ch 9: the intrapsychic domain - psychoanalytic approaches to personality
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
what is the basis of psychoanalytic theory?
instincts (provide energy)
→ libido (life)
→ thantos (death)
→ psychic energy
source of energy in everyone that fuels motivation
explain the unconscious motivation and the mind
conscious
pre-conscious
unconscious
what is id?
primitive and dominant in infancy
drives all urges
pleasure principle
primary process thinking
wish fulfillment
what is ego?
contrains “id“ within reality
develops around 2-3 yo
reality principle
secondary process thinking
what is super ego?
internalizes values, morals (around age 5)
the conscience
not necessarily reality-based → people can set their own standards
what are the dynamics in personality - anxiety?
objective anxiety: real threat
neurotic anxiety: id-ego conflict
moral anxiety: id/ego & super ego conflict
the ego functions to minimize anxiety & cope with threats via defence mechanisms
what is repression?
preventing unacceptable thoughts, feelings, urges from reaching conscious awareness
what is denial?
insisting that things are not as they seem by refusing to see facts
what is displacement?
a threatening/unacceptable impulse is directed from its source to non-threatning target
what is rationalization?
generating acceptable reasons for outcomes that otherwise appear socially unacceptable
what is reaction formation?
to reduce an urge, one may show an opposite reaction
what is projection?
project own unacceptable desires, urges &/or qualities onto others
related to false consensus effect
what is sublimation?
channeling unacceptable insticts into a socially desirable activity
how is psychosexual stages and personality determined?
conflict resolution
balance of pleasure vs. demands
people’s defence mechanisms
the (psychosexual) stages reached
→ occurs at human nature level
what are the psychosexual stages and personality?
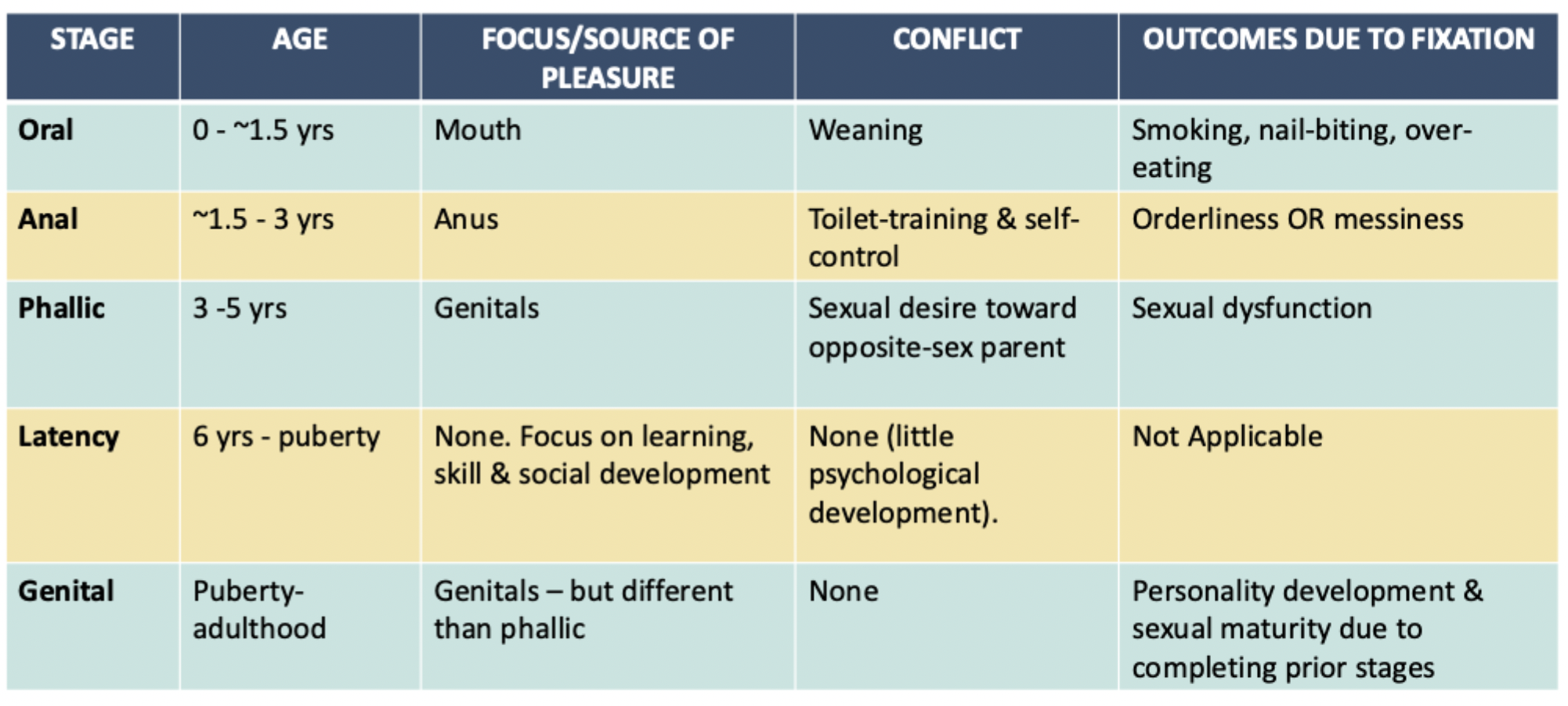
what is psychoanalysis?
form of psychotherapy used to treat mental health difficulties/disorders & to restructure personality by making the unconscious conscious
1st goal: identify unconscious thoughts/feelings
2nd goal: once patient is aware of this material, help them deal with it maturely/realistically
what are techniques for revealing the unconscious?
free association: patients relax & say what is on their mind (unfiltered context)
dream analysis: dream interpretation (content & meaning)
manifest content: actual content
latent content: what content means
how are projective tests used?
following the previous techniques
→ interpretation(s) - (by psychoanalyst)
→ insight (by patient)
→ cognitive understanding of one’s problems & corresponding intense emotional experience
what is the process of psychoanalysis?
as progress is made toward insight there might be…
resistance: patient sets up unconscious obstacles that work against progress
transference: reaction (displacement) toward therapists as if therapist were someone in patient’s life
what is the impact of freud’s contributions?
led to “talk therapy” & more modern forms of psychological treatment
his works have been integrated into society at large
his works have guided many research questions in psychology
among the few to develop a theory at the human nature level