Hybridization
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Denaturation
separation of 2 strands
double stranded to single stranded
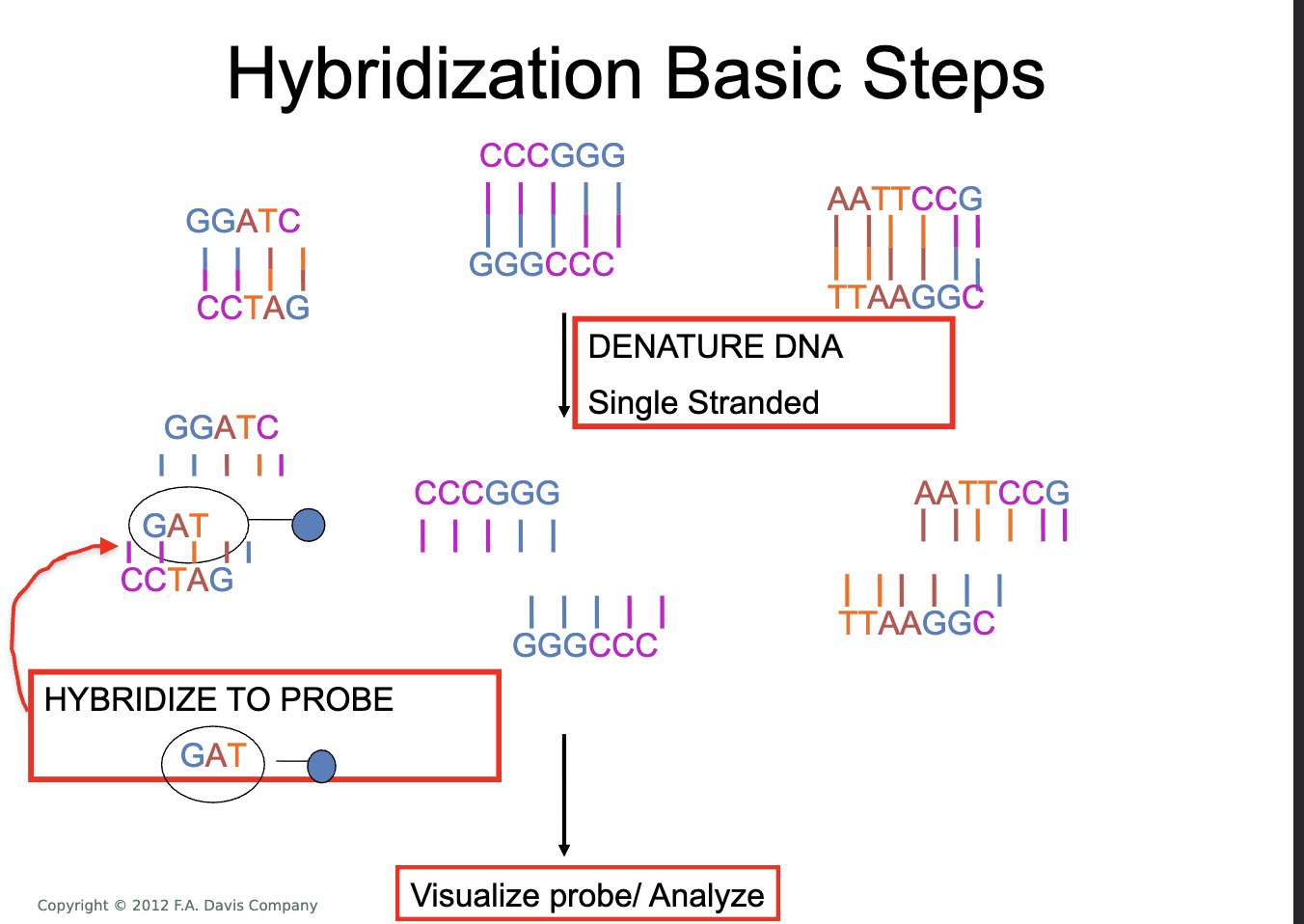
Hybridization
joining of 2 complementary strands
single stranded to double stranded
Hybridization purpose
detection of a specific DNA or RNA sequence within your sample
VERY important technique in molecular
probe and target have complementary sequences
in optimized conditions the probe and target hybridize, anneal to each other
temperature, hybridization buffer
Target
DNA (gDNA, PCR product)
RNA
Probe
DNA
RNA
oligonucleotides
small pieces of DNA 18-50 bp long
must be complementary to target DNA
antiparallel
not identical
specific for target
must be labeled for visualization
Probe rules
need to recognize target ONLY
longer the probe, the more specific
shorter sequences can be useful for finding small mutations
hybridization conditions (stringency) affect the bidning
high = less forgiving
temp, pH, salt concentration
Probe must be labeled
labeling makes probe visible
high specific activity (small amt, highly visible)
radioactivity: 32P
Biotin
Fluorescent
Enzymes
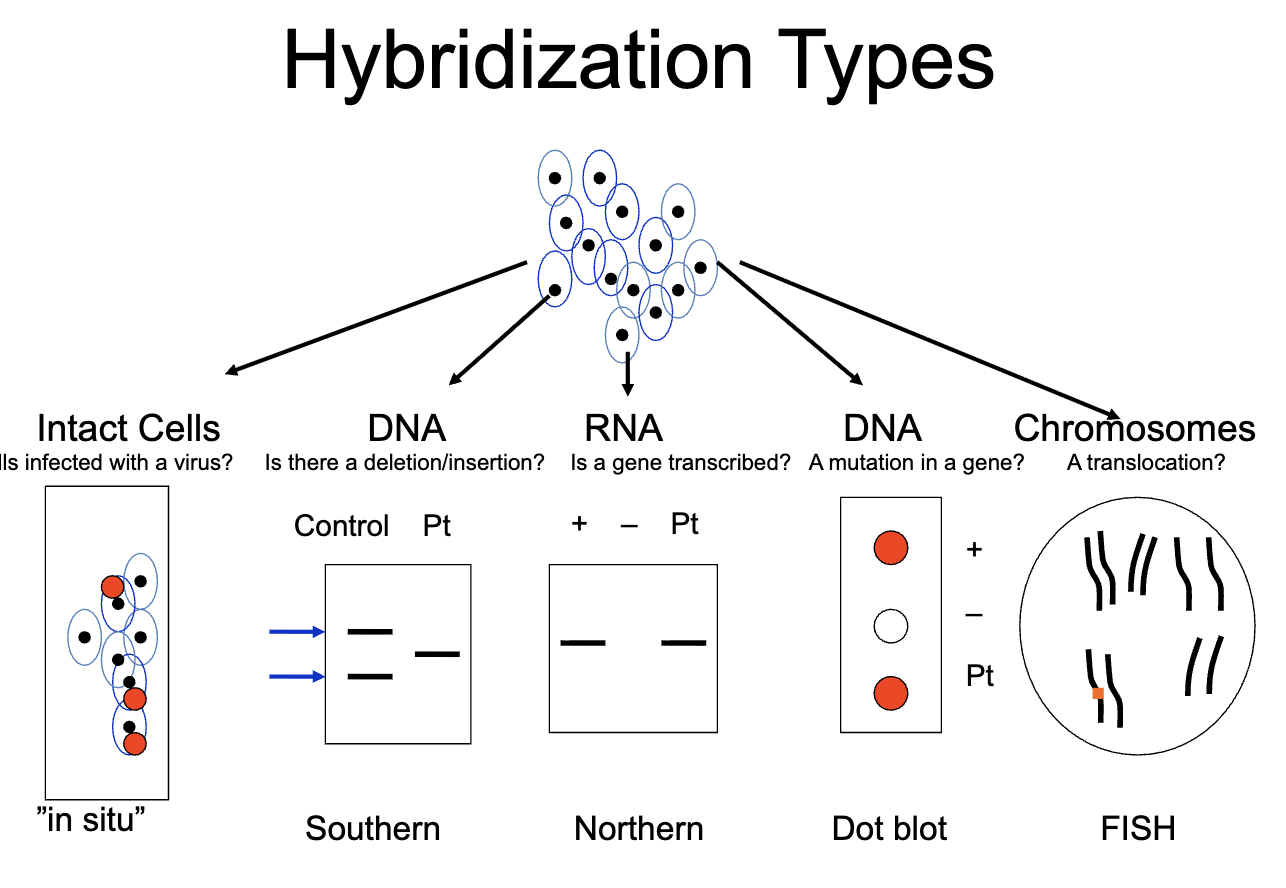
Hybridization types
southern blot
northern blot
“in situ” hybridization
fluorescent “in situ” hybridization. FISH
Dot blot/ reverse dot blot/ slot blot
microarrays
solution hybridization
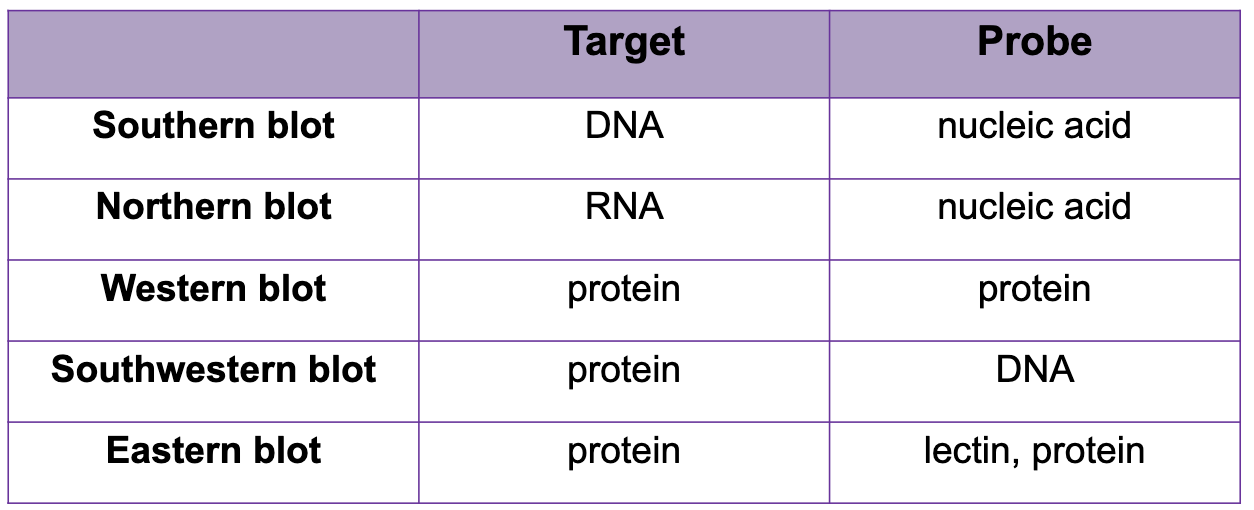
Southern blot
developed by edwin southern
allows analysis of any specific gene or region without having to separate it from a complex background
Southern Blot info
target and probe is DNA
information obtained:
presence of a particular sequence in genome
size of DNA fragment
Southern blot steps
DNA purification, fractionation, electrophoresis
denaturation
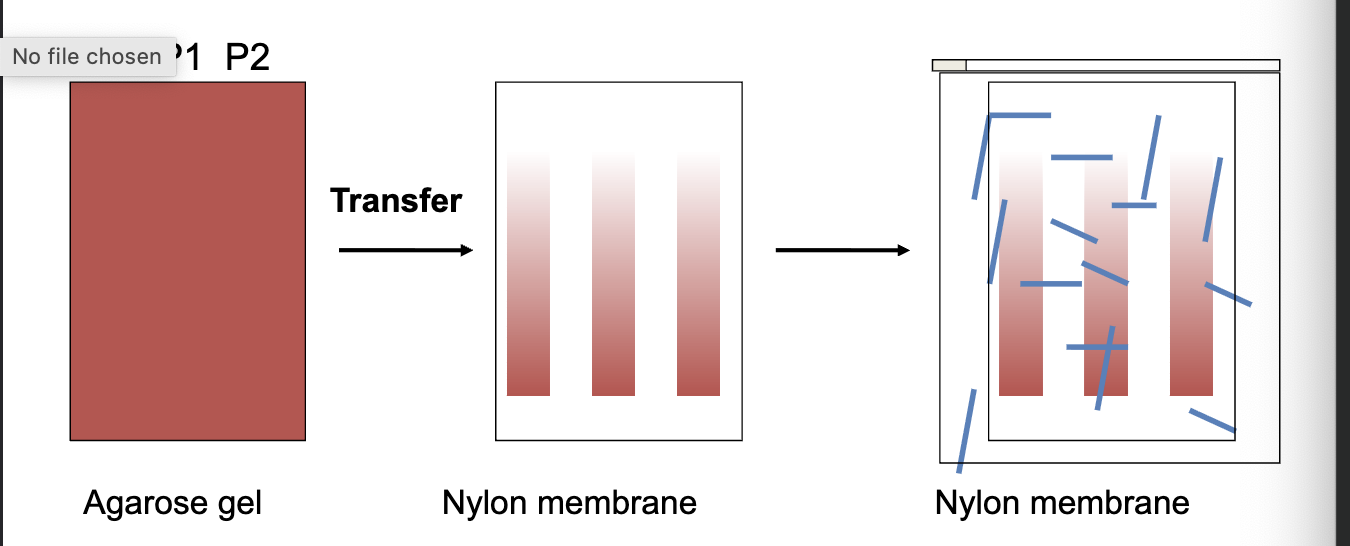
transfer onto membrane
hybridization with labeled DNA probe
detection
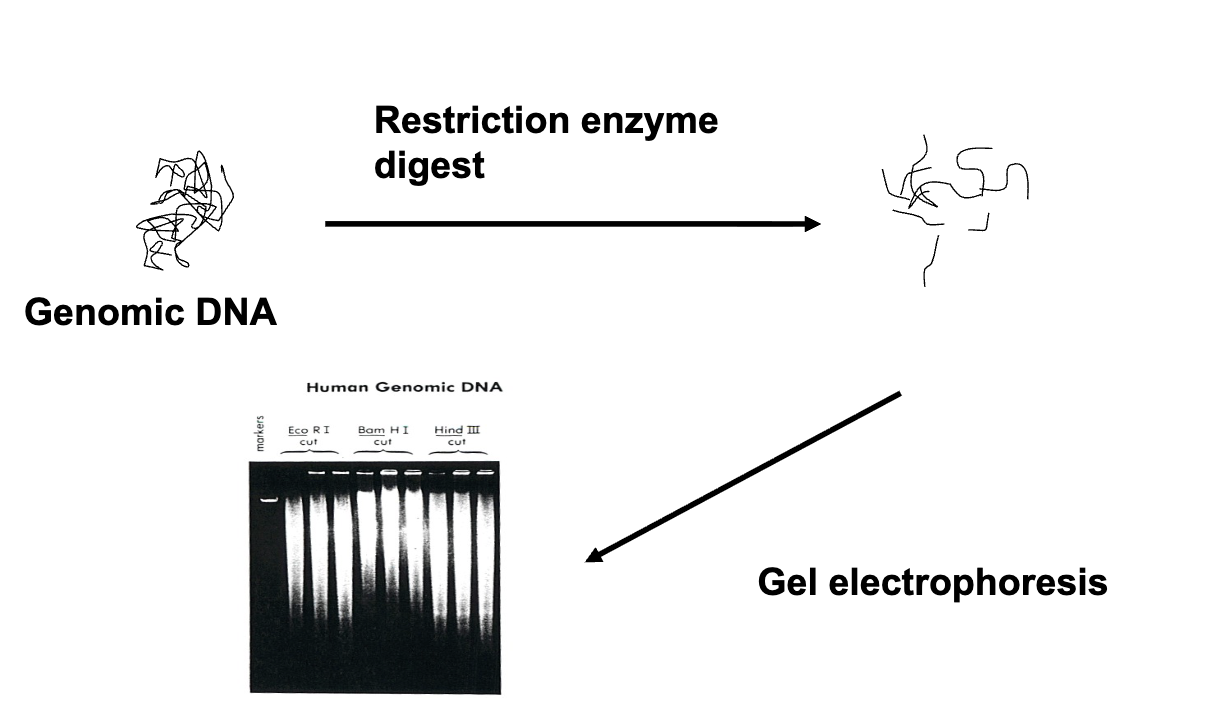
Gel prep before transfer to membrane
Depurination
fractionate DNA
acid solution
Denaturation
separation of DNA strands. Obtain single strand of DNA
alkaline, high salt solution
Neutralization
Neutralize gel
tris, high salt solution
Transfer to membrane
membrane: DNA binding media that gives solid support
nitrocellulose membrane
nylon membrane. Neutral or + charged
special membrane
Southern blot: DNA transfer
electrophoresis
vacuum transfer
electrophoretic
Hybridization details
once DNA is transferred to membrane, hybridization of probe determines which DNA fragment is seen
membrane
hybridization buffer
contains blocking agents to reduce bg (BSA, RNA, DNA, dry milk)
labeled probe
temps: 37-65°C (2-16hrs)
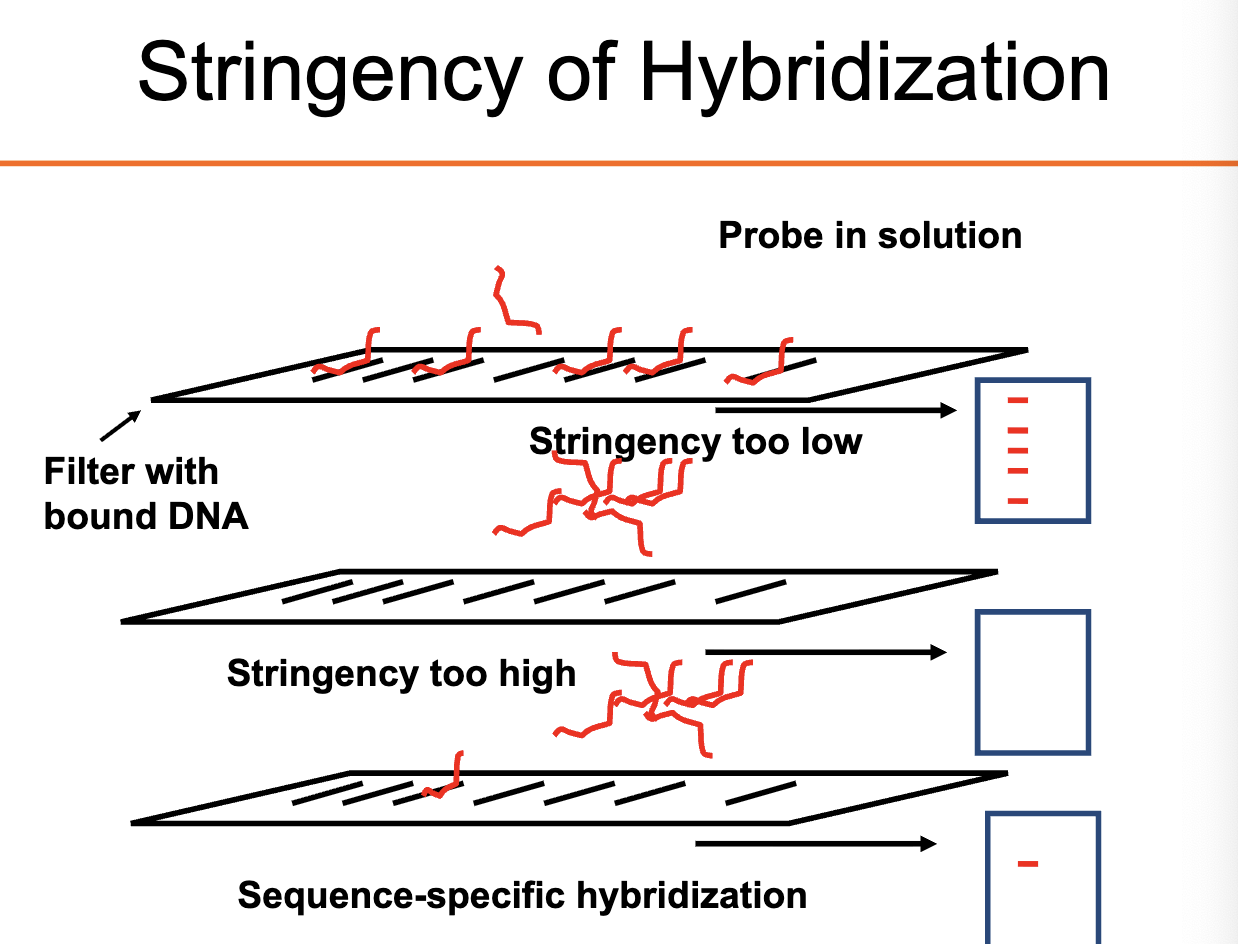
Hybridization steps - washes
low stringency. High salt, room temp
high stringency. Low salt, high temp
hybridization steps - detection
X-ray film
color development
Southern blot applications
genetics, oncology (translocations, gene rearrangements)
typing/classification of organisms
cloning/verification of cloned DNA
forensic, parentage testing (RFLP, VNTR)
Northern blot
target: RNA
probe: DNA
information obtained:
presence/abundance of mRNA (lvls of gene expression), tRNA, rRNA
size of RNA
alternative splicing
Filter based hybridization technologies
Northern blot steps
RNA purification (obtain mRNA)
no restriction digests
gel electrophoresis
RNA transfer onto membrane
hybridization of membrane with labeled DNA probe
detection
Dot blot
simplified southern/northern blot
no gel electrophoresis or transfer
mixture of molecules is applied directly on a membrane, followed by probe hybridization
no complex blotting procedures → time saving
no information about size of detected molecule
only confirms the presence or absence of molecules detected by probe
DNA microarray technology
used to investigate multiple genomic sites simultaneously
small, solid support
thousands of diff unlabeled DNA probes
specimen DNA is labeled and hybridized to probes
“reverse dot blot” methods
DNA microarrays uses
genome-wide expression analysis
which mRNA is produced?
CGH: comparative genome hybridization
analyzes genomic DNA
detect chromosomal duplication/deletion
In situ hybridization
target: DNA or RNA
probe: DNA
cells, tissues onto slides
information obtained:
presence of DNA or RNA sequence
correlation with histopathology
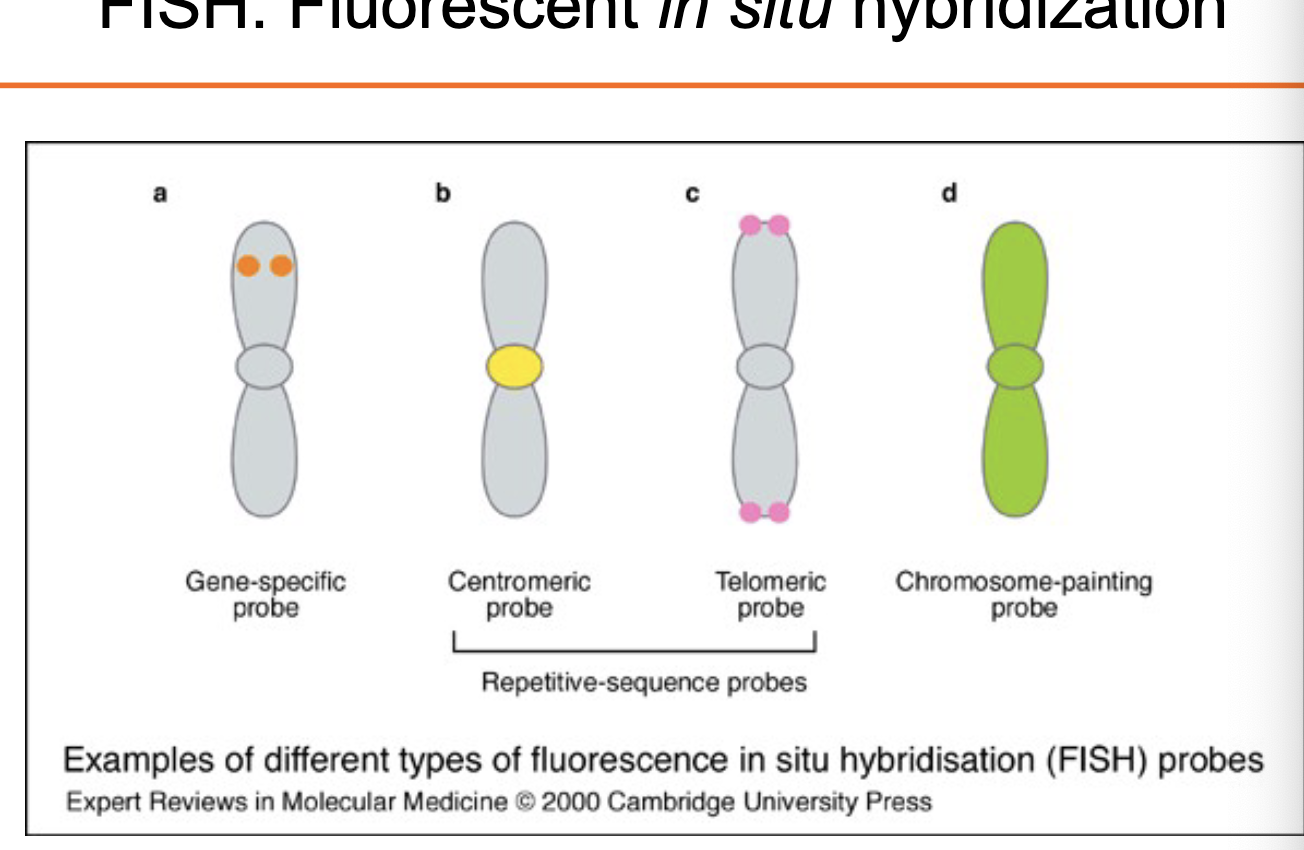
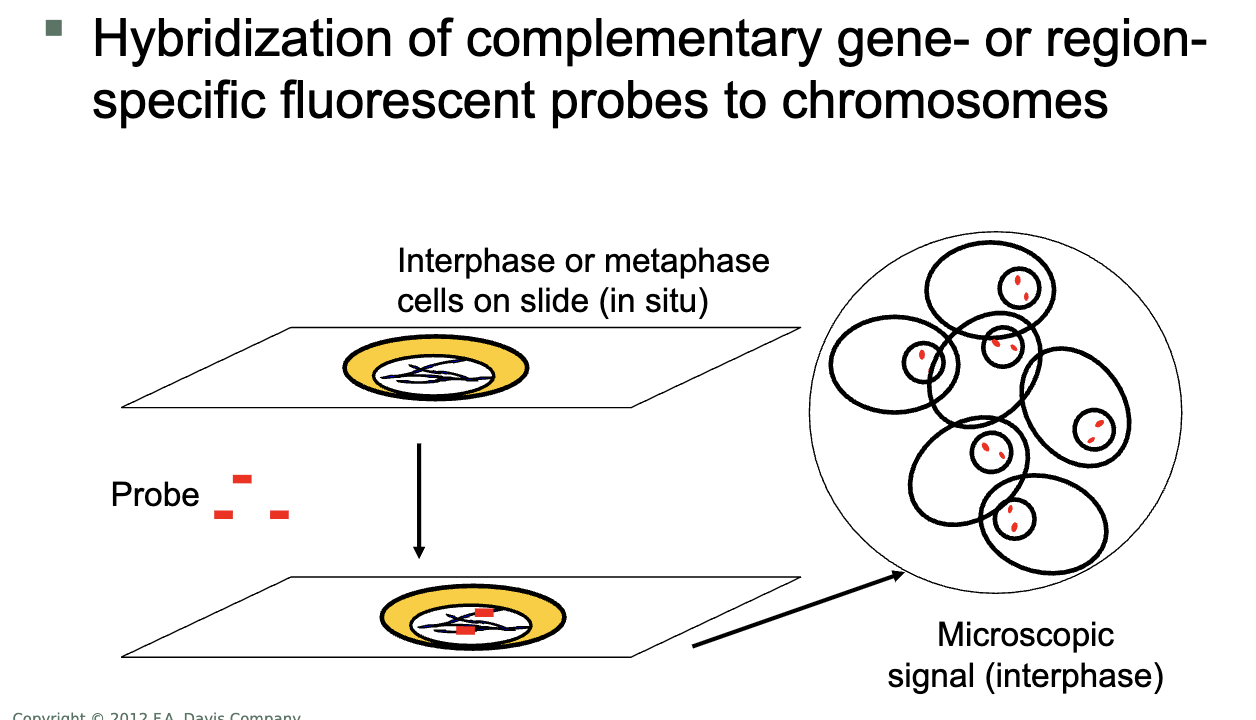
FISH: fluorescent in situ hybridization
probe: DNA
target: DNA
metaphase chromosomes or interphase nuclei
probes. fluorescent labeled
various types of probes used
detect chromosomal abnormalities
translocations, deletions, aneuploidies
detect and/or monitor a disease
Different FISH probes