MIB- Lecture 8 - 7/11 - Intracellular trafficking and survival
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
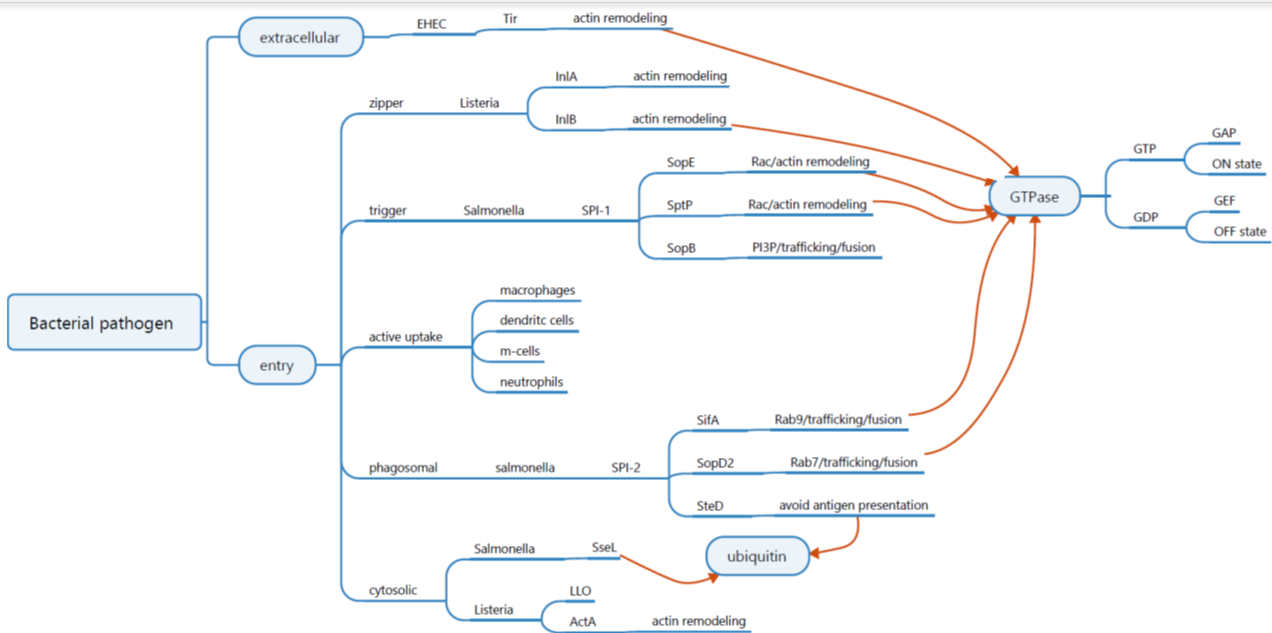
EHEC
pathogenic strain of e. coli → entero-haemorrhagic E. Coli
causes gastro-intestinal disease with bloody diarrhea
Epithelial cells are changed upon infection
loss of microvilli
Locus of enterocyte effacement (LEE) → encodes for type III secretion system
intimin (adhesin) → binds Tir receptor
Translocated Intimin Receptor (Tir) → inserted via type 3 secretion → phosphorylated;
recruits cytoskeleton proteins
nucleation of actin fibers
pedestal is formed
EHEC wants to adhere to epithelial cells, washed away less easily
function T3SS
needle like-complex → inserts proteins into host cell
It secretes effector proteins → directly from bacterial cytoplasm in the cytoplasm of the host
Effector proteins: interfere in host-cell processes → signal transduction cascades (virulence factors)
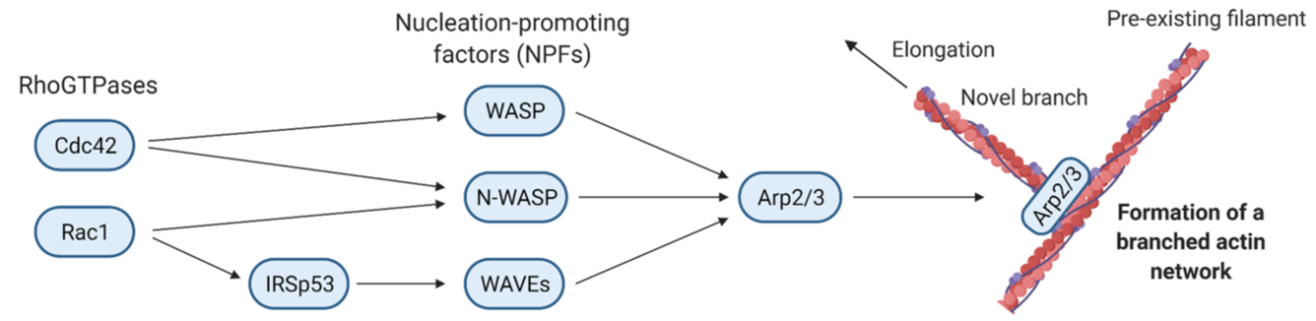
Actin polymerization via NFPs
NFP= Nucleation promoting factors → WASP, N-WASP, WAVEs
Activated by the small GTPases CDC42 and Rac1
The NPFs activate Arp2/3 which results in the formation of a branched actin network
Tir interacts with ISRp53 → bypassing required host signalling. this results in actin being able to be made, resulting in the pedestal being formed
advantages and disadvantages of life on the inside of cells
Advantages
Shielded from humoral antibodies
Less competing bacteria for the same resources
disadvantages
Endocytosed bacteria are on route to the lysosome
Iron limitation
Antigen presentation on MHCII
in close contact with innate immune receptors
Salmonella and the 2 different pathogenicity islands
T3SS used to inject molecules into host to induce uptak
then the salmonella will enter in a vacuole
avoid degradation
avoid recognition
salmonella has 2 different type 3 secretion systems (needs both)
Two pathogenicity islands → SPI-1 and SPI-2
Spi-1
Encodes for several bacterial proteins for secretion system and effector protein
Effectors translocate into host cells to mediate triggered bacterial uptake
Spi-2
Encodes for several bacterial proteins for secretion system and effector protein o
Effectors trans-locate into host cells to mediate intracellular survival
molecular pathway how Salmonella enters the host cell
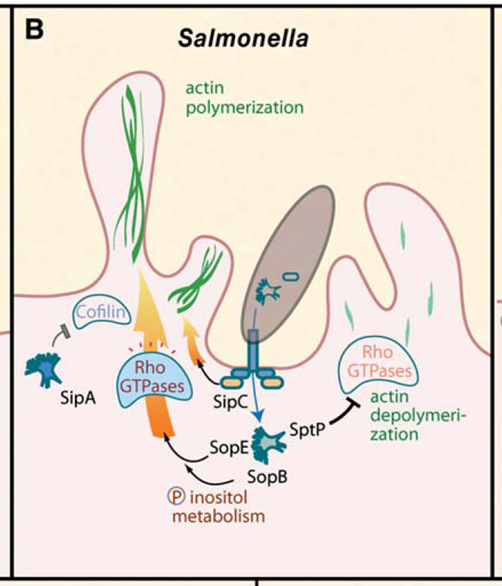
SopE: Activates Rho GTPases directly (like Rac1 and Cdc42), which drive actin polymerization. This process forms protrusions on the host membrane, facilitating bacterial entry.
SipA: Stabilizes actin filaments to strengthen these protrusions.
SopB: activates GTPases indirectly via inositol phosphate metabolism, further modifying the actin structure.
when inside SopE is inactivated by SptP
Small GTPases
molecular switches that can be on or off
On actin there are Ras-like proteins → Rho
Ras-like proteins can be swithed on and of by GTP → it is on when it is bound by GTP
GAP= GTPase de-activating protein → switched it of by releasing the GTP (changing GTP to GDP) from the protein
GEF= guanine exchange factor → Switches the protein on by binding GTP
NPF = nucleating promoting factor → is a ras-like protein and can be switch on and off → it is functional when it is switched on
NPF only on when GTPase is in on phase
explain the roles of SopE and SptP in entering the host cell
Spi-1 entry into cells via actin polymerization → regulated by SopE
SopE is a GEF → switches on → actin polymerization
SopE is regulating the activation of the NPF → switching it on results in the actin formation for cell entry
you also need to turn SopE off otherwise the cell would die
SptpP turns the NPF off
SopE and SptP are injected simultaneously → so what regulated this?
SopE has higher affinity, they both compete for the same protein. Because SopE is switched off earlier (has a shorter half life) it can do its job and then it dies off and SptP can do its job
Spi-1 effector sopE is selectively degraded because it contains lysines → it is degraded by ubiquitination → so the actin polymerization is inhibited
SopE turn on is activating the actin polymerization - SptP inhibits the actin polymerization
Salmonella containing vacuole
Salmonella secretes SopB → positive feedback loop
SopB activated PtdIns3P which activates Rab5
SopB → recruitment of Rab5 and production of PI(3)P this is an early endosomal phosphoinositide
Without Rab5 and PI(3) → no progression to late endosome
being an early endosome is not ideal for long term →
type 3 secretion only activated when it is acidified
lower pH needed for second secretion system
salmonella avoiding degradation, Salmonella SPI-2
Salmonella needs to fuse with lysosome → there are a lot of things that degrade in this
SPI-2 is activated at an acidic pH
SPI-2 secreted effectors regulate membrane recruitment containing vacuole for growth nutrients and avoidance of degradation -
SPI-2 secreted effector down regulate MHCII to prevent detection
SPI-2 encodes a Type III secretion system → required for the survival in epithelial cells and macrophages
How does salmonella avoid degradation, Rab 5, 7 and 9
Salmonella interferes with transport route to the golgi of the lysosomes
Rab9 → the function is transport proteins from the trans golgi network to late endosomes
Rab9 is essential for delivery of cathepsins to lysosomes from the Golgi
Cathepsins are proteases responsible for protein degradation in lysosomes
Salmonella SifA binds and thus inactivates the proteins SKIP and Rab9(GTP) → reducing lysosomal degradation
intracellular trafficking
Early to late endosome → Rab5
Late endosome to lysosome → Rab7
FYCO1 and RILP are Rab7 effectors regulating lysosome formation
Salmonella SopD2 binds with Rab7 (then FYCO1 and RILP can not bind anymore) effector recruitment → no lysosomes can be formed
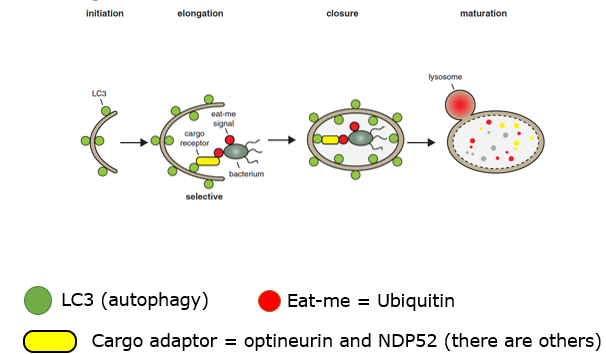
how is autophagy prevented - salmonella
salmonella is flagged with ubiquitin
autophagosome is formed, this autophagosome is tagged with LC3 → surrounds salmonella and fuses with lysosome to degrade it
Salmonella escapes this by secreting SseL → this enzyme removes ubiquitin → preventing the autophagy
Avoiding recognition (salmonella)
MHC-II antigen presentation → causes the recognition of Salmonella
Avoiding recognition: Salmonella SPI-effector SteD (protein) reduces surface MHC-II
It activates MARCH8 and this adds ubiquitinate to MHC-II and causes the degradation
Listeria monocytogenes
gram positive bacteria causes listeriosis. symptoms; fever, muscle pain, headache, stomach - gastrointestinal problems
It can grow and reproduce itself inside the host cells → virulent foodborne pathogens
Efficient in placental invasion and fetal infection
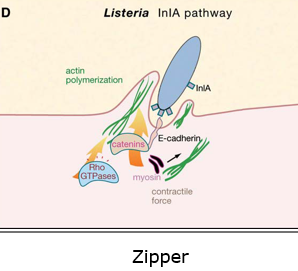
It uses Zipper to enter the host → via host surface proteins
Internalization and spread of listeria monocytogenes
It enters via zipper mechanism; uses receptors on host cells to enter → InIA and InIB trigger endocytosis
InlA important for the internalization of listera via E. cadherin
First it ubiquitinates E-cadherin
It recruits Clathrin mediated machinery → so it can start endocytosis
Then it remodels actin via Arp2/3 and endocytosis starts
InlB is important for the internalization of Listeria via Met receptor
expressed in brain and placenta
It ubiquitinates the Met receptors
It recruits Clathrin mediated machinery → so it can start endocytosis
Then it remodels actin (Arp2/3) and endocytosis starts
LLO (produced by listeria) → allows listeria to escape vacuole into host cell cytosol. listeria makes ActA → recruits Arp2/3 → produces actin polymerization → tail behind bacteria → bacteria propel through cytoplasm → listeria is pushed into neighbouring cells
Escape into cytosol advantages and disadvantages
advantages;
shielded from humoral antibodies
less competing bacteria for resources
nutritional heaven
disadvantages
autophagy
innate immune system
How does Listeria avoid lysosomal degradation (escape from phagosome)
secretion of LLO, a pore forming protein
secretion of bacterial phospholipase A and B (PlcA, PlcB)
LLO makes pore in membrane needs cholesterol, bacteria also have a membrane, bacteria are not a target because they do not have cholesterol
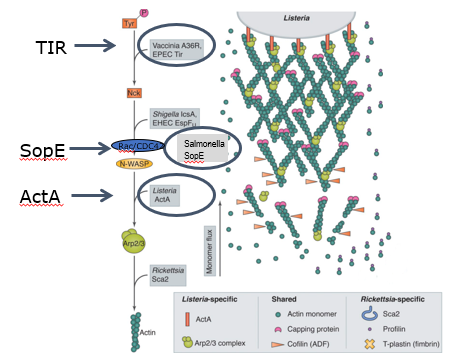
how do salmonella, EHEC, listeria all manipulate ARP2/3 complex
TIR → important for initiating actin polymerization at the site of bacterial entry
SopE (salmonella) → activates Rac/CDC42 signaling pathway → leads to actin polymerization via N-WASP → drives internalization of salmonella
ActA (listeria) → this protein produced by listeria mimics WAVE complex → activating ARP2/3 → leads to actin polymerization
m marinum also uses actin tails to spread around cells
Escape autophagy - Listeria
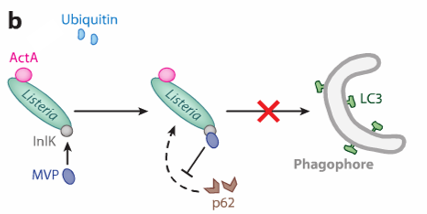
Listeria prevents the binding of autophagy adapter molecules
InIK (produced by listeria) binds MVP (major vault protein) this prevents the recruitment of autophagy adaptor proteins (P62). no recruitment. no formation of phagophore
p62 is necessary to link ubiquitinated pathogens to autophagic machinery (LC3 protein) for degradation
overview slide