Cross Sectional Anatomy II Abdomen Common Pathology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
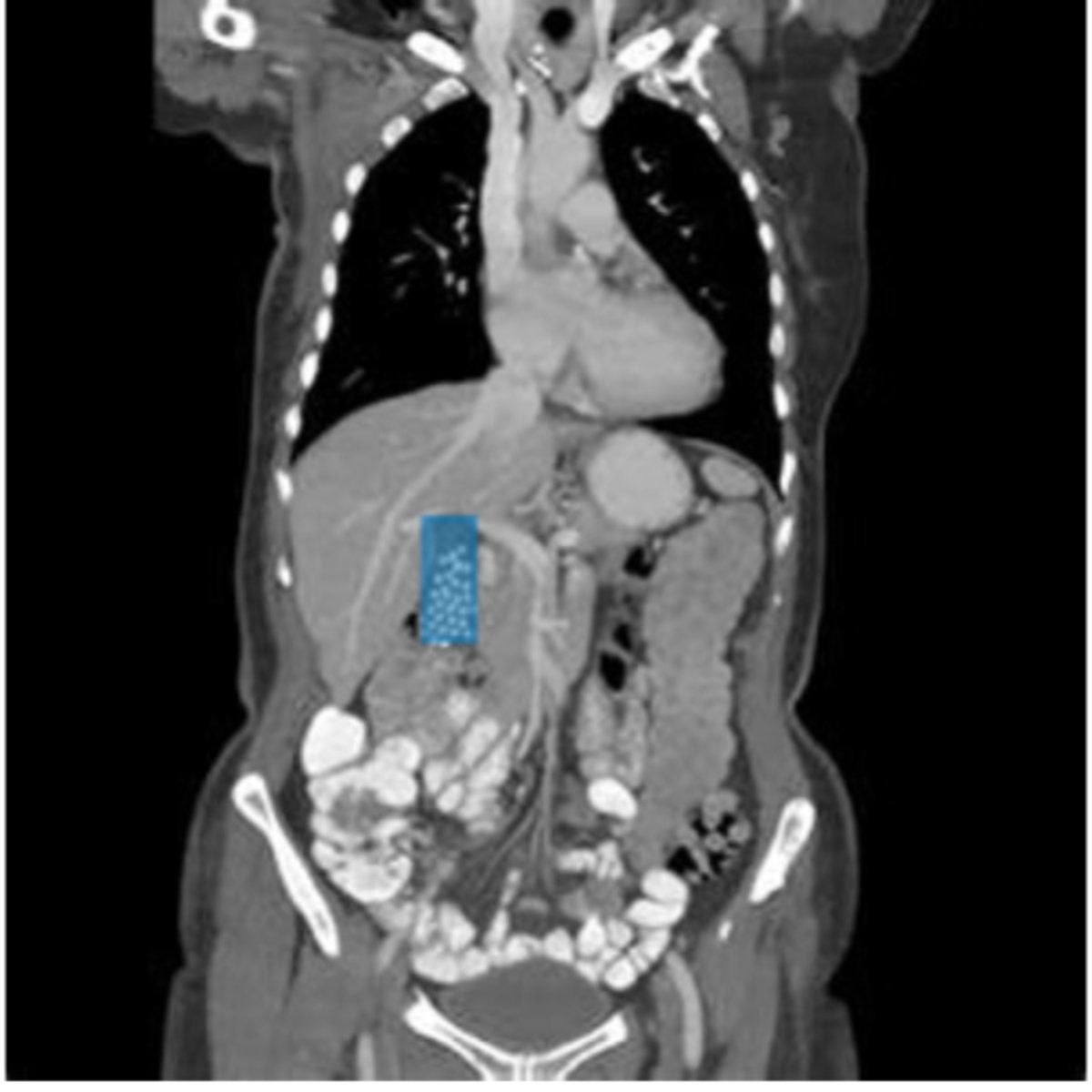
What is pancreatitis?
Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas.
What is the most common cause of pancreatitis?
The most common cause of pancreatitis is alcoholism.
What are the other causes of pancreatitis?
Other causes of pancreatitis include gallstones, trauma, and pancreatic cancer.
What are the common symptoms of pancreatitis?
Patients with pancreatitis present with abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, fever, mild jaundice, and mild pleural effusion.
How does pancreatitis appear on CT images?
Pancreatitis presents as diffuse enlargement of the pancreas with soft tissue stranding of the peripancreatic fat. Intrapancreatic and peripancreatic fluid collection may also be seen on CT images.
What are hemangiomas?
Hemangiomas are the most benign hepatic tumors.
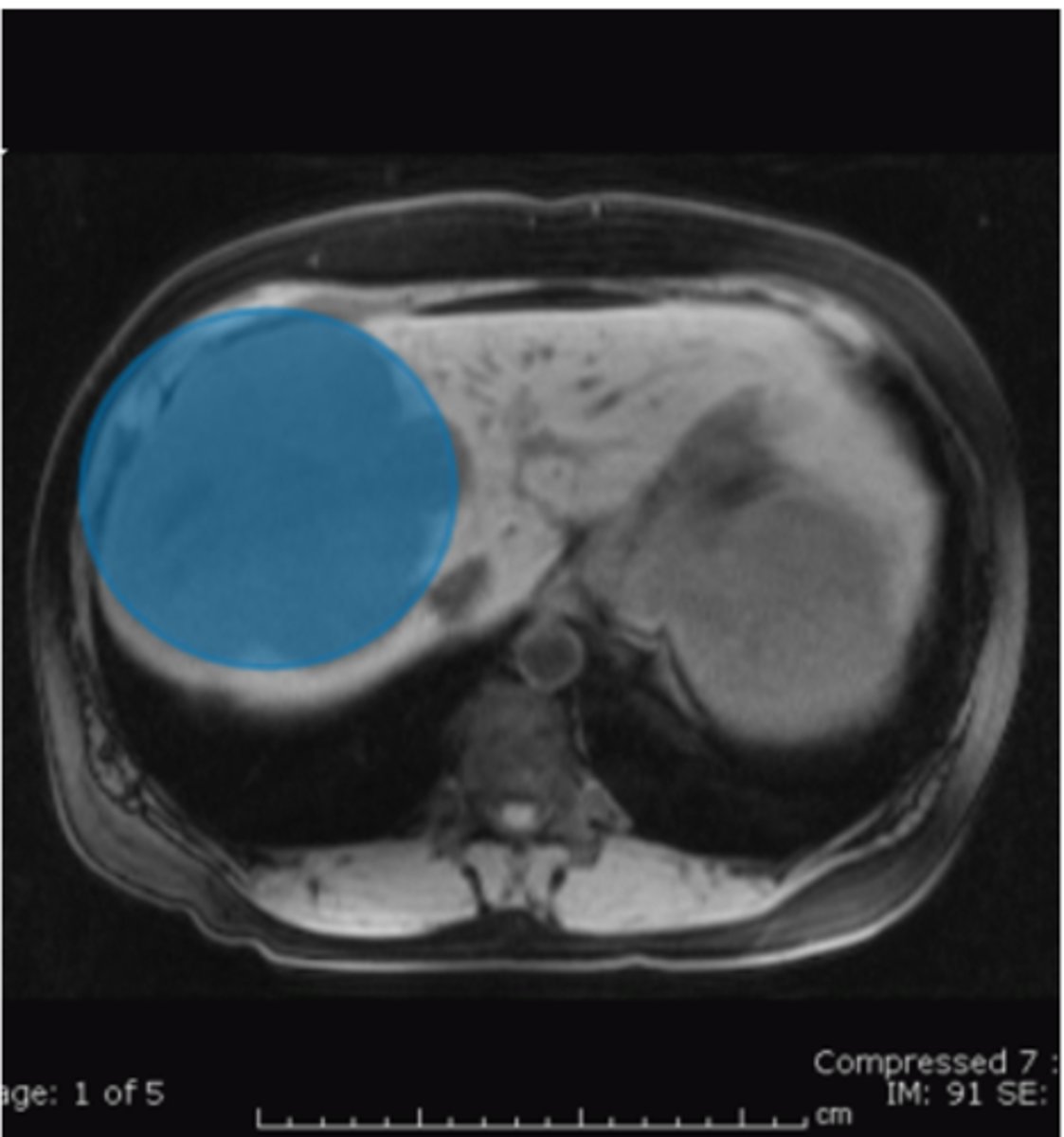
How are hemangiomas usually discovered?
Hemangiomas are usually an incidental finding on a CT or MRI abdominal exam.
What is used to delineate hemangiomas from other hepatic tumors?
IV contrast is used to delineate hemangiomas from other hepatic tumors.
How does sequential scanning over a period of time demonstrate hemangiomas?
Sequential scanning over a period of time demonstrates progressive contrast filling of the lesion.
What percentage of hemangiomas are symptomatic?
Only a small percentage of hemangiomas are symptomatic.
What is choledocholithiasis?
Choledocholithiasis is a calculi or stone in the common bile duct.
What are the symptoms of common bile duct obstruction due to a stone?
Patients may experience epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, fever, and jaundice.
How are gallstones demonstrated on coronal CT of the abdomen?
Gallstones are demonstrated on the coronal CT as a high attenuation or bright area within the gallbladder.
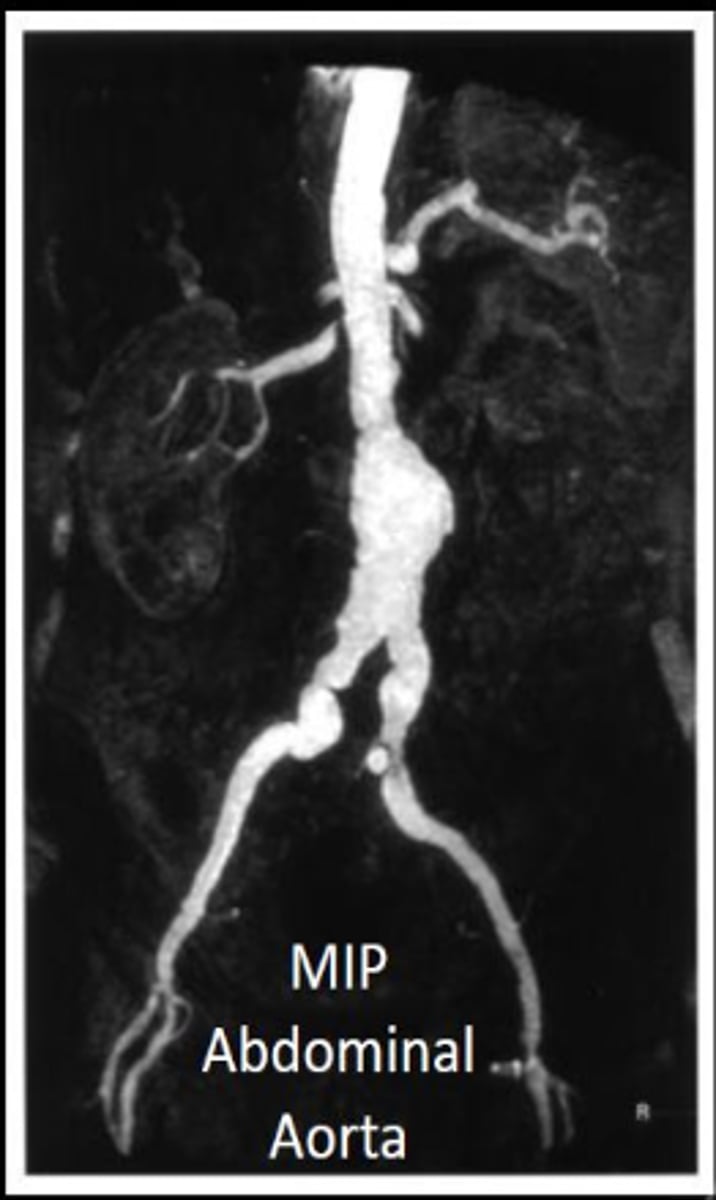
What is the best noninvasive study for diagnosing choledocholithiasis?
MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is the best noninvasive study for the diagnosis.
What type of MRI image is displayed in the context of choledocholithiasis diagnosis?
The MRI image displayed is a maximum intensity projection (MIP).
Where can renal calculi or kidney stones form throughout the urinary tract?
Renal calculi or kidney stones may form anywhere throughout the urinary tract.
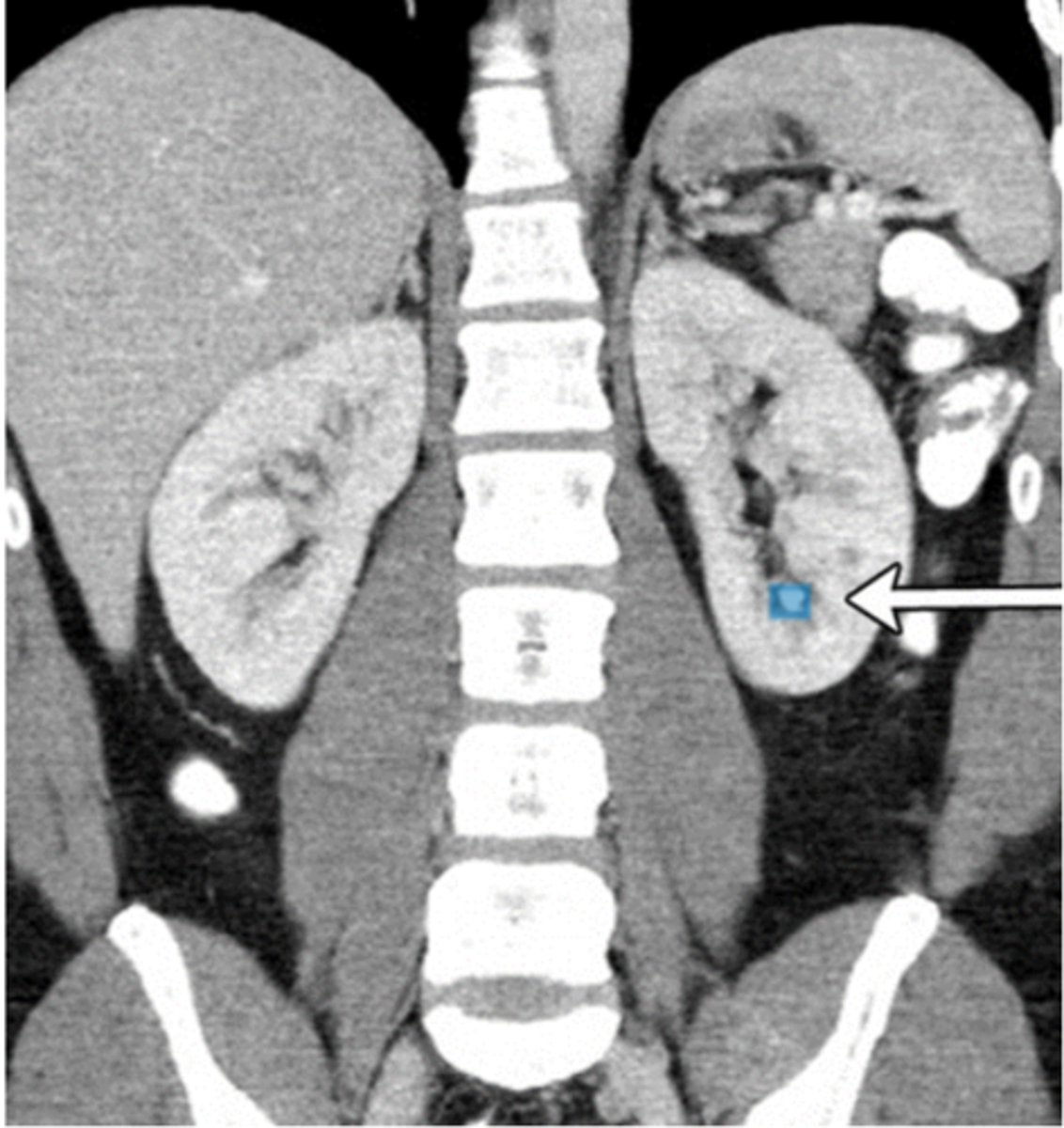
What are the common symptoms of renal calculi or kidney stones?
Patients complain of back pain, hematuria, nausea, vomiting, and dysuria.
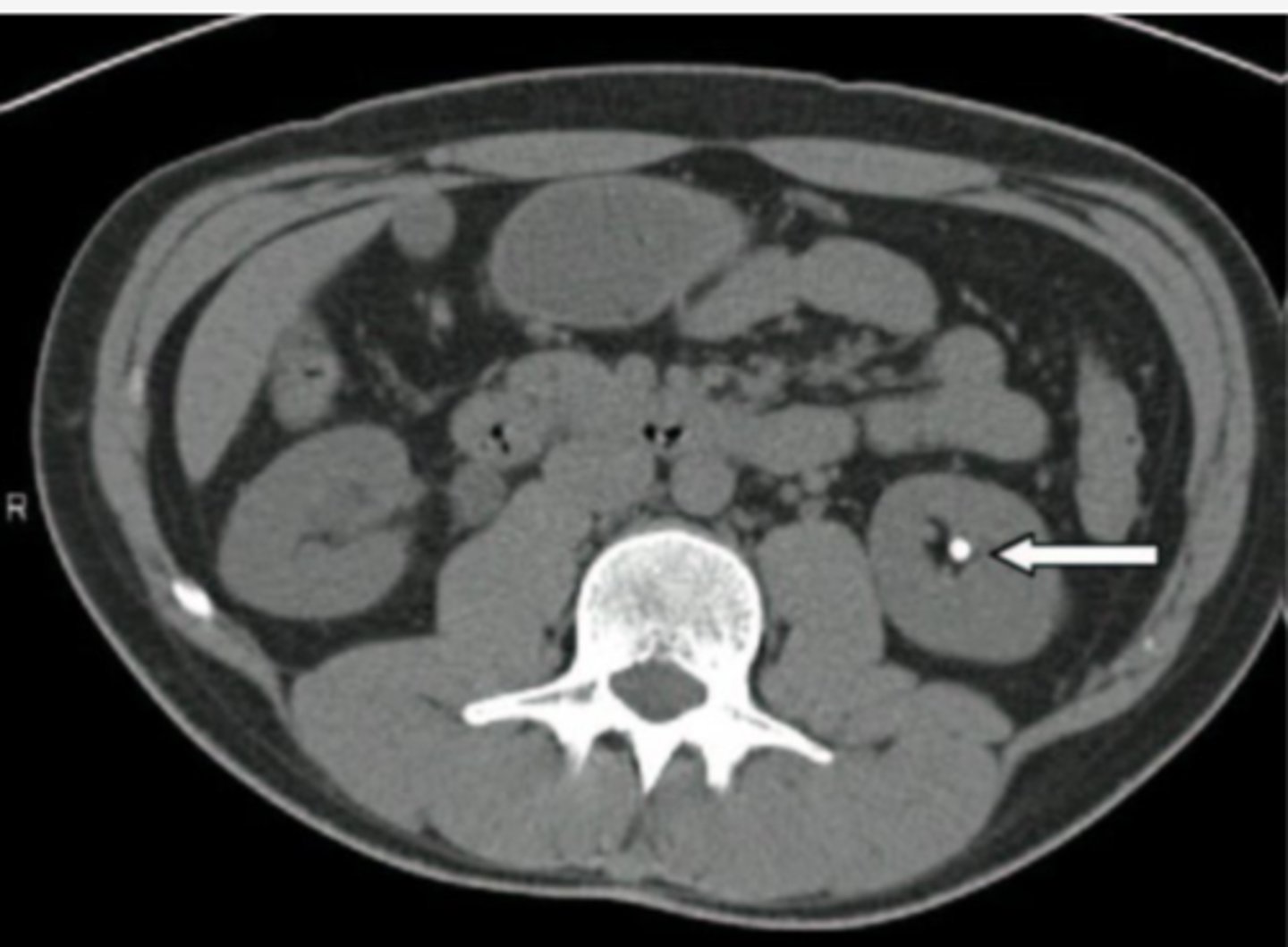
What is the modality of choice for imaging renal calculi or kidney stones?
Non-contrast CT is the modality of choice and is gradually replacing the intravenous pyelogram (IVO).
What does a non-contrast CT demonstrate in cases of renal calculi or kidney stones?
A non-contrast CT may demonstrate a calcified stone in the kidney, hydronephrosis, hydroureter, and perinephric soft tissue stranding.
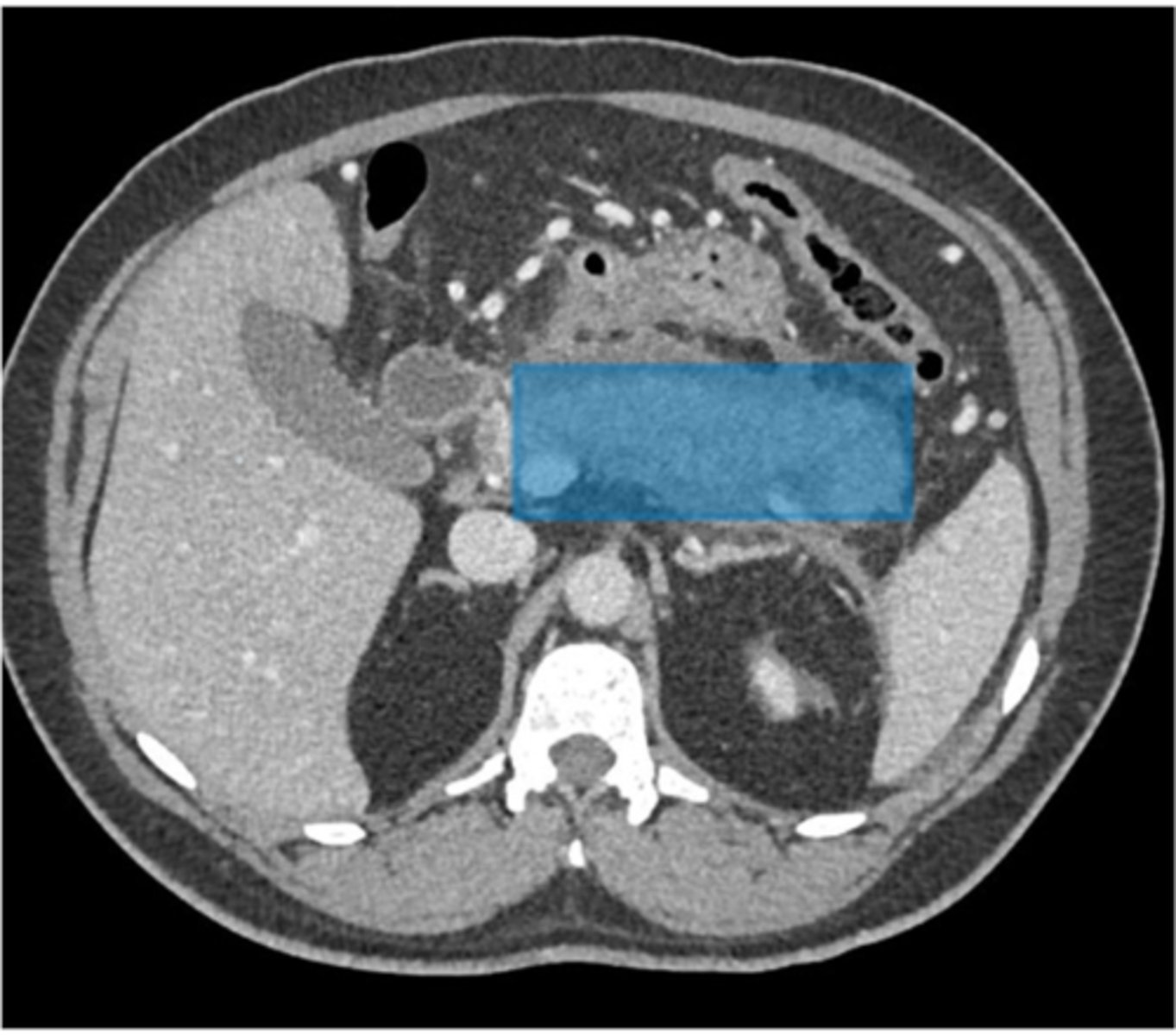
What can result in lacerations to organs in the abdomen?
Blunt or penetrating abdominal trauma, complications of surgery or interventional procedure
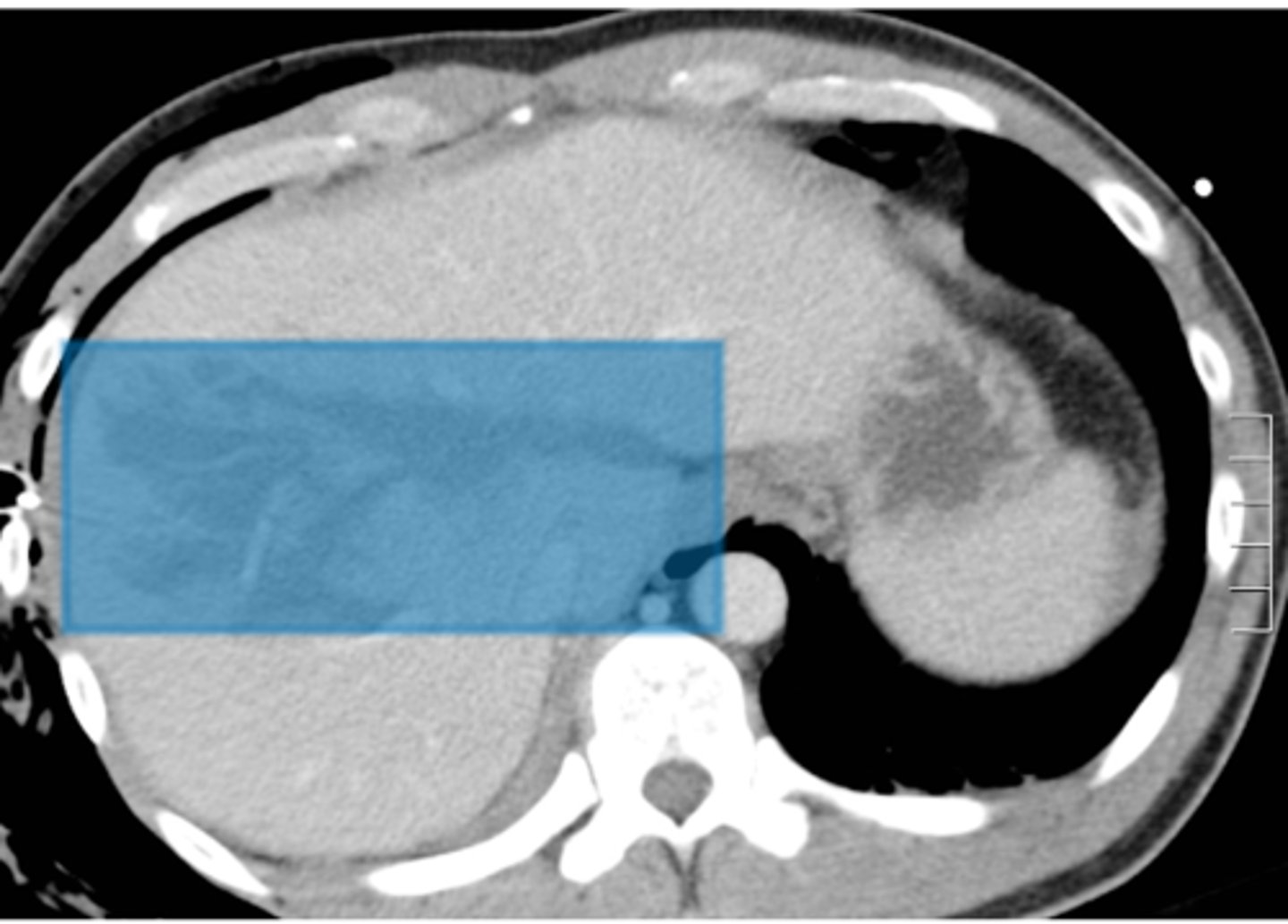
What symptoms do patients complain of in case of lacerations to organs?
Abdominal pain from the trauma
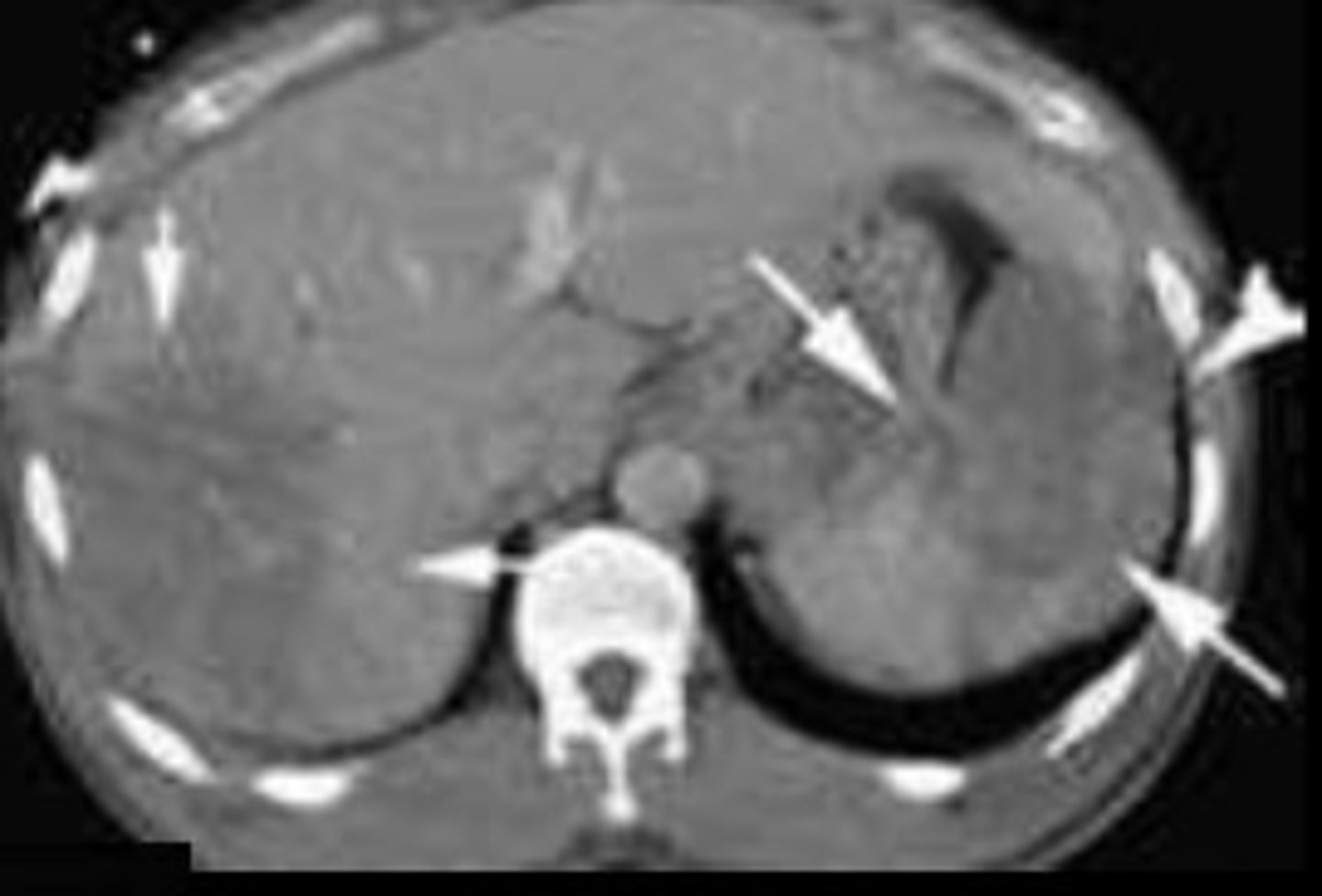
What complication may the patient experience as a result of lacerations to organs in the abdomen?
Hypovolemic shock caused by inadequate blood volume
What is the imaging modality of choice to detect lacerations to organs in the abdomen?
CT with IV contrast
Why may a non-contrast study not reveal the injury of lacerations to organs in the abdomen?
It may not reveal the injury as indicated by the image labeled 'A'
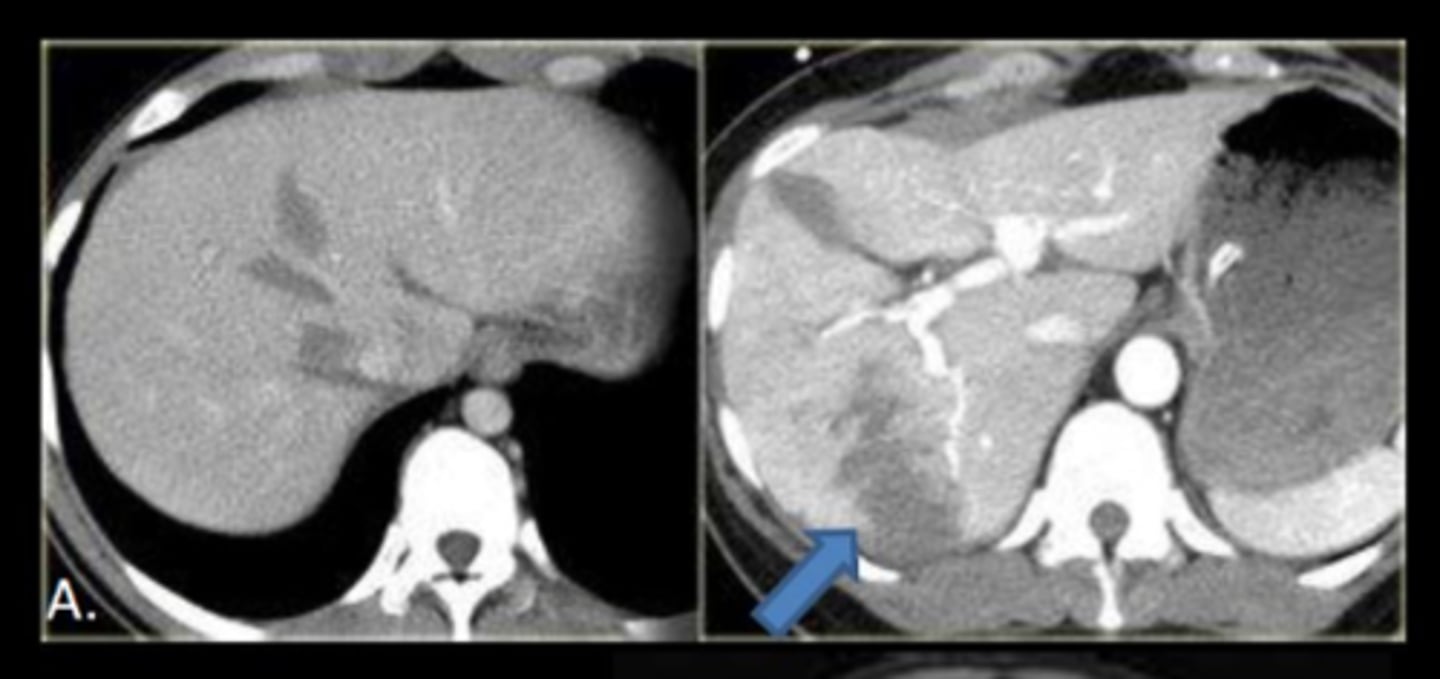
How does IV contrast help in demonstrating lacerations to organs in the abdomen?
IV contrast will demonstrate the laceration as a hypodense area
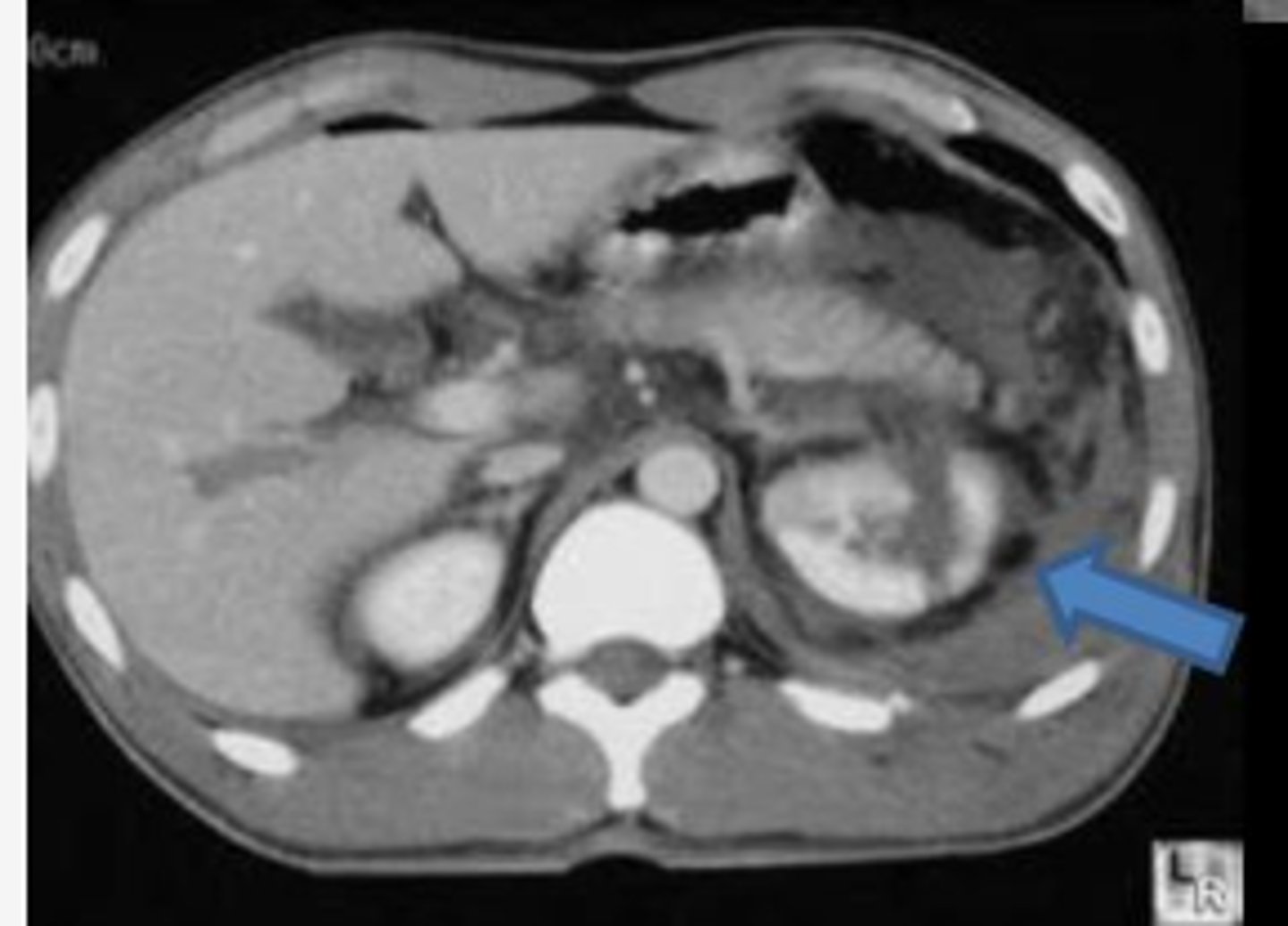
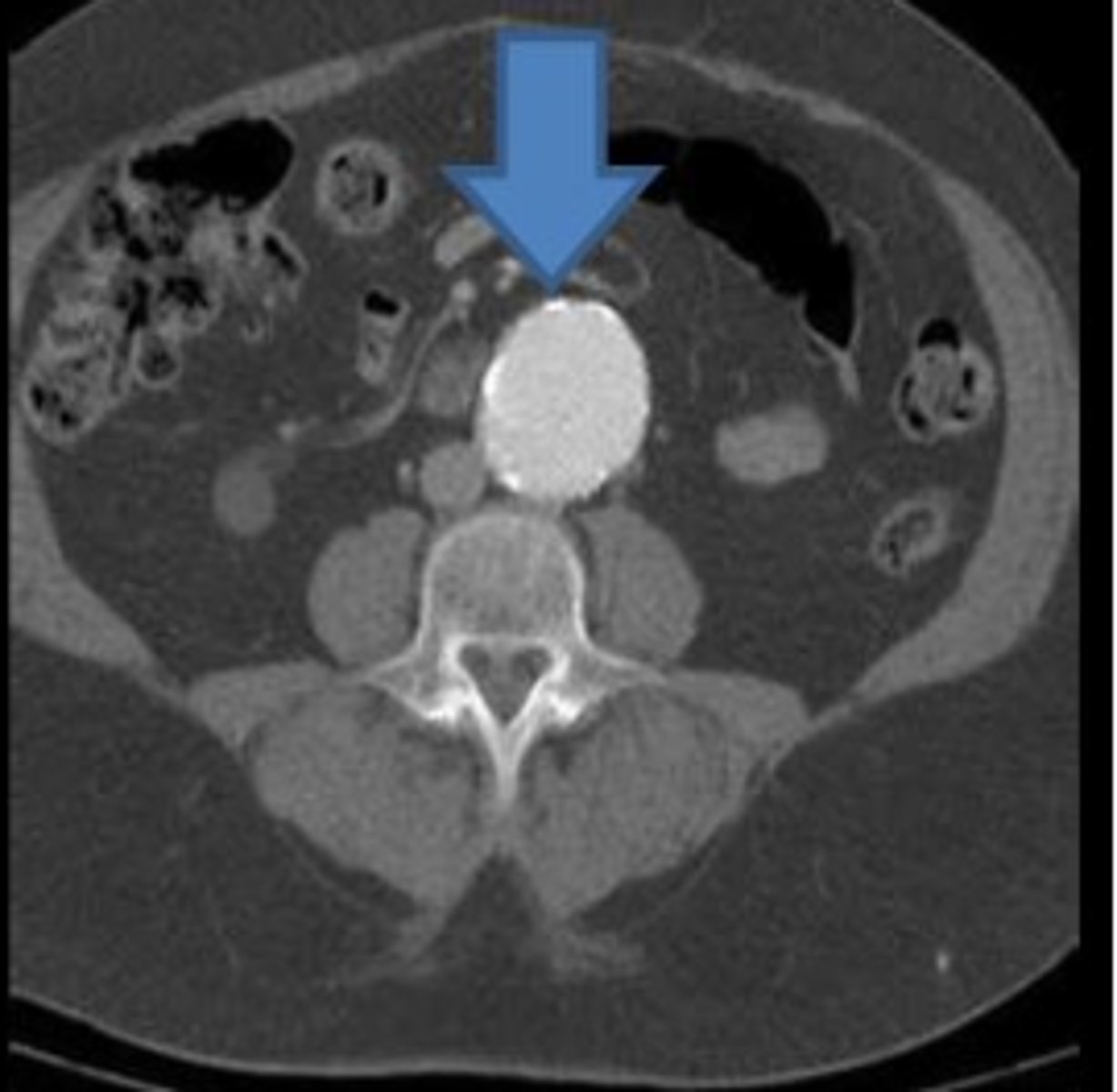
What is an aortic aneurysm?
An outpouching or enlargement of the aorta.
What does a rupture of the aorta involve?
A traumatic tearing or laceration of the aorta.
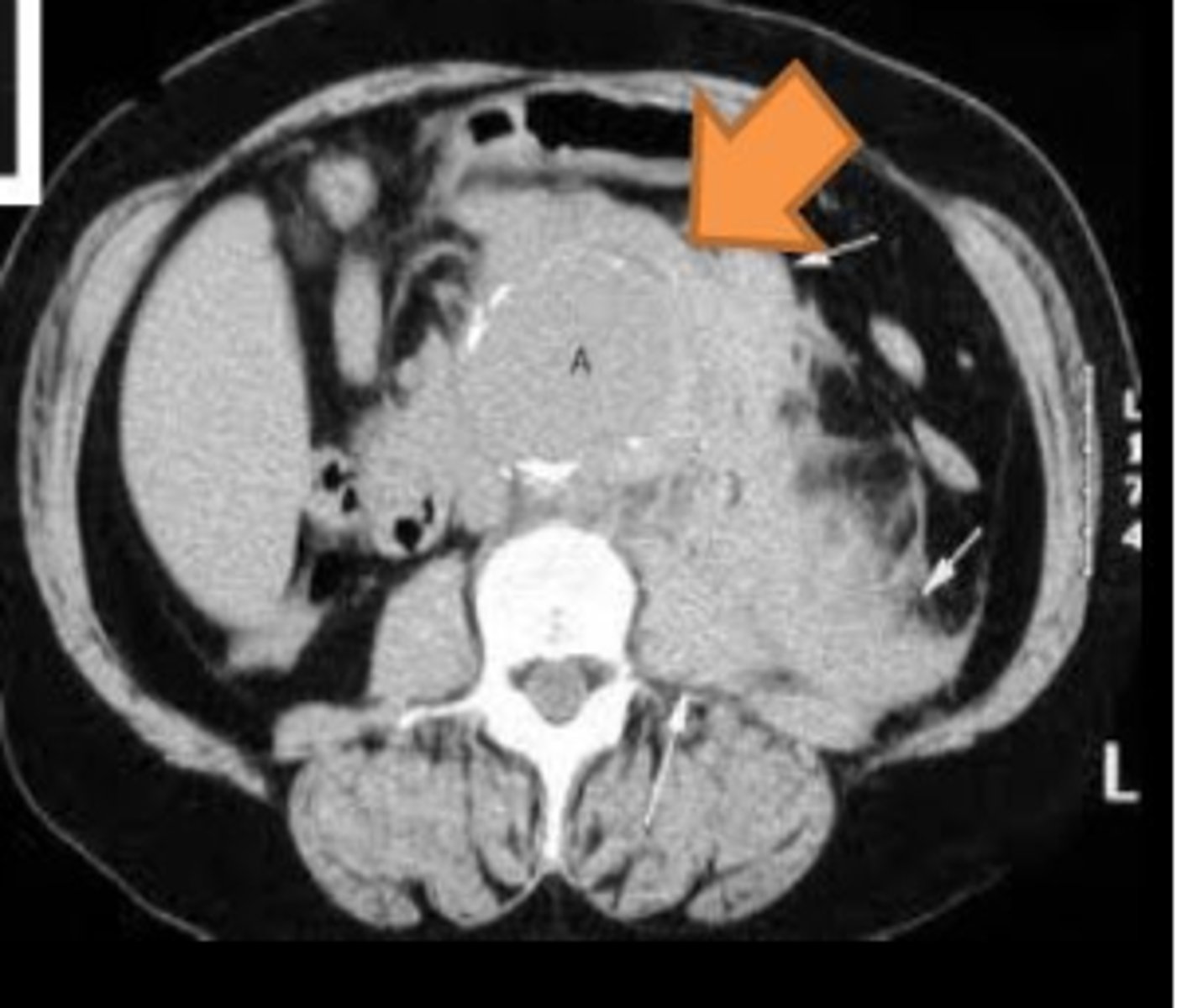
Abdominal aneurysms are generally asymptomatic (True/False)
True