Earth Science - Chapter 1 - Introduction to Earth Science
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Science
A way of learning about the natural world through observations and logical reasoning.
Attitudes of scientists
Curiosity;
Honesty;
Open-Mindedness;
Skepticism, and
Creativity
Skills of scientists
Observing;
Inferring and;
Predicting.

Observing
The process of using one or more of your senses to gather information.
Your senses include: sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell.

Inferring
Interpreting observations based on prior knowledge or experience.

Predicting
The process of forecasting what will happen in the future based on past experience or evidence.

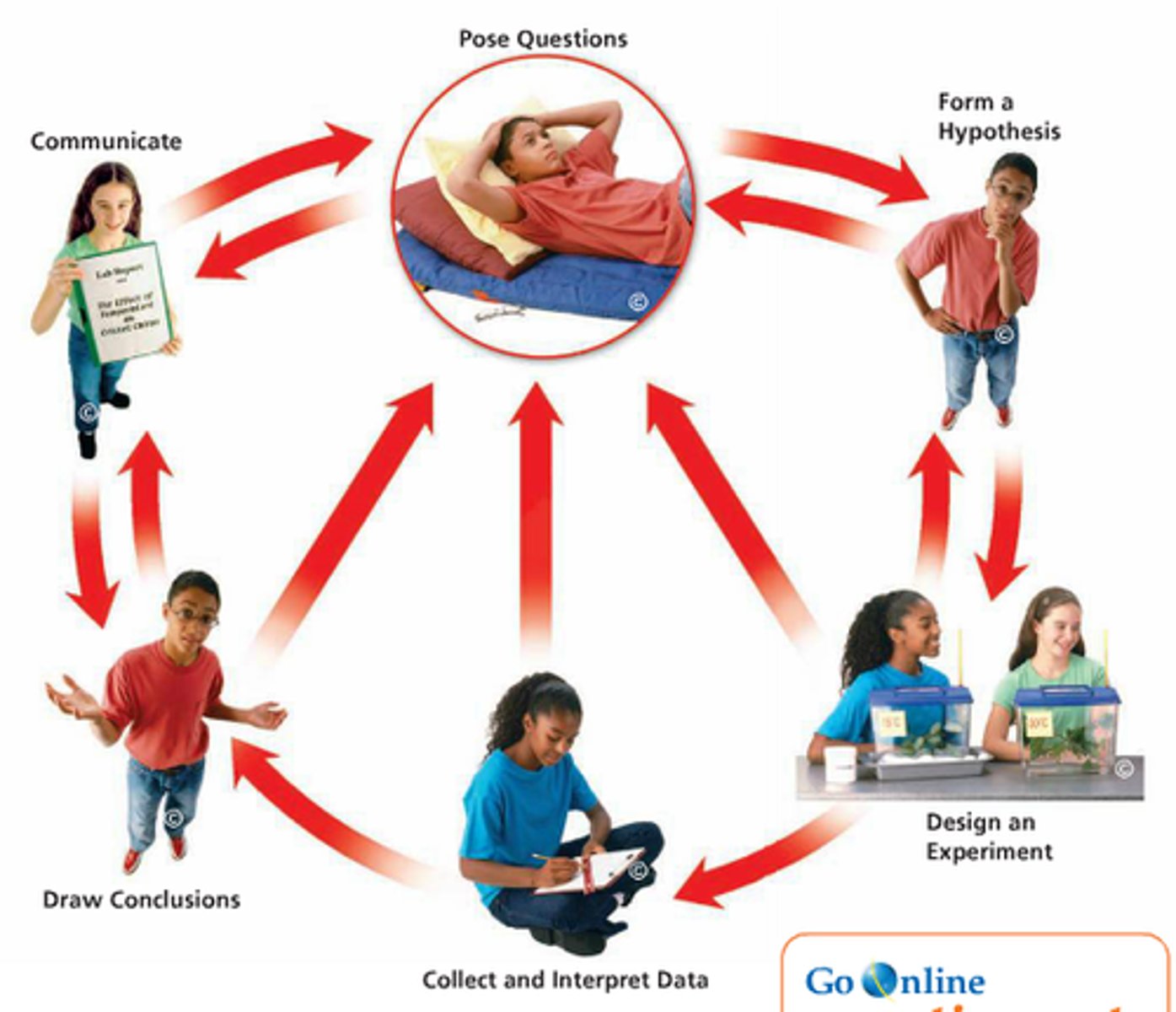
Scientific Inquiry
The ongoing process of discovery in science;
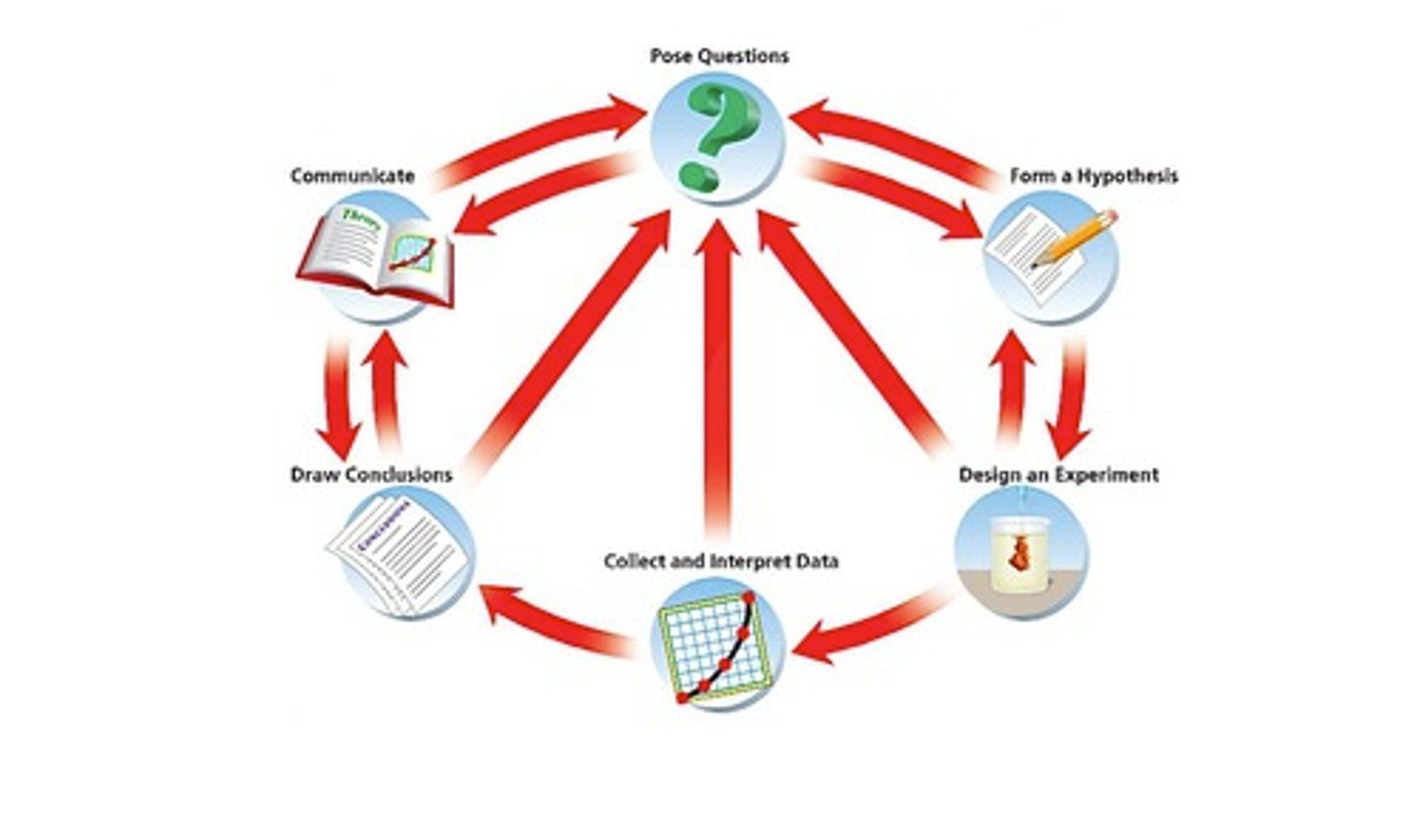
Steps of a Scientific Inquiry
1. Collecting Facts : posing questions
2. Developing a Hypothesis;
3. Observing and Experimenting: designing an experiment, collecting and interpreting data;
4. Accepting, modifying, or rejecting the hypothesis:
5. Drawing conclusions and
6. Communicating the results of the experiment.
Scientific Inquiry
The ongoing process of discovery in science;
The diverse ways in which scientists study the natural world and propose explanations based on evidence they gathered.
Hypothesis
A possible explanation for a set of observations or answer to a scientific question; It must be testable.

Controlled Experiment
An experiment in which only one variable is manipulated at a time.
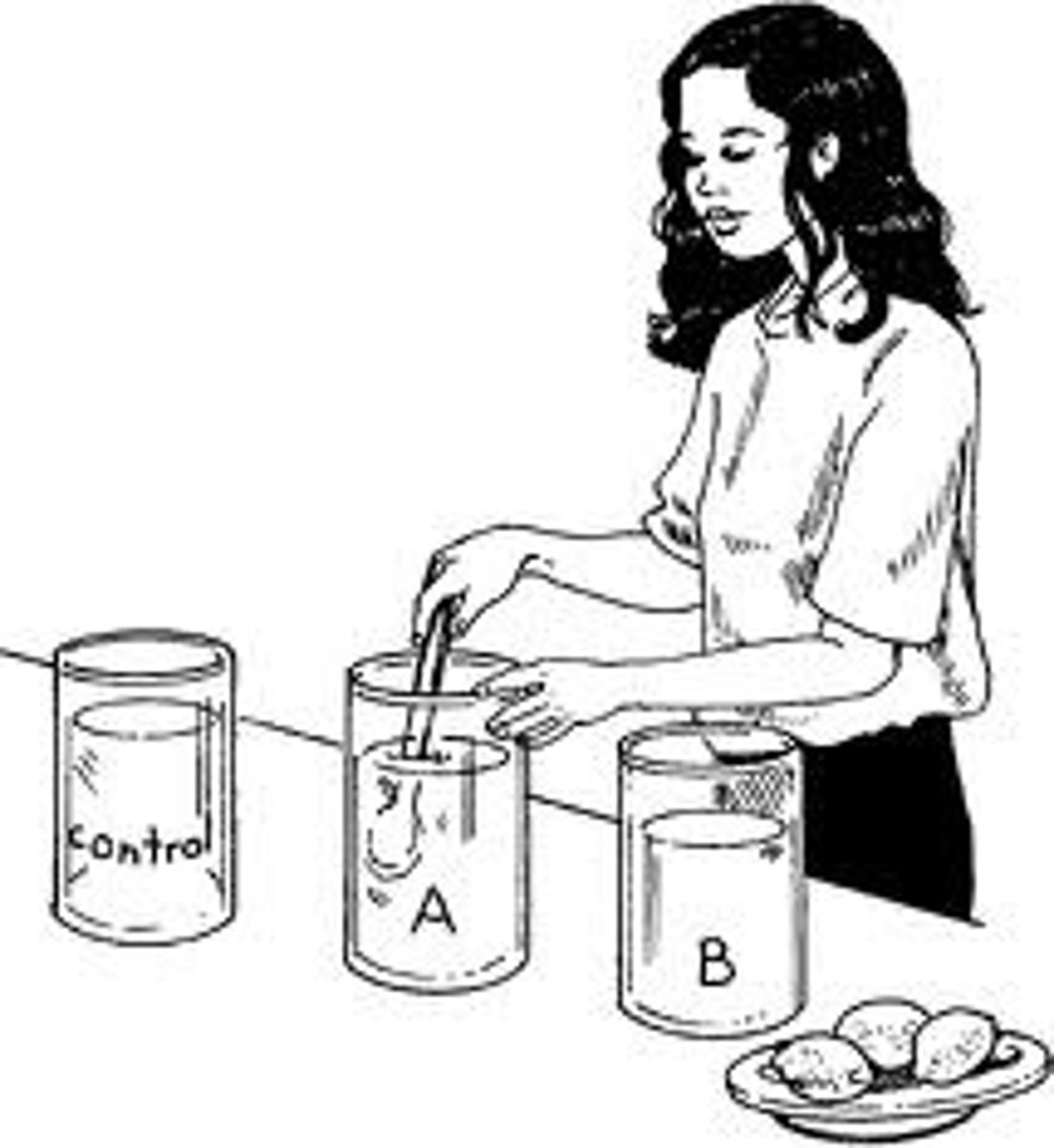
Variable
A factor that can be change in an experiment.

Manipulated Variable
The one factor that a scientists changes during an experiment.
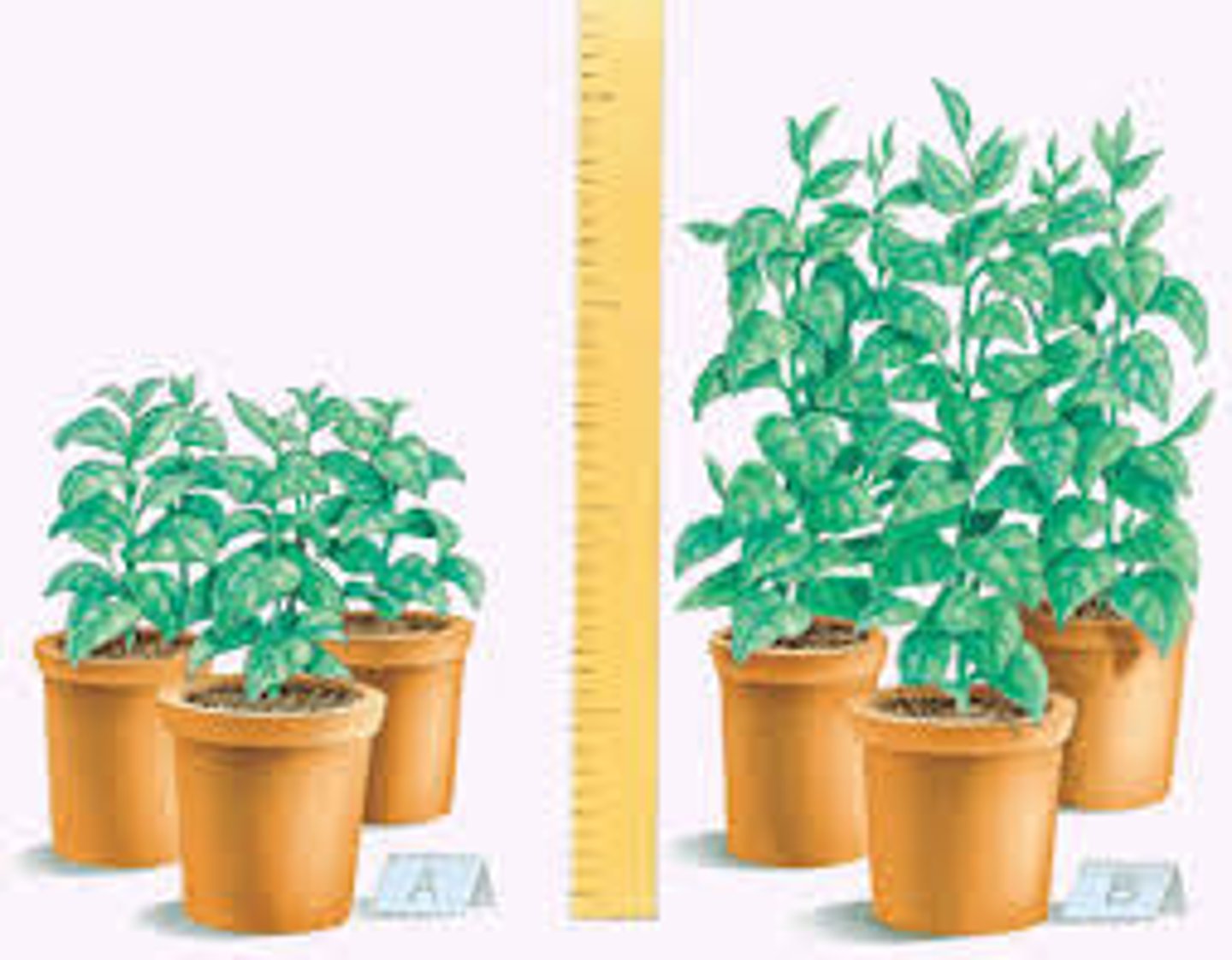

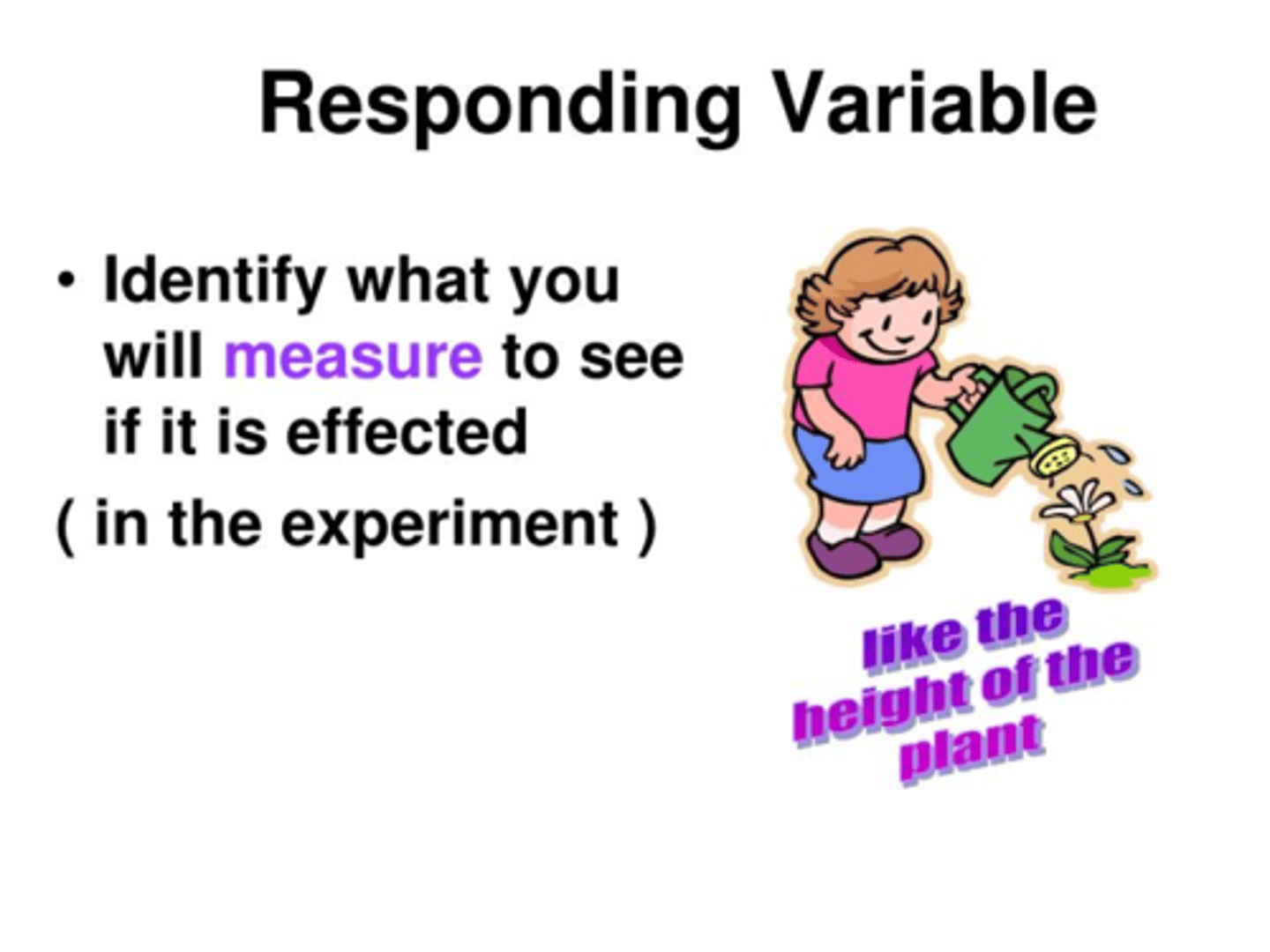
Responding Variable
The factor that changes as a result of changes to the manipulated, or independent, variable in an experiment.
Data
Facts, figures, or other evidence gathered through observations.
Scientific Theory
A well-tested concept that explains a wide range of observations.

Scientific Law
A fact about nature; describes what scientists expect to happen every time under a particular set of conditions;
It has been proven to work 100%.

Earth System or Earth Structure
1. Lithosphere,
2. Hydrosphere,
3. Atmosphere,
4. Biosphere
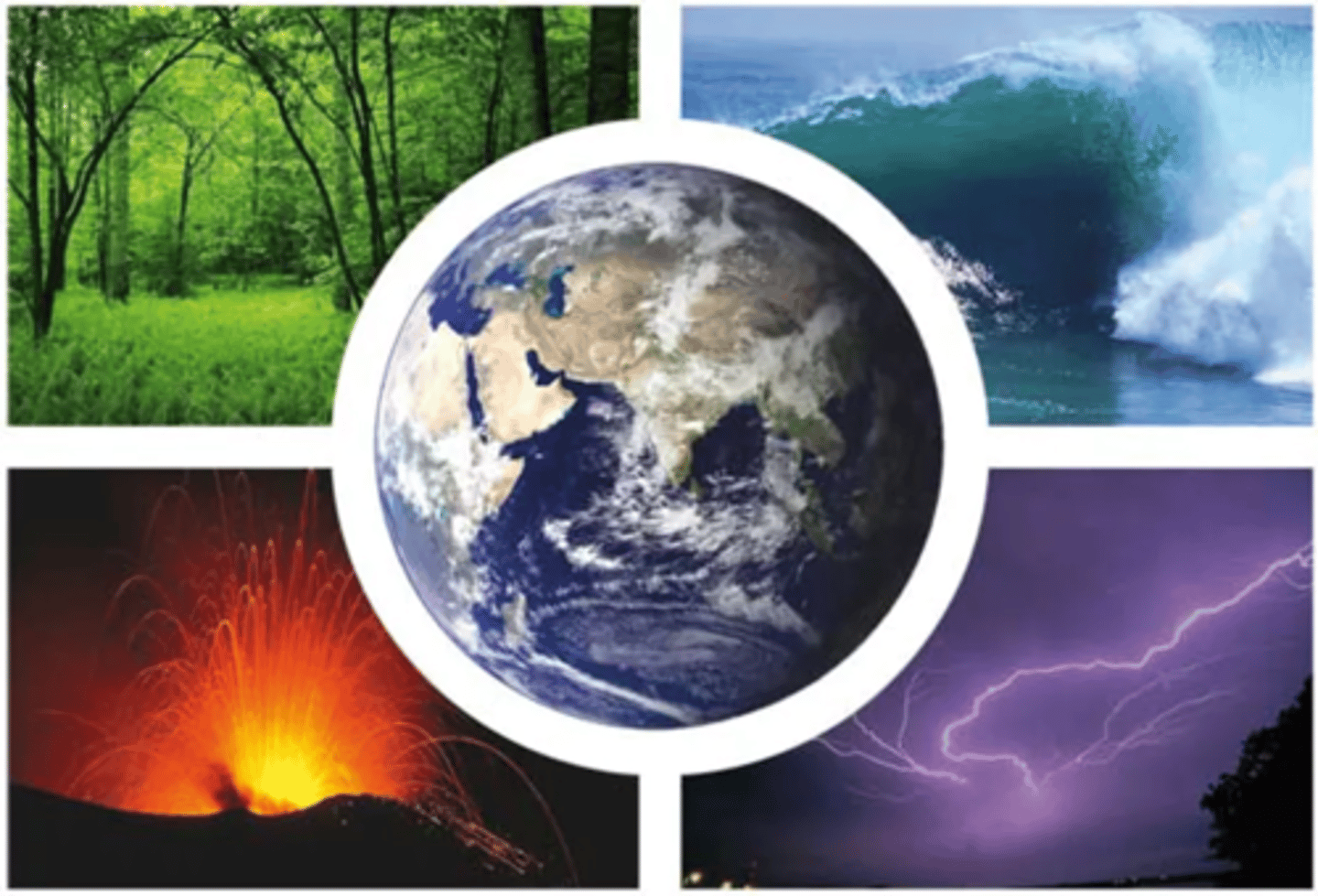

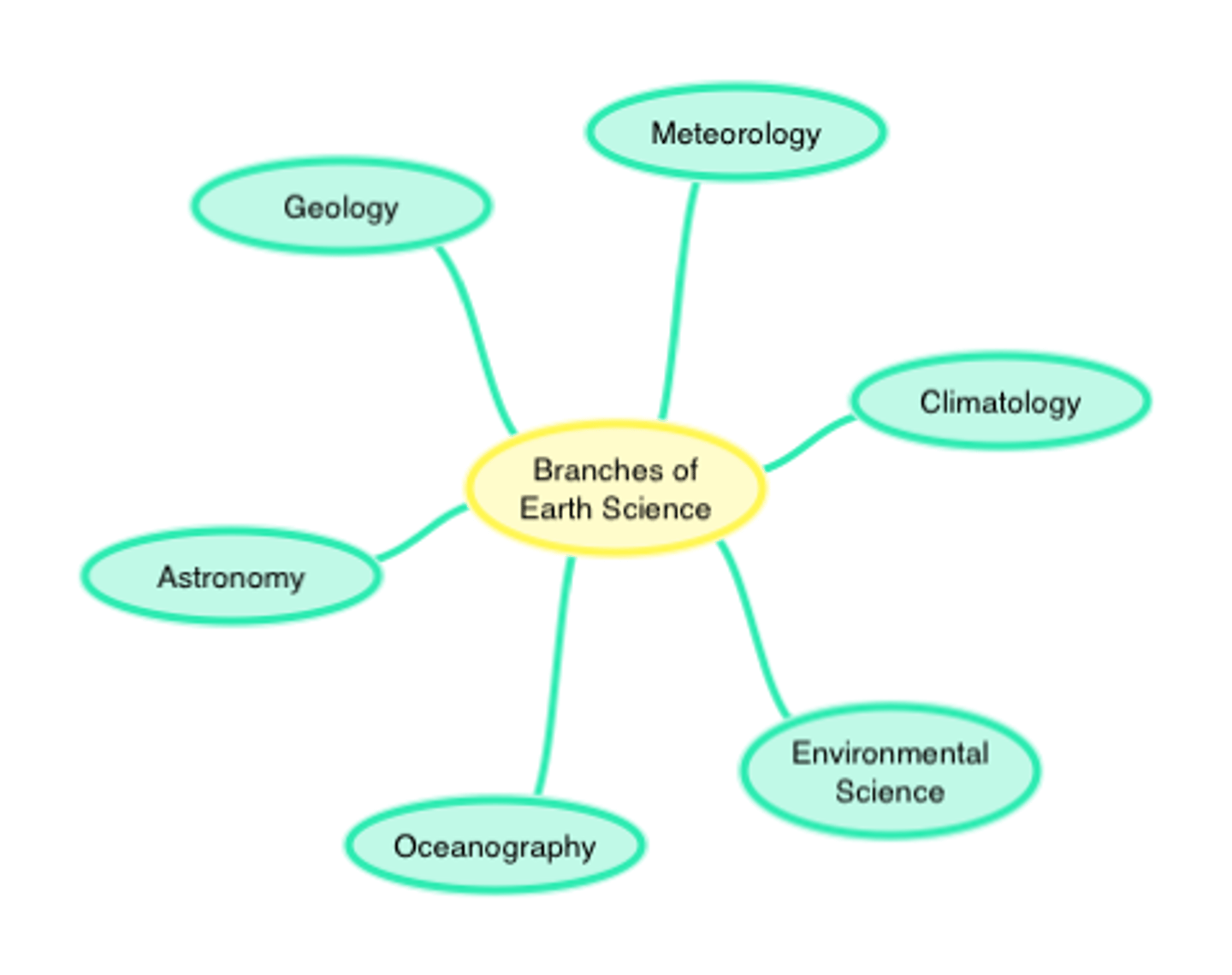
Branches of Earth Science
1. Geologist
2. Oceanography
3. Meteorologist
4. Astronomer
5. Environmental Scientist
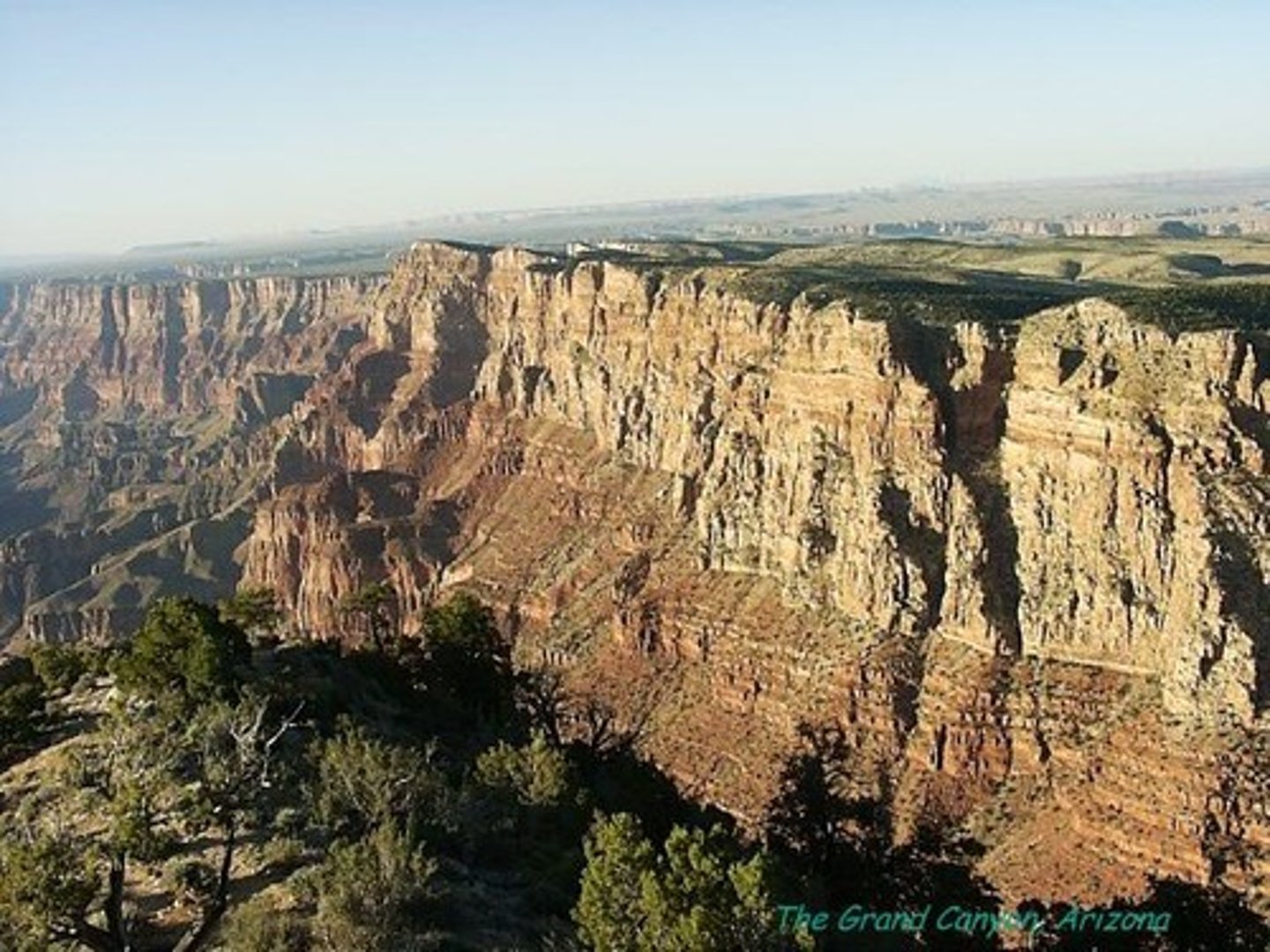
Geology
The study of what the Earth is made of and how it was formed.A science that studies rocks, layers of soil, etc., in order to learn about the history of the Earth and its life. : the rocks, land, processes of land formation, etc.

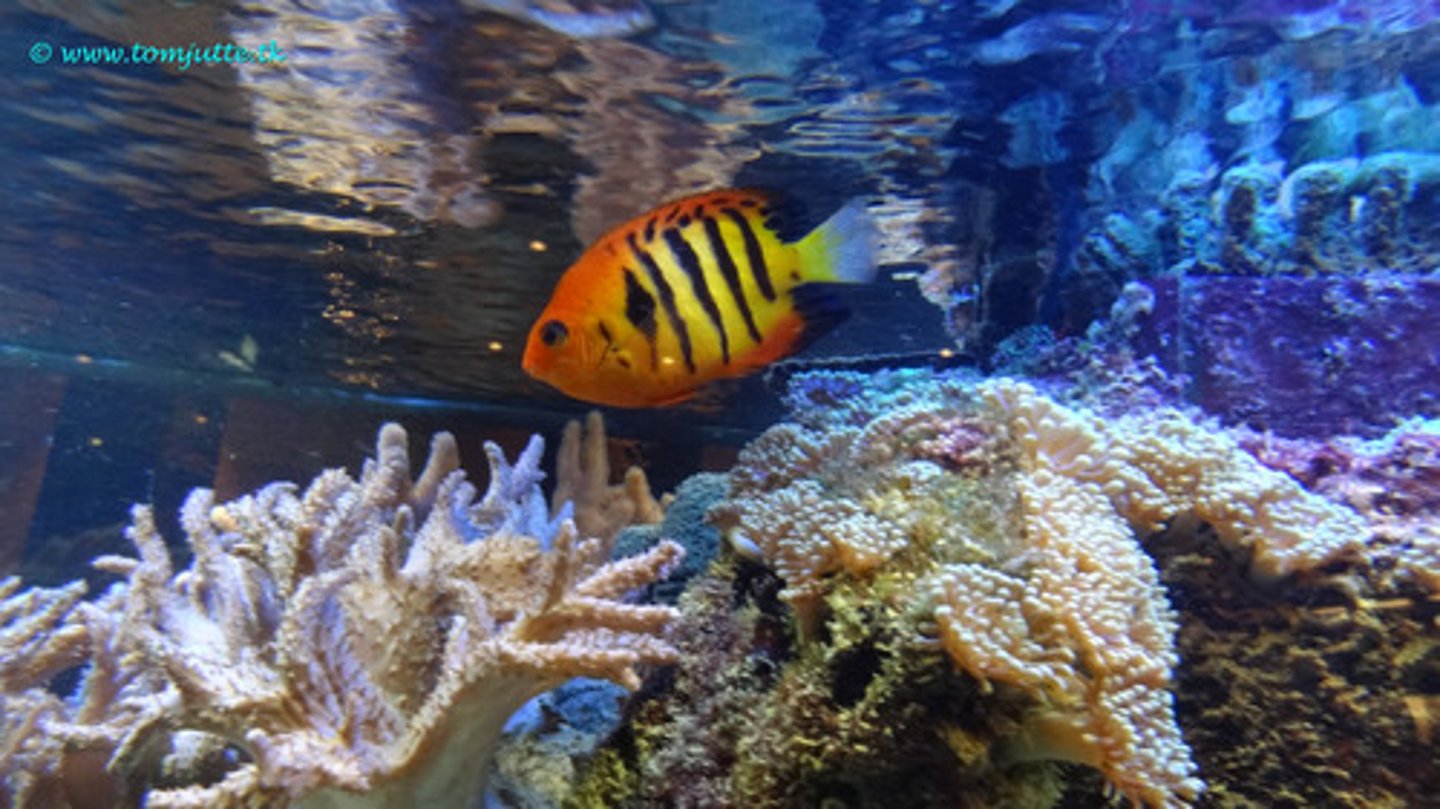
Oceanography
The scientific study of oceans, the life that inhabits them, and their physical characteristics, including the depth and extent of ocean waters, their movement and chemical makeup, and the topography and composition of the ocean floors.
-also includes ocean exploration.

Meteorology
The science dealing with the atmosphere and its phenomena, including weather and climate;
The atmospheric conditions and weather of an area.

Astronomy
The study of outer space, including planets, galaxies, black holes, and stars.

Environmental Science
The science of the interactions between the physical, chemical, and biological components of the environment, including their effects on all types of organisms but more often refers to human impact on the environment.

Scientific Model
Can be material, visual, mathematical, or computational and are often used for things that are too big/small or very complex

Technology
Is the application of scientific knowledge for practical purposes; Is how people change the world around them to meet their needs or to solve practical problems

Goal of Technology
Improve the way people live.
Technology includes knowledge and processes, not just things.

Engineer
a person who is trained to use both technological and scientific knowledge to solve practical problems.

Safety in the Lab
1. Always clean up your work area
2. Turn off and unplug any equipment
3. Wash your hands.
4. Use all safety equipments (goggle, gloves, etc.)
5. Follow directions strictly.

Safety in the Field
1. Good preparation helps you stay safe
2. Always clean up your work area
3. Wash your hands.
4. Use all safety equipments (suns cream, goggle, gloves, etc.)
5. Follow directions strictly.
6. Never work alone and without a supervision of an adult.

What to do in case of an accident
Tell your teacher immediately, no matter how minor the accident.

Lithosphere
the solid, rocky outer layer of the earth
Biosphere
Consists of all life on Earth and all parts of the Earth in which life exists
Hydrosphere
All the water on earth
Atmosphere
A thin layer of gases surrounding Earth