[2.2] UNLV Biol 191L Lab 2 Bacteria and Protists
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
- Prokaryotes have no nucleus or membrane bound organelles
-Prokaryotes have circular double stranded DNA
- Eukaryotes have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles and linear DNA
- Both can reproduce and respond to the environment
-both have cytosol
Autotroph
an organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide.
Heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer
Saprotophic
organisms that send out digestive enzymes into the environment and afterward pick up the resulting nutrients. Commonly called decomposers.
Prokaryotic cells
have circular double-stranded DNA, no true nucleus and no membrane-bound organelles.
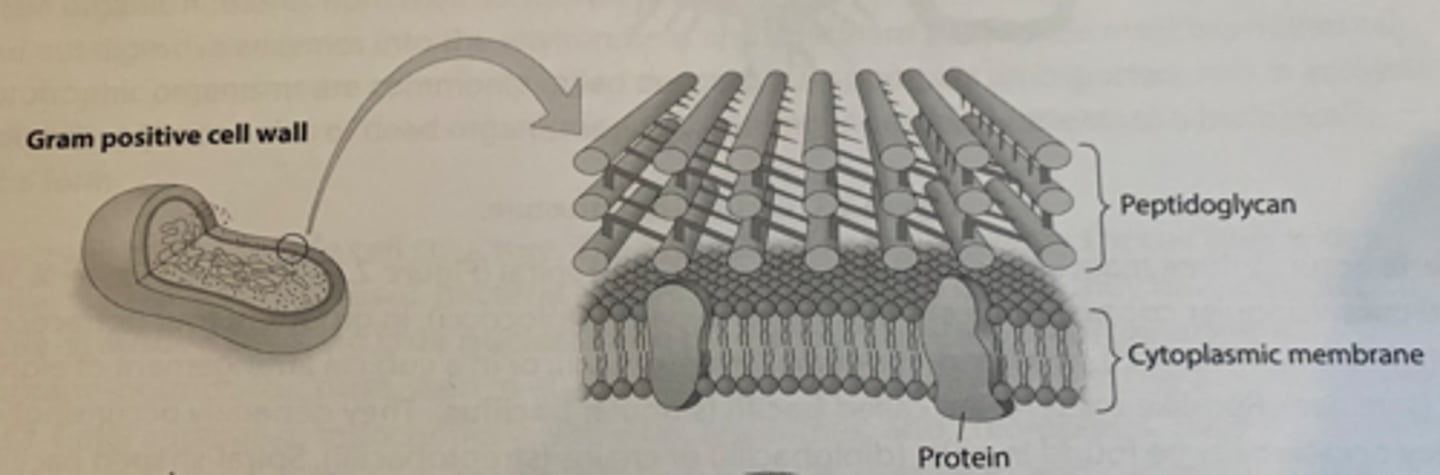
peptidoglycan
A type of polymer in bacterial cell walls consisting of modified sugars cross-linked by short polypeptides.
pili
Appendages that allow bacteria to attach to each other and to transfer DNA
Flagella
A long, whip-like filament that helps in cell motility. Many bacteria are flagellated, and sperm are flagellated.
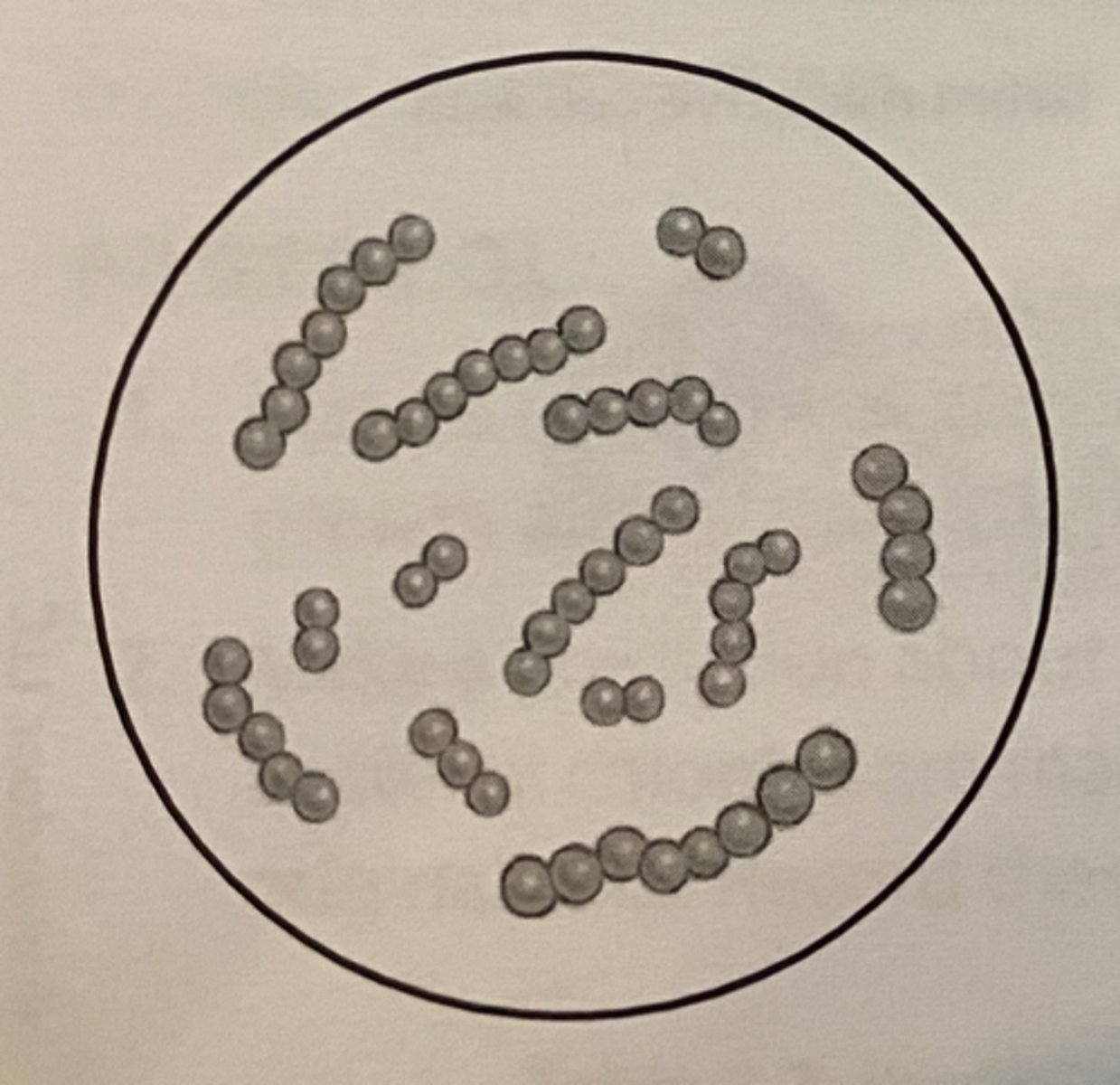
Cocci
spherical bacteria
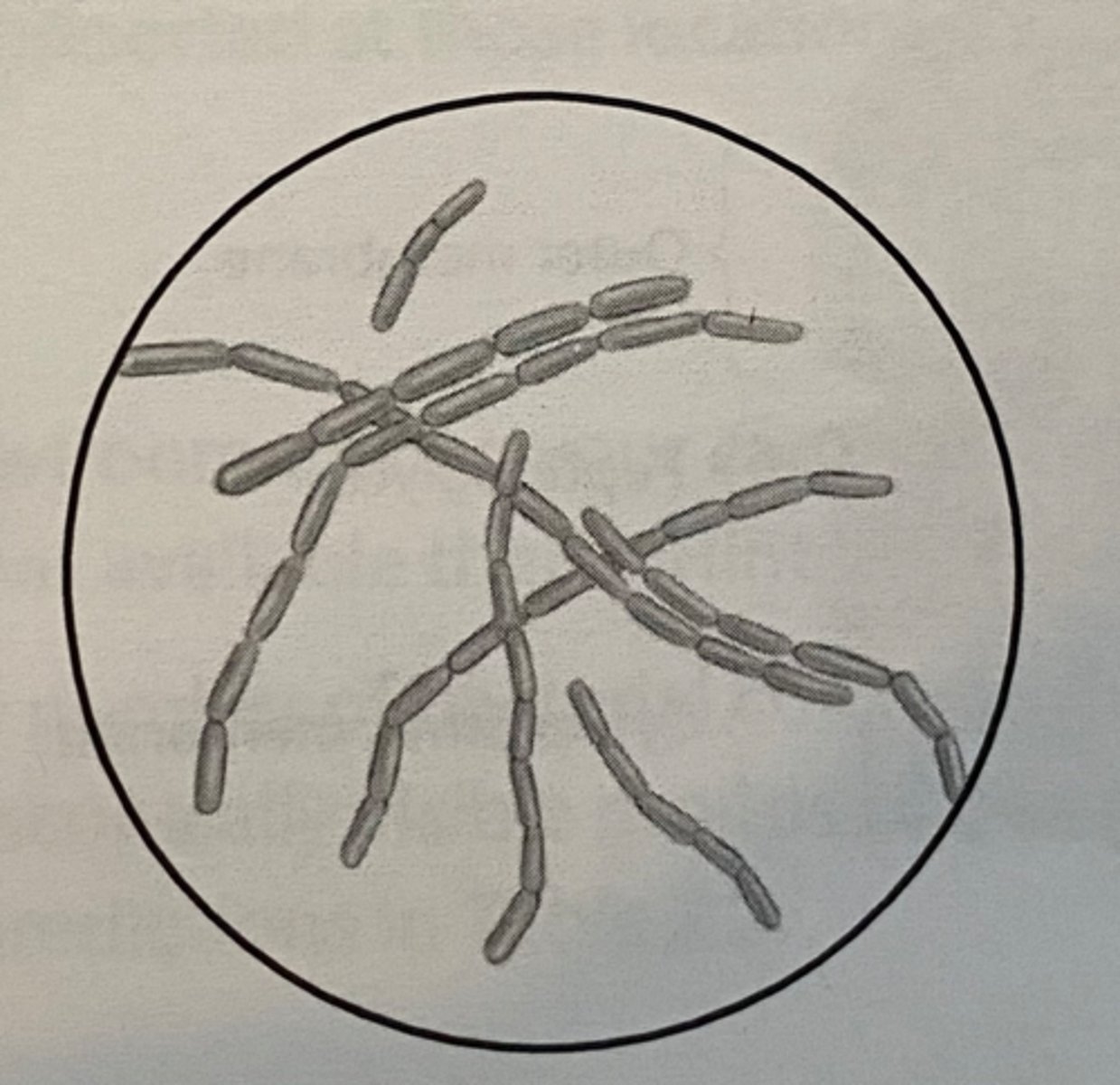
Bacilli
Rod shaped bacteria
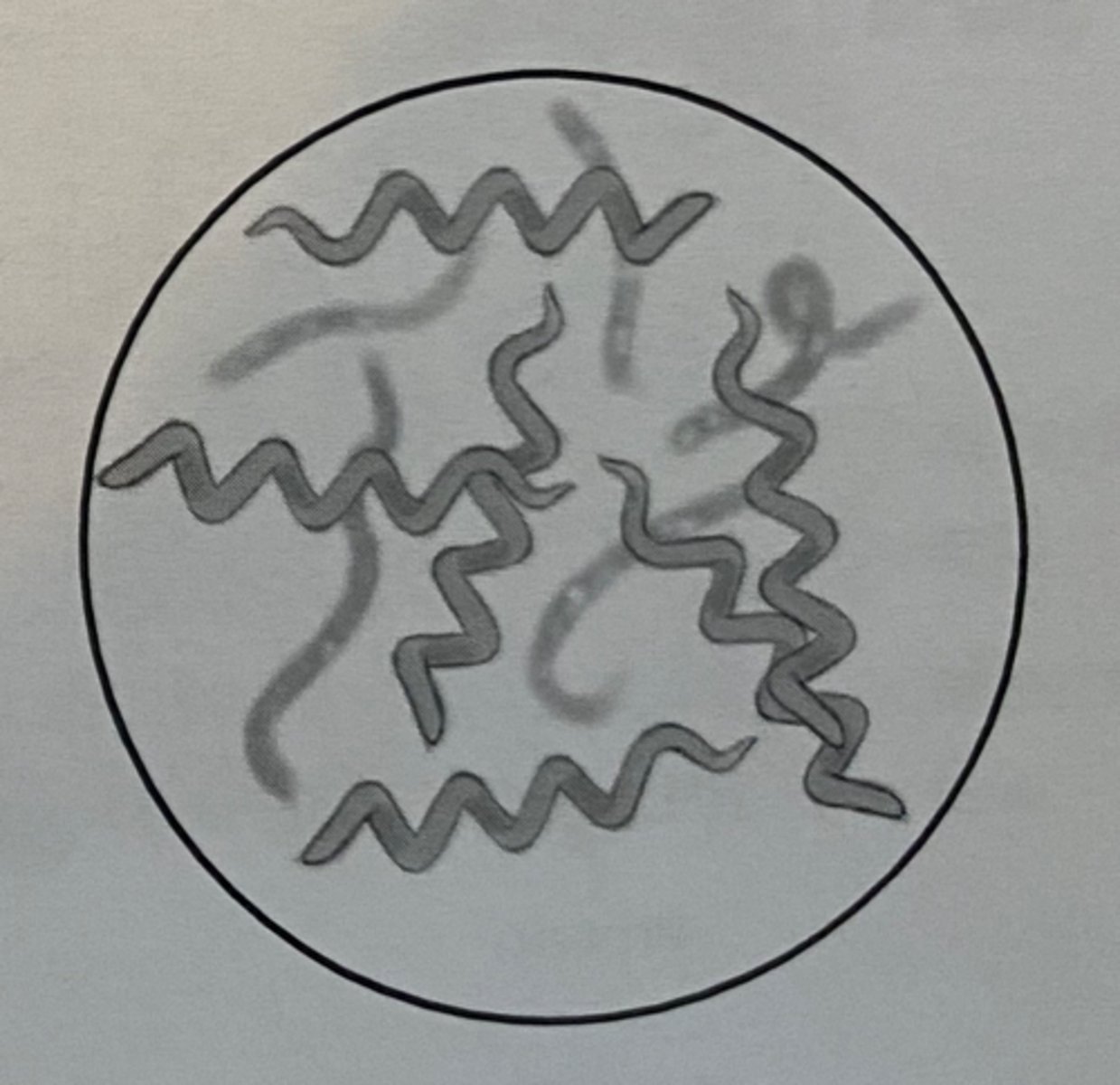
Spirilla
spiral shaped bacteria
diplo
pairs
tetra
prefix for 4
staph
clusters (bunches)
strep
chain
Gram positive
bacteria have a cell wall that is composed of between 60% and 90% peptidoglycan. Multiple layers of peptidoglycan cause the cell wall to be approximately 20-80 mm thick. Appear purple after Gram Staining.
Gram negative
bacteria have a cell wall that contains only 10-20% peptidoglycan. Appear pink after gram staining
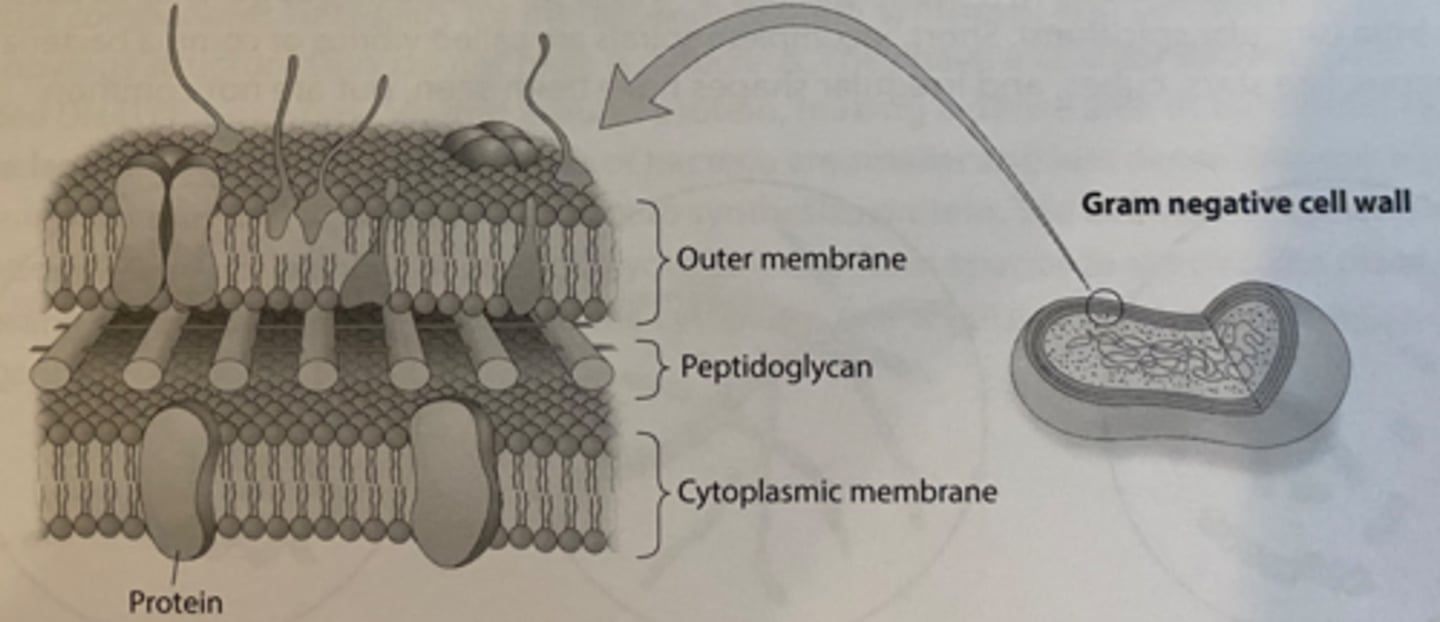
penicillin
works by attaching to the peptidoglycan of Gram positive cells, but is ineffective against Gram negative cells
Three broad groups of protists
plant-like autotrophs (algae), animal-like heterotrophs (protozoa), fungus-like absorptive heterotrophs (slime molds)
Three structural arrangements of protists
Unicellular, colonial, filamentous
unicellular protists
live as single cells, Amoeba & Paramecium
colonial protists
cells attached to each other but each remains metabolically independent, such as Volvox
Filamentous protists
chains of cells attached end to end, such as Spirogyra
Physarum (slime mold)
phagocytic predators that engulf their prey, moves with cytoplasmic streaming
phagocytic cells
organisms that hunt for and physically engulf their prey
plasmodium
an aggregate of many cells that forms a large visible mass. (Physarum form a ________ to move faster and find better conditions for food.)
Phylum Acrasiomycota
cellular slime molds - (Dictyostelium) individual amoebas retain their cell membranes in the plasmodial stage
Phylum Myxomycota
acellular slime molds (Physarum) in the plasmodial state the individual cell membranes break down, making the entire plasmodium on large, multinucleated cell
cytoplasmic streaming
The motion of cytoplasm in a cell that results in a coordinated movement of the cell's contents.
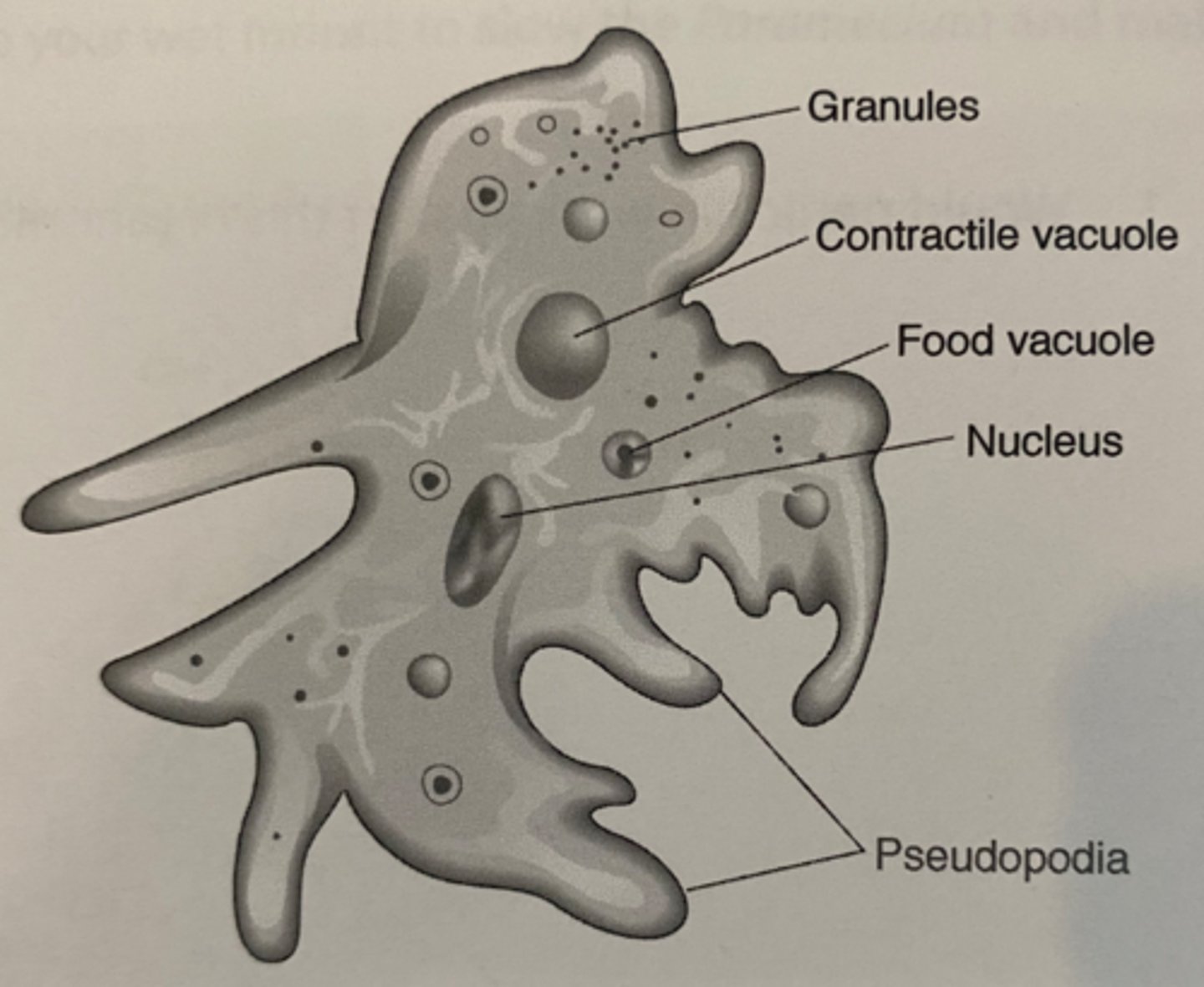
pseudopodia
A cellular extension of amoeboid cells used in moving and feeding.
Amoeba protozoa
uses psuedopodia for movement and phagocytosis
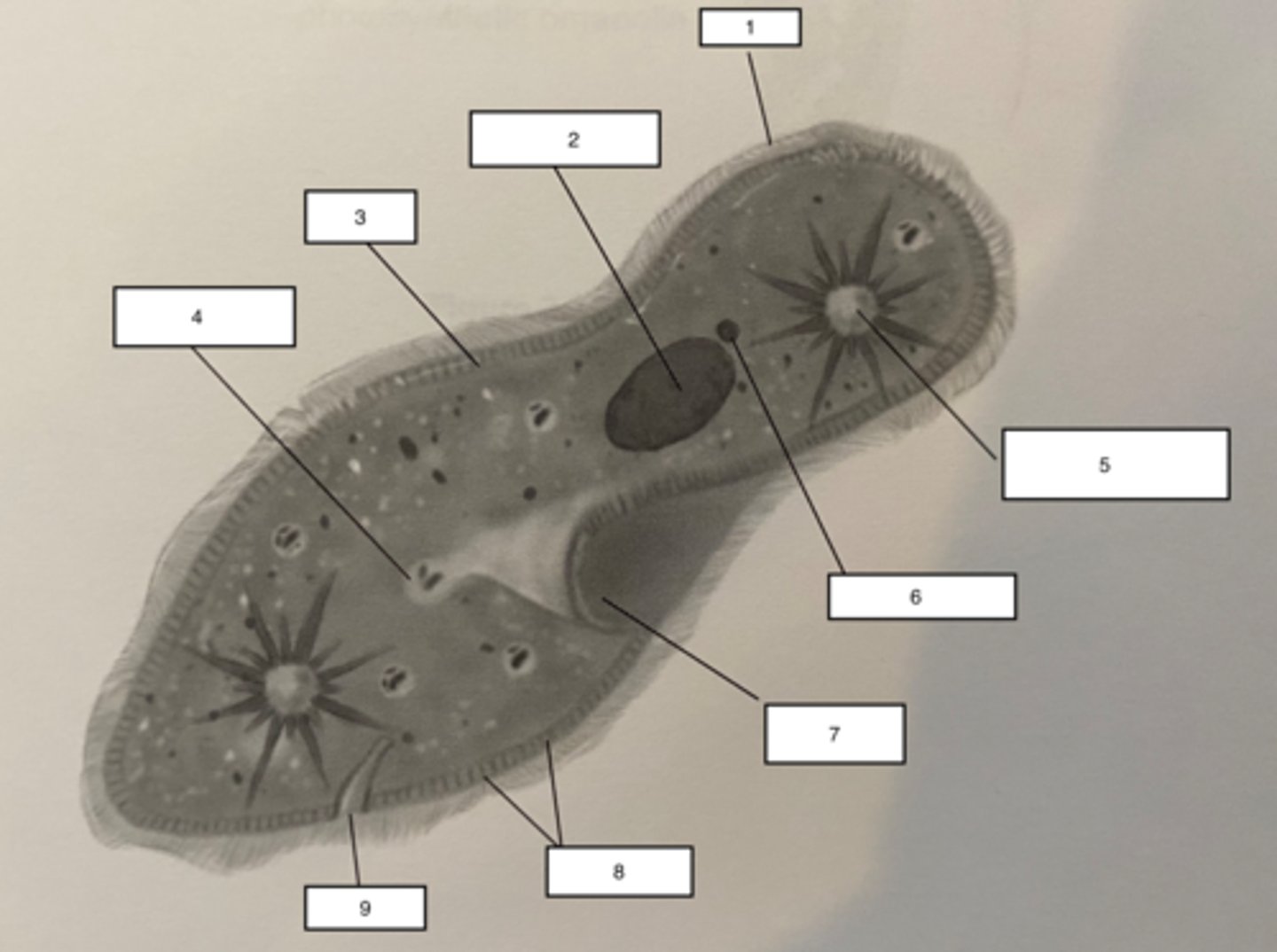
Paramecium protozoa
complex organism with two nuclei, trichocytes, and a contractile vacuole
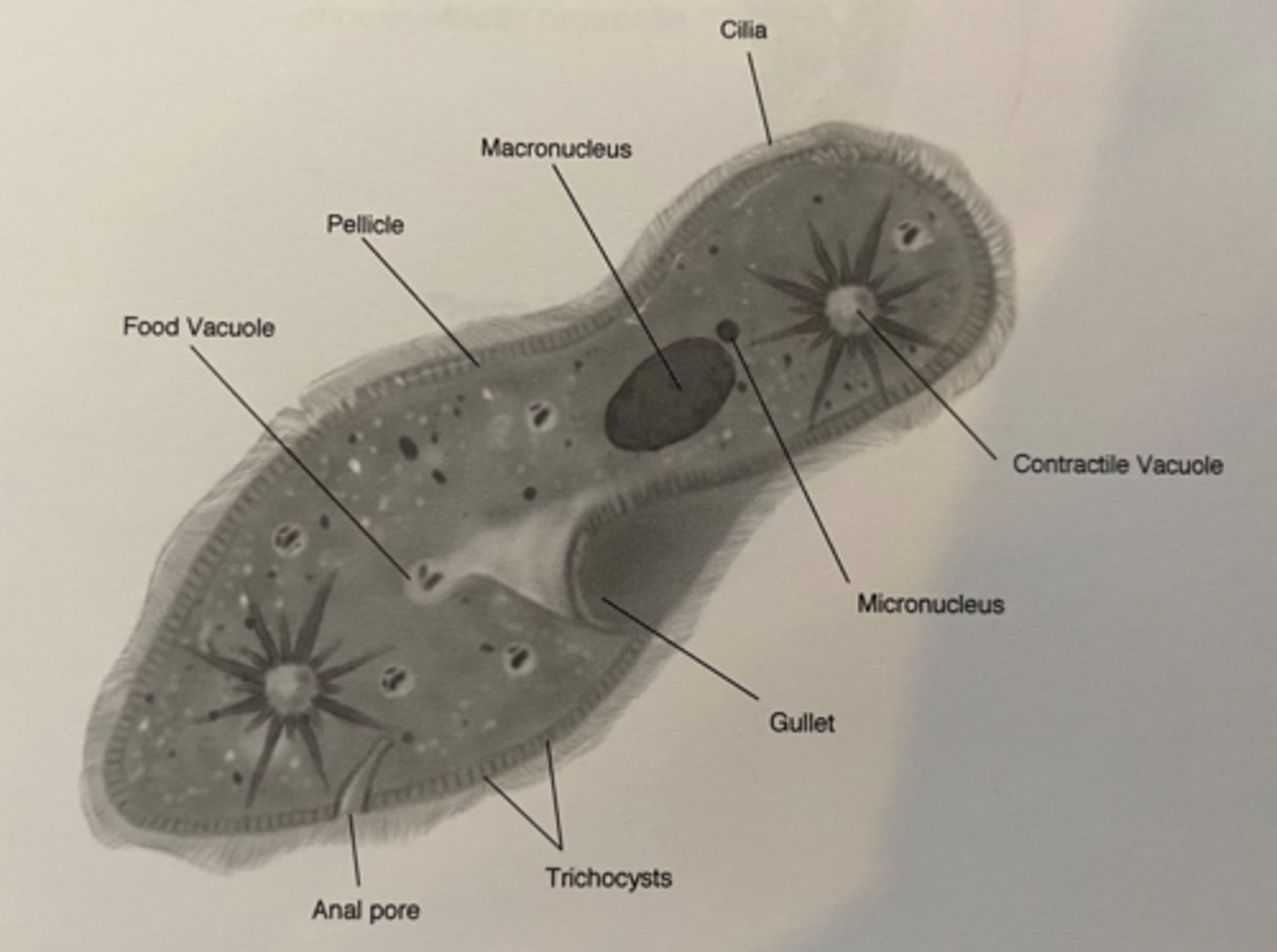
Pellicle-3
outer layer of the Paramecium, contains alveoli (found at the base of the cilia), the cell membrane and trichocysts.
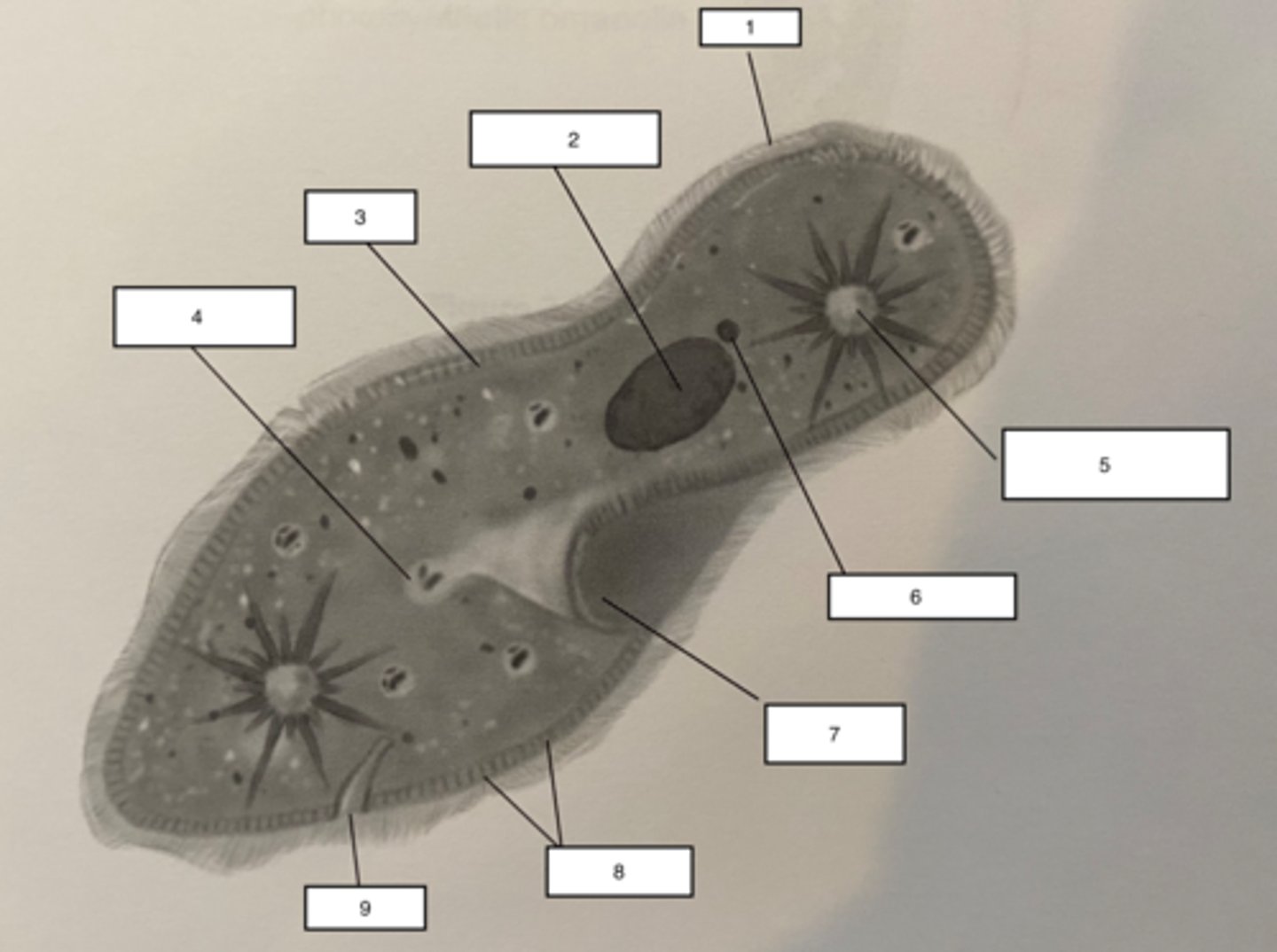
Trichocysts-8
a type of defensive organelle that can be shot outward from the Paramecium when there is a threat
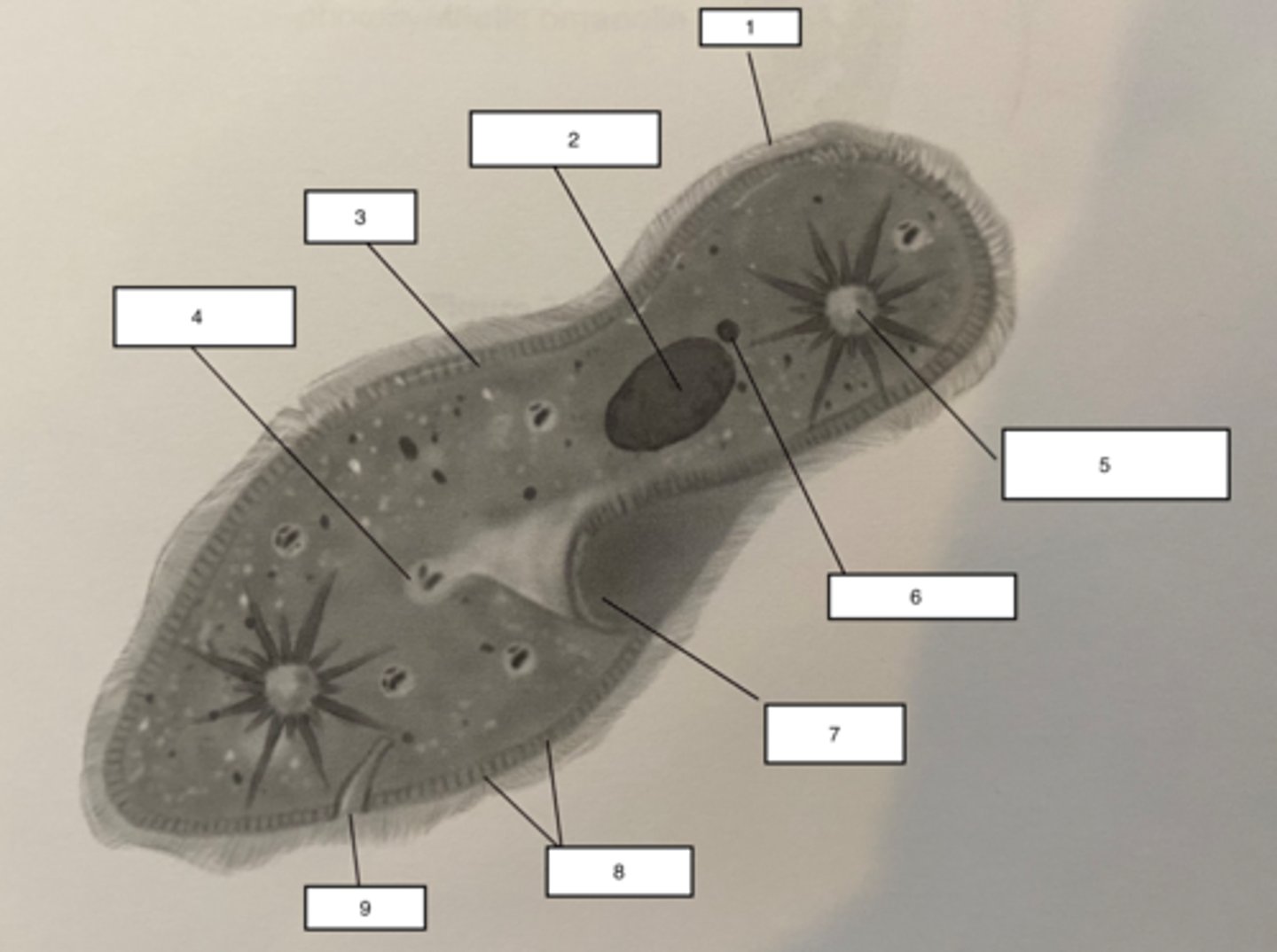
Cilia-1
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
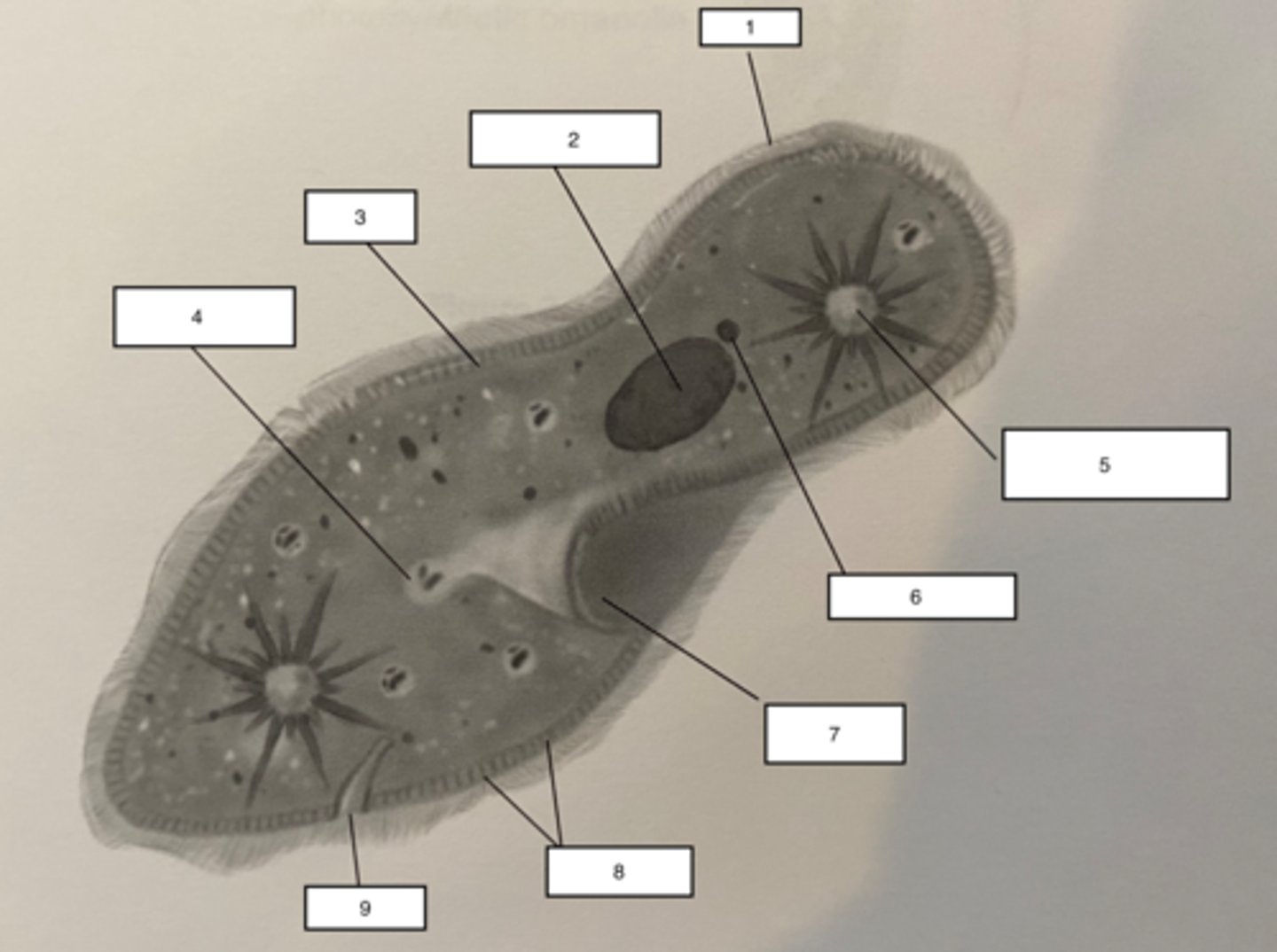
contractile vacuole-5
The cell structure that collects extra water from the cytoplasm and then expels it from the cell
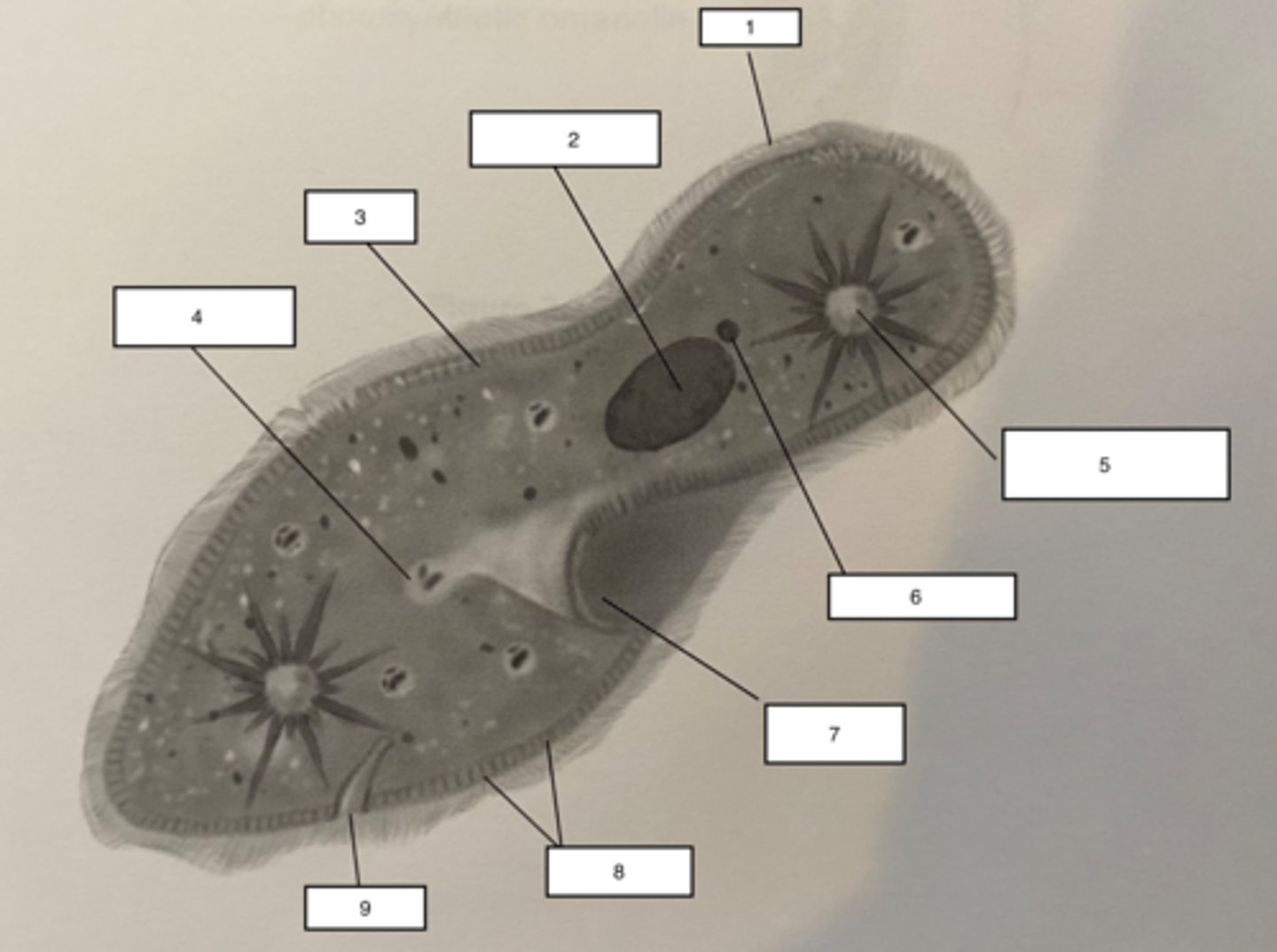
micronucleus-6
the smaller of a ciliate's two nuclei; contains a "reserve copy" of all of the cell's genes, critical to a Paramecium's ability to reproduce
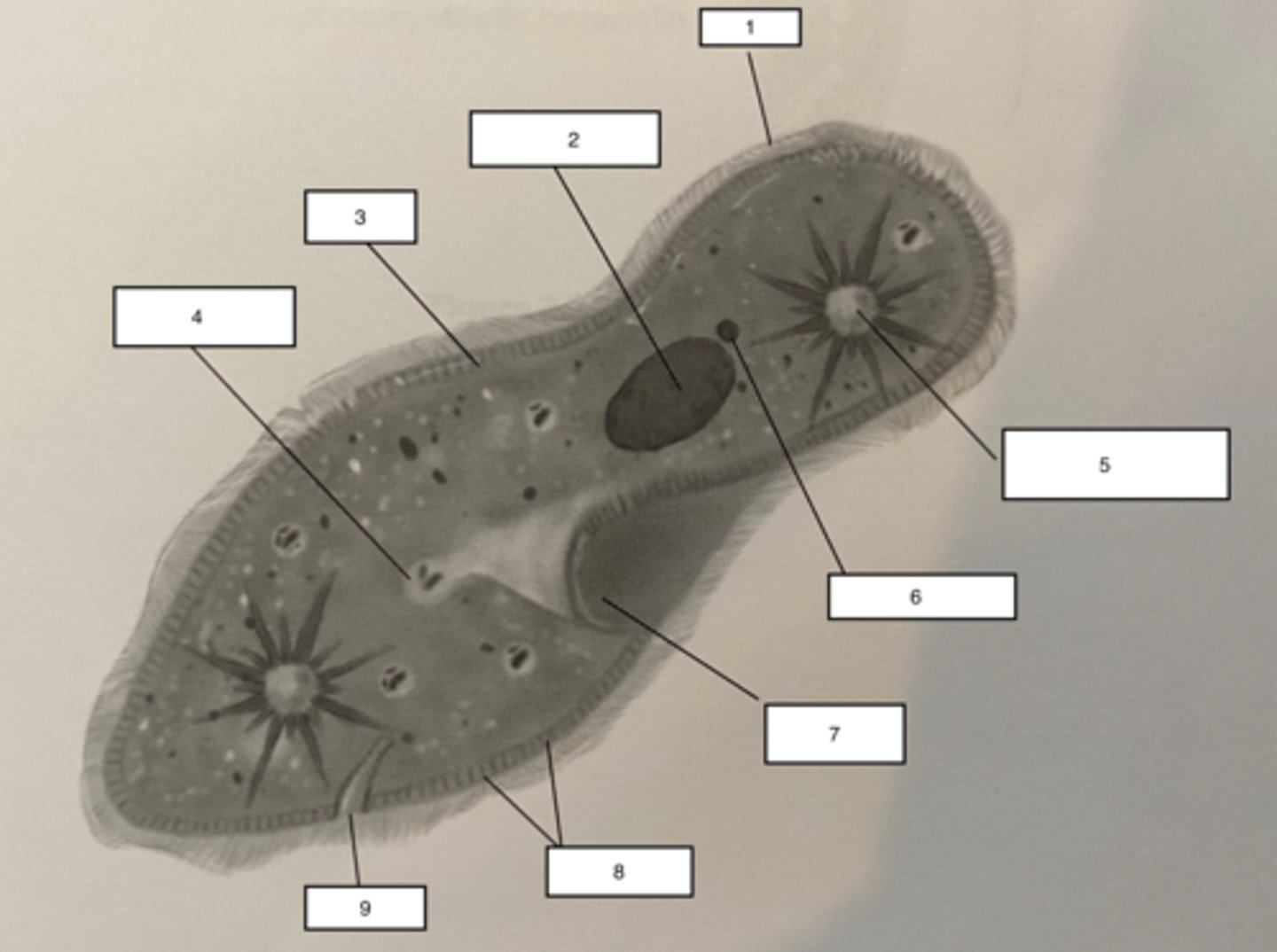
macronucleus-2
the larger of a ciliate's two nuclei, contains multiple copies of most of the genes that the cell needs in its day-to-day existence
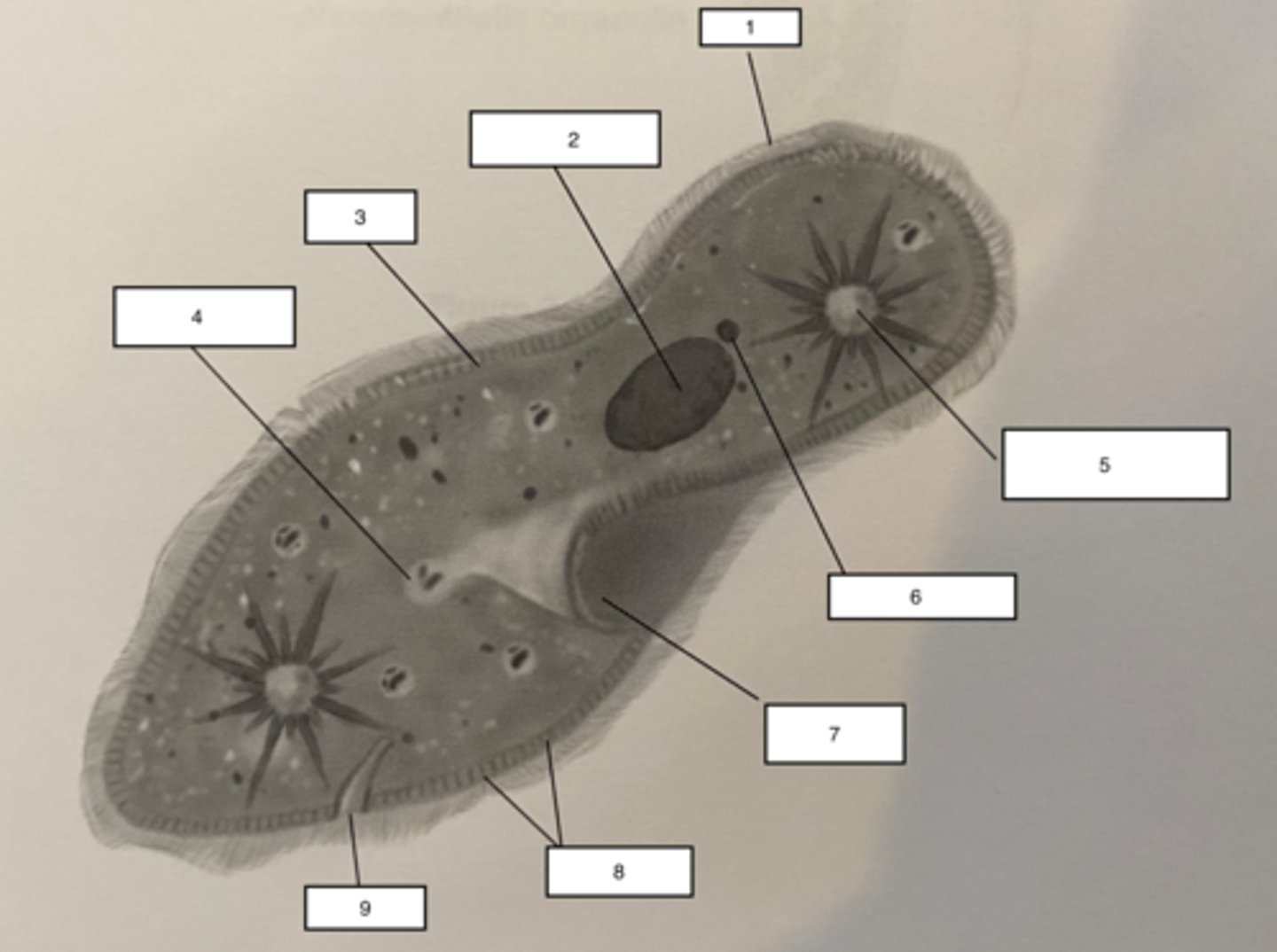
Food Vacuuole
4
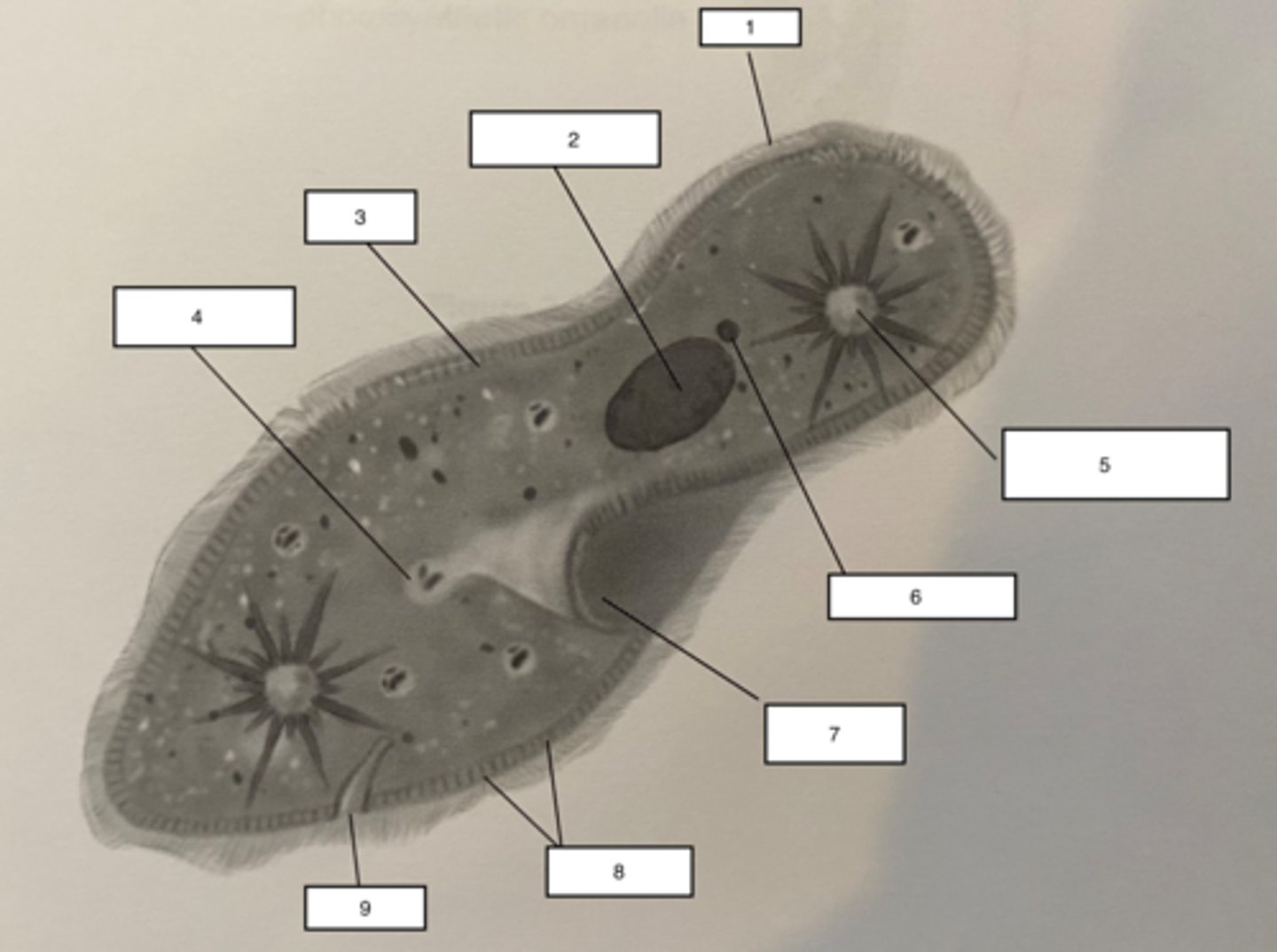
Anal pore
9
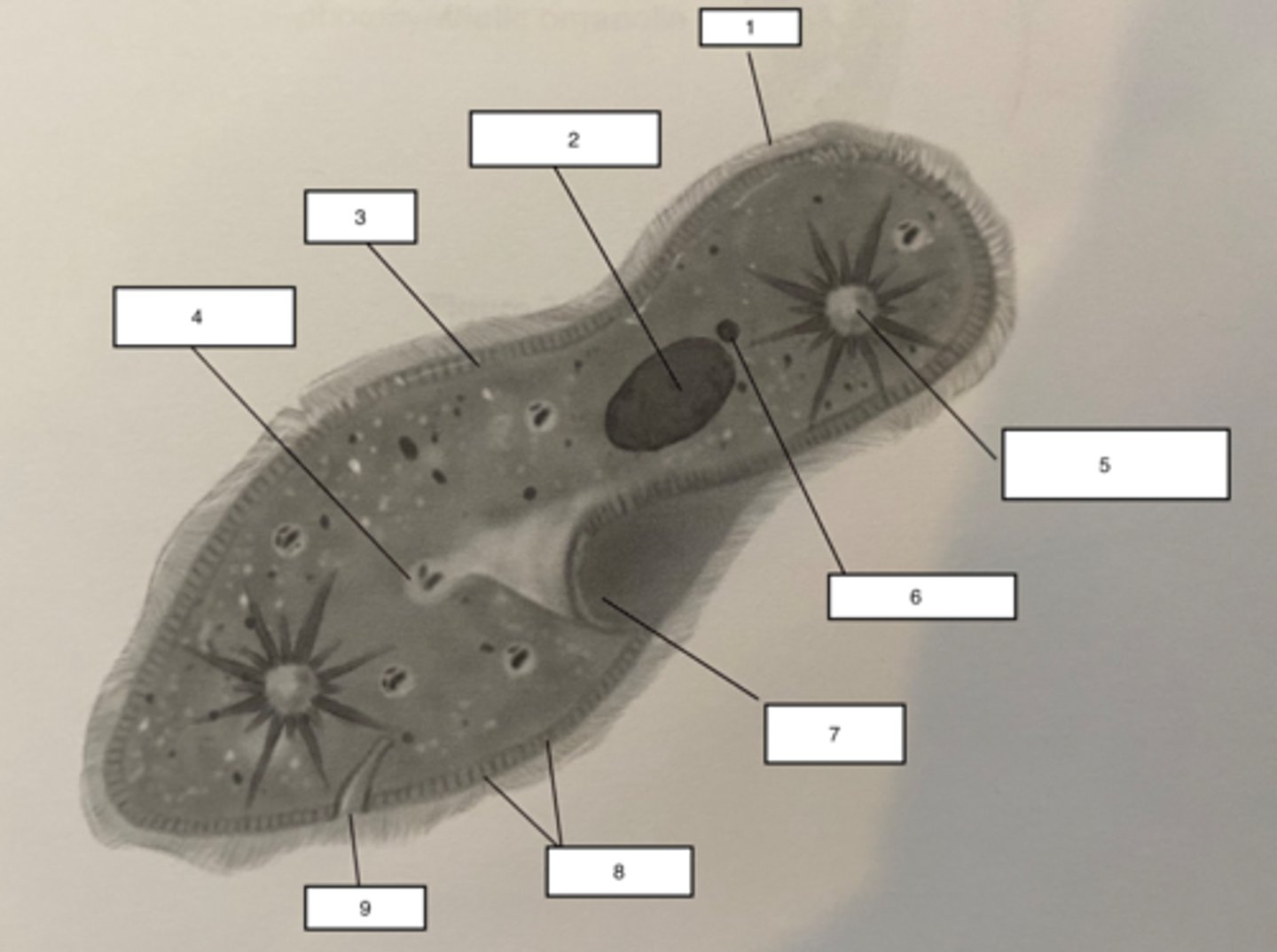
Gullet
7
Euglena protozoa
unicellular organism with flagella and an eyespot
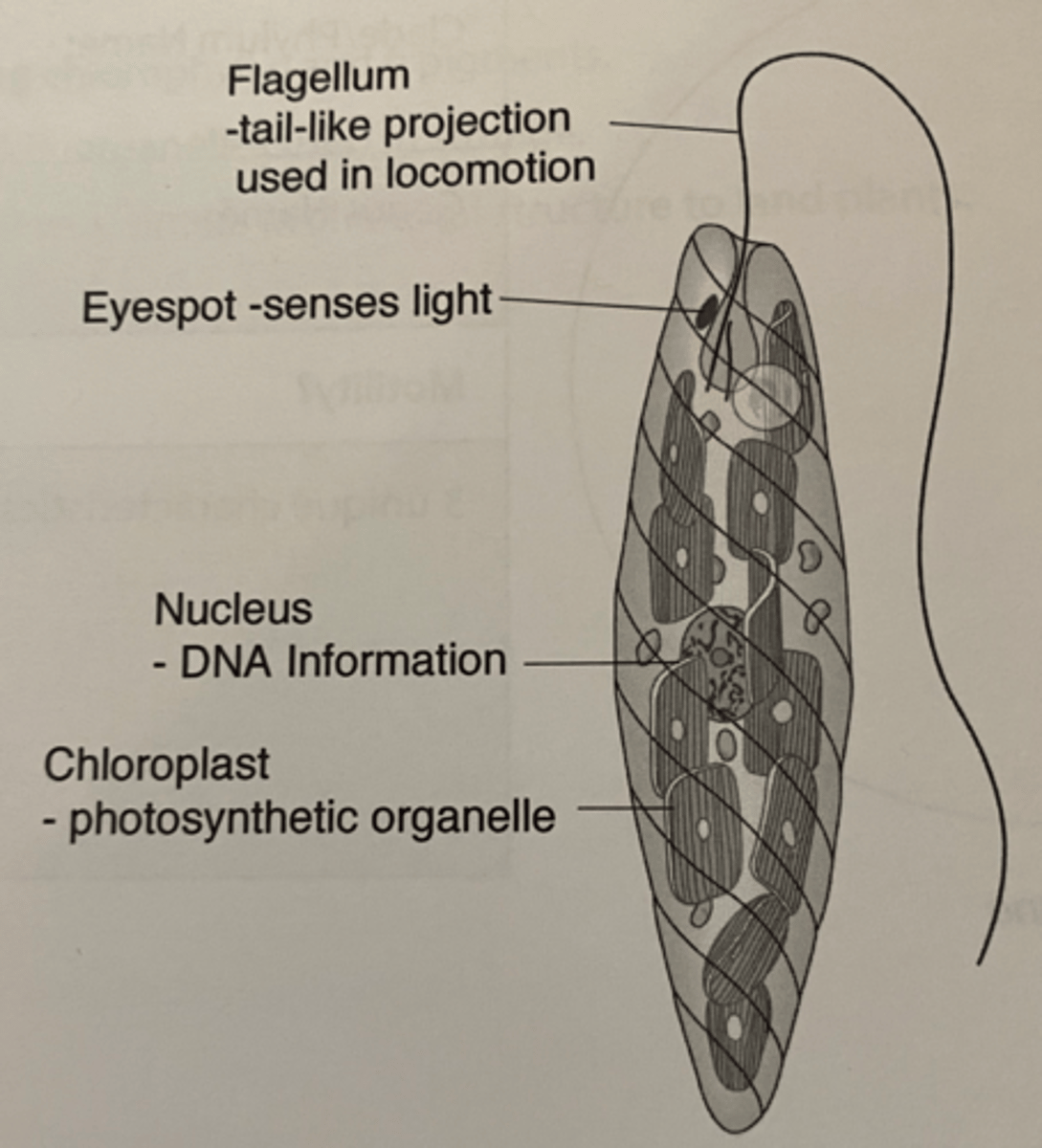
Mixotrophic
Organism that can use autotrophic and heterotrophic means of gaining nutrients
Isogamy
Motile male and female gametes that look exactly alike
Heterogamy
motile male and female gametes that look alike except that the egg is larger
oogamy
male gametes are small and motile, female gametes are large and stationary
Evidence for green algae as ancestors of today's land plants
-beginnings of multicellularity, where cells perform specific functions
-appearance of sexual reproduction, even thought asexual reproduction is most common
green algae characteristics
-primarily aquatic
-photosynthetic
-store starch
-cell wall
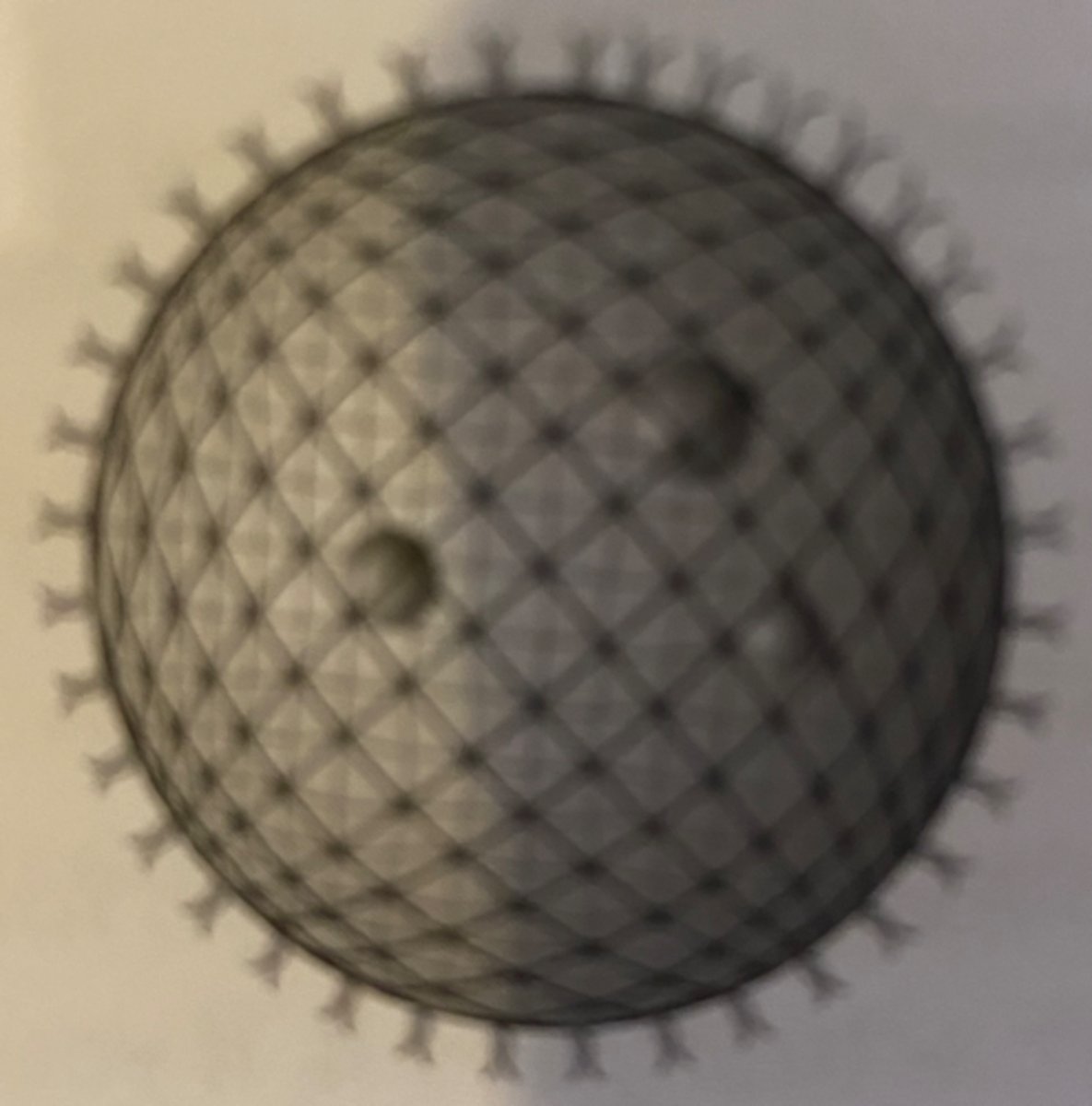
Volvox (Algae)
a green, single-celled aquatic organism that forms minute, free-swimming spherical colonies. has specialized cells for sexual (oogamous) and asexual reproduction, eyespots

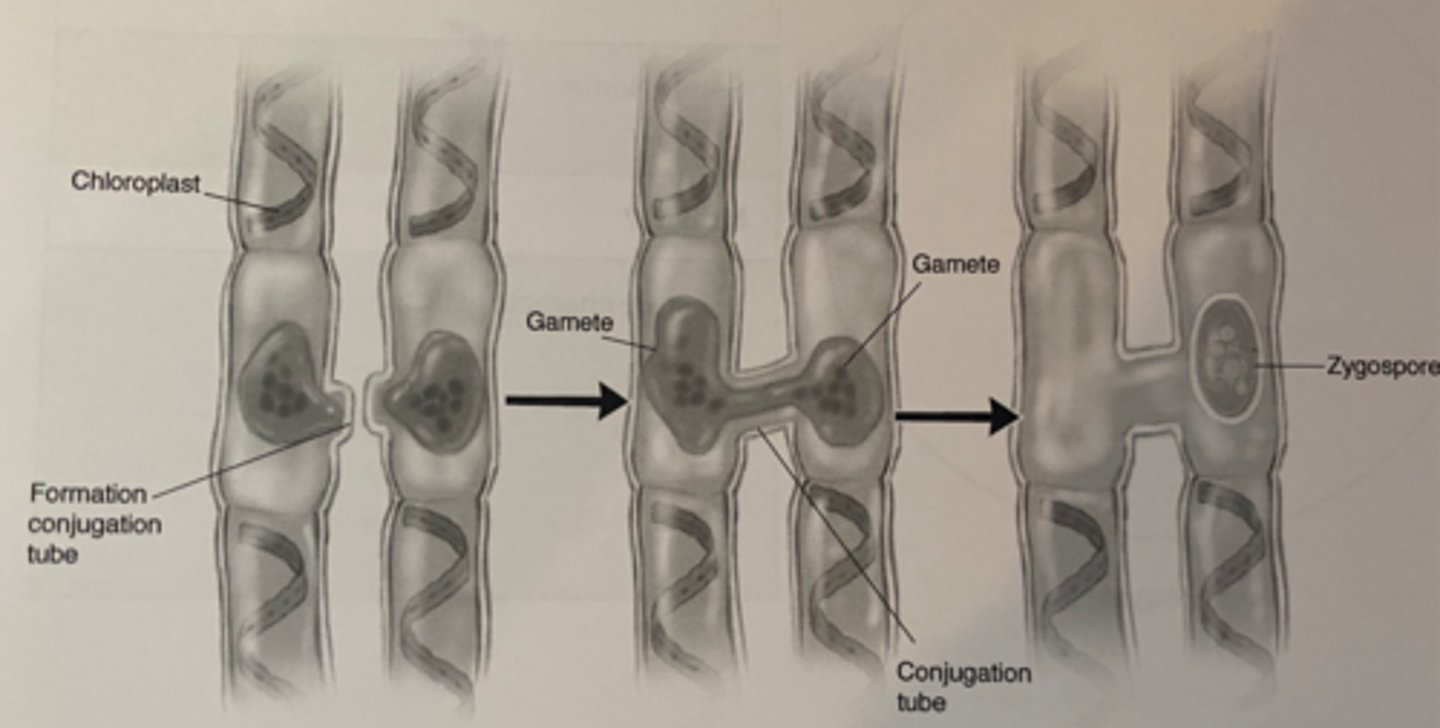
Spirogyra (Algae)
-long thin strands
-spiral chloroplasts
-isogamous sexual reproduction through conjugation
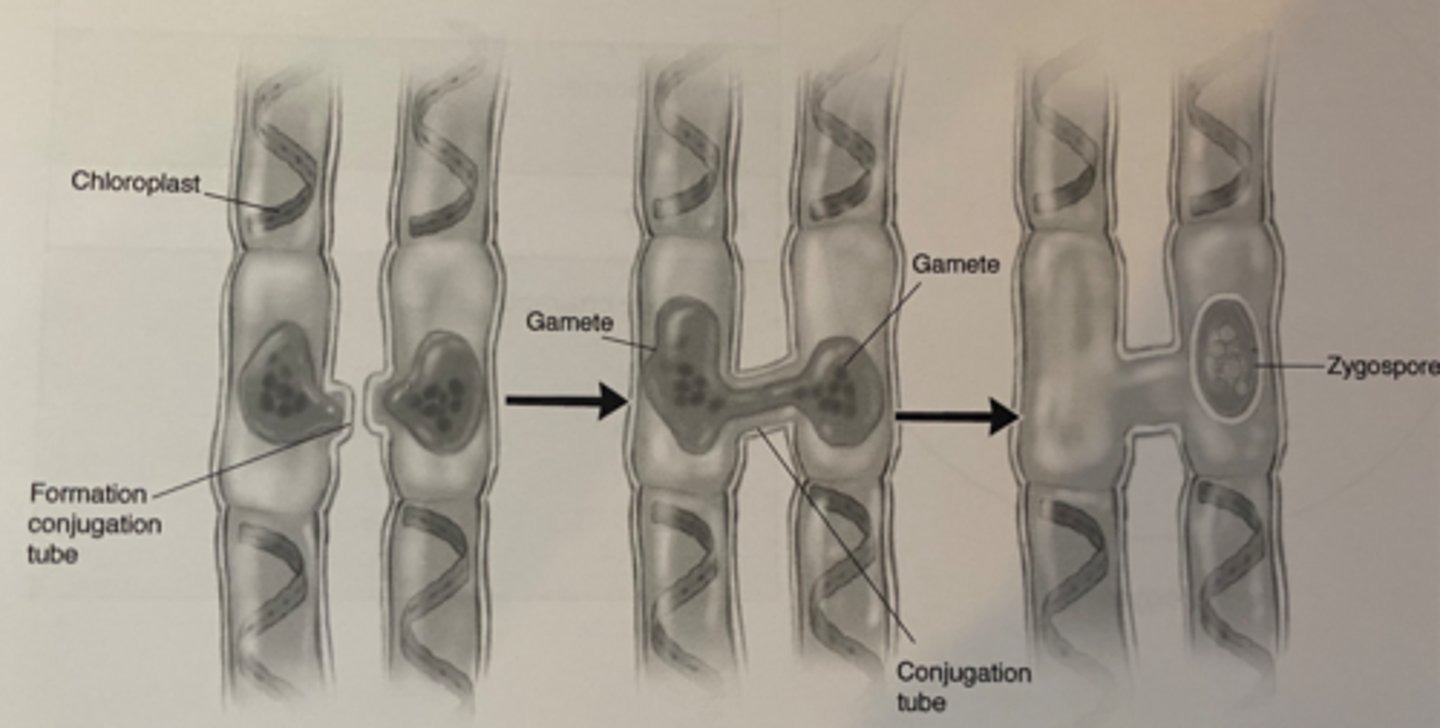
conjugation tube
Cytoplasmic connection between two cells through which DNA passes during conjugation.
Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena
Three Protozoa