L3: Macromolecules
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Cells are mostly composed of…
Water and macromolecules.
An organic molecule is a molecule that:
Contains at least one C-H bond.
What are examples of nucleic acids?
DNA and RNA
What are the monomers of DNA?
Deoxyribonucleotides
What are the monomers of RNA?
Ribonucleotides
What is the basic composition of the nucleotides of nucleic acids?
A sugar bonded to a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base.
What’s the sugar in DNA?
Deoxyribose
What’s the sugar in RNA?
Ribose
Ribose and deoxyribose are:
5-Carbon sugars
What’s attached to each carbon in nucleic acids?
(1’) → Bonded to nitrogenous base
(2’) —> Bonded to H (deoxyribose) or OH (ribose)
(3’) —> Bonded to OH
(4’) —> Important but don’t need to know.
(5’) —> Bonded to phosphate
What polymers have directionality?
Nucleic acids, proteins, and carbohydrates.
What does polarity mean in regard to monomers?
Different “ends”; different functional groups at different ends of the molecule.
All polar monomers are added in:
The same orientation.
What’s on the 5’ end of nucleic acids?
The phosphate group
What’s on the 3’ end of nucleic acids?
The hydroxyl group bonded to the 3’ carbon.
What bond links nucleic acids?
Covalent phosphodiester bond
Carbohydrates are also known as:
Polysaccharides
What’s a dimer
Two monomers bonded
What bond connects monosaccharides and where?
A glycosidic bond between the 1’ and 4’ carbon.
What are the ends of polysaccharides?
4’ and 1’.
Do lipids have directionality/polarity?
No. They’re structurally diverse.
What linkage forms between the glycerol head and fatty acid tail of lipids?
A covalent ester bond.
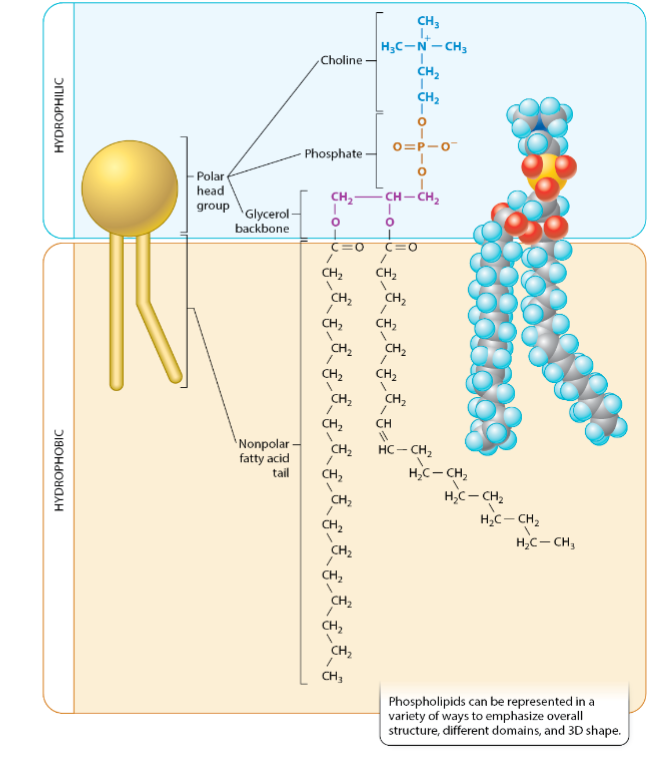
What’s the structure of phospholipids?
Polar head
Non-polar tail
Amphipathic
Can hydrophobic molecules still interact with water?
Yes, but relatively weak interactions (e.g. oil droplets still have to touch water; ID-PD)
What are macromolecules?
Larger molecules that are assembled from small repeating subunits.
Macromolecules — Subunits
Polymers — Monomers
Molecules like DNA, RNA, proteins and polysaccharides have directionality or polarity because:
Each end of the molecule has a different functional group
Lipids are chemically diverse molecules that share the property of:
Being hydrophobic
Where are nucleic acids in prokaryotes?
Nucleoid and Plasmids (DNA); Cytoplasm (RNA)
Where are nucleic acids in eukaryotes?
Nucleus, Mitochondria, and Chloroplast (DNA and RNA); Cytoplasm (RNA)
Examples of carbohydrates?
Starch and cellulose
Where are carbohydrates in prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Cell wall: structural support
Glycoproteins and glycolipids
How does a macromolecule get its directionality?
Monomers have distinct ends. (polarity)
Polymerization occurs in one direction, bonding opposite ends of monomers.
Results in a macromolecule with two distinct ends. (directionality)
How are nucleic acids synthesized?
Phosphodiester bond forms when 3’ OH attacks the 5’ Phosphate of incoming nucleotide.
5’ to 3’
How are carbohydrates synthesized?
Monosaccharides form a Glycosidic bond via a dehydration synthesis reaction.
Hydroxyl groups combine —> water released
How are triglyceride molecules synthesized?
Hydroxyl groups of glycerol combine with hydroxyl groups of 3 fatty acids: dehydration synthesis
Ester bonds
What macromolecule type is ATP?
Nucleic acid
Are carbs energy sources?
Yes.
What’s the backbone of a phospholipid?
Glycerol
Why is polymerization not spontaneous?
Creating polymers means creating more organized states, less entropy, and a positive free energy.
Identify which molecules are generally taken up from growth media versus molecules that are synthesized by cells.
Bacterial cells need some kind of carbon source* (often a sugar), nitrogen, and minerals.
With these things as starting materials, cells can make the various macromolecules (carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, lipids) and they can also produce CO2 via respiration.