Pathophysiology of cough
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is cough?
a protective mechanism that ensures removal of mucus, noxious substances, and infectious organisms from the larynx, trachea, and large bronchi
an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for cleaning the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign material
How is cough stimulated?
the cough center in the medulla oblongata receives stimuli and intiates the reflex response, cough receptors in the pharynx, larynx, trachea or lungs may be stimulated by air, dryness of mucous membranesm, or excessive secretons, afferent nurones into centre
What is the mechanism of cough?
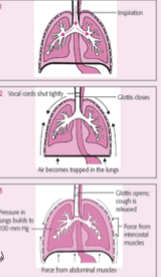
impulse is transmitted from cough centre in the medulla to the larynx and to intercostal and abdominal muscles, deep inspration is followed by closure of the glottis, relaxation of the diaphragm, and contraction of the abdominal and intercostal muscles, the increcreased pressure in lungs opens epiglottis to release the forceful, nosy expiration
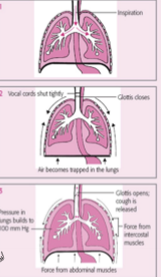
Why are coughs load?
explosive air goes through the vocal cords
What are RARs?
rapidly adapting (cough) receptors - respond to mechanical stimuli, cigarette smoke, ammonia, acidic and alkaline solutions, hypotonic and hypertonic saline, pulmonary congestion, atelectasis, and bronchoconstriction, use mylinated fibres allowing fast mechanical response to stimuli, allows to be rapidly adapting
What are SARs?
slowly adapting (cough) receptors, it is questionable whether they are involved in the cough reflex
What are nociceptors on C-fibres?
respond to chemical stimuli as well as inflammatory and immunological mediators such as histamne, bradykinin, prostaglandins, substance P, capsaicin, acidic pH. non-mylinated so signal slow
What is capsaicin?
inflammatory substance produced by the body, causes you to cough when ill
What is the etiology of cough?
exogenous - smoke, dust, fumes, foreign bodies
endogenous - upper airway secretions, gastric contents
any disorder resulting in inflammation, constriction, inflitration or compression of the airways
What are the most common causes of chronic cough in non smokers?
postnasal drip, asthma, and GORD
When should you refer a cough to a doctor?
persistant or associated with chest pain,fever, weight loss or blood-tinged or coulored sputum
What is a productive cough?
when secrerions are expectorated
What are the types of cough?
dry - laryngitis, dry pleurisy, smoking cough, begining of acute bronchitis, pneumonia, lung abscess, TB, lung cancer
wet - acute viral, pneumonia, bronchitis, TB, brochiectatic disease
How does GORD cause cough?
when lying down, the acid coming up triggers the cough reflex
What is the difference between sputum and phlegm?
sputum is after it leaves the body
etiology of acute cough?
upper respiritory infection, pneumonia, pulmonary embolus, and congestive heart failure
etiology of sub acute cough?
post-infectious due to persistant airway inflammation and/or postnasal drip after viral, pertussis, mycoplasma or chlamydia infections
etiology of chronic cough?
in smoker asthma, COPD or bronchogenic carcinoma, eosinophillic bronchitis, esophageal disease, post nasal drip, ACE inhibitor side effect, smoking
How do expectorants (mucokinetics) work?
increases leaking of fluid out of the lung, this increases the liquid concentration of mucous in the airways making it easier to remove from the airway, this decreases cough
How do mycolytics work?
they break bonds in the mucous making it easier to remove from the airway as it is less dense, can be nebulised into face masks or mouthpiece or instilled directly into the respiritory tract through a tracheostomy
What are pharyngeal demulcents?
soothen the airway, no pharmacological reaction, e.g. lozengers
How do antitussives work?
suppress cough by depressing cough centre
What are the three types of antitussives?
centrally active (narcotics and non-narcotics e.g. dextromethorphan), peripherally acting (lidocaine and antihisamines), locally acting (throat lozengers or cough drops)
How do locally acting antitussives work?
may suppress cough by increasing the flow of saliva and by containing demulcents or local anesthetics to decrease irritation of pharyngeal
What do local anastetics do (cough related)?
bind to Na⁺ channel inside cell, prevent activation of action potential
What is dextromethorpham?
OTC oral cough suppressant, chemically related to codeine, acts on brain to supress cough but not pain relieving and addictive like codeine, acts on sigma 1 receptor
What is diphenhydramine?
acts on brain to suppress cough, antihistamine, non narcotic, H1 receptor anagonist
What are codeine and hydrocodeine in terms of cough syrup?
oral cough supressents that need prescription
What is Guafenesin?
most common expectorants, availible alone or as an ingredient, authorties don’t recomend use and no research studies support this
What are the two agents recommended for use as mucolytics?
sodium chloride solution and acetylcysteine
What are camphor and menthol?
topical cough medicines, ointments rubbed on throat and chest as a thick layer, anaesteruc action of vapors belived to releave cough, availible for steam inhalation as well, menthol available as lozengers and compressed tablets