Ochem - Ch. 22: Metabolic Pathways for Carbohydrates
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chem 106
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
What are the three stages of metabolism?
Stage I: Digestion & Hydrolysis; Stage II: Glycolysis & β-oxidation; Stage III: Citric Acid Cycle & ETC.
What is the difference between anabolic and catabolic pathways?
Anabolic: builds molecules and requires energy
Catabolic: breaks down molecules and releases energy
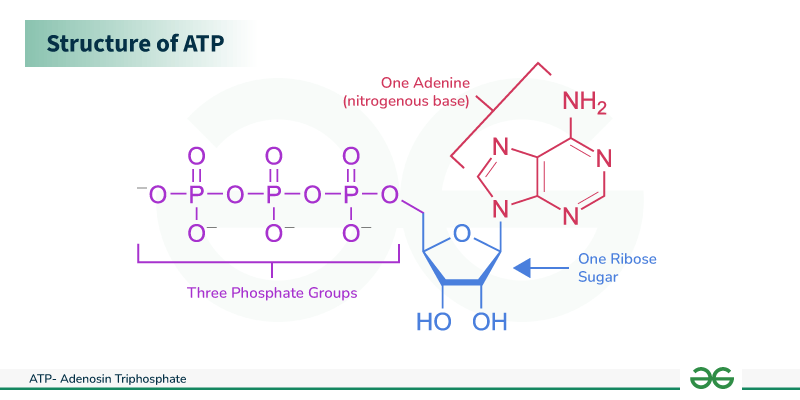
Describe the structure of ATP.
Adenosine (adenine + ribose) + 3 phosphate groups.
How does ATP drive cellular reactions?
By transferring a phosphate group to reactants, increasing their energy.
What is the function of NAD+/NADH and FAD/FADH2?
Electron carrier in redox reactions during metabolism.
NAD+/NADH: oxidation of alcohol → aldehyde
FAD/FADH2: oxidation of alkane → alkene
What does coenzyme A do?
Transfers acetyl groups in metabolic pathways.
What are the products of dietary carbohydrates hydrolysis and where does it occur?
Glucose, fructose, galactose (from starch, maltose, lactose); occurs in mouth and small intestine.
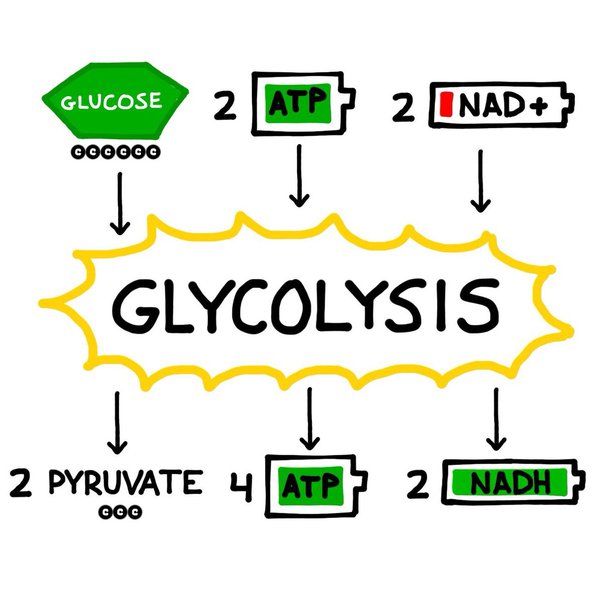
What are the starting materials and products of glycolysis?
Starts with glucose, ends with 2 pyruvate, 2 ATP (net), and 2 NADH.
How is glycolysis regulated?
By key enzymes (e.g., hexokinase, phosphofructokinase) and allosteric effectors.
What happens to pyruvate under aerobic conditions?
It is converted to acetyl CoA and enters the citric acid cycle.
What happens to pyruvate under anaerobic conditions?
It is reduced to lactate in humans.
What is glycogenolysis?
The breakdown of glycogen into glucose, promoted by glucagon and epinephrine.
What is glycogenesis?
The synthesis of glycogen from glucose, promoted by insulin.
What is gluconeogenesis?
The synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources like amino acids or lactate.