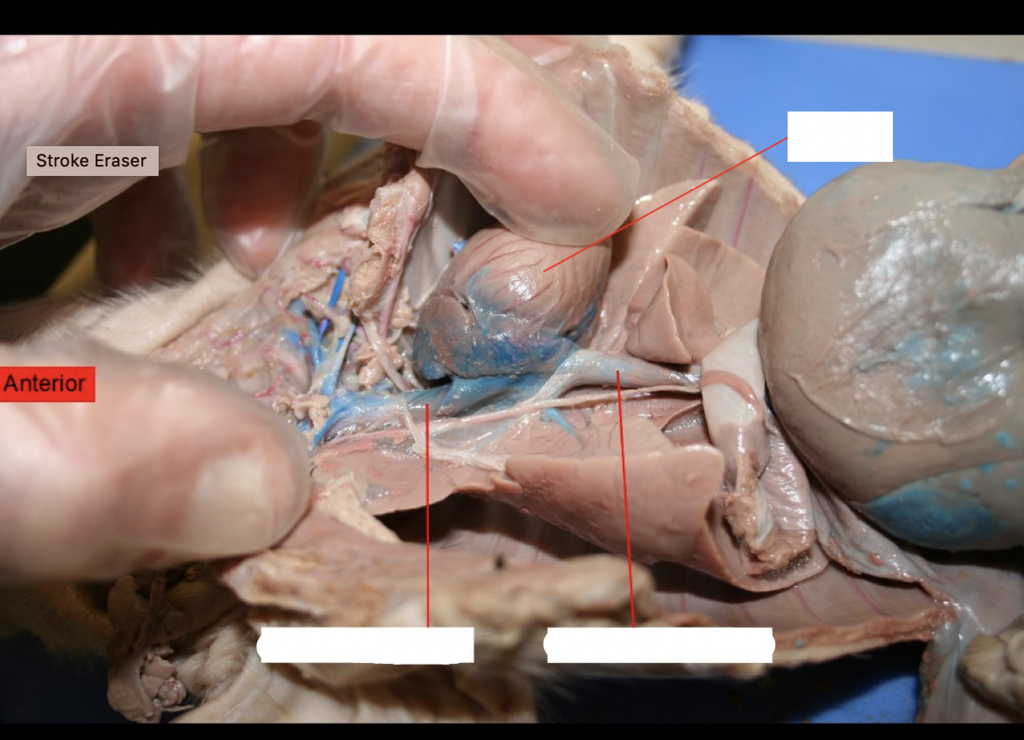
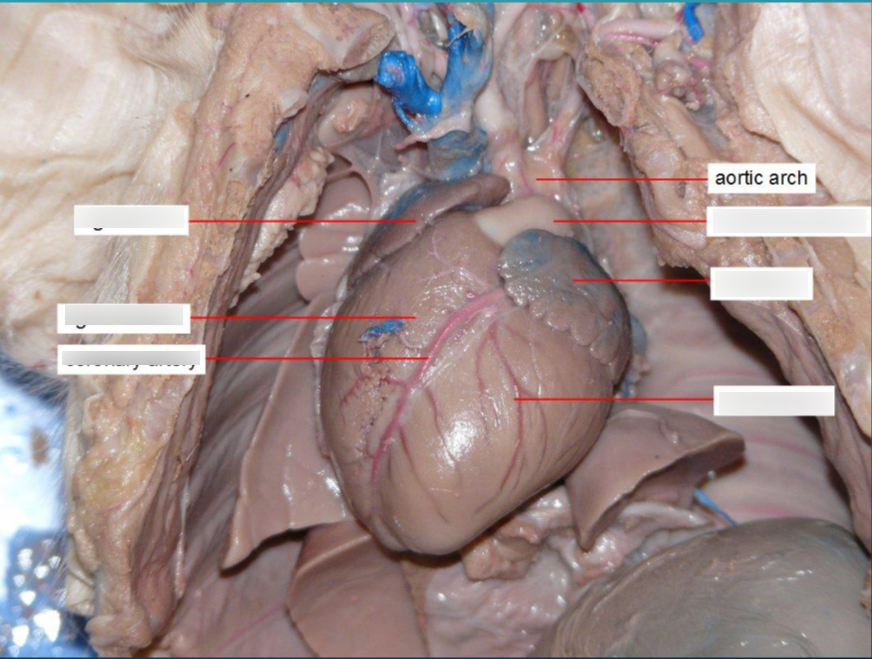
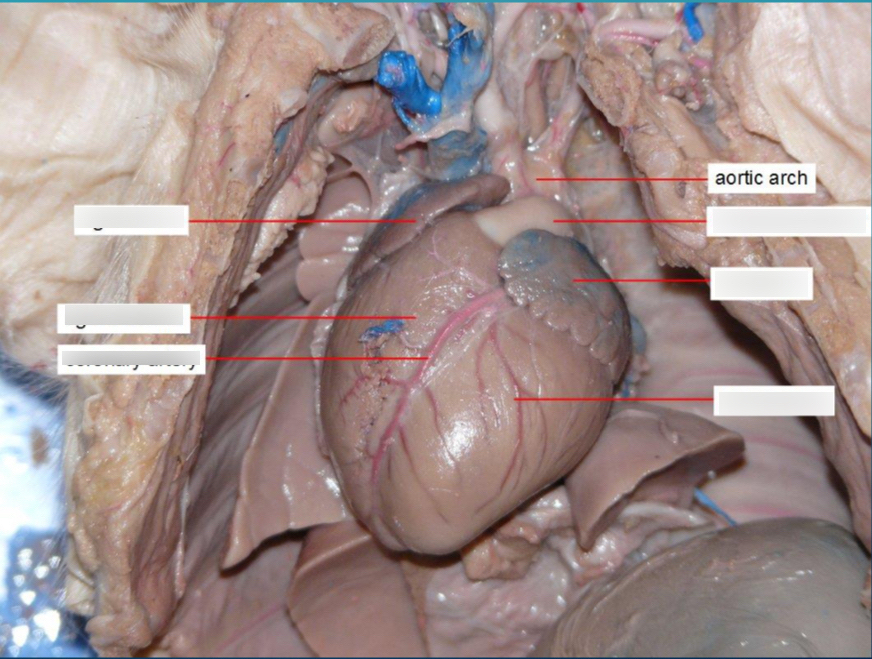
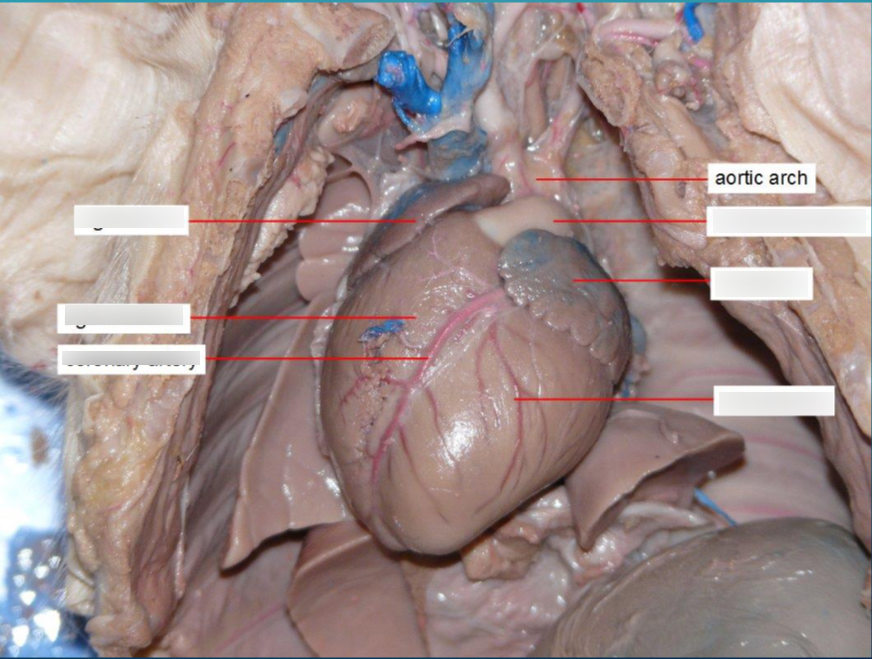
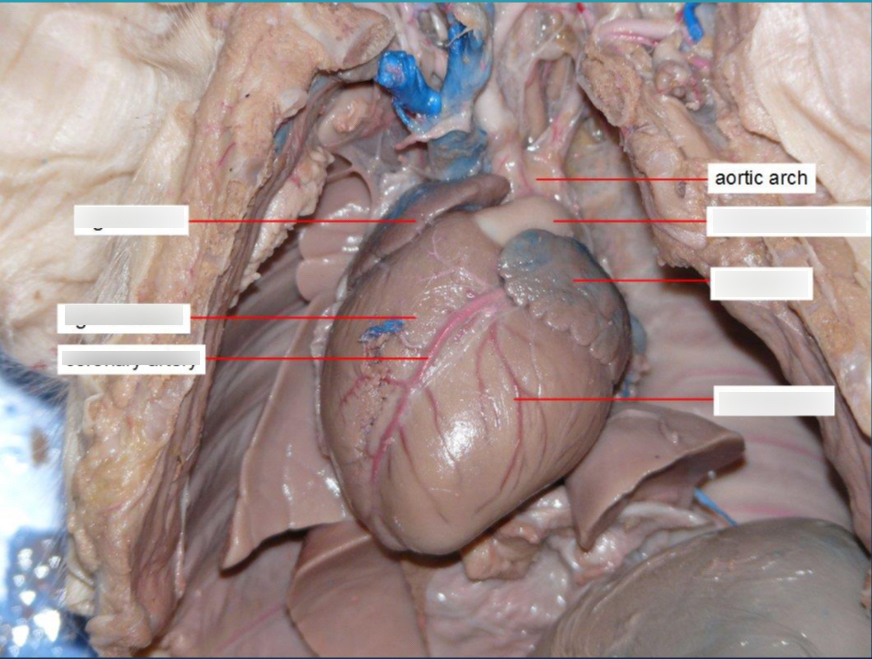
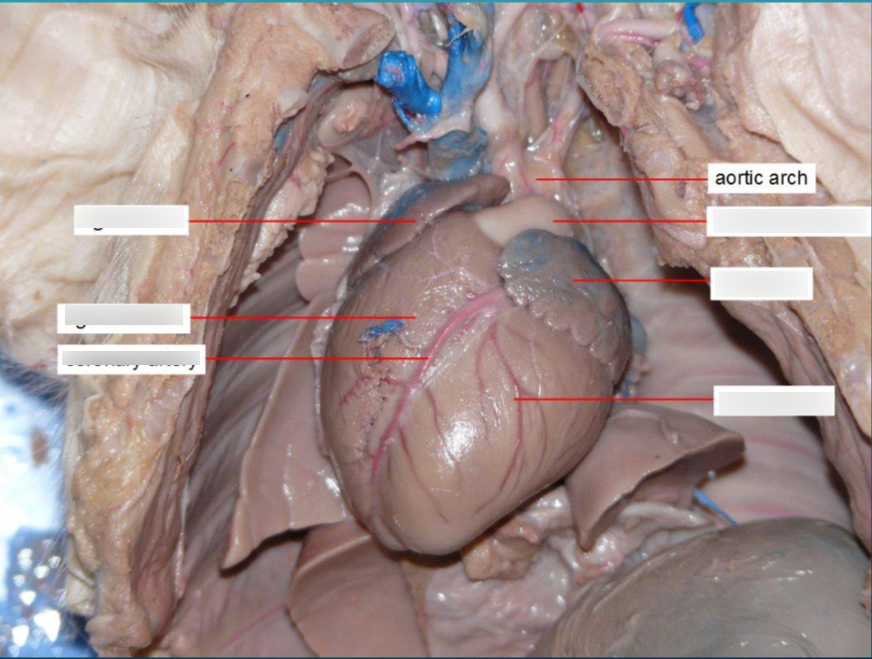
Aortic Arch
bends between the ascending and descending aorta.
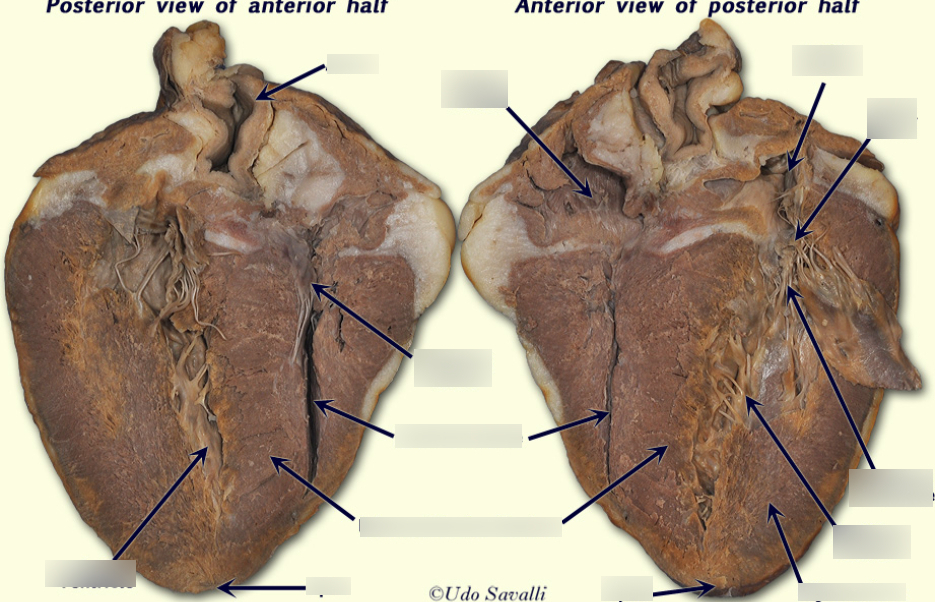
Aorta
The largest artery in the body that carries oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the body.
Pulmonary Trunk
A large vessel that branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries, carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Coronary Arteries
Arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle itself.
Right Atrium
The chamber of the heart that receives deoxygenated blood from the body via the vena cava.
Left Atrium
The chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins.
Right Ventricle
The chamber of the heart that pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation.
Left Ventricle
The chamber of the heart that pumps oxygenated blood to the entire body.
Myocardium
The muscular layer of the heart responsible for contraction.
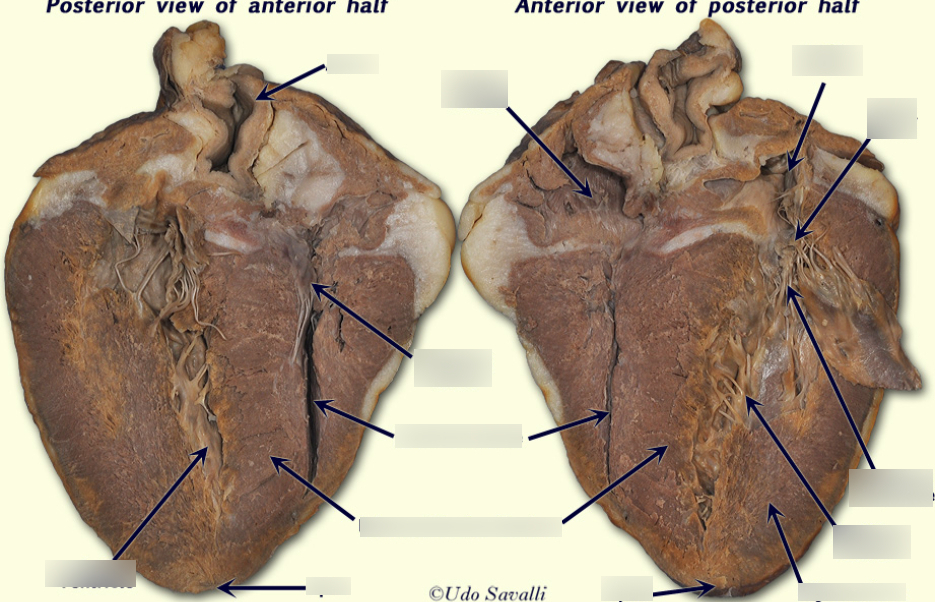
Chordae Tendineae
Tendinous strands that connect the valves of the heart to the papillary muscles.
Papillary Muscle
Muscles that contract to prevent the inversion or prolapse of the heart valves.
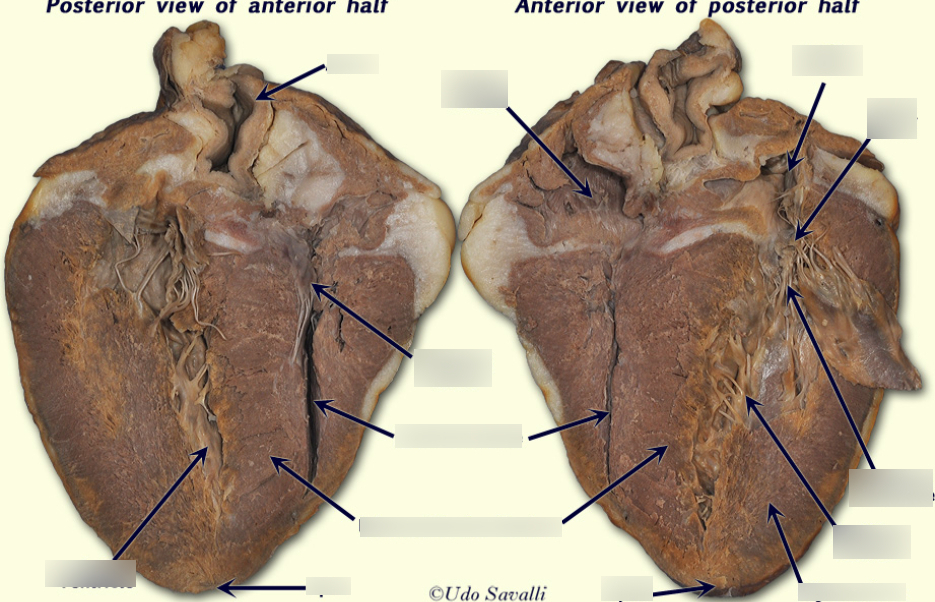
Semilunar Valve
Valves located at the exits of the right and left ventricles, preventing backflow of blood.
Atrioventricular Valves
Valves located between the atria and ventricles, preventing backflow into the atria when the ventricles contract.
Tricuspid Valve
The valve located between the right atrium and right ventricle, preventing backflow of blood into the atrium.
Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve
The valve located between the left atrium and left ventricle, allowing blood to flow from the atrium to the ventricle while preventing backflow.
Oxygenated Blood Vessels
Blood vessels that carry oxygen-rich blood; primarily the pulmonary veins and systemic arteries.
Deoxygenated Blood Vessels
pulmonary arteries and systemic veins.
Sphygmomanometer
An instrument used to measure blood pressure by constricting an artery and then measuring the pressure required to occlude it.
Systolic Pressure
The pressure in the arteries during the contraction of the heart muscle.
Diastolic Pressure
The pressure in the arteries when the heart is at rest between beats.
Stethoscope
A medical instrument used to listen to internal sounds of a body, primarily used for heartbeats and blood flow.
Path of Blood Through the Heart
right atrium, right ventricle, the lungs via the pulmonary arteries, left atrium via the pulmonary veins, the left ventricle,out to the body through the aorta.
Flow of Blood Through Vessels
The sequence of blood flow: Arteries → Arterioles → Capillaries → Venules → Veins.
White Matter
Regions of the spinal cord that contain myelinated axons, primarily involved in the transmission of signals between different parts of the nervous system.
Grey Matter
Regions of the spinal cord that contain the cell bodies of neurons and are involved in processing information.
Meninges
Three layers of protective tissue covering the brain and spinal cord; the outer layer is called the dura mater, which is tough and white.
Dura Mater
The tough, white outer layer of the meninges that provides protection to the brain and spinal cord.
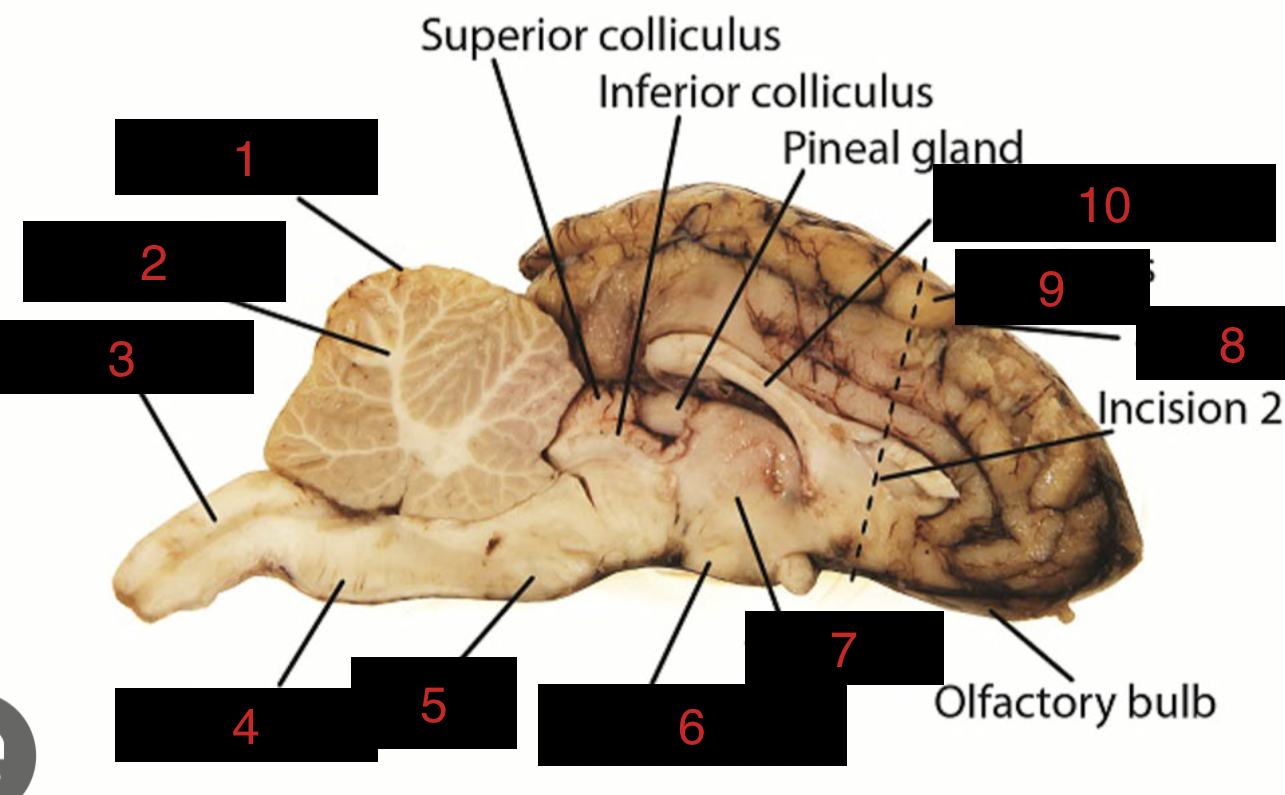
Sheep Brain Structures
Anatomical features of the sheep brain used for comparative studies with human brain structures.
Cerebellum
1
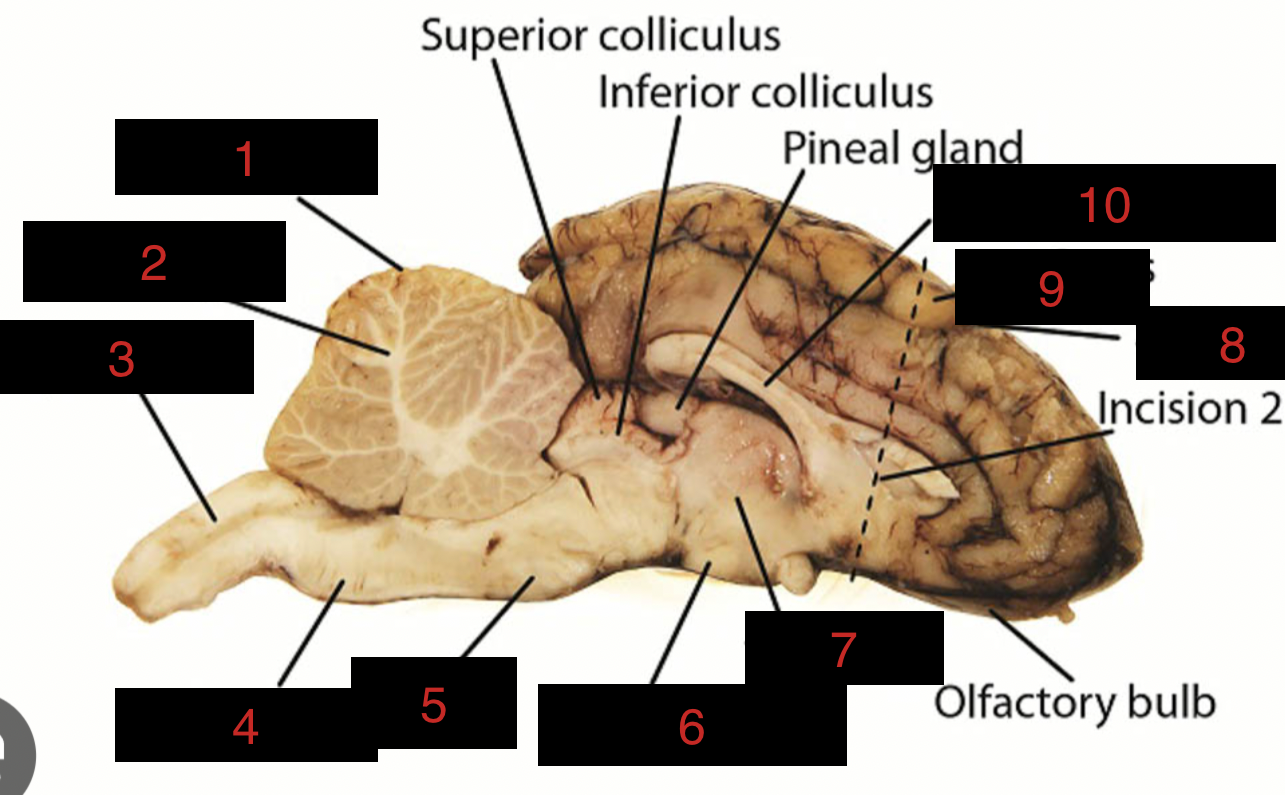
spinal cord
3
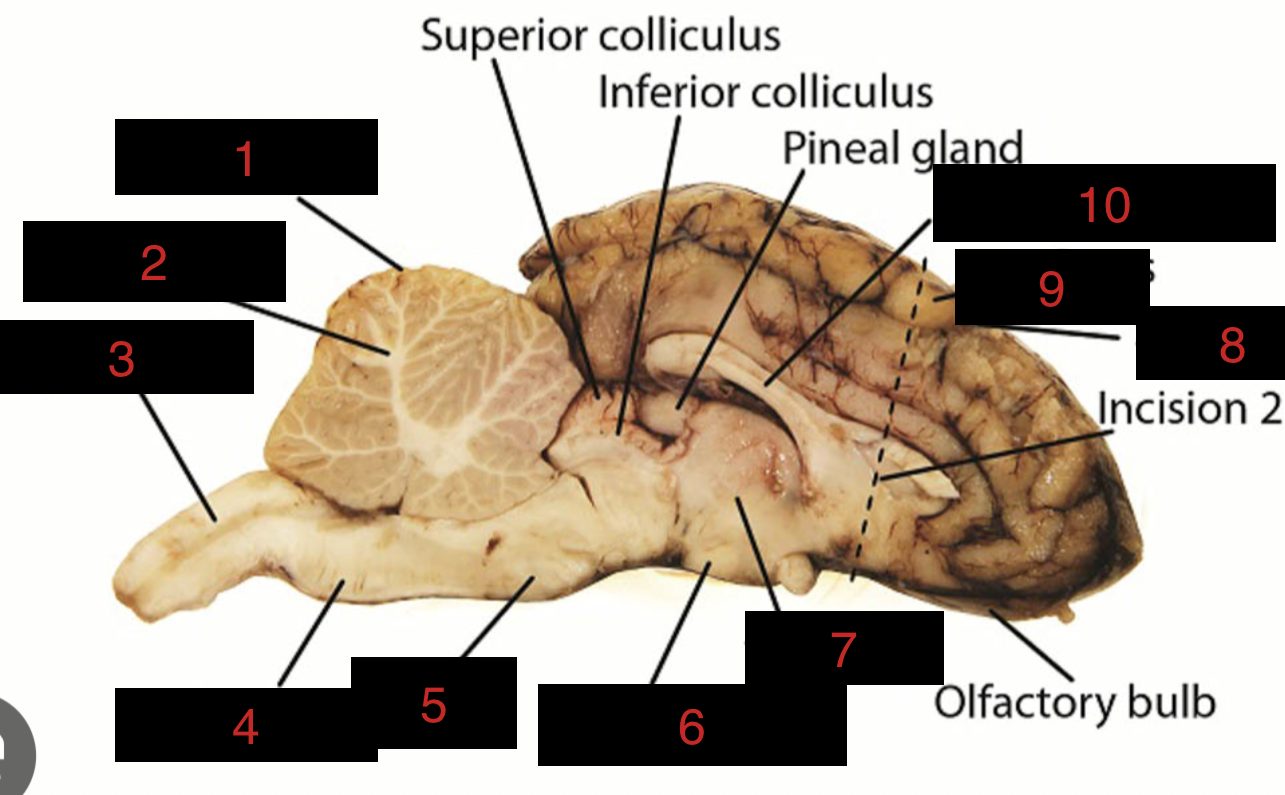
medulla oblongata
4
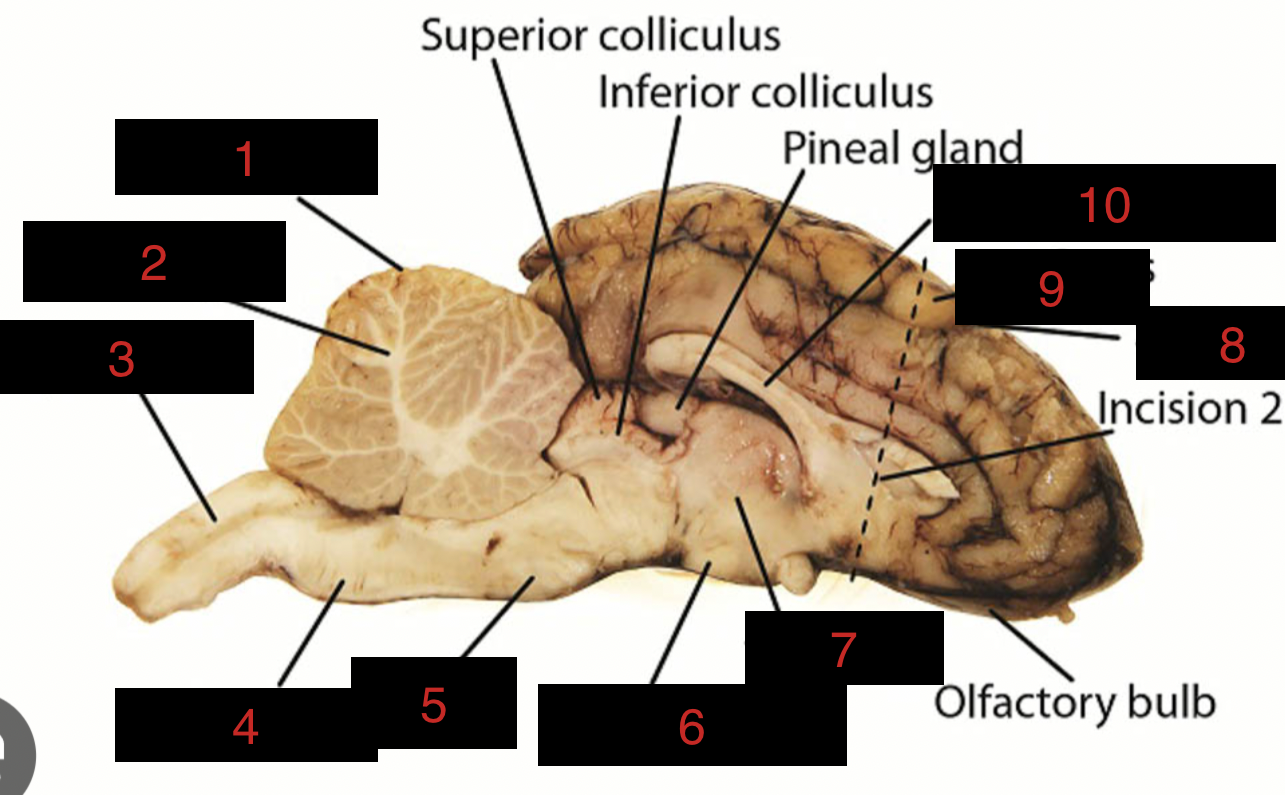
pons
5
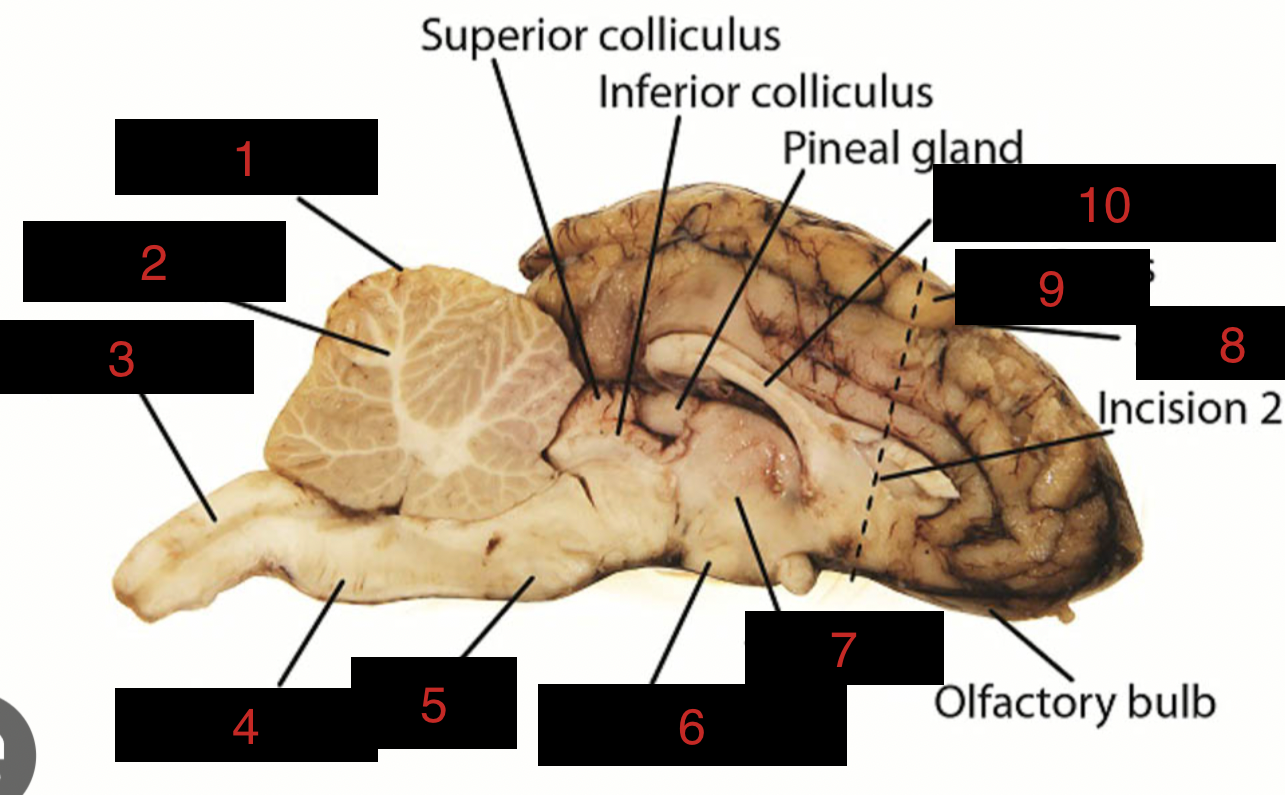
midbrain
between 5 and 6
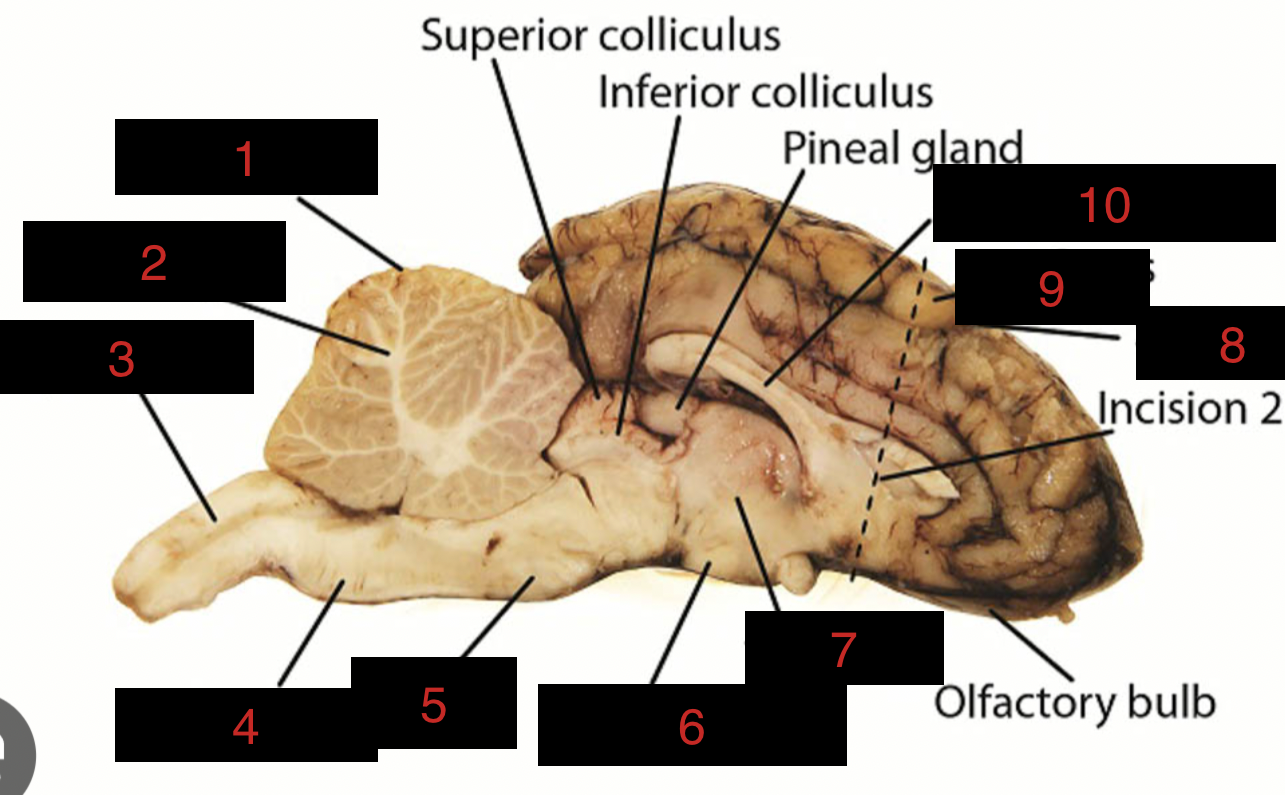
hypothalamus
6
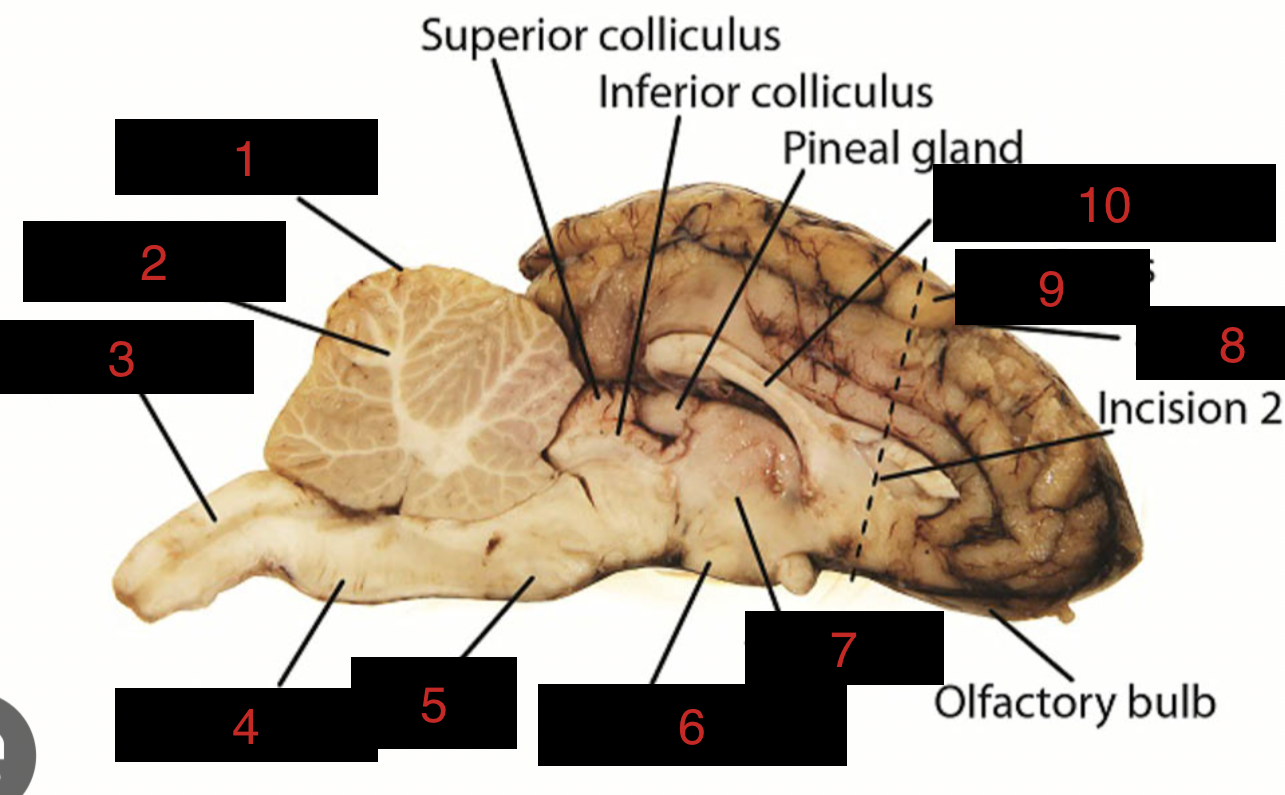
thalamus
7
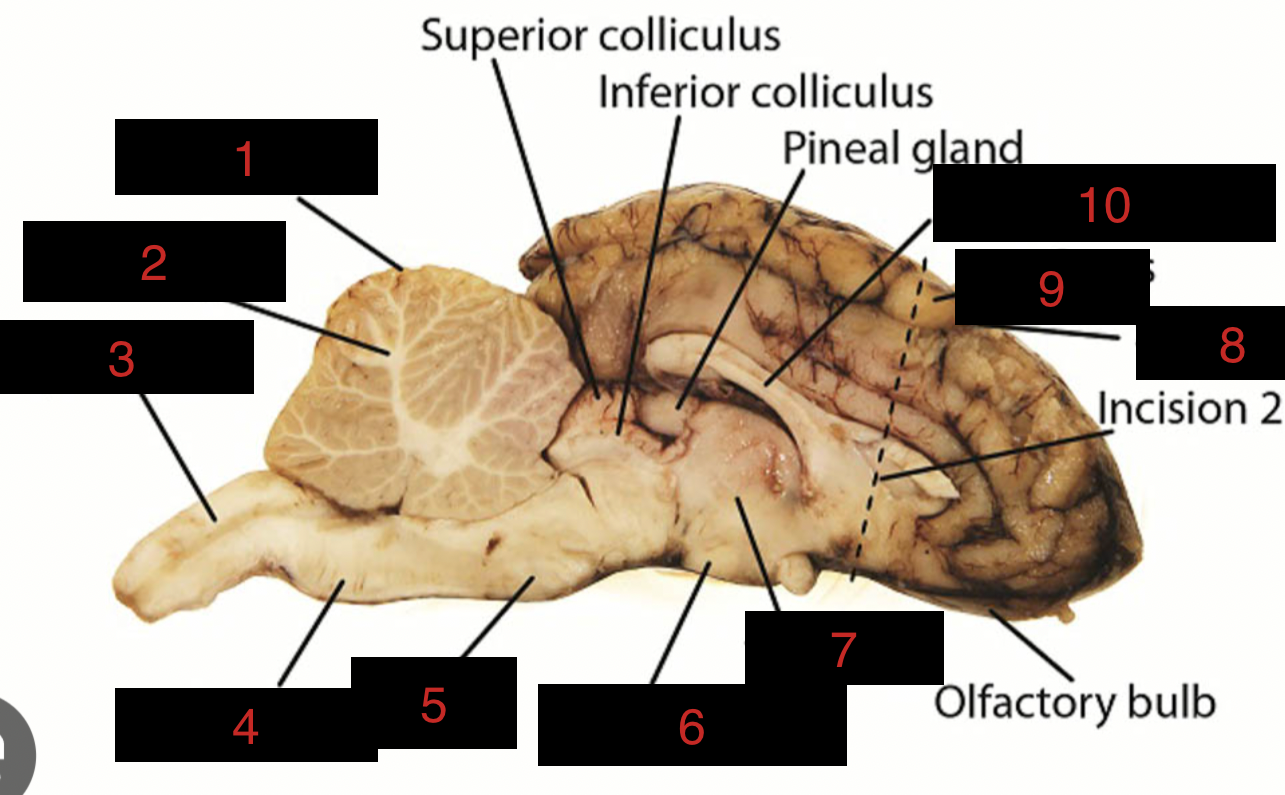
sulci
8
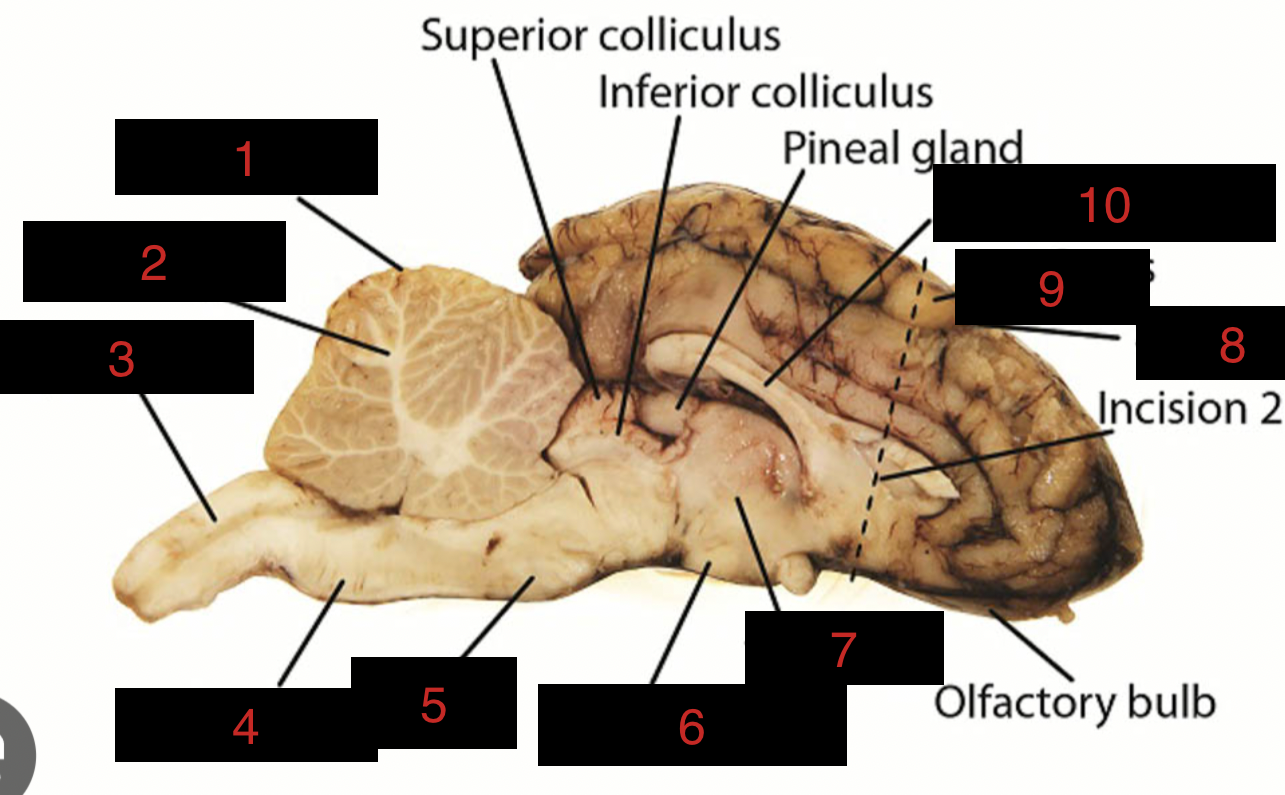
gyri
9
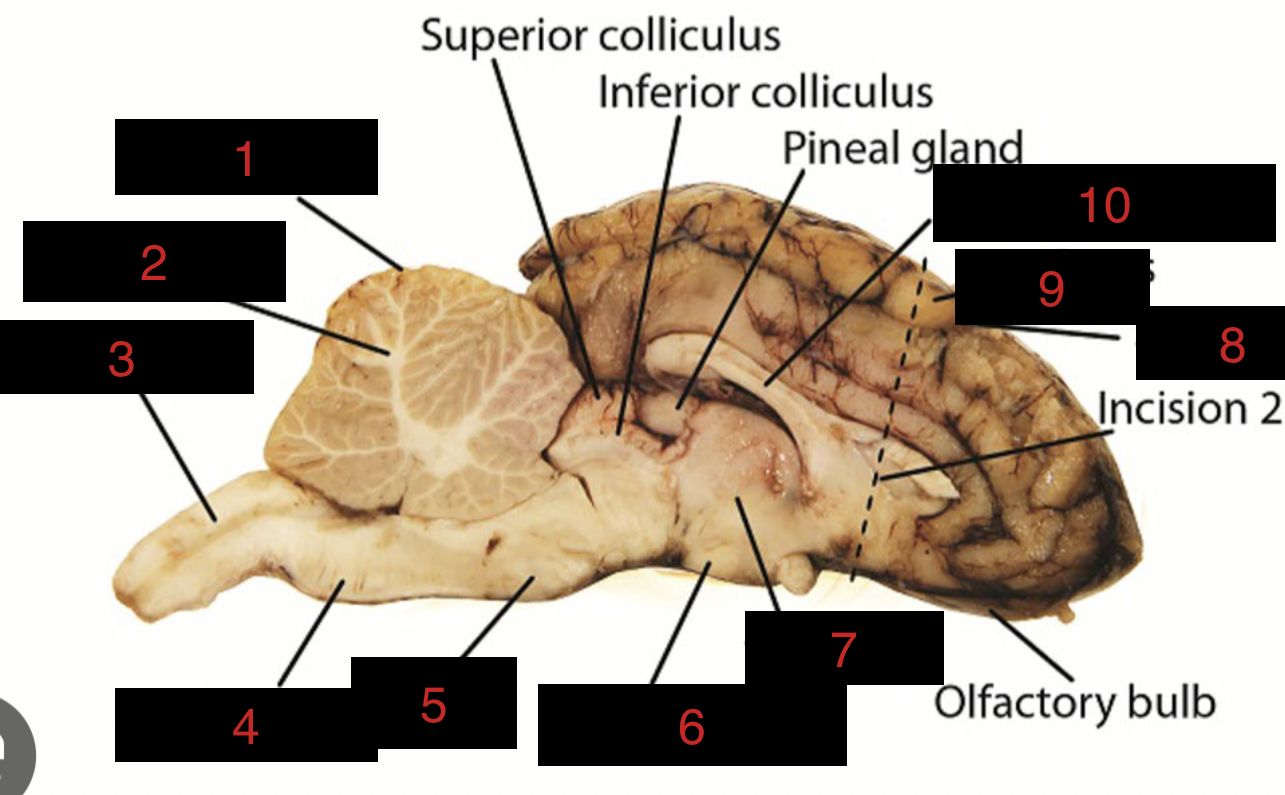
corpus callosum
10
occipital lobe
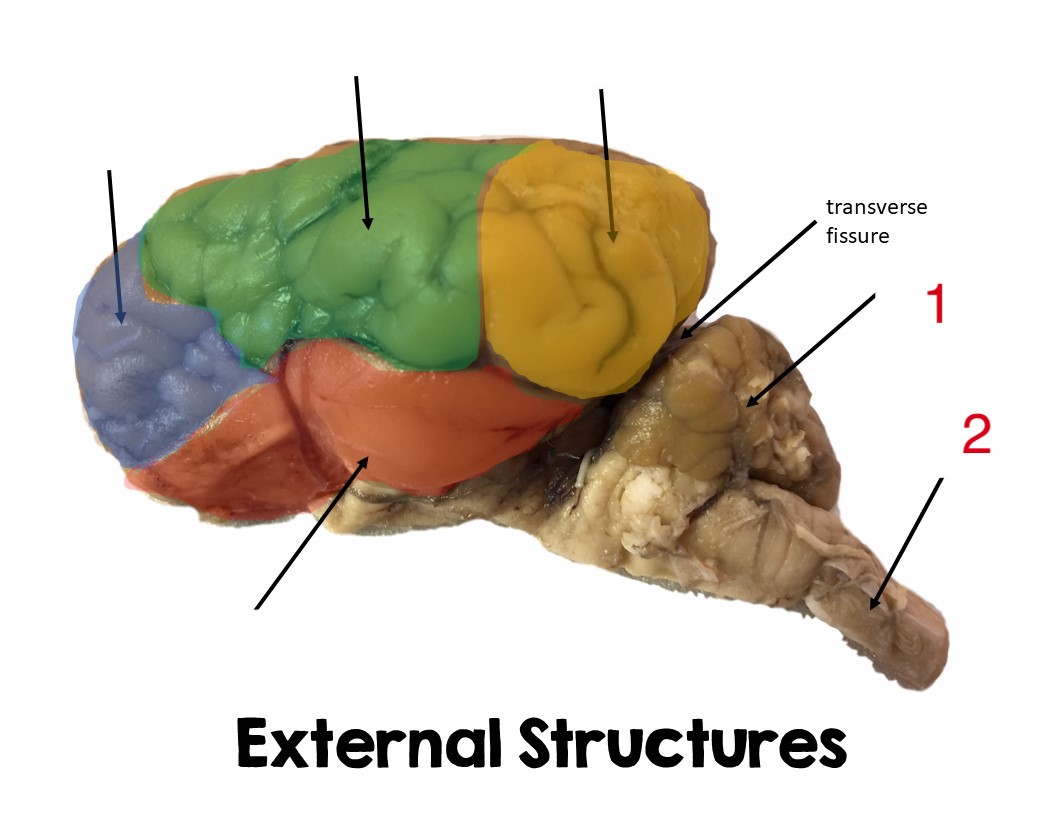
yellow
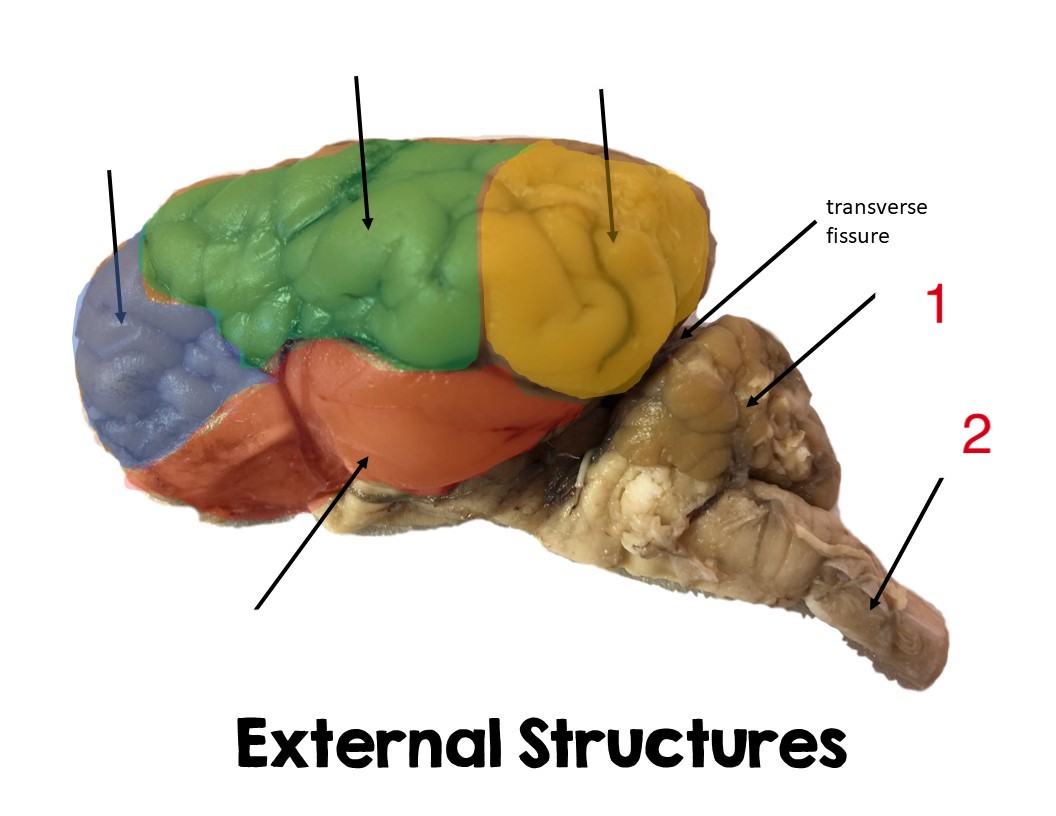
pariental lobe
green
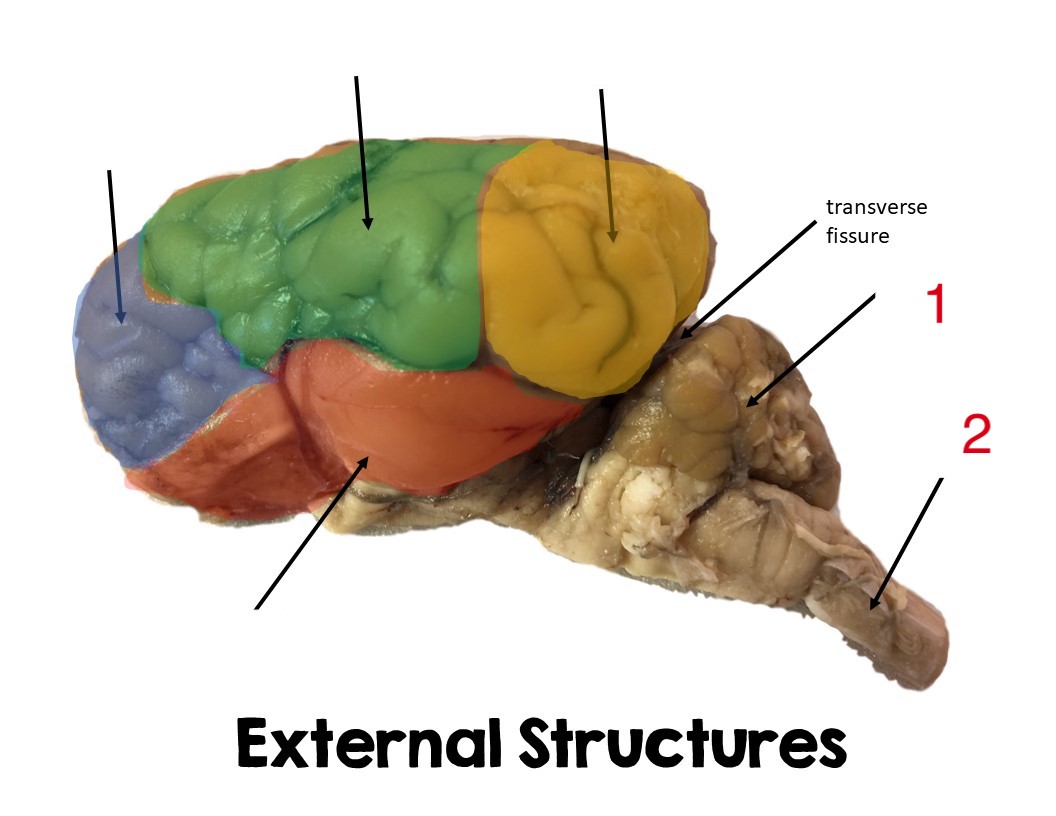
temporal lobe
red
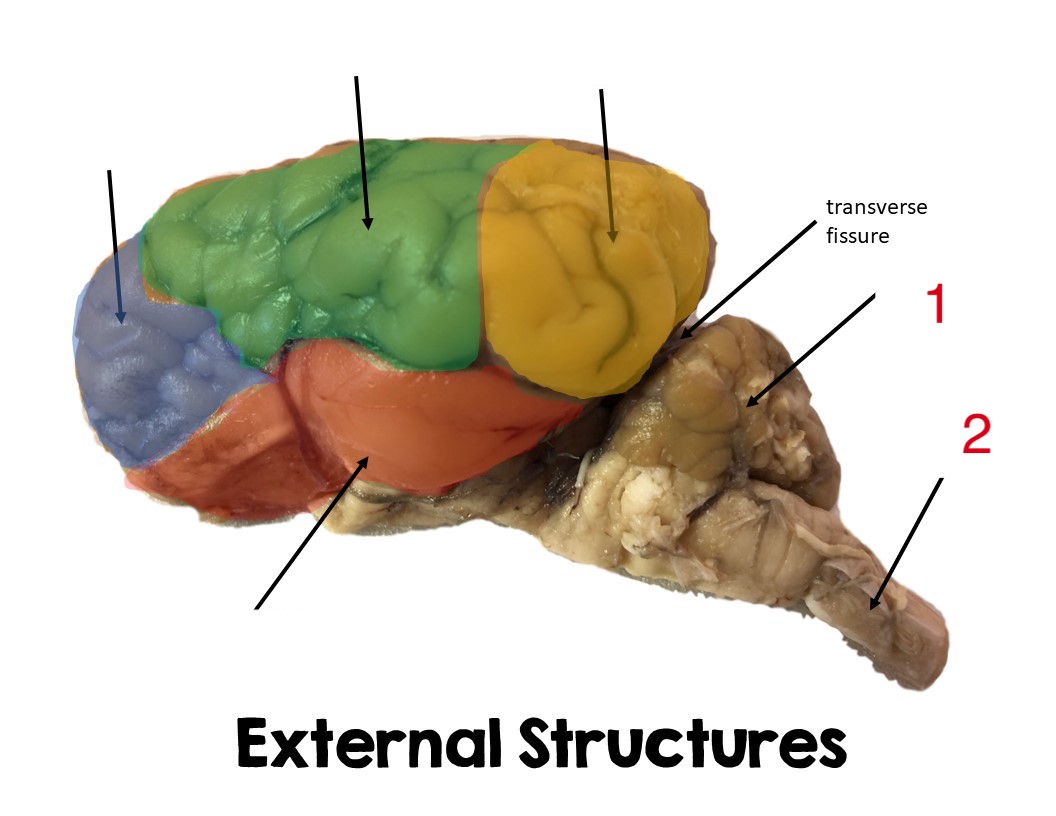
frontal lobe
blue
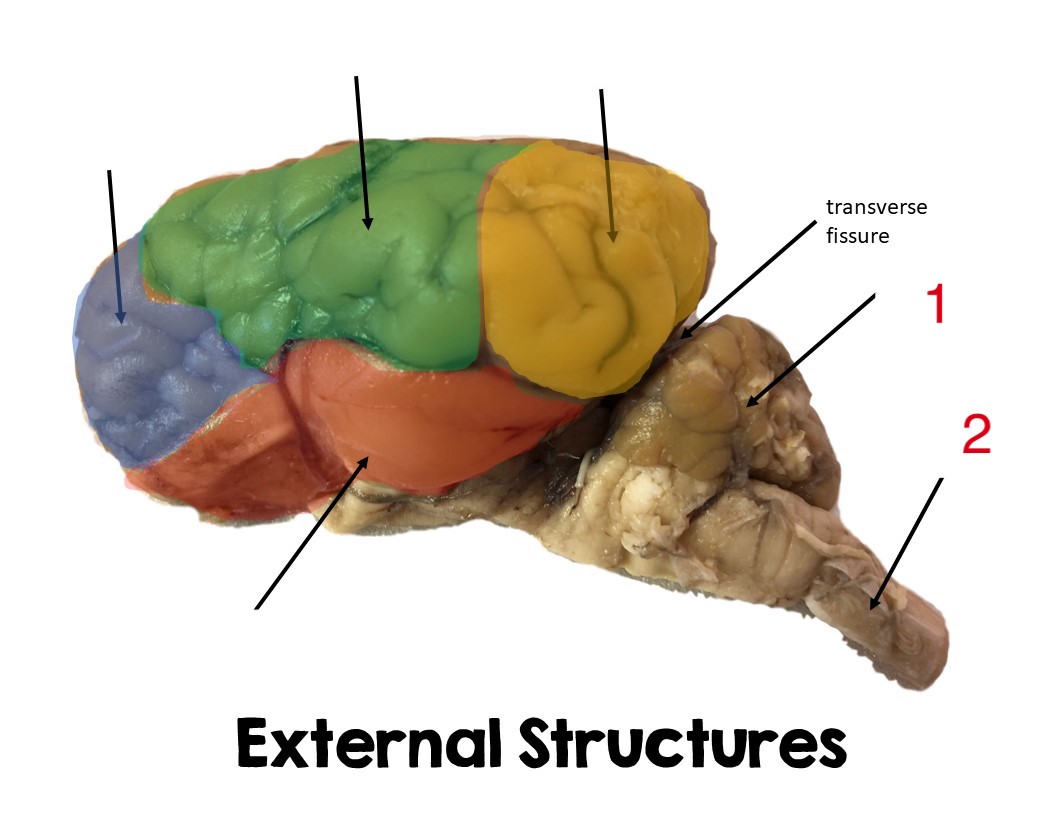
cerebellum
1
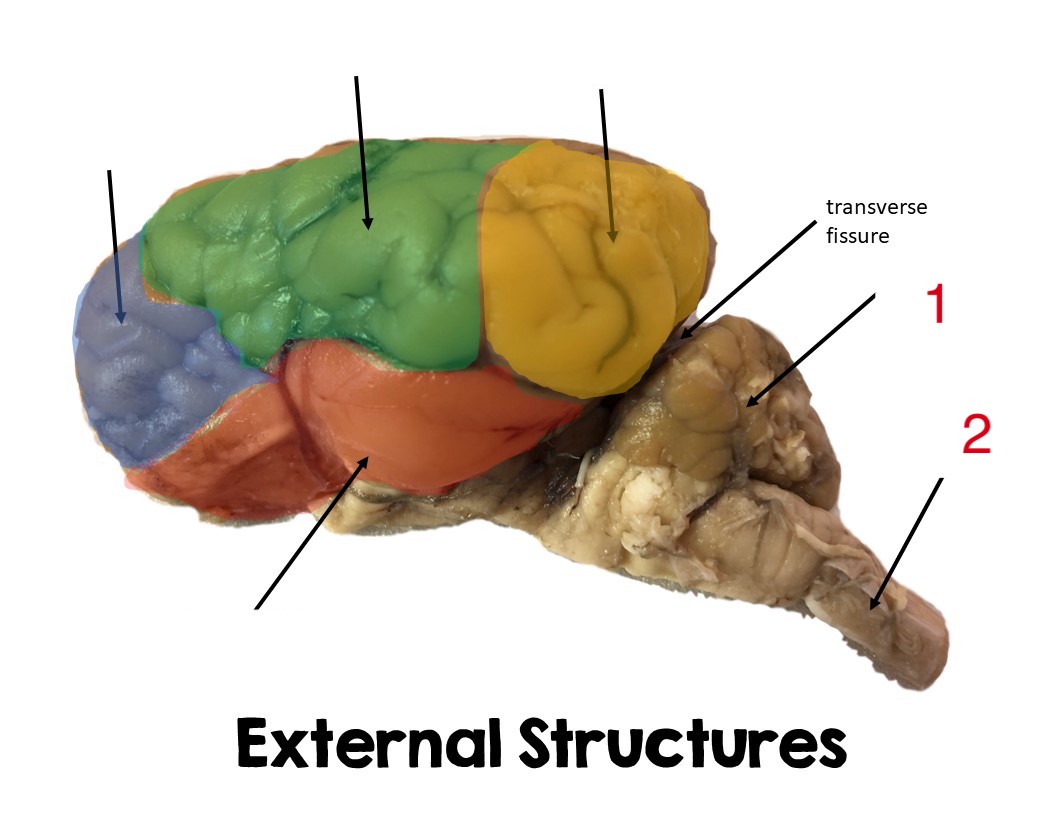
Spinal cord
2
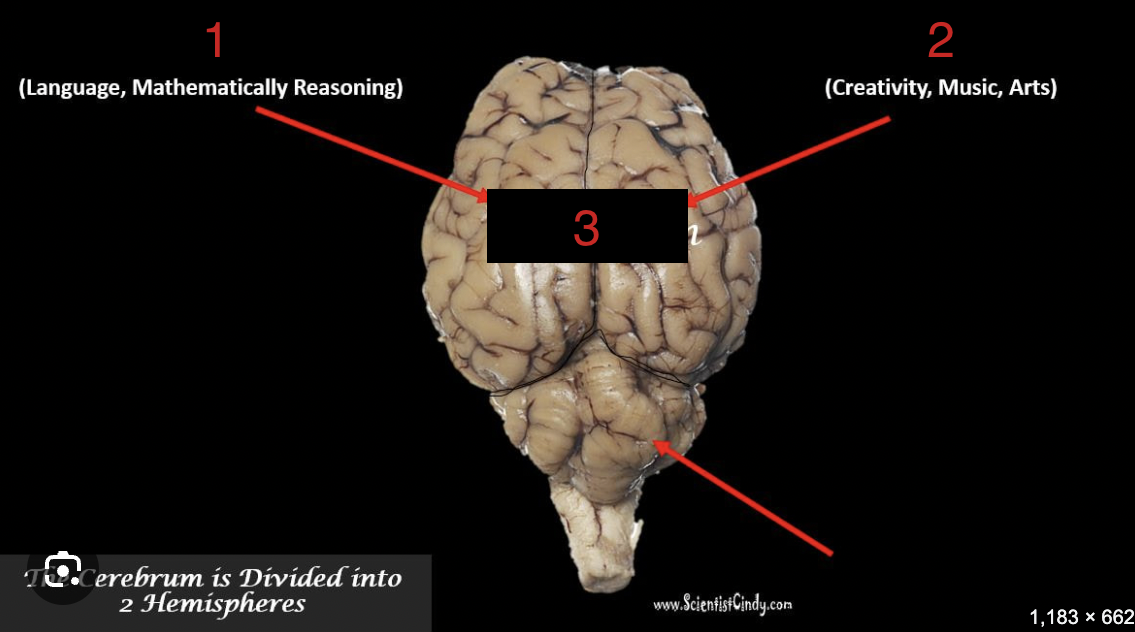
left hemisphere
1
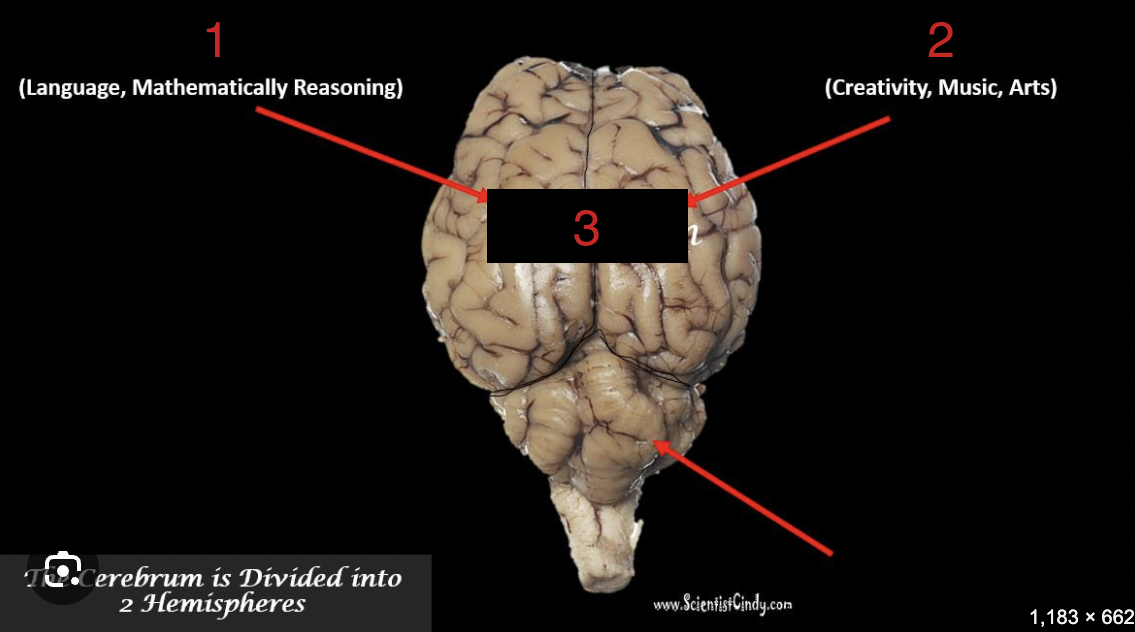
Right hemisphere
2