Plant Taxonomy: Angiosperms: Inflorescences and Fruit
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
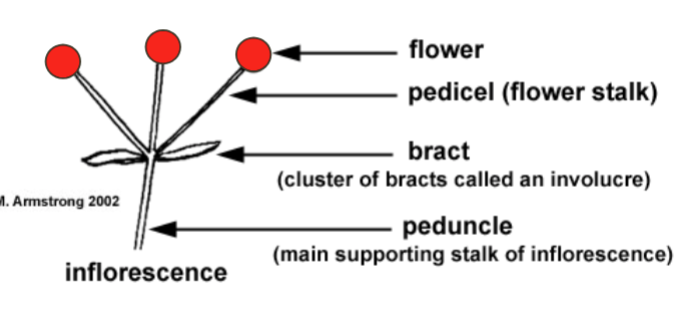
Inflorescnece
A cluster of flowers on a branch or system of branches
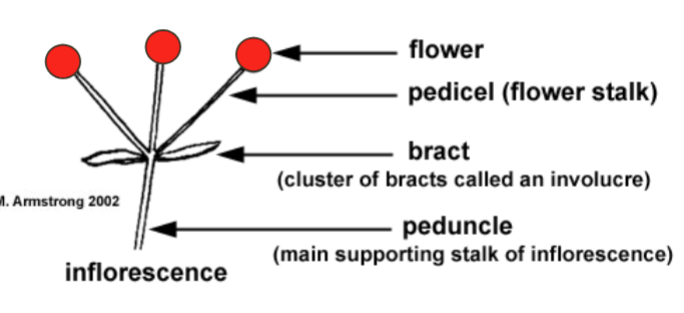
Flower
The reproductive structure of a plant, often containing petals, stamens, and pistils
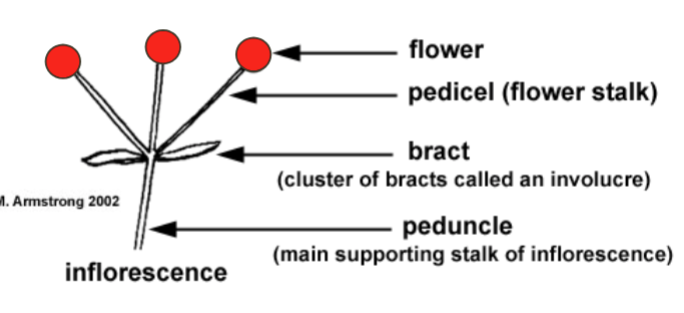
Pedicel
The small stalk that attaches a single flower to the main stem of the inflorescence
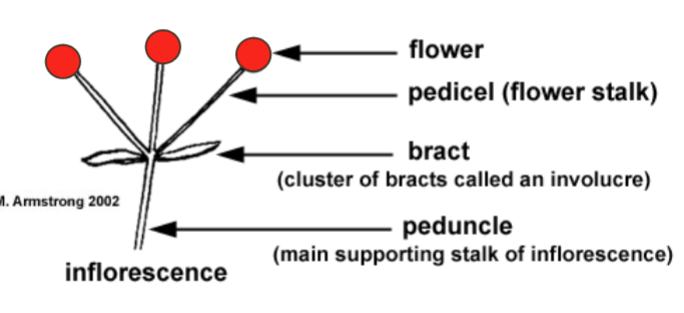
Bract
A modified leaf located at the base of a flower or inflorescence, sometimes resembling petals
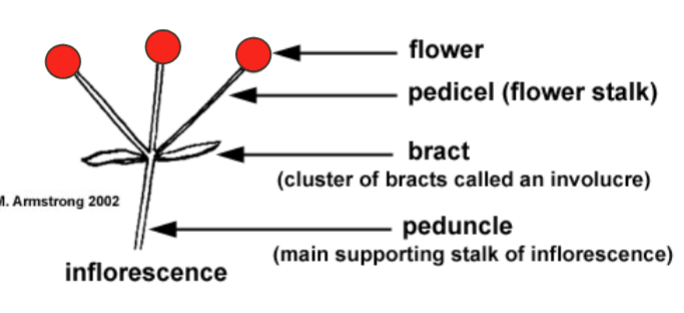
Peduncle
The main stalk that supports the entire inflorescence or solitary flower

Determinate
The first flower to bloom is at the top
These inflorescences are called cymes

Indeterminate
The first flower to bloom is at the bottom

Raceme
Indeterminate inflorescence
Flowers are attached to the rachis by pedicles

Spike
Flowers are attached directly to the rachis
Indeterminate inflorescence

Catkin
A spike inflorescence with imperfect flowers of a single sex
Indeterminate inflorescence
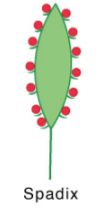
Spadix
A spike in which the rachis is swollen and fleshy
Indeterminate inflorescence
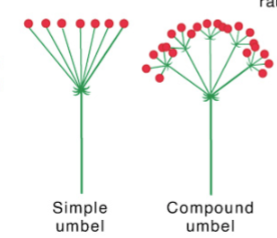
Umbel
Flower pedicles are all attached at the same point on the peduncle or rachis
Indeterminate inflorescence
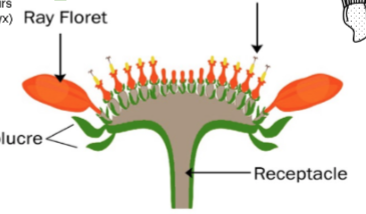
Capitulum
Disk and ray florets are arranged on a head to mimic a large flower
Indeterminate inflorescence
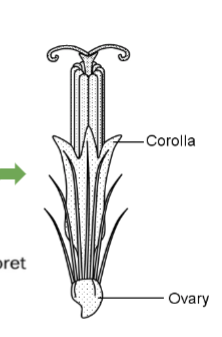
Disk florets
Florets in the middle of a capitulum and are radially symmetrical
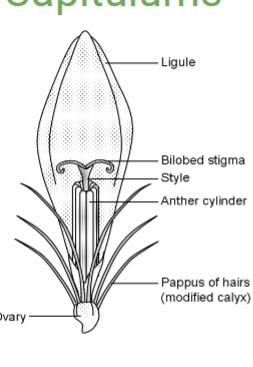
Ray florets
Florets on the edge of a capitulum
mimic petals, are often very showy, and are bilaterally symmetrical
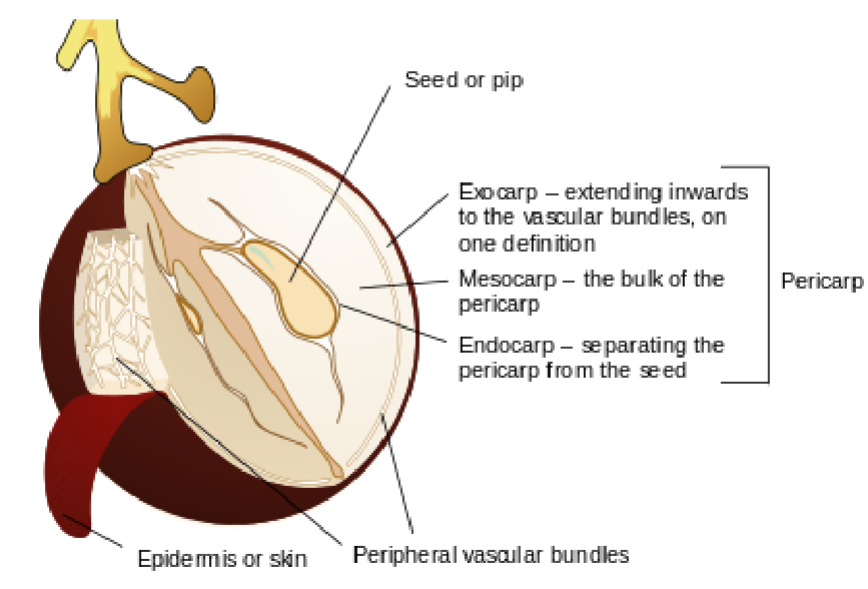
Seed
The fertilized ovule that contains the embryo of a new plant
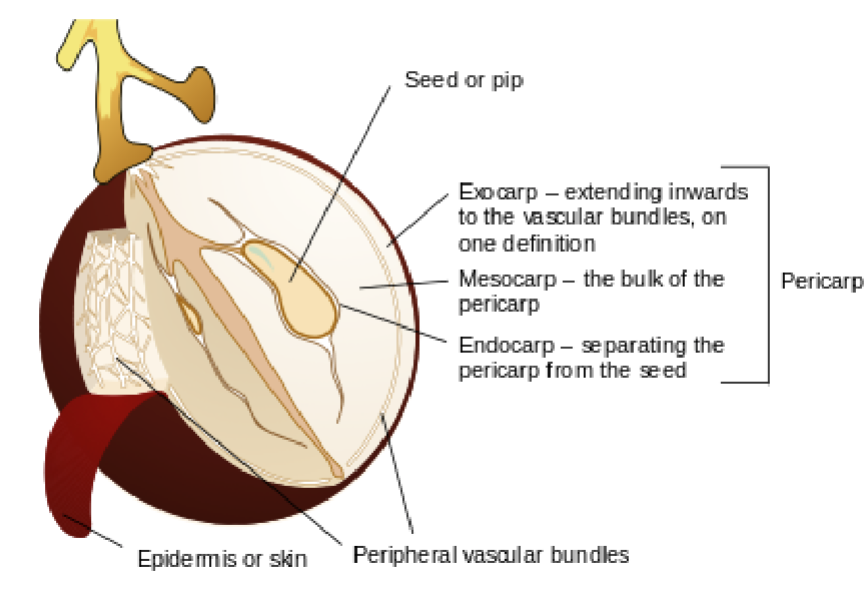
Pericarp
The part of a fruit formed from the ovary wall
Surrounds and protects the seed(s)
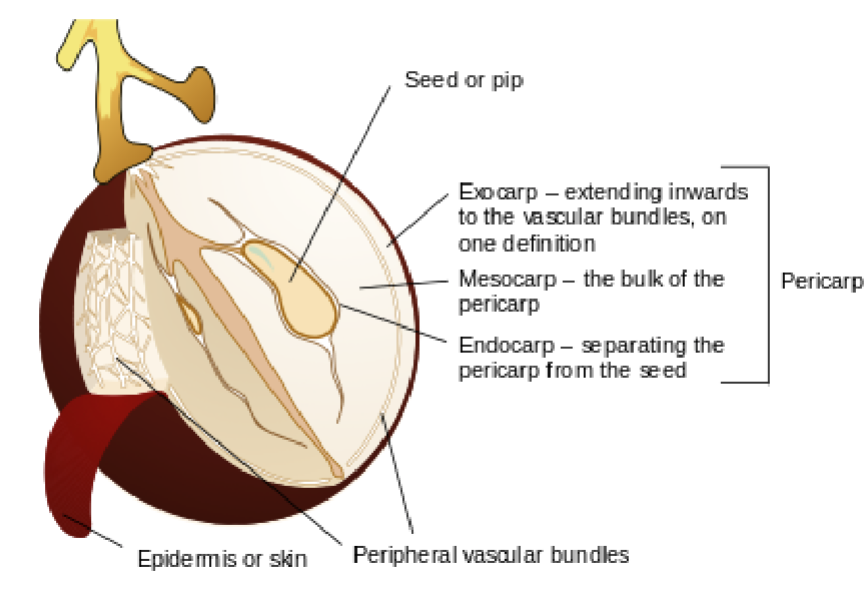
Exocarp
Outermost layer of the pericarp
Often forms the skin of the fruit
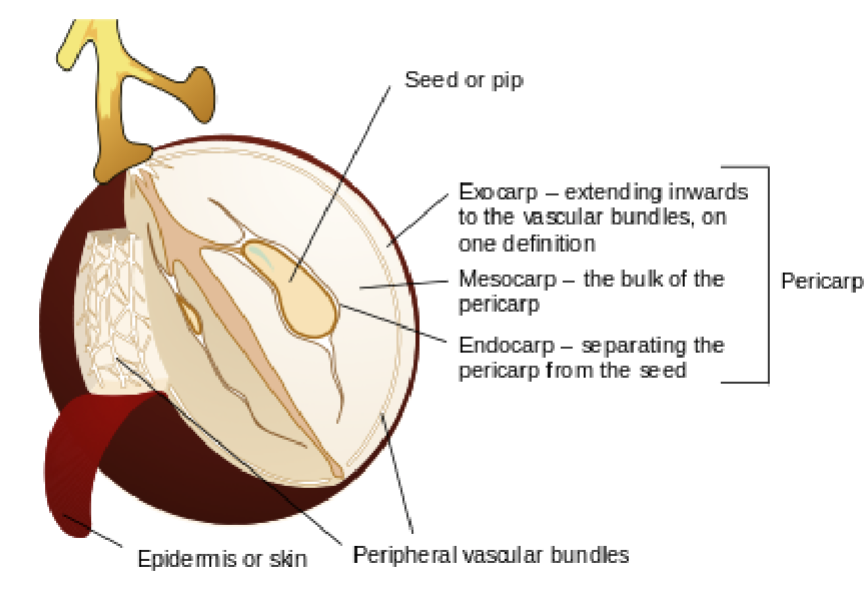
Mesocarp
Middle layer of the pericarp
Usually the fleshy or juicy part of the fruit
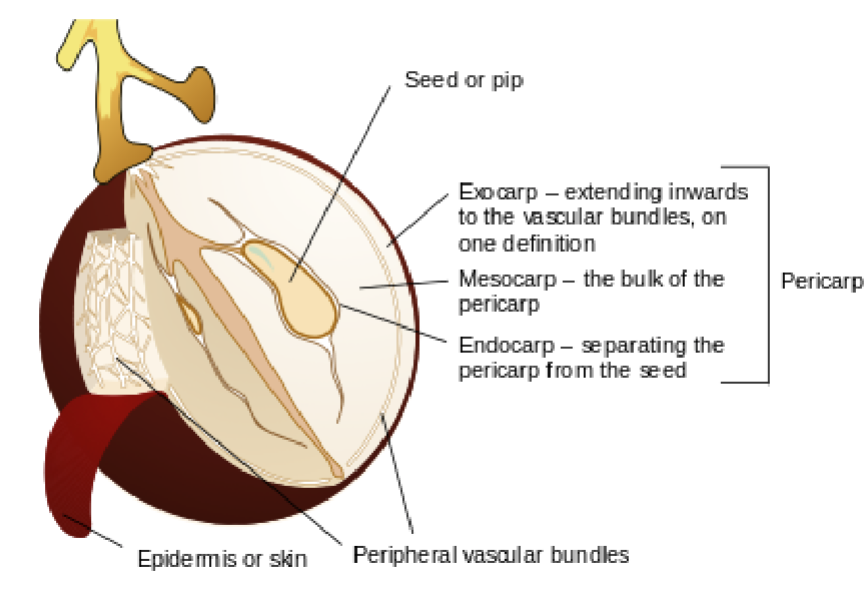
Endocarp
Innermost layer of the pericarp
Directly surrounds the seed(s)
May be hard or soft
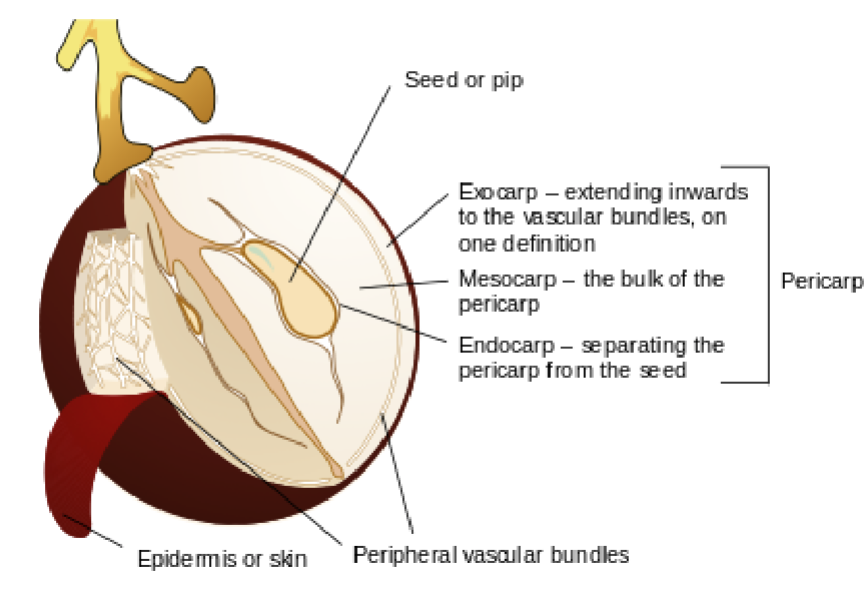
Skin
Outer covering of the fruit
Typically referring to the exocarp when it is tough or noticeable
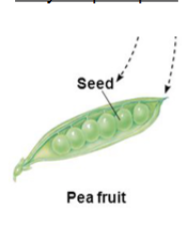
Simple fruit
Derived from one flower with a single or syncarpous pistil
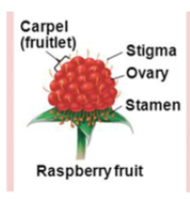
Aggregate fruit
Derived from one flower with multiple pistils

Multiple fruit
Derived from multiple flowers on a single axis
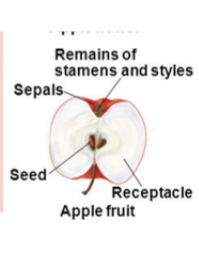
Accessory fruit
Derived from a flower part other than the pistil
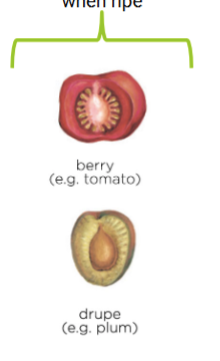
Fleshy fruit
Pericarp soft and juicy when ripe
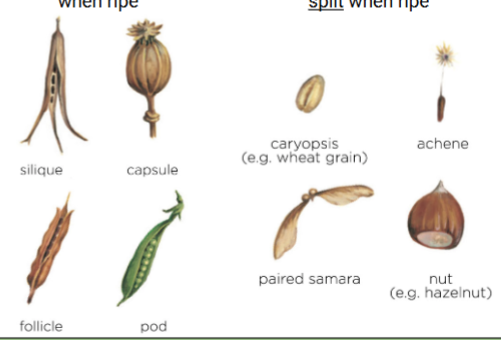
Dry fruit
Pericarp hard or papery when ripe

Dehiscent fruit
Splits open when ripe
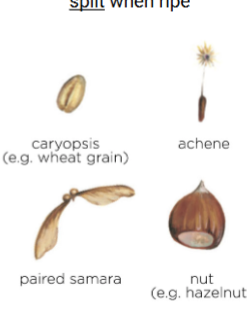
Indehiscent fruit
Does not split open when ripe
Types of simple fruit
Simple fleshy fruit
Simple, dry, indehiscent fruit
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
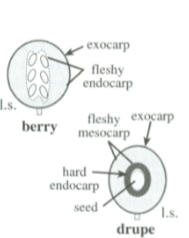
Berry
Simple, fleshy fruit
Exocarp and fleshy endocarp
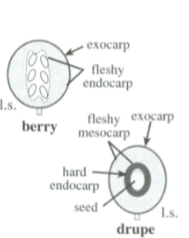
Drupe
Simple, fleshy fruit
Stony, hardend endocarps, often called “pits”, that surrounds and protects te seed, surrounded by a fleshy mesocarp
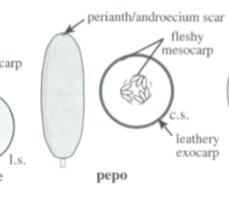
Pepo
Simple, fleshy fruit
Fleshy mesocarp and leathery exocarp
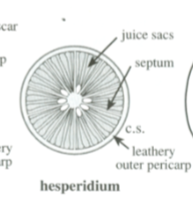
Hesperidium
Simple, fleshy fruit
Juice sacs divided by septum with a leathery outer pericarp
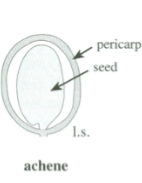
Achene
Simple, dry, indehescent fruit
Hardened pericarp surrounding an unattached seed
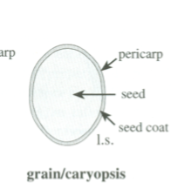
Grain/Caryopsis
Simple, dry, indehiscent fruit
Seed fused to pericarp
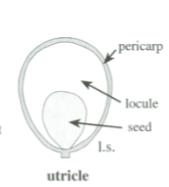
Utricle
Simple, dry, indehiscent fruit
Pericarp is inflated at maturity, resulting in a large locule
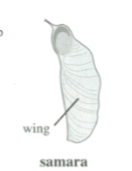
Samara
Simple, dry, indehiscent fruit
Winged fruit containing a seed
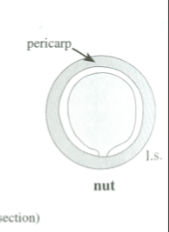
Nut
Simple, dry, indehiscent fruit
Hardened, thick pericarp surrounding an unattached seed
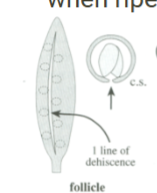
Follicle
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
One line of dehiscence
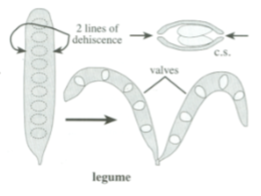
Legume
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
Two lines of dehiscence
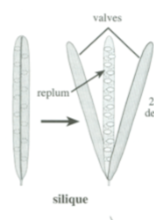
Silique
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
Two lines of dehiscence, leaves behind a replum, longer than wide
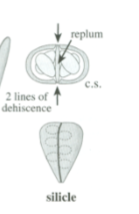
Silicle
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
Two lines of dehiscence, leaves behind a replum, wider than long
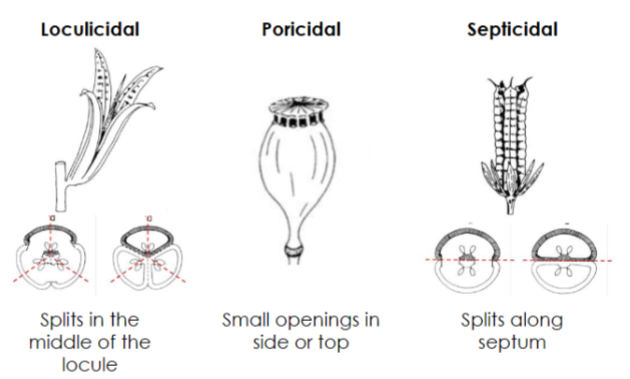
Capsules
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
Develop from flowers with syncarpous pistils
Loculicidal, poricidal, septicidal
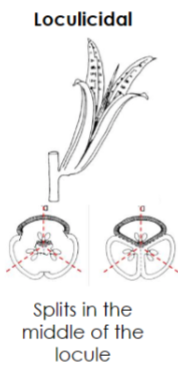
Loculicidal capsule
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
Splits in the middle of the locule, or cavity
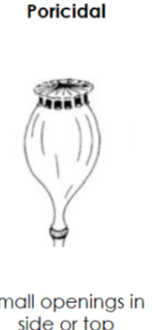
Poricidal capsule
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
Small openings on the top or side
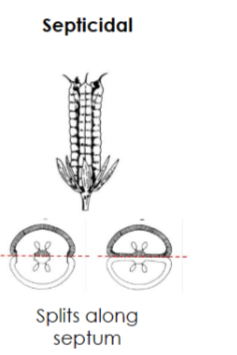
Septicidal capsule
Simple, dry, dehiscent fruit
splits along a septum
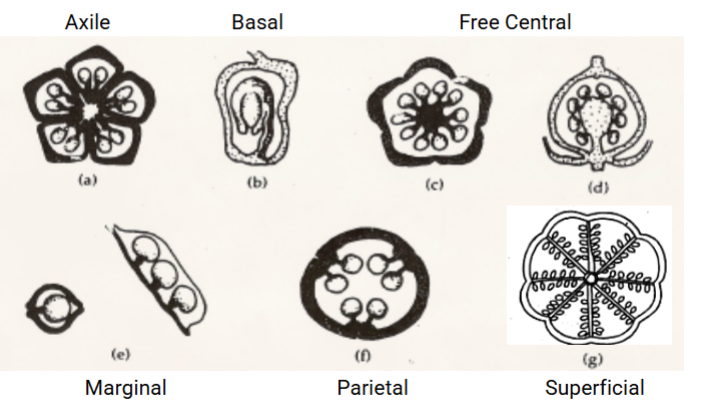
Placentation
The arrangement of ovule in the ovary
Axile, basal, free-central, marginal, parietal
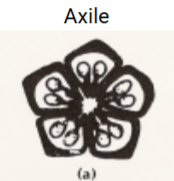
Axile placentation
Ovules attached to the central axis of ovary with two or more locules
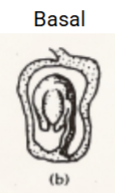
Basal placentation
Ovule positioned at the base of a single-loculed ovary
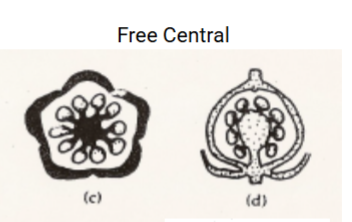
Free-central placentation
Ovules attached to a free-standing column in the center of a single-locule ovary
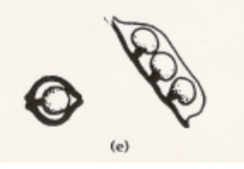
Marginal placentation
Ovules attached to the juxtaposed margins of a simple pistil

Parietal placentation
Ovules attached to the walls of the ovary