MLT 118 Exam 5
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Which of the following is not part of measure central tendency :
A. Median
B. Mode
C. Range
D. Mean
Range
The value that occurs within the greatest frequency is the…
Mode
The value at the center or midpoint of the observations is the….
Median
The calculated average of the values (add all value and divide by total number of values)
Mean
Most clinical chemistry tests are…
quantitative
The following are measures of central tendency?
Mode
Mean
All listed
Median
All listed
Obtaining the same result after testing the same specimen three times is called test:
Precision
The ability to obtain the published result on a control specimen is referred to as:
Accuracy
A procedure with a coefficient of variation of 10% is considered:
Imprecise
The results of a precision study cholesterol are shown below.
What is the coefficient of variation for the study?
Mean = 150 mg/dL
Standard deviation = 15 mg/dL
10.0% (5% is the limit)
What is the Coefficient of Variation for a set of numbers when:
1 SD = 6.8, mean = 80, and the (range for ± 1 SD = 73.2 - 86.8)?
8.5%

The 99% confidence limit refers to values that fall within:
Range equal to the mean plus or minus two standard deviations
Range equal to the mean plus or minus one standard deviation
Range equal to the mean plus or minus four standard deviations
Range equal to the mean plus or minus three standard deviations.
Range equal to the mean plus or minus three standard deviations.
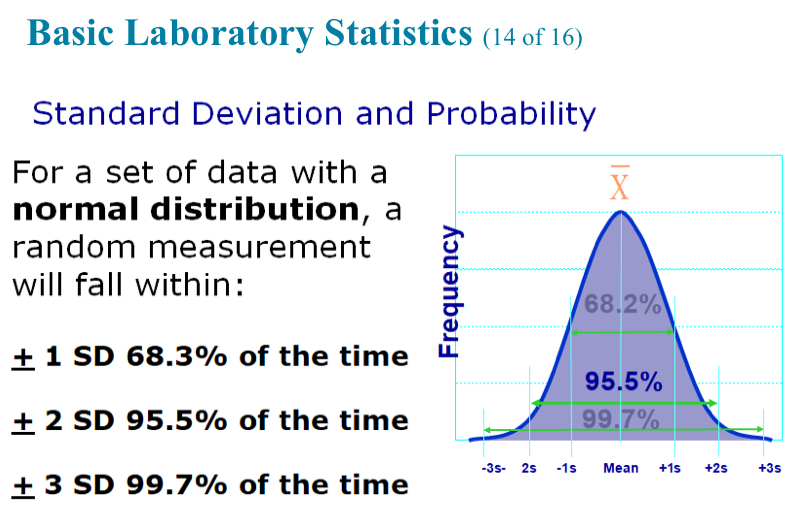
In a normal distribution of results, the mean value +/- 2 SDs will include what percentage of the population?
95.5%
99.7%
68.2%
100.0%
95.5%
A cross-reacting compound in a serum sample may result in which of the following?
A) A reliable result
B) A precise result
C) An accurate result
D) A discordant result
B) A discordant result
What does the equation TP/(TP + FN) measure?
Sensitivity
Specificity
Positive Predictive Value
Negative Predictive Value
Sensitivity
Testing of unknown specimens from an outside agency that provides validation of the quality patient results is:
Internal Quality Control
External Quality Control
Electronic Quality Control
Proficiency Testing
Proficiency Testing
If the QC result for the normal level of control is outside the range defined for that control level, normal patient results may be reported. True or False?
False
What are the 95% confidence limits for a control mean of 140mg/dL and a standard deviation (s) of 2.5mg/dL?
138 - 142
132.5 - 147.5
137.5 - 142.5
135 - 145
135-145
Exp. 95% confidence limits is ± 2S so take the mean (140) and ± it by 2 to get the low and high ranges.
Proportional error in a method is characterized by which of the following?
The magnitude of the error increases as the concentration of analyte increases.
The magnitude of the error stays the same over a wide concentration range.
The magnitude of the error decreases as the concentration of analyte increases.
The magnitude of the error is inversely proportional to concentration.
The magnitude of the error increases as the concentration of analyte increases.
A deterioration of Quality control while in use can result in which of the following types of errors?
Transcriptional
Clerical
Systematic
Random
Systematic
The result of a precision study of glucose are shown below. What is the coefficient of variation for this study?
Mean= 100mg/dL Standard Deviation= 5mg/dL
7.5%
10%
2.5%
5%
5%
1 2S is what kind of rule? Warning or Rejection?
Warning
2 2S is what kind of rule? Warning or rejection?
Rejection
R4S is what kind of rule? Rejection or Warning?
rejection
> 3S is a…warning or rejection?
rejection
= 2SD of one analyte is a…
warning
± 1 SD is what percentage?
68.3% (of the time)
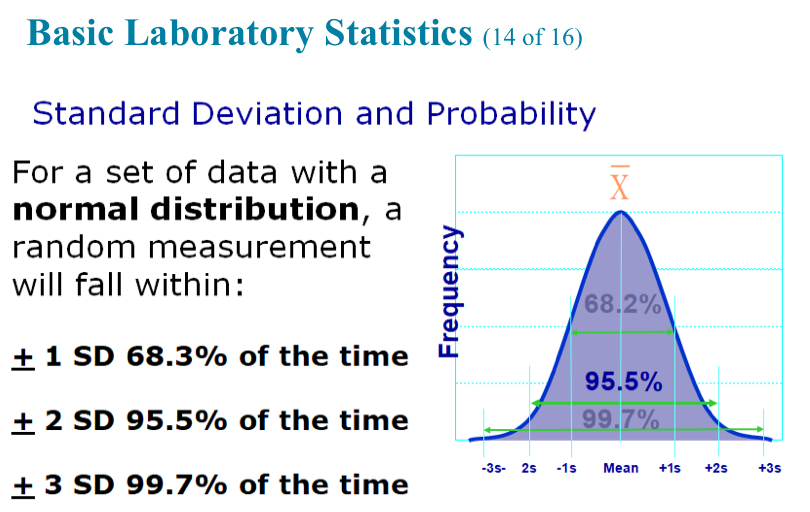
± 2 SD is what percentage?
95.5% (of the time)
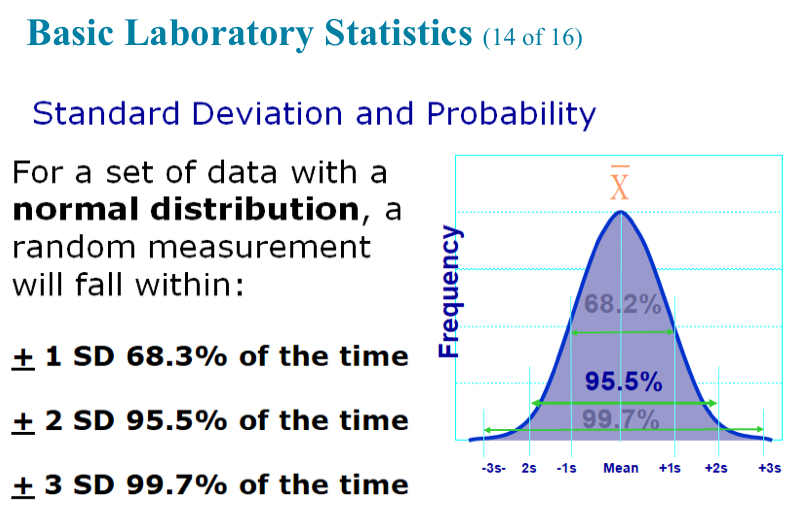
± 3 SD is what percentage?
99.7% (of the time)
If a test is said to have sensitivity of 95%, statistically, this means that it will:
Detect 5 out of 100 true positives
Miss 5 out of 100 true negatives
Detect 5 out of 100 true negatives
Miss 5 out of 100 true positives
Miss 5 out of 100 true positives
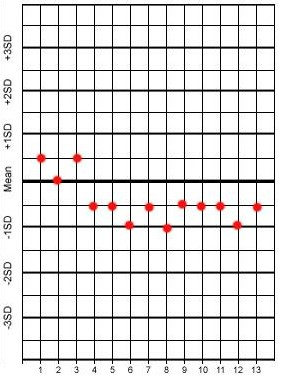
Which type of error is represented in the image below?
Systematic
Occurs without prediction or regularity
Random errors
Operator technique or pipetting mistakes are considered…
random errors
Error that is consistently low or high, constant as well.
Systematic Errors
Deterioration of reagents in use and Deterioration of control material while in use are considered…
systematic errors
Which of the following best describe random error?
Results may be either above or below the mean.
Results are consistently below the mean.
Results are consistently above the mean.
Results must eb either above or below the mean, but must be the same percentage away from the mean.
Results may be either above or below the mean.
Clinical laboratory personnel have the least control over which of the following conditions?
A. Pre-examination variables
B. Examination variables
C. Post-examination variables
D. All of the above
A. Pre-examination variables
What is a lyophilized control?
A control that does not resemble human blood.
A control that is dehydrated to powder.
A control that is outside of the expected range.
A control that is made directly by the laboratory.
A control that is dehydrated to powder.
The preparation of a Levey-Jennings quality control chart for any constituent of serum requires:
A minimum of 20-30 analyses of control serum over a period of 20-30 days.
20-30 analyses of control serum on one day, one batch.
Daily analyses for 1 month with the use of aliquots from more than one lot control serum.
20-30 analyses performed by one person.
A minimum of 20-30 analyses of control serum over a period of 20-30 days.
A Levy-Jennings chart is considered post-analytical phase of Quality assurance cycle.
A) True
B) False
False, it’s analytical.
A 1(3s) quality control rule violation is defined as:
A) One control result that exceeds ±3s
B) One control result that exceeds ±1.3s
C) Three consecutive controls results that exceed ±3s
D) One control result that exceeds ±4s
A) One control result that exceeds ±3s