Digital Marketing & eCommerce Review Flashcards
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover essential vocabulary and concepts from Digital Marketing and eCommerce relevant to exam preparation.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Evaluate, if it makes sense to invest 2 Euro per click in a PPC ad campaign on Google!
It makes sense in situations that result in direct response or selling a product or service online. Also, in the event of creating a good first impression, PPC works well in this arena. Another cost aspect to pay attention, is the lack of economies of scale, meaning the more traffic an ad generates the higher the costs. There is no bulk discount. Advertisers also may experience junk traffic and some PPC websites send PPC ads to the dark, sketchy alleys of the Internet where some ads have no business being.
avr booking value: 4%
100 clicks = 2.100 = 200 euro
100 * 4% = 4 reservations
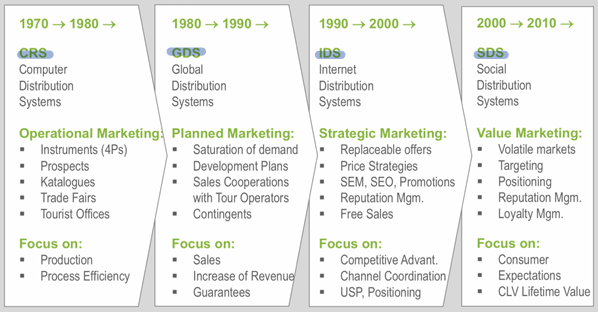
Explain how IT, distribution and marketing developed through the past forty years!
see image
Sales Volume
The amount of sold/rented goods/service in a period of time(roomnights, cars, consulting days)
Revenue (Turnover)
Sold amount multiplied by price per piece (room revenue, food and beverage revenue)
Yield
Total economic performance of a company (revenue + yield on capital + yield on investments)
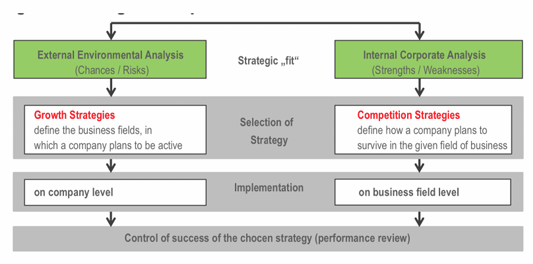
Define Corporate Strategy and the goal of strategic planning on corporate level!
The corporate strategy is the decision pattern of a company, its intentions, purposes or goals and a complex bundle of measures (actions). A strategy defines the basic orientation of a company on the market:The strategy defines the industries in which the company wants to compete, and defines which resources are necessary to turn the company's competencies into competitive advantages.
The goal of strategic planning is to ensure sustainably the existence and profitability of the company by building and defending competitive advantages which lead to above-average returns on investment.
Which two types of fundamental strategies need to be defined on corporate level?
see image:
Explain the relationship between cost, market share and profitability?
The higher market-share the higher profitability your Company will have . alchol market, hotel market, drug market (XD)
Specifically, as market share increases, a business is likely to have a higher profit margin, a declining purchases-to-sales ratio, a decline in marketing costs as a percentage of sales, higher quality, and higher priced products
List the four factors that cause the cost degression effect!
(1) Degression of fixed costs,
(2) efficiency through Learning effects,
(3) synergy effects through alliances / cooperations
(4) sales and purchasing power effects.
Explain is the fundament of a competitive advantage in customers’ perception!
Competitive advantage arises, if the price/value ratio (value for money) has 3 characteristics:
1. Special value for customers through an important, perceived performance advantage.
2. Permanent difference to the competition that cannot be made up.
3. Awakens a willingness to pay a price which permanently exceeds the costs of the service offer.
Name and explain the two types of competition strategies?
What drives the profit?
Difference Leader: profit driven by premium price -
Brand Strategy: profit driven by sales valume.

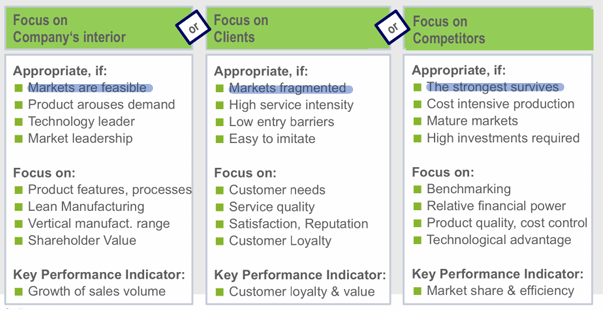
Describe the three fundamental orientations of companies?
When is each appropriate?
Company interior, Clients, competitors.
Outline the basic structure of a marketing strategy and explain briefly each step!
The goal of a marketing strategy is to achieve a competitive position in a given market.
Segmenting:
1. Selection of segmentation variables and segmention of the market
2. Profiling of each segment
Targeting:
3. Evaluation of attractiveness and profitability of each segment
4. Selection of target segments
Positioning:
5. Selection of segment specific positioning
6. Development and application of a concept
List and explain briefly the eight (8) components (working points) of a marketing plan!
1. Management Summary Concise, clear summary of the marketing plan >> What needs to be done, why, when, how, by whom, with which success measurement?
2. Market Study >> Macro environment, market trends, competition, products, distribution, consumption
3. SWOT Analysis >> Derivation of strengths, weaknesses, business opportunities, threats and risks
4. Business model, business plan >> Focus, strategic- operational - financial goals, measurement of achievement (KPIs)
5. Marketing Strategy >> Selection of the strategy to achieve the objectives (segmenting, targeting, positioning)
6. Marketing Mix (Product, Communication, Distribution, Price policy) >> Determination of budget, schedule, resources (personnel, skills, know how, plan B)
7. Success prognosis >> Forecast/estimation of the foreseed/expected financial impact of the company profit/loss
8. Monitoring of progress and achievement of objectives >> Results, personnel performance, profitability: products/markets/channels/campaigns/customers
Name and specify the five (5) components of a research plan!
◼ Data source: primary (new own study), secondary (existing external study)
◼ Survey method: observation, survey, group discussion (focus group), experiment
◼ Survey instrument: questionnaire, technical equipment (e.g. eye tracking)
◼ Sampling plan: Population, sample size, selection procedure of the sample
◼ Form of questioning: Written (postal / online), telephone, personal (face-to-face)
Name and explain the four (4) quality criteria of statistics and market research!
Objectivity (independence) The results of the experimental procedure must be independent of the person performing it (in terms of execution, evaluation and interpretation) and intersubjectively verifiable. So, if an other investigator/interviewer conducts the study, then with the same result.
Reliability (formal accuracy and reliability) The experimental procedure must be free of random errors, i.e. the measurement procedure and result must be repeatable.
Validity (conceptual correctness and validity) The found result must be valid, i.e. the examined must actually be recorde. The measurement procedure must actually measure what it claims to measure.
Representativeness (significance in terms of generalizability) The results of a sample may only deviate from the true value of the population with a certain probability of error.
List the three (3) components of a sampling plan!
Population, sample size, selection procedure
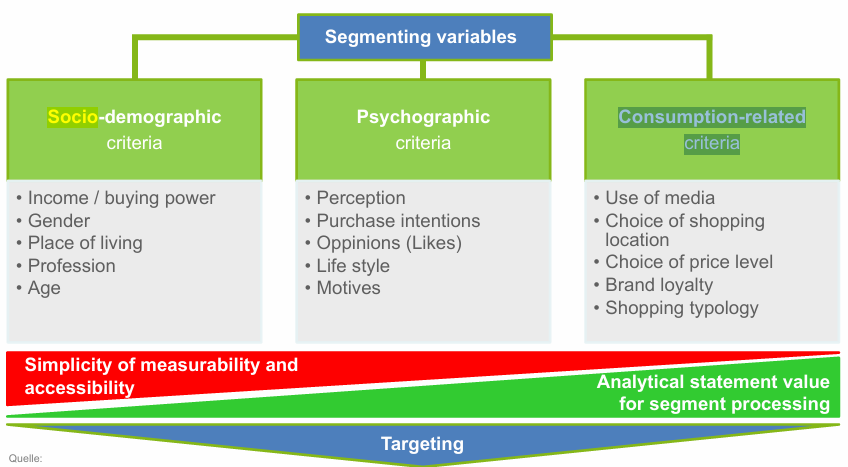
Which criteria (variables) are suitable for customer segmentation? Pros and cons
Socio-demographic criteria
Psychographic criteria
Consumption-related criteria
Definition of a brand according to David Olgily and under impact-oriented aspects?
Brand is, as advertising strategist David Ogilvy said: "the consumer's idea of a product".
Brands are - according to the impact-oriented definition - "images in the minds of consumers providing an identification and differentiation function to influence the selection behavior".
Define the positioning of a brand and what is a claim of a brand
Positioning of brands aims to distinguish a good from the competition so that it can be perceived by the buyers as special (unique) and unmistakable. Brands express their specialty in form of claims.
Claims of a brand are a kind of performance promise– through personality (brand identity), consistent quality, constant price-performance ratio, continuity in the advertising appearance and sales presence (ubiquity) in distribution channels used by target groups. A claim can express the following messages:
◼ Benefit - “What benefits will I gain from this product?” (e.g. feature, function, emotion)
◼ Reason to Believe - “Why should I trust this product?” (e.g. ingredients, composition, certification)
◼ Targeting- “Who is this product for?” (e.g. for specific occasion or person)
What needs to be considered from the view of consumers when preparing a positioning?
Claims of a brand are a kind of performance promise.
Benefit (what use), Reason to Believe (Why trust), Targeting (For who)
List the four (4) most important requirements of successful positioning
◼ The sought-after benefit must be important / relevant for the buyer.
◼ The benefit (quality) must be clearly perceptible by the buyer.
◼ The company must be competent to fulfill the benefit and expectations of the target consumers.
◼ The promised benefit should stay permanently stable and remain relevant for the buyer.
Explain what a Copy Strategy is and list the eight elements a copy consists of!
Copy strategy is the specification for an advertising campaign:
◼ It documents all strategic and creative requirements for the campaign.
◼ Copystrategy is the foundation for developing a brand message and architecture.
◼ Copystrategies serve as the agency's briefing from the client, form the framework for the creation and serve as a fee basis for the commissioned agency services.
The elements of a copy strategy usually include (illustrated by the example of Golden Well Hotel):
◼ Objective: Awareness and unique, attractive, premium positioning in a competitive market
◼ Target group:Couples, who want to spend a romantic time and explore the history of Prague
◼ Positioning: Small Luxury Romantic Hideaway Hotel
◼ Consumer Benefit:Histrocial residence with panaroma view from every guestroom and restaurant
◼ Reason Why: Genious location, rich history, former residence of a famous astronomer
◼ Key Visual: Panorama terrace showing a set dining table prepared for a candlelight dinner
◼ Slogal: Discover the secret gem and feel the magic of a genious location
◼ Tonality: Romantic, private retreat.
Define Customer Journey Analysis and what is the purpose/benefit of this analysis?
The phases during the customer journey are Awareness, Consideration, Intent and Decission.
Google tracks the customer journey (touchpoints) of various travel websites via Google Web Analytics.
◼ In England, the awareness phase is dominated by the influence of display advertising (banners).
◼ In USA the influence of social media dominates in the awareness phase.
◼ Consideration and intent can be effectively triggered by email advertising.
◼ In the intent phase (active search) consumers in both countries are influenced mainly by Paid Search.
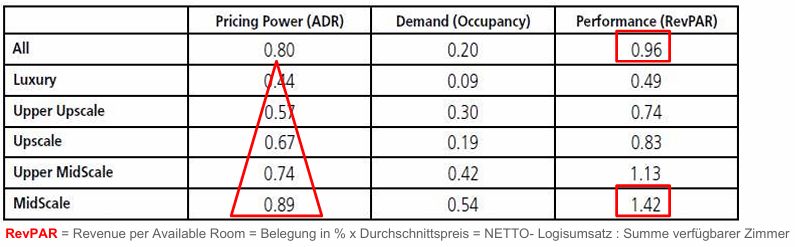
Summarize the impact of online reputation on hotel performance (Chris Anderson study)!
Prof. Anderson's analysis of the impact of ReviewPro's Global Review Index (GRI) - an indicator for the online reputation of hotels comes for the cities of Berlin, Chicago, London, Madrid, Miami, Milan, L.A., New York, Prague, Rome, San Francisco on the following result:
◼ A 1% improvement in online reputation increases the RevPAR by 0.96% (see 1st line)
◼ This effect is the stronger the lower the category of the rated hotel!
◼ For3-star hotels, a 1% improved reputation increases the RevPAR by 1.42%. ( 6th row )
◼ Presumably, an improved reputation reduces the uncertainty regarding service quality.
Calculate the RevPAR and ARR (turnover 10.000 Euro, available rooms 80, occupied 60)
RevPAR = 10000/80 = 125
ARR = 10000/60 = 166.7
Does an average 4-star hotel outperform by the discount- or premium-price strategy?
Premium price strategy
Explain the modern rate structure of international hotels serving various target groups!
Best Available Rate (BAR) should be in Rate Parity, means on the same level across all distribution channels and given to every distribution partner.
All Travelers, Business travelers, Leisure weekend travelers, Leisure holiday travelers.
Outline the horizontal price differentiation, explain its benefit for revenue management!
A constructuve solution to attract different types of consumers avoiding a price dumping is the application of restricted special offers for various target groups by horizontal price differentiation.
Horizontal price differentiation, a product is offered to different target groups at different prices. This strategy works well, if the target gruops can be separates - by different times, regions, channels ... Effectively, several price-quantity combinations fill the space under the function more than one price. The result is a larger total revenue (turnover) skimmed off the market ("consumer surplus").
List rate types for online travel agencies, business travel agencies and tour operators
Tourist Travel Agencies and Online Travel Agencies (OTAs) ◼agencies do not sell, but arbitrate/conciliate accommodation facilities and earn a commission
◼these type of agencies mainly work for leisture travellers and offfer published rates
◼usually the offer hotels at rack rates, best available rates and promotion rates
Business Travel Agencies
◼these type of agencies mainly work for business travellers and MICE travellers
◼they are organised and belong to various international agency networks, so called consortias
◼usually the offer hotels at published rack rates, best available rates and promotion rates and at confidential preferred rates, negotiated corporate rates and negotiated government rates. Negotiated rates are usually non-commissionable. Daily delegate rates apply in MICE travel segment.
Merchants and Tour Operators
◼these type of distributors sell accommodation facilities in hotels based on a contracted allotment of rooms
◼they buy the rooms at a so called Net Rate to keep them available and sell the rooms at published rates
◼these resellers make their profit through a mark-up- a difference between purchase price and retail price
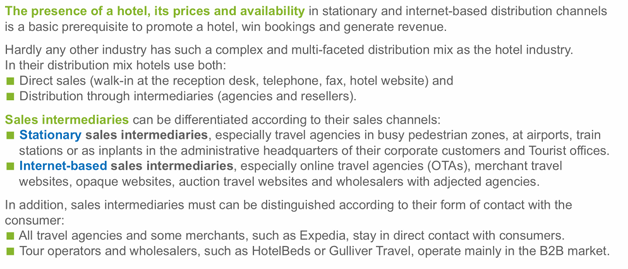
Explain why producers (hotels) need distributors (intermediates)?
Because distributors have a broad reach (Billboard Effect). They cover the operating distance between producers and consumers and some even extend the scope of services through added benefits.
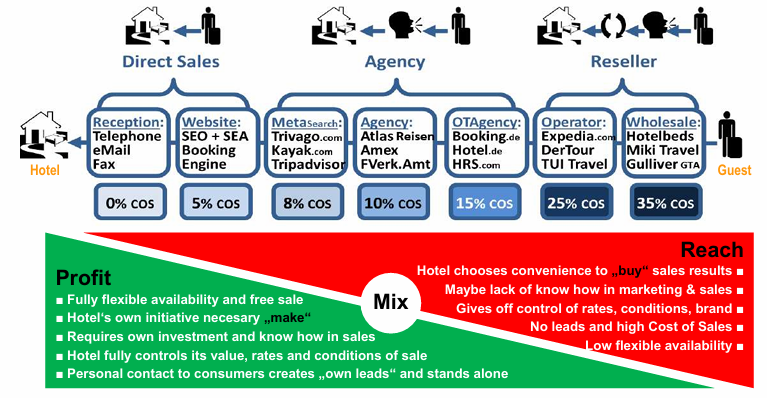
Outline the distribution mix of hotels and explain the trade off!
Compare and explain the business model of merchants and agencies!
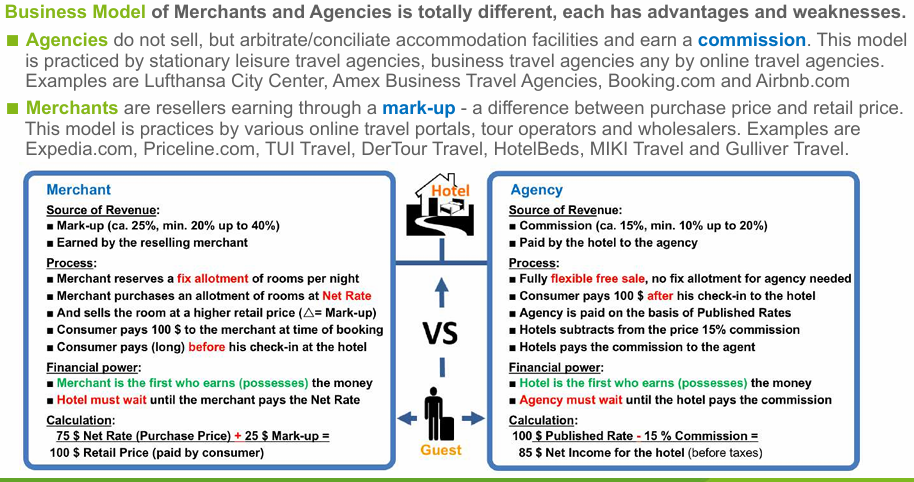
List and explain the main five (5) business models of distributors and name examples!

Explain the meaning of targeting quality of various categories of media!
Billboard Effect: Hotels can demonstrably gain in direct sales and generate more bookings via their own website by maximally expanding their presence on online travel agencies (OTAs).
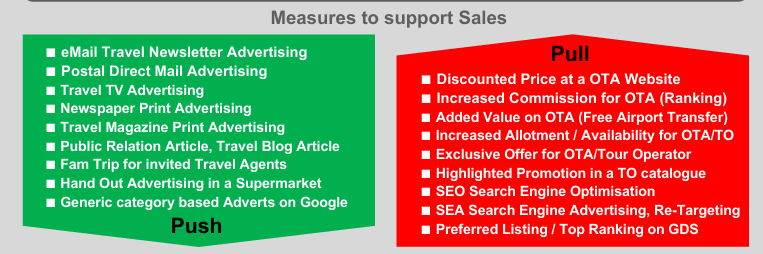
Explain the difference and benefit of Push Promotion and Pull Promotion!
Presence of hotels in distribution systems is a basic prerequisite to generate bookings and revenue. However, presence alone is not enough because the distribution channels are usually filled with more or even numerous competitors.

List and name three (3) different measures (examples) of Pull and Push Promotion!