Calculus Final Exam
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
when is a function said to be injective?
if whenever f(a)=f(b), then a=b.
do vert line tests or horiz line tests determine if you have a function?
vertical line tests
do vert line tests or horiz line tests determine if you have a one-to-one function?
horizontal line tests
even function
f(-x)=f(x)
odd function
f(-x)=-f(x)
true or false: a function has an inverse iff it is injective
true
logb(AC)
logbA+ logbC
logbb= ?
1
logb(A/C)
logbA-logbC
logbAR
RlogbA
log 1 = ?
0
if logaB = n, an=?
b
if f(x) = bx, f-1(x) = ?
logbx
if f(logbx)=x, what does blogbx=?
x
trig identity
cos2+sin2=1
sin (pi/6)
1/2
cos (pi/6)
(sqrt3)/2
sin (2x) = ?
2 sinx cosx
sin (A+B)
sinAcosB + sinBcosA
sin2x= ?
1/2(1-cos 2x)
cos2x = ?
1/2(1+ cos 2x)
logbx
(logax)/(logab)
how to find horizontal asymptotes
if the degree of the denominator is greater - > the asymptote is y=0.
if the degrees are equal - > ratio of the the leading coefficients
if the degree of the numerator is greater - > no horizontal asymptote
the tan line to the curve y = f(x) at point f(x, f(x)) has the slope m =
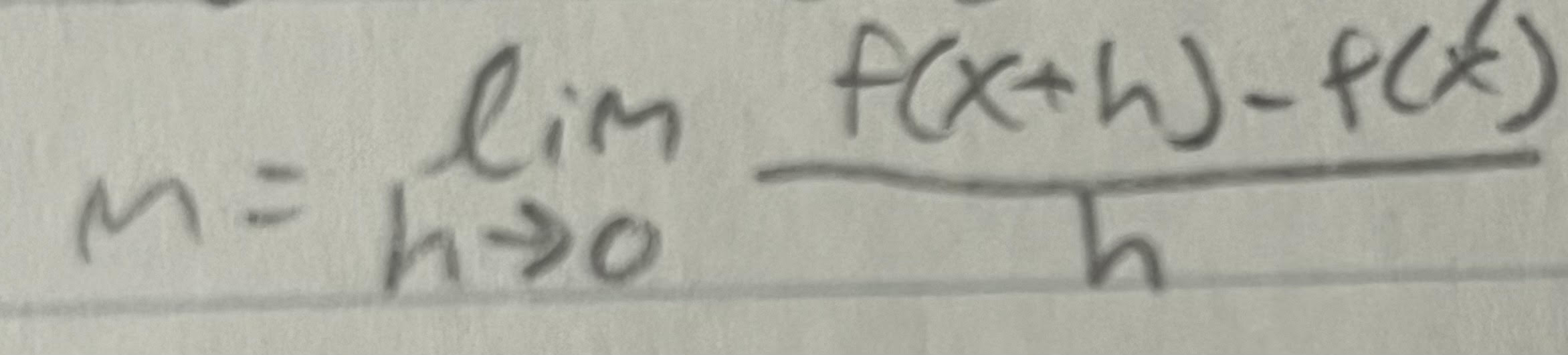
a3-b3
(a-b)(a2+ab+b2)
a3+b3
(a+b)(a2-ab+b2)
Squeeze Theorem
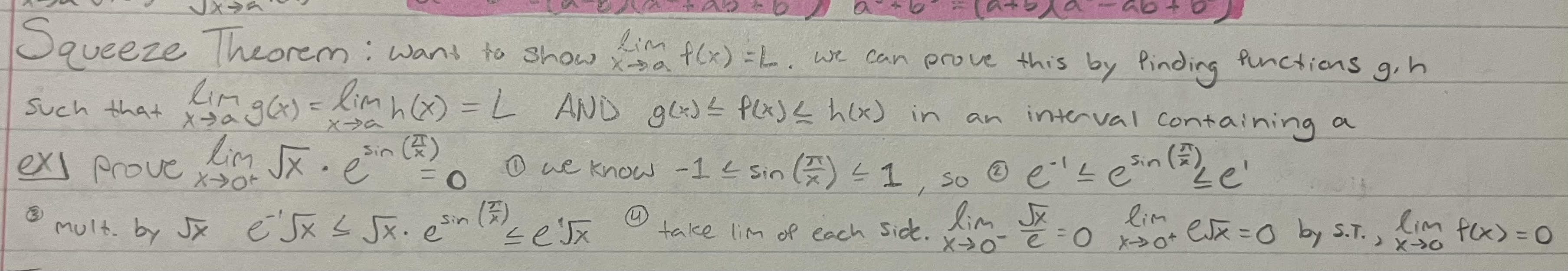
Intermediate Value Theorem
f(x) is cont. on a closed interval [a,b] then for any N between f(a) and f(b) we can find c in the interval (a,b) s.t. f( c ) = N
d/dx C = ?
0
d/dx ex = ?
ex
theorem about composition of functions
if g is cont. at a and f is cont. at g(a) then their composition f(g (x)) is cont. at a.
d/dx xn = ?
nxn-1
(f+ g)’ = ?
f’ + g’
(cf(x))’ = ?
c f’(x)
d/dx f(g(x)) =
f’(g(x)) g’(x)
(f(x)g(x))’ =
f’(x)g(x) + f(x)g’(x)
(f(x)/g(x))’ =
(f’(x)g(x) - f(x)g’(x))/g2(x)
cos’(x)
-sin (x)
sin’(x)
cos (x)
tan’(x)
sec2(x)
sec’ (x)
sec (x) tan (x)
csc’(x)
-csc (x) tan (x)
cot’(x)
-csc2(x)
d/dx (au)
auln (a) du/dx
equation for linearization
y = f(a) + f’(a)(x-a)
y = mx to b form : y = f’(a)x + b
where b = f(a) - f’(a)a
sinh x
(ex-e-x)/2
cosh x
(ex+ e-x)/2
tanh x
(ex-e-x)/(ex+ e-x)
sinh (-x) =
-sinh (x)
so sinh (x) is odd
cosh (-x)
cosh (x)
so cosh (x) is even
hyperbolic trig identity (DIFFERENT than the reg one)
cosh x2-sinh x2=1
critical number
any x-value in the domain where f’(x) is either 0 or UND
where must abs. max and min of cont. function [a,b] occur?
@ crit pts or endpts
Rolle’s Theorem
Let f(x) be cont on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b). If f(a) = f(b), then there exists c in (a,b) s.t. f’( c ) = 0
Mean value theorem
let f(x) be cont on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b). Then there exists a c in (a,b) s.t. (f(b)-f(a))/(b-a) = f’( c )
there may be more than 1 value of c
if f’(a) < 0 is f decreasing or increasing near a?
decreasing
if f”(a) > 0 is f concave up or concave down?
concave up
2nd derivative test
let c be in the domain of f(x) where f’( c ) = 0 and suppose f’’(x) is cont. near c. if f’’ ( c ) > 0 then f has a local min at c. if f’’( c )< 0 then f has a local max at c.
L’hopital’s rule
if a limit has the indeterminant form 0/0 or inf/inf, you can take the derivatives of the numerator and denominator seperately to find the limito
optimization
take derivative of eqn and find max/min
slant asymptote definition
y=mx + b is said to be a slant/oblique asymptote to f(x) if lim x→+- inf f(x) - (mx + b) = 0
antiderivative of xn
1/(n+1) xn+1+C
antiderivative of x-1
ln |x| + C
how to find horizontal asymptotes
if the numerator’s degree is less than the denominator’s, the HA is y=0. if they are equal, it’s the ratio of their leading coefficients. if the numerator’s degree is greater, there is no HA. for other functions, take the lim as x→+- infiniti