SOC150 Final
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What is evaluating research?
approaching it w own terms + asking questions
(eg: Does this researcher accomplish what they say their goals are? Does the researcher justify the methods they used? Do the claims, or arguments, the research makes match the evidence that they present? Are they transparent about the relative strengths and limitations of their project?)
Social Location Bias
tendency to perceive and interpret the world based on own social position
(eg: Prof. Tanaka thinks oldest siblings are burdened w more responsibility as children, making them better leaders and more attuned to others’ emotions… she is an older sibling)
Reflexivity (a way to combat social location bias)
acknowledging how social location affects ones vision of the world; practice of critically examining one's own role in the research process
authors of most ethnographic work will divulge their social location + discuss how they attempted to account for potential bias
Scientific Methods (a way to combat social location bias)
example of application:
In Born to Rebel (1996), Sulloway used statistical analysis of historical data to argue that firstborn children are more likely to be conservative and identify with authority, while laterborn children are more likely to be liberal and rebel against authority.
He argued that birth order is more important than sociological groupings like gender, race, class, and age in predicting people’s social attitudes.
BUT in a 1999 article, Freese, Powell and Carr pointed out that Sulloway’s data is limited to famous historical figures (white, upper-class males) + that societal structures were based off on gender, social class, race, rather than birth order
Population
cluster of ppl that you are interested in
Sample
cluster of ppl from which you gather data
Probability Sampling (a sampling strategy)
where all ppl in population hv equal chance of being chosen for sample
allows researchers to make claims abt larger populaions w/ confidence
Non-probabiity Sampling (a sampling strategy)
where ppl chosen for sample are not random- not equal chance for each person to be chosen
allow researchers to make theoretical contributions (not claims abt populations)
Operationalizing dichotomously
measurement can only hv 2 values
(eg: Freese operationalized birth order dichotomously w/ 2 values: firstborn or laterborn (decided to exclude only children and those with step- or half-siblings because they compromise the analysis)
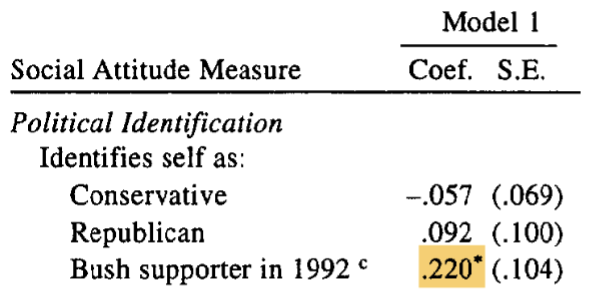
Regression (statistical technique)
studying linear relationships among variables
coefficients represent relationship between ind. (X) + dep. (Y) variable
Positive coefficient = as X increases, Y increases.
Negative coefficient = as X increases, Y decreases.
eg: (in picture) pos. coefficient supports hypothesis that first borns are more conservative; neg. doesn’t support
in Model 1, authors find that firstborns are not more likely to identify as conservative, but they are more likely to identify as a Republican/Bush Supporter.
Statistical Significance
likelihood that relationships would be caused by something other than chance
P-Value (represents statistical significance)
statistical measure of probability that a reported result happened due to chance (ie: probability that they isn’t a relationship betw. variables + probability that null hypothesis is correct)
expressed in numbers: 0.10, 0.05, 0.01 → 10%, 5%, and 1% likelihood that relationship between variables happened due to random chance
lower p-value = lower likelihood that observed relationship happened due to random change
higher p-value = research failed to rej. null hypothesis
when p < 0.05 (5%), data considered statistically significant
results presented in research paper w/ asterisks (*) besides number = statistically significant (will show at bottom of table what asterisks mean; often *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001) no asterisk = p > 0.05, not statistically significant)
Confidence Intervals (can be shown thru p-values)
level of certainty that relationship is not due to random chance
Models (bivariate, multivariate analysis)
Bivariate Analysis: relationship betw. 2 variables
Multivariate Analysis: relationship betw. many diff variables @ same time
Control Variables
something that is held constant so the relationship between the main variables can be observed more clearly + eliminate its effect frm consideration
Being a responsible consumer of research
think abt what info has been provided to you when assessing social scientific findings (source? study funding? how do media outlets report findings of research?)
scholarly journal article: will get a lot of information about research process
BUT a discussion of social scientific research in a popular magazine or newspaper: probs won’t find same level of detailed info
Polling Methodology
usually incl. methodology (before polls that don’t!)
(in picture) highlighted text means that true value in pop. is within ±3.1% of values stated in poll (eg: if poll found 5% of voters are Green, true value is somewhere in betw. 1.9% to 8.1%) + confidence level 19/20 (95%, p < 0.05) means that 19 out of 20 times the true population value would fall within margin of error
data weighted according to census data

Margin of Error
statistic expressing the amount of random sampling error in the results of a survey
Weighted Sample
a sample where each unit is assigned a weight to adjust for sampling bias
Survey Research
(quantitative method) researcher presents a set of predetermined questions to an entire group/sample of individuals
useful when researcher wants to explain features of very large grps
quick way of gaining general details abt population of interest to prepare for more in-depth study using more time-consuming methods
Strengths/Weaknesses of Survey Methods
Strengths: cost-effective, generalisable, high reliability, versatility
Weaknesses: inflexibility, validity
Cross-Sectional Survey
showing a snapshot of what’s happening @ one point in time
Longitudinal Survey
tracking change over time
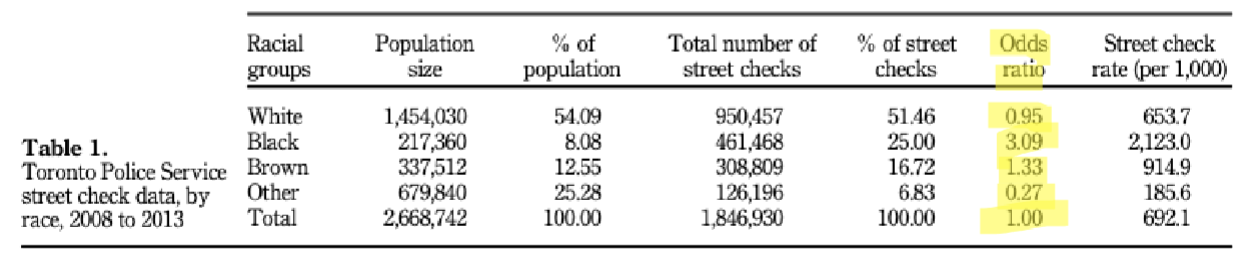
Odds Ratio
odds of an event happening in one grp compared to it happening in another grp
odds ratio > 1.00 means more likely for an event happening in one grp than in total population (eg: (in picture) black ppl 309% more likely (3.09x) to be stopped by police than total population)
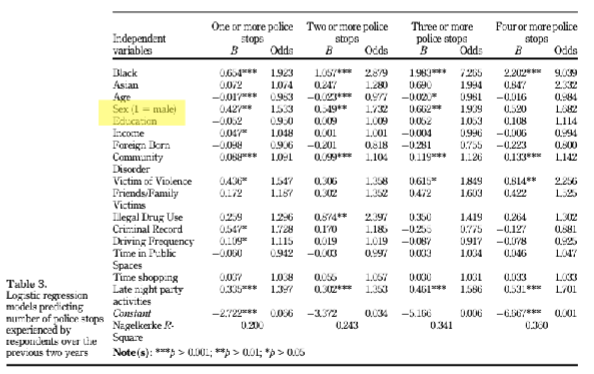
Logistic Regression
statistical method that uses 1+ social variables (e.g., age, education, income) to find probability of a yes/no outcome (e.g., votes vs. doesn’t vote)
expressed as odds ratio
Dummy Variables
possible outcomes coded in binary terms as either 0 or 1
eg: authors note that for sex, 1 = male (meaning they used 0 to represent female, the reference group; results for sex represent men compared to women)
Systemic Racism
patterns of behaviour, policies or practices that create and maintain the power of certain racial groups over others, or reinforce the disadvantage of certain racial groups
Experiment
method of data collection designed to test hypotheses under controlled conditions
Breaching Experiments
consciously breaking everyday social norms + observing other ppl’s reactions to them
Harold Garfinkel theorized that there are everyday, implicit understandings that govern social behaviour, but ppl hv trouble naming those understandings bc they are taken for granted
eg: facing the back of the elevator, haggling over prices @ the grocery store
experiments should NOT break a law, offend anyone, or endanger yourself/others in any way.
Social Desirability Bias
tendency to underreport behaviours that respondents think they will be looked down on + overreport behaviours that they think will make them look good
experiments are better at preventing social desirability bias than surveys
Classic Experiments (+ its key features)
tests effect of a stimulus by comparing experimental grp (exposed to stimulus) + control grp (not exposed)
3 Key Features: independent/dependent variables, pretesting/posttesting, and experimental/control groups.
Lec 9: Experiments (case studies)
The Doll Test (Mamie + Kenneth Clark (1947))
black + white children given white + brown skinned dolls; were asked which doll they wanted to play with + which one was ‘good’ / ‘bad’ + which doll looked most like them
found that most children preferred white doll to black one, some children would cry + run out of the room when asked which doll looked most like them
doll test used in US Supreme Court case Brown v. Board of Education, which overturned “separate but equal” schools
replicated in 2020; researcher found that even Black girls in a racially diverse preschool showed strong preferences for non-black dolls
observational study! (more natural)
Audit Study (Oreopolous (2011))
resumes w/ English, Chinese, Pakistani, and Indian sounding names were sent to over 3000 real job openings
applicants w/ Asian names, Canadian experience + education = 28% less likely to get a callback than Anglo names, Applicants with Asian names, foreign education + experience are 62.5% less likely to get a callback
also found that large company employers discriminate less than small employers
Informed Consent
used for ethical research, but some experiments depend on participants not knowing full implications of the research
eg: Stanley Milgram conducted experiments involving 3 ppl:
Experimenter who was in charge of the session
The “teacher”, who was led to believe they were assisting in the experiment, but who was actually the real subject of the experiment
The “learner”, who the teacher was led to believe was the subject of the experiment.
“teacher” was told that the experiment was about whether the threat of punishment enhances learning BUT the real experiment was whether the “teacher” would continue to inflict pain on the learner when told to.
study participants traumatised by the experiment- is it ethical to involve ppl in experiments that they haven’t given informed consent for?
External + Internal Validity
External Validity: does stimulus applied to the experimental grp actually resemble the stimuli that ppl will encounter in the real world?
Internal Validity: did stimulus actually produce the observed effect? or was it some other factor?
Field Experiments
blend experimental methods w field-based research; stimulates real-world interactions + relies on real contexts
instead of asking STEM professors to rate CVs, a field experiment would send CVs to actual postdoc openings
Ascribed + Achieved Status
Ascribed: social positions ppl inherit at birth/acquire involuntarily over life course (eg: male, Black, mother, widow)
Achieved: social positions ppl obtain thru their own actions (e.g. university graduate, lawyer, criminal)
Correspondence Studies
audit studies that reply on paper submissions rather than in-person
Blind Hiring
when applicants interview/audition anonymously to hide identifying info abt them
eg: most major orchestras (in the 70-80s) started this process, auditioning behind a screen. Goldin and Rouse (2000) found that when the same people auditioned with and without a screen, the success rate for women in blind auditions was almost always higher than in non-blind auditions.
limitations: due to increasingly professionalized training, there is very little difference in technical skill of top musicians (orchestras should look beyond technical ability, instead to things like their talent as an educator)
Interviews
method of data collection involving 2+ ppl exchanging info. thru a series of questions + answers
questions designed by a researcher to elicit information frm interview participants
open ended questions (qualitative)
The Interview Guide
list of topics/questions that interviewer hopes to cover during course of interview, incl. possible probes for more info.
like a to-do list (so its often called semi-structured interview)
audio is transcribed (turned into a written record of what was said) after the interview
Goal of Analysis
reach conclusions by condensing large amts of data to smaller bits of understandable info
Codes (beginning of analysis)
shorthand representations of more complex set of issues/ideas
Coding
process of identifying codes in ones qualitative data
involves identifying themes across interview data by reading interview transcripts until researcher has a clear idea abt themes has come up across interviews
Open Coding
reading transcripts line by line + making note of whatever categories or themes seem to stand out
Focused Coding
narrowing themes identified in open coding by reading thru notes you made while conducting open coding + identifying related themes
Strengths + Weaknesses of Interviewing

Ethnography (aka Field Research/ Participant Observation)
(qualitative method) observing, interracting w/ ppl in their natural setting
combines techniques frm participant observation, interviewing, analysing documents created by ppl observed
Descriptive Field Notes
notes describing observations as straightforwardly as possible
Analytic Field Notes
notes including researcher’s impressions abt his observations
Researcher Positions
Positionality
researcher’s social location in terms of race, gender, class, sexuality, etc
important bc research can be shaped by researchers potential biases
Strengths + Weaknesses of Ethnography

Mixed Methods
combination of 2+ types of data collection/analysis (qualitative + quantitative)
Mixed data-collection studies
based on 2+ kinds of data (eg: field notes, administrative records) OR 2 means of collecting them (eg: interviewing + controlled experimentation)
Mixed data-analysis studies
use 1+ analytical technique OR cross techniques + types of data (eg: regression to analyse interview transcripts)
Benefits of Mixed Methods
balances breadth + depth (or nomothetic + idiographic approaches)
helps validate research findings through triangulation
compensates for weakenesses of single methods
captures complexity of social life
Statistical Discrimination
occurs when ppl make assumtions abt individuals based on their perception of their grp’s average characteristics (eg: “its not that I hate them, its just that they are more likely to take leave for a religious holiday”)
rationale for racial profiling- still discrimination!!
an ecological fallacy (avoid!!)
Verstehen
(Max Weber) understanding the meaning of social action from the actors pov
by stepping into the shoes of others, we treat actors as subjects, rather than objects.
interpretivist approach
a type of empathy
Feminist Standpoint Theory
Dorothy Smith theorised that bc men + women are in diff positions in society, they hv developed distinct standpoints; to understand + change this, we need to understand ppl’s everyday lived experiences @ micro level
this theory argues that all knowledge is fixed + partial (goes against idea of impartiality in positivist science)
STRENGTH: link betw. theory + practice + the ability to generate a problematic thru everyday lived experience
Ideological Apparatus
set of ideas + beliefs that ruling class use to shape how people think + behave
help maintain social order, making dominance of ruling class seem acceptable/desirable.
Relations of Ruling
(developed by Dorothy Smith) how society is structured thru institutions, often reflecting men’s interest in order to reproduce + legitimise men’s power in society
Problematic
a set of questions dev. frm women’s lived experiences that help us investigate social relations + power structures that shape everyday life
addresses problem of how we are related to society
cannot rely on questions for an understanding of the relationships— our job to investigate this!
Outsider Within
unique standpoint prod. frm being both included + excluded frm a particular social milieu
Recursive Dispossession
a repeated or ongoing process of losing access to resources, power, or rights (gets worse over time)
Talking Circles
participants go around in a circle sharing their answers to questions, incl. researcher!
culturally appropriate, conversational research method
OCAP (Ownership, Control, Access, Possession)
First Nations principles regarding collection, use, disclosure of info regarding first nations
Ownership= relationship of FN to its cultural knowledge
Control= all aspects of info. management (data collection, storage, destruction)
Access= FNs must hv access to their info + be able to make decisions abt access to info.
Posession= physical state/location of data
CARE Principles (rights related to open data for FNs)
Collective benefit
Authority to control data
Responsibility to engage respectfully w/ communities
Ethics to minimise harm + maximise benefit
Relationality
viewing society and ppl as connected bc being in existence means being ‘in relationship’; no one is isolated
in indigenous lens, there is a connection betw. ppl and nature
Axiology
study of values/ judgements in research
What are the problems and potential solutions when it comes to ethical research with Indigenous communities?
PROBLEMS: can harm community + fail to get research findings bc marginalised community has been over-researched
SOLUTIONS: establish trust + rapport w participants, being interviewed by a peer, OCAP, CARE
Audit Studies
when field experiments measure discrimination
Deva Pager found that job applicants had significantly fewer callbacks when they had a criminal record vs no criminal record. Black applicants w/o criminal records got fewer callbacks than white applicants w/ criminal records
race plays a bigger role than criminal record in employment!
formed basis for Ban the Box movement (employers should get rid of box that ex-felons hv to tick on job application abt crim. record)
Exploratory studies (a mixed method)
hypothesis generation and testing
often @ early stages of research, done to test whether they should conduct a more extensive study
Explanatory studies (a mixed method)
finding out why quantitative trends are happening
to explain why particular phenomena work in the way that they do (cause + effects of phenomenon studied)
Triangulation (a mixed method)
cross-checking and strengthening findings
using several/ a combination of different research strategies
Policy intervention (a mixed method)
finding out the impact and lived experiences of social policies
actions undertaken by individuals, organizations, or governments to address social problems and influence social outcomes