A3 - Quantitative indicators for energy, water and raw material use
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Definition drying of food products
Removing water from a solid or liquid feed by using (hot) air
Examples of food driers
Cabinet (tray) driers or belt driers
For vegetables, fruit products, breakfast cereals
Bin driers
Grain
Heated air is forced upward through the mass.
Moisture is removed gradually from bottom to top.
Slow but cost effective
Spray drying
From liquid to powder
Milk powder, instant coffee
Fluidized-bed driers
Peas, sliced vegetables, grains, powder.
Hot air is blown through a perforated bed, causing the particles to become suspended and behave like a fluid.
Freeze drying
Chicken meat or mushrooms for dry soup mixes.
Freeze → lower pressure → water to gas.
What foods are produced by spray drying?
milk powders
Instant coffee and tea drinks
Powdered egg product
Cheese powders
Soymilk powder
It is important for these powers that when they come in contact with water that they solubilize and become the original product again.
Separation
Can be done by centrifugation
Liquid/liquid separation
Liquid/Solid separation
Liquid/liquid/solid separation
Types of membrane filtration
From largest to smallest pores:
Microfiltration
Ultrafiltration
nanofiltration
Reverse Osmosis
W – Wise
M – Monkeys
C – Can
P – Paint
B – Beautiful
S – Scenes
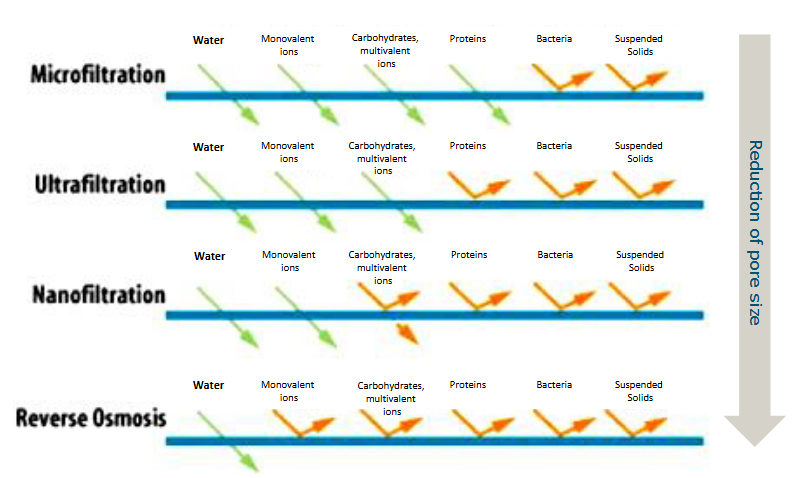
What is ultrafiltration?
Removal of macromolecules from water
Retention/rejection for proteins high, retention/rejection for small molecules low.
Relatively low pressure and high fluxes.
Permeate recovery
Flow of the permeate relative to the feed.
Says something about flow
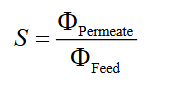
Rejection coefficient
R = 0 → component permeates freely through the membrane
R = 1 → component is completely retained by the membrane
R is different for different components.
Says something about concentration
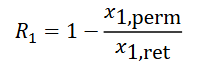
Removal of low-molecular weight components from water
Desalination
Water treatment
Concentration
Dealcoholizing
Flux and retention determined by membrane
Pressure-drive process, moderate cross-flow velocities.
Retentate vs Permeate
Permeate goes through membrane, and retentate does not.