Hildebrant - AP Human Geography Unit 2
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
population distribution
The pattern in which humans are spread out on Earth's surface
Eurasia
the land mass formed by the continents of Europe and Asia; holds nearly 70% of humanity
Ecumene
the portion of the Earth with permanent human settlement
Population Clusters
Heavily populated areas of the Earth; East Asia, South Asia, Europe, Southeast Asia.
Megacity
City with more than 10 million people
Metacity
A city with a population over 20 million
developed country
a modern, industrialized country in which people are generally better educated and healthier and live longer than people in developing countries do
developing country
A country that has low industrial production and little modern technology
Snow Belt
States located in the northern and midwestern parts of the country
Sun Belt
U.S. region, mostly comprised of coastal areas and southeastern and southwestern states, which has grown most dramatically since World War II.
Rust Belt
northeastern and Midwestern states of US in which heavy industry has declined....leaving behind the closed and rusty factories....
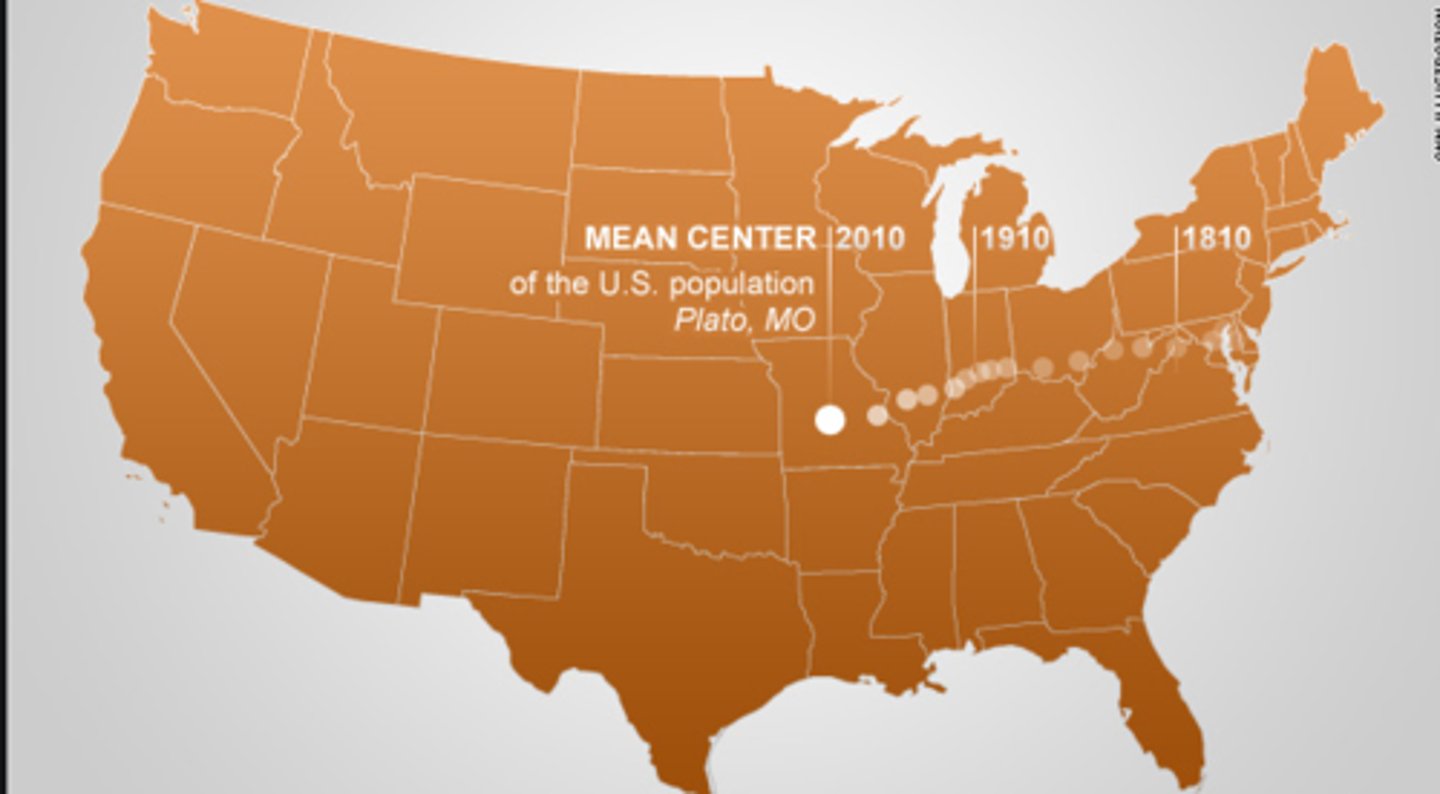
mean center of population
over time, the central point of population in the US shifted to the West as settlers migrated in larger and larger numbers away from the east coast
population density
The number of individuals in an area of a specific size
arithmetic (crude) density
The total number of people divided by the total land area.
Physiological Density
The number of people per unit of area of arable land, which is land suitable for agriculture.
Agricultural Density
The ratio of the number of farmers to the amount of arable land
carrying capacity
The largest population that an area can support on a sustainable basis
human well-being
the state of being comfortable, healthy, or happy.
malaria
A disease caused by mosquitoes implanting parasites in the blood.
population composition
Structure of population in terms of age, sex and other properties such as marital status and education
age structure
Percentage of the population (or number of people of each sex) at each age level in a population.
US Census
*A government count of the people conducted every 10 years (1980, 1990, 2000, etc.)
*Required by Article I of the U.S. Constitution for the reapportionment of representatives among the states in the House of Representatives
dependency ratio
The number of people under age 15 and over age 64 compared to the number of people active in the labor force
youth dependency ratio
The number of young dependents in a population (usually people younger than 15 years of age) that every 100 working-age people must support
elderly dependency ratio
The number of elderly dependents in a population (usually people older than 64 years of age) that every 100 working-age people must support
generation
A group of people born around the same time; similar cultural and societal influences
GI Generation (Greatest Generation)
people born before 1924; came of age during Great Depression; fought in WW II
Silent Generation
1924-1945; frugal, "waste not, want not", Korean War, Civil Rights Movement
Baby Boomer Generation (1946-1964)
Post WW2 through mid 1960s spike. Peaked in 1957. Defined by America's need to accommodate growing families and the spike in suburbia. The baby boomer generation also grew up in the backdrop of the Civil Rights Movement, the Cold War, the Vietnam War, the moon landing and the 1970s.
Generation X (Gen X)
1965-1980. came of age in an environment that is more tolerant of religious, cultural, and ethnic differences.
Generation Y (Millennials)
the largest generation in the US..... As a group, they are better educated than any generation before them, but they have also been hobbled by financial crises, including the Great Recession of 2007-2009. They seem wary of Wall Street and have delayed pursuing the "American dream": owning a home, getting married, having kids, finding a good job, and investing in a retirement account.
Generation Z (Gen Z)
Generational cohort of people born between 2001 and 2014. Also known as Digital Natives because people in this group were born into a world that already was full of electronic gadgets and digital technologies, such as the Internet and social networks.
sex ration
The ratio of the number of men to number of women in a population
Androcentrism
A phenomenon in which a culture demonstrates a marked preference for males (India & China)
infanticide
act of killing an infant
Population Pyramid
A bar graph representing the distribution of population by age and sex.
demographic equation
The formula that calculates population change. The formula finds the increase (or decrease) in a population. The formula is found by doing births minus deaths plus (or minus) net migration. This is important because it helps to determine which stage in the demographic transition model a country is in.
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The total number of live births in a year for every 1000 people alive in the society.
low birth rate
A crude birth rate between 10 and 20 births per 1000 people
transitional birth rate
A crude birth rate between 20 and 30 births per 1000 people
high birth rate
A crude birth rate of more than 30 per 1000 people
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children a woman will have throughout her childbearing years. (from age 15 - 49)
replacement fertility rate
The average number of children needed to replace both parents and stabilize population over time
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
The total number of deaths in a year for every 1,000 people alive in the society.
gender roles (sex roles)
patterns of work, appearance, and behavior that a society associates with being male or female
Infant Mortality Rate (IMR)
The total number of deaths in a year among infants under one year of age for every 1,000 live births in a society.
child mortality
Deaths of children under five years of age
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
The difference in births and deaths in a population, usually expressed as a percentage; does not take into account migration into or out of an area.
Zero Population Growth (ZPG)
When a country has the same number of births and deaths in a given year, its RNI is zero
doubling time
the time required for a population to double in size
Rule of 70
A tool for calculating the doubling time of a population by dividing 70 by a country's rate of natural increase (RNI)
Epidemiology
Branch of medical science concerned with the incidence, distribution, and control of diseases that affect large numbers of people.
pestilence
a fatal epidemic disease
degenerative diseases
Diseases that cause further breakdown in body cells, tissues, and organs as they progress
Malthusian Theory
focuses on how the exponential growth of a population can outpace the arithmetic growth of the food supply and lead to social degradation and disorder
cornucopian theory
a theory positing that human ingenuity will result in innovations that make it possible to expand the food supply
carrying capacity
the largest population that an environment can support at any given time
antinatalist
Policies that discourage people from having children (China's One Child Policy)
Pronatalist
a government policy that encourages or forces childbearing, and outlaws or limits access to contraception
4-2-1 family structure
A family structure that consists of 4 grandparents, 2 married adult children, and one child
women's empowerment
The increased autonomy of women to make choices and shape their lives
Women's status
The degree of equality between men and women with respect to access to and control over both physical and social resources in the family, community, or society at large
median age
the age at which 50 percent of a population is older and 50 percent is younger
life expectancy
A figure indicating how long, on average, a person may be expected to live
Mindar
The robot Buddhist priest in Japan
social mobility
the movement between different positions within a system of social stratification in any given society
Ravenstein's Laws of Migration
A set of 11 "laws" that can be organized into three groups: the reasons why migrants move, the distance they typically move, and their characteristics.
Brain Drain
the loss of highly educated and skilled workers to other countries
Brain Gain
a phenomenon where a country/place gains more educated, young, and skilled people through migration
intervening obstacles
An environmental or cultural feature of the landscape that hinders migration.
intervening opportunities
The presence of a nearer opportunity that greatly diminishes the attractiveness of sites farther away.
guest worker
a person with temporary permission to work in another country
Internal Migration
Migration within a country
The Great Migration
movement of over 300,000 African American from the rural south into Northern cities between 1914 and 1920
Jim Crow Laws
Limited rights of blacks. Literacy tests, grandfather clauses and poll taxes limited black voting rights
Black Belt
The area of the south where most slaves were held, stretching from South Carolina across to Louisiana
forced migration
Migration caused by forces out of one's control, such as disasters, social conflicts, or developmental projects.
refugee
A person who has been forced to leave their country in order to escape war, persecution, or natural disaster
Internally Displaced Person
a refugee within his or her own country
ethnic cleansing
the mass expulsion or killing of members of an unwanted ethnic or religious group in a society.
Repatriation
A refugee or group of refugees returning to their home country, usually with the assistance of government or a non-governmental organization.
diaspora
A dispersion of people from their homeland
rust belt
The manufacturing region in the United States that is currently debilitated because many manufacturing firms have relocated to countries offering cheaper labor and relaxed environmental regulations.
ecumene
The proportion of the earth inhabited by humans.
US Congressional reapportionment
conducted every 10 years in response to the decennial census