Exam 2 OChem 2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Electron Donating substituents (EDG):
H, CH3, -OCH3, NR2
Electron Withdrawing substituents:
CN, Ketones, Esters, NO2, SO3H
Electron donating substituents are
ortho-para directors
Electron withdrawing substituents are
meta directors
Is the diene a nucleophile or an electrophile?
nucleophile; electron rich
Is the dienephile a nucleophile or an electrophile?
electrophile; electron poor
Sp2 hybridzed means 3 centers of electron denisty. T or F
T
How to determine non aromatic molecules?
if not in a “ring” or if double bonds are not connected
How to determine aromatic molecules?
Pi*e=4n+2, planar (more stable), n=2,6,10
How to determine anti aromatic molecules?
Pi*e=4n, non planar, n=0,4,8
Steps to do EAS mechanism:
generate good electrophile
have electrons (from double bond) grab onto floating halogen; may need to draw resonace structure
remove bond and have base (need to create it) remove hydrogen (regains pi bond)
final product
What does reagent Zn —> HCl do?
put an amine (NH2) on a benzene; have to go through nitation first
What reagent initiates nitration?
H2SO4
What does H30+ do?
remove blocking group (dil. H3O+) and adds OH
What does Zn(Hg) —> Cl do?
reduces ketones
The 1,4 addition is
the most stable, thermal product (100 degrees celcius), bromine on least substituted side
The 1,2 addition is
least stable, kinetic product, bromine on most substituted side of the double bond
What does the reagent SOCl2 do?
turns aldehyde into an acyl hailide (replaces OH with Cl)
What does reagent Br2; FeBr3 do?
adds bromine to benzene
What does reagent SO3; H2SO4 do?
sulfuric acid blocking group
What does reagent CO2 —> H3O+ do?
reacts with grignards to make carboxylic acids
What does reagent H2; Pt do?
reduces alkenes
Nitration must occur before a amine (NH2) is added. T or F
T
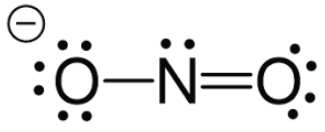
How do you get this electrophile? (Nitration)
Use H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) to protonate OH group on NO3 molecule to make water; push out arrow to make H2O the leaving group