Psychology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/212
Earn XP
Last updated 1:53 AM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
213 Terms
1
New cards
1. Psychology (definition)
The study of behavior and mental process( what people do, think, and feel, also be applied to animals)
2
New cards
3. Psychology is a combination of…
Philosophy and science/anatomy
3
New cards
Goals of Psychology
1\. Describe - what is happening(gather information on the observation)
2\. Explain - why (hypothesis and theories are formed as the observation develops more)
3\. Predict - what they will do in future situations
4\. Influence - to find a way to help
2\. Explain - why (hypothesis and theories are formed as the observation develops more)
3\. Predict - what they will do in future situations
4\. Influence - to find a way to help
4
New cards
Wundt – Structuralism
“father of psychology” structure of the mind/parts of the mind used __introspection(thoughts, images, feelings, and sensations)__
5
New cards
James – Functionalism
How the mind works and its functions- did not believe you can measure consciousness - looked at evolution & how it helps develop behaviors that impact function in society(felt that thinking, learning, and other parts of the human mind could only exist because it helps us survive as species)
6
New cards
Psychodynamic -- Freud
to uncover Unconscious thoughts/ desires
* to uncover Unconscious thoughts/ desires, where patients unconscious thouhgts are seen as the main motivation for behavior
* Freudian Slips: Slips of the tongue that reveal unconscious feelings/ desires
* Dream Analysis:desires show up in dreams
* Psychological Problems: Too many emotions build up and lead to mental illness
* to uncover Unconscious thoughts/ desires, where patients unconscious thouhgts are seen as the main motivation for behavior
* Freudian Slips: Slips of the tongue that reveal unconscious feelings/ desires
* Dream Analysis:desires show up in dreams
* Psychological Problems: Too many emotions build up and lead to mental illness
7
New cards
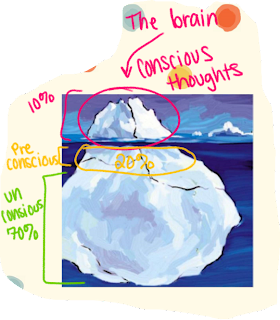
3 levels of consciousness (+ diagram)
1. Conscious - now aware
2. Preconscious - not aware of at the moment, but can remember a few memories
3. Unconscious - totally out of awareness.
8
New cards
Free Association
technique where patients says whatever comes to mind
9
New cards
Behaviorism
(BF Skinner & J.B Watson) observational behavior, behavior is learned through reinforcement( if a behavior is rewarded it would continue) and punishment(if someone is punished for behavior, the behavior will stop) .
10
New cards
Humanistic (self-actualization)
(Abraham Maslow & Carl Rogers) self-actualization, achieving personal growth.
11
New cards
Cognitive (self-talk)
the thought process, conversions you have in your head, and the way you think about yourself or other things(through studying a person’s cognition, psychologist can understand a person’s behavior)
12
New cards
Biological
Physical changes in brain & body(genetics, chemical reactions, hormones)
* looks at the physical aspects of the brain and its impact on behavior
* Seeks to understand how genetics and chemical reactions affect behavior
* Heavy focus on the anatomy of the brain and body
* looks at the physical aspects of the brain and its impact on behavior
* Seeks to understand how genetics and chemical reactions affect behavior
* Heavy focus on the anatomy of the brain and body
13
New cards
Sociocultural
person’s culture, ethnic identity, gender identity to explain behavior
14
New cards
Case study
a detailed study of one individual or group in great detail
15
New cards
Observational studies
laboratory observation: the study of behavior in a controlled situation. Naturalistic observation: watching behavior without interacting with the environment
16
New cards
Surveys
use interviews and questionnaires to gather information about attitudes, experiences, or opinions
pro: great way to get a lot of information in a short amount of time
negative: people can still lie on survey and skew the data
pro: great way to get a lot of information in a short amount of time
negative: people can still lie on survey and skew the data
17
New cards
\n Correlational studies (negative/positive)
A mutual relationship or connection between two or more things.
18
New cards
Correlation Coefficient
Numbers representing the direction(+,-) and strengths of the relationship between 2 variables. (Close to -1 the stronger)
19
New cards
Representative/random Sample
when you are not able to use the entire population, so a representative sample(small group) gives a “snapshot of the population.
20
New cards
Hypothesis
Hypothesis
21
New cards
Independent/dependent variables
Independent variable: what is being changed/manipulated by the researcher
Dependent variable: what is being measured by the researcher.
Dependent variable: what is being measured by the researcher.
22
New cards
Control/experimental groups
Control Group - Group that doesn't get special treatment(no IV)
Experimental group(the one that is being tested): group that received special treatment = IV
Experimental group(the one that is being tested): group that received special treatment = IV
23
New cards
Random assignment
separate participants into groups, assigning participants by a chance to group
24
New cards
Placebo
The placebo effect is when an improvement of symptoms is observed, despite using a nonactive treatment.
25
New cards
Single/double-blind studies
Single-blind(participants do not know there “assignments”)
Double-blind(researcher nor participants know their “assignments' ') students nor persons gathering data know which group is controlling or experimental group.
Double-blind(researcher nor participants know their “assignments' ') students nor persons gathering data know which group is controlling or experimental group.
26
New cards
Longitudinal/cross-sectional studies
Longitudinal - people of same age are studied and studied over a period of time as they grow/develop(longer time to complete takes 15 to 20 years
Cross- sectional: people of different ages examined at the same point in time(shorter period of time usually happens only once.
Cross- sectional: people of different ages examined at the same point in time(shorter period of time usually happens only once.
27
New cards
Informed Consent
Researcher must explain the study to the participants, to what they are agreeing to and have written consent.
28
New cards
Debrief
should be able to discuss the procedure and the finding switch the psychologist, they should be told if they have been divided and given the reason why.
29
New cards
Protection of Participants
CANNOT traumatize the participants, be protected mentally and physically harm.
30
New cards
Deception
Participants cannot be misled or wrongly informed about the aim of the research.
31
New cards
Confidentiality
participant must be kept anonymous, unless told otherwise
32
New cards
Withdrawal
participants should be able to leave a study any time if they feel uncomfortable
33
New cards
Psychodynamic Perspective
1. (belived that personality is formed by experiences in early childhood): **Distinctive and relatively stable pattern of behavior, thoughts, motives and emotions that characterizes an individual**
* **belived that personality is formed by experiences in early childhood**
* **Psychoanalysis = focused on the unconscious because it stores all of our memories, emotions and thoughts which influence our behavior even though we are unaware of them**
* **He believed that traumatic events in childhood force thoughts & emotions into the unconscious mind(free association)**
34
New cards
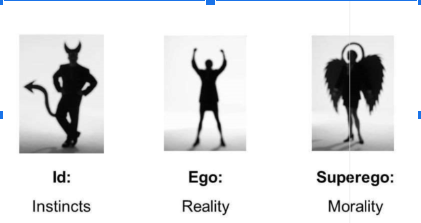
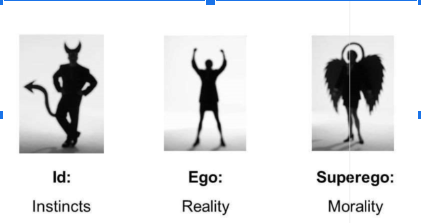
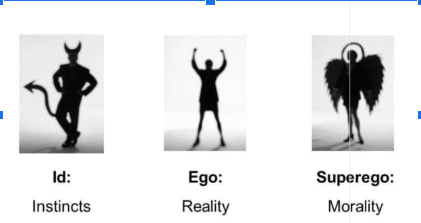
ID
* **Biological drives & demands for immediate gratification**
* **Operates on the pleasure principle - “I want it now syndrome”**
* **Operates on the pleasure principle - “I want it now syndrome”**
35
New cards
Ego
* **Rational, thoughts, decision making aspects of personality(you get to choose what is right and wrong)**
* **Operates in terms of the reality principle and acts as a “compromiser” between the id and superego**
* **Operates in terms of the reality principle and acts as a “compromiser” between the id and superego**
36
New cards
Superego
* **Represents morality and authority**
* **Operates on the moral principle - right/wrong and good/bad**
* **Operates on the moral principle - right/wrong and good/bad**
37
New cards
Defense Mechanisms
(Methods used by ego(conscious self)protect itself against anxiety caused by a conflict between the id’s demands & superego’s constraints - a problem if it causes self-defeating behavior and emotional problems
38
New cards
**Repression**
* **We avoid painful thouhgts by forcing them into the back of your mind(avoid, ignore, backburner)**
* **Ex: …Wintess a murder, not remember the details when asked by police**
* **Ex: …Wintess a murder, not remember the details when asked by police**
39
New cards
**Regression**
* **we retreat to behaving or thinking like a child in order to avoid adult issues**
* **Throwing a temper tantrum when not getting what you want**
* **Throwing a temper tantrum when not getting what you want**
40
New cards
**Displacement**
* **We vent anger against non-threatening people and objects**
* **Ex: Angry at mom, takes out anger on family dog**
* **Ex: Angry at mom, takes out anger on family dog**
41
New cards
**Projection**
* **We ascribe our own unacceptable feelings or behaviors to other people**
* **Ex: You want to break up with bg/gf, accuse him/her of wanting to break up with you**
* **Ex: You want to break up with bg/gf, accuse him/her of wanting to break up with you**
42
New cards
**Rationalization**
* **We try to create logical explanations of our behavior in order to justify it)**
* **Ex:...Want to go to the movies with firdns, so justify goig instead of studying for exams by stating you would have failed anyways.**
* **Ex:...Want to go to the movies with firdns, so justify goig instead of studying for exams by stating you would have failed anyways.**
43
New cards
**Denial**
* **We refuse to receive “reality” in order to protect ourselves from it( If you dont like whats happening in reality, you will deny that it is actually happening)**
* **Ex:...Get rregection letter from college of choice, but still tell everyone you are going**
* **Ex:...Get rregection letter from college of choice, but still tell everyone you are going**
44
New cards
**Sublimation**
* **we energy(negative energy - anger) on prosocial activities in order to avoid undesirable activities**
* **Ex: …Like to hit things to take up boxing as a hobby**
* **Ex: …Like to hit things to take up boxing as a hobby**
45
New cards
**Reaction Formation**
* **we express feelings that are oppsotoe to undesirable ones we feel( opposite of the way we actually feel)**
* **Ex: Really dislikes psychology teacher, but tell everyone how much you love him/her**
* **Ex: Really dislikes psychology teacher, but tell everyone how much you love him/her**
46
New cards
Erik Erikson’s Theory of Psychosocial Development:
Describes the impact of social experiences on our sense of self, stages are cumulative and gradual
47
New cards
**Trust v. Mistrust**
**(1 yr old)**
**= infant require dependable care and comfort**
**= If the baby feels that they receive dependable care and that they can trust the work around them, they will have success in this stage**
**= Success: They learn to trust people**
**= Failure: Parents are neglectful; influence future relationships.**
**= infant require dependable care and comfort**
**= If the baby feels that they receive dependable care and that they can trust the work around them, they will have success in this stage**
**= Success: They learn to trust people**
**= Failure: Parents are neglectful; influence future relationships.**
48
New cards
**Autonomy v. Doubt**
**( 2 yrs)**
**= Child attempts to master physical skills (crawling, walking, running, talking)**
**= success: Leads to self control and confidence**
**= Failure: leads to feeling inadequate**
\n
**= Child attempts to master physical skills (crawling, walking, running, talking)**
**= success: Leads to self control and confidence**
**= Failure: leads to feeling inadequate**
\n
49
New cards
**Initiative v. Guilt**
**(3-5 yrs)**
**= Children need to be assertive in exploration and play(initiative)**
**= if adults crtizicie chidlren for their curisodity at this stage, this may lead to feelings of gult for “being a nuisance”**
**= Success: Feeling capable of leading and making decisions**
**= Failure: can lead to self doubt**
**= Children need to be assertive in exploration and play(initiative)**
**= if adults crtizicie chidlren for their curisodity at this stage, this may lead to feelings of gult for “being a nuisance”**
**= Success: Feeling capable of leading and making decisions**
**= Failure: can lead to self doubt**
50
New cards
**Industry v. Inferiority**
**(6-12 yrs)**
**= Industry - developing a sense of competence at useful skills and tasks**
**= Inferiority - Pessimism and lack of confidence in ability to do well**
**= Child compares themselves to others to develop a sense of achievement**
* **Success = Feeling competent to handle situations later in life**
* **Failure = creates a sense of inferiority**
**= Industry - developing a sense of competence at useful skills and tasks**
**= Inferiority - Pessimism and lack of confidence in ability to do well**
**= Child compares themselves to others to develop a sense of achievement**
* **Success = Feeling competent to handle situations later in life**
* **Failure = creates a sense of inferiority**
51
New cards
**Identity v. Role confusion**
**(12-18 yrs)**
**= Teens must try ti achie a sense of identity**
**= figure out the roles you would like to occupy as an adult**
* **Success= Fidelity = feeling confident enough in your own skin to accept others even if you hve ideological differences**
* **Failure = Repression and role confusion. May experiment with many different roles/lifestyles.**
**= Teens must try ti achie a sense of identity**
**= figure out the roles you would like to occupy as an adult**
* **Success= Fidelity = feeling confident enough in your own skin to accept others even if you hve ideological differences**
* **Failure = Repression and role confusion. May experiment with many different roles/lifestyles.**
52
New cards
**Intimacy v. isolation**
**(18-20 yrs)**
**= Major conflict in this stage of life is from loving, intimate relationships with other people**
**= Important event- romantic relationship**
* **Success= Leads to fulfilling relationships with others**
* **Failure= Feelings of isolation and loneliness**
**= Major conflict in this stage of life is from loving, intimate relationships with other people**
**= Important event- romantic relationship**
* **Success= Leads to fulfilling relationships with others**
* **Failure= Feelings of isolation and loneliness**
53
New cards
Trait Theory
(A tendency to respond in a certain way in many different kinds of situations)
* Trait theories can be applies to everyone and that the trait can be measured
* Trait theories can be applies to everyone and that the trait can be measured
54
New cards
**3 Criteria’s of personality traits**
55
New cards
1. **Consistency**
**Individuals must be somewhat consistent across situations in their behaviors related to the trait. For example, if they are talkative at home, they tend to also be talkative at work**
56
New cards
2. **Stability**
**A trait must also be somewhat stable over time as demonstrated behaviors related to the trait. Ex: talkative at 30, also taltavie at 40**
57
New cards
3. **Individual Differences**
**People differ from one another on behaviors related to the trait. People differ on how frequently they talk and so personality traits such as talkative exist.**
58
New cards
Gordon Alport
( Defined common traits(those that apply to everyone) and Individual traits(those that apply more to specific person)
59
New cards
Cardinal Traits
Characteristics that is so pervasive that the person is almost identifies with that trait. Ex: Oprah = Sociability)
60
New cards
Central Traits
Charaacterisitics that makes us predictable (ways people would describe you…usally 5 to 10 main central traits - ex, Kindness, honesty, friendliness)
61
New cards
Secondary Traits
Characterisitcs that dont have a great impact on us but that show our preferences for different items like food and music(more changeable, ex; shyness, irritability)(less consistent)
62
New cards
Scale
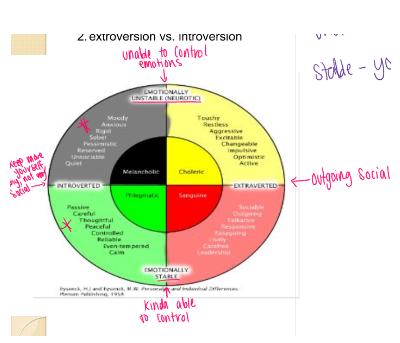
63
New cards
OCEAN theory(the big five)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IB1FVbo8TSs
64
New cards
**O**penness to experience
* **describes people who are open-mided and willing to try intellectual experiences, new ideas or creative experiences**
Oposite is **Resistance** to new experiences…being predictable, conforming and unimaginative
Oposite is **Resistance** to new experiences…being predictable, conforming and unimaginative
65
New cards
**C**onscientiousness
* **Identifies individls who are dutiful, dedicated to completing tasks, organized, and responsible**
Opposite is **Impulisveness…** Includes tendencies such as carelessnness, giving up reality and bring irresponsible
Opposite is **Impulisveness…** Includes tendencies such as carelessnness, giving up reality and bring irresponsible
66
New cards
**E**xtroversion
* **associated with warm talkatviness, and being energetic**
Opposite is **Intoroversion** … being quiet, shy and cautious
Opposite is **Intoroversion** … being quiet, shy and cautious
67
New cards
**Agreeableness**
* **involves being cooperative, kind, trusting and goon-natured**
Opposite is **Antagonism**…being abrasive, iratible, suspicious and jealous
Opposite is **Antagonism**…being abrasive, iratible, suspicious and jealous
68
New cards
**E**motional Stability
* **identities individuals who experience things relatively easily without getting upset**
Opposite is **Neuroticism…** being constantly angry or worried or complaining all the time..tend to look for the bad rather than the good.
Opposite is **Neuroticism…** being constantly angry or worried or complaining all the time..tend to look for the bad rather than the good.
69
New cards
Social(those around you) Cognitive(your thought process) Theory
believed that observational learning, modeling, and thought processes lead to personality(Emphasize the importance of both the influences of other people’s behavior and of a person’s own expectations for learning)
70
New cards
Albert Bandura
* Believed that people mostly learn through imitating models.
* Where the term “role models” comes from.
* Albert Bandura is most famous for conducting the Bobo Doll experiment
* Where the term “role models” comes from.
* Albert Bandura is most famous for conducting the Bobo Doll experiment
71
New cards
Process of Experiment the Bobo Doll
* He had 2 groups of children watch an adult play with a bobo doll
* One adult acted aggressively towards the doll
* One adult was nice playing with the doll
* Children were then let into the room to play with the doll
* Findings:
* He found that children exposed to aggressive behavior acted aggressively towards the dolls.
* What does this tell us about Social Learning Theory and role models? = Observation role models affect our behavior
* One adult acted aggressively towards the doll
* One adult was nice playing with the doll
* Children were then let into the room to play with the doll
* Findings:
* He found that children exposed to aggressive behavior acted aggressively towards the dolls.
* What does this tell us about Social Learning Theory and role models? = Observation role models affect our behavior
72
New cards
Julian Rotter
* focused more on the cognitive process when developing personality.
* Believed that personality was a set of potential responses to situations.
One pattern he looked at was a person’s **locus of control.**
* Believed that personality was a set of potential responses to situations.
One pattern he looked at was a person’s **locus of control.**
73
New cards
**Locus of Control=**
The tendency for people to assume that they either have control or do not have control over events and consequences in their lives.
74
New cards
**Internal locus of control**
* **Assume their actions directly impact their consequences**
* **People with an ILC usually have high achievement/ success**
* **People with an ILC usually have high achievement/ success**
75
New cards
**External locus of control**
* **Believe their fate is controlled by others or luck.**
* **People with ELC usually develop depression and give up easily**
* **People with ELC usually develop depression and give up easily**
76
New cards
Humanistic Theory
* Reminder= Humanists believe that we all strive for self actualization.
* To do this, we develop a self concept to help us get there.
* Self Concept= how we perceive our behaviors, abilities and unique characteristics.
* To do this, we develop a self concept to help us get there.
* Self Concept= how we perceive our behaviors, abilities and unique characteristics.
77
New cards
1. Self Image=
2. Self-esteem=
3. Ideal self=
1. How you perceive yourself
2. How much value, you place on yourself
3. How you wish you were really like
* These can be influenced by the words and actions of the people who are important to us (parents, peers, teachers, etc)
78
New cards
Real Self vs Ideal Self
* Real self= one’s actual perception of your traits and abilities
* Ideal Self= who you want to be
* Influenced by people you look up to at first, but as you grow older this is more up to you.
* If there is a mismatch between the real self and ideal self= anxiety
* Ideal Self= who you want to be
* Influenced by people you look up to at first, but as you grow older this is more up to you.
* If there is a mismatch between the real self and ideal self= anxiety

79
New cards
How messages are sent in the nervous system
When cells are stimulated past a certain minimum point and emit and signal, which is action potential.
80
New cards
Diagram of neuron
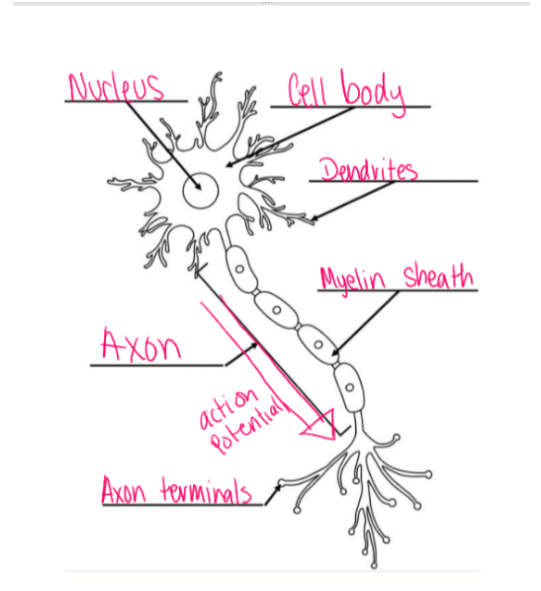
81
New cards
Central Nervous System vs. Peripheral Nervous System
* Central nervous system only consists of the brain and spinal
* While the Peripheral Nervous System consists of small branches of nerves that reach other parts of the body.
* While the Peripheral Nervous System consists of small branches of nerves that reach other parts of the body.
82
New cards
What each nervous system controls
* Somatic NS = what you control, like writing on a piece of paper
* Autonomic NS = what you don’t control, like breathing, heart beat, etc
* Sympathetic NS = prepares the body to deal with emergencies or stress activities
* Parasympathetic NS = works to control your body down to recover from a stressful activity.
* Autonomic NS = what you don’t control, like breathing, heart beat, etc
* Sympathetic NS = prepares the body to deal with emergencies or stress activities
* Parasympathetic NS = works to control your body down to recover from a stressful activity.
83
New cards
The neurotransmitters and what they control
* Endorphins = pain reduction, please sensation
* Acetycholine = involved in musction action, memory, and cofniitve functioning,
* Dopamine = involved in learning, memory, emotions, and movement.
* Serotonin = involved in sleep, appetite and mood
* Acetycholine = involved in musction action, memory, and cofniitve functioning,
* Dopamine = involved in learning, memory, emotions, and movement.
* Serotonin = involved in sleep, appetite and mood
84
New cards
Endocrine System
85
New cards
Pituitary Gland
\- “master gland”, directed by the hypothalamus, sends hormones to other sites in the body, and secretes hormones while you are sleeping( controls the endocrine system, tells other glands what to produce, also responsible for growth hormone)
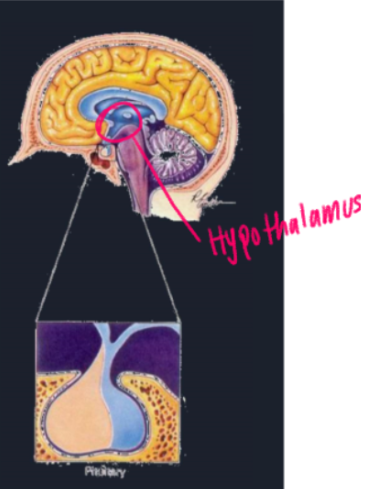
86
New cards
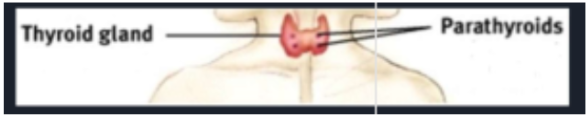
Thyroid
Thyroxine = regulates metabolism(high and low)(how fast body burns through energy)
87
New cards
Adrenal glands
* Adrenaline( epinephrine & norepinephrine)
* Adrenaline hypes you up!!
* Adrenaline hypes you up!!
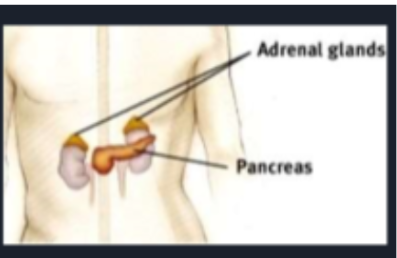
88
New cards
Gonands(sex Glands)
Progesterian(Ovaries)/Estrogen(Testes- Testosterone)
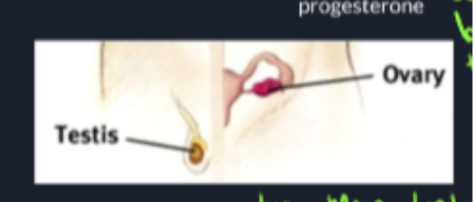
89
New cards
Types of nervous systems and their impact on the body
90
New cards
Peripheral NS
* Somatic NS = what you control, like writing on a piece of paper
* Autonomic NS = what you don’t control, like breathing, heartbeat, etc
* Autonomic NS = what you don’t control, like breathing, heartbeat, etc
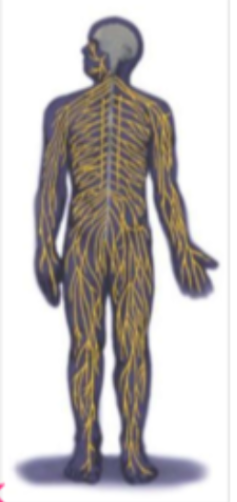
91
New cards
Branches off from Autonomic NS
* Sympathetic NS = prepares the body to deal with emergencies or stress activities(hypes you up)
* Parasympathetic NS = works to control your body down to recover from a stressful activity(calms you down)
* Parasympathetic NS = works to control your body down to recover from a stressful activity(calms you down)
92
New cards
Central NS
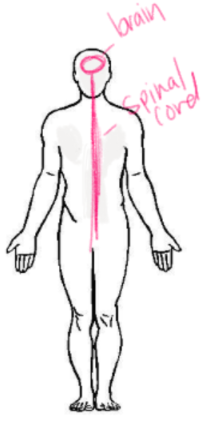
93
New cards
Phineas Gage Case Study
He was a railroad foreman who was working to clear a plath on the rails, As Gage was filling a filling a hole with dynamite, it exploded sending a rod through Gage’s head. Which caused his personality and grealy changed, and often was short-tempered and said innaporpritate words. It prevented him of his thoughts and ideas. Gage damaged his Frontal lobe, thus showed science what the frontal lobe controls.
94
New cards
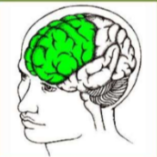
Frontal Lobe
* Reasoning
* Planning
* creative thinking
* emotional control
* Personality
* movement(motor cortex)
* Planning
* creative thinking
* emotional control
* Personality
* movement(motor cortex)
95
New cards
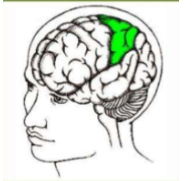
Parietal Lobe
* Touch
* Pressure
* Temperature
* pain(sensory cortex)
* Pressure
* Temperature
* pain(sensory cortex)
96
New cards
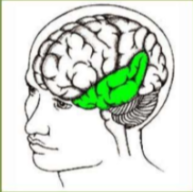
Temporal Lobe
* Auditory stimuli(hearing)
* Memory (hippocampus)
* Emotion (amygdala)
* Speaking
* Memory (hippocampus)
* Emotion (amygdala)
* Speaking
97
New cards
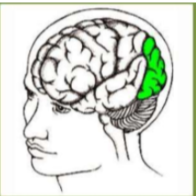
Occipital Lobe
Concerned with the many aspects of vision.
98
New cards
Cerebella
Controls balance for walking and standing and other complex motor, also controls muscles action so that the body can move smoothly,
99
New cards
Medulla
Manages heart rate circulation and breathing, transmits signals between the spinal cord and different parts of the brain, controls autonomic processes like sneezing and swallowing.
100
New cards
Pons
It handles unconscious processes and jobs, like breathing and the **sleep cycle,** it also controls muscles and carries information from the senses in your face and head. Also, manage your pain signals from anywhere below your neck, your balance, and your movement.