History of Ecology/Population Growth
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
natural history
description of nature (primarily taxonomy)
natural philosophy
discovering the laws of nature
Ernst Haeckel
created the term “ecology”
“ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny”
Alexander Humboldt
conceived “terrestrial physics” was the first to study relationship between organisms and their environment
Charles Darwin
highlighted the complexity of species interactions
Eugene Odum
father of ecosystem and modern ecology. created the unifying concept of the ecosystem
population
a group of interbreeding organisms of the same species living within the same area
demography
study of things that affect population growth
r
per capita rate of increase
λ
growth rate per unit of time
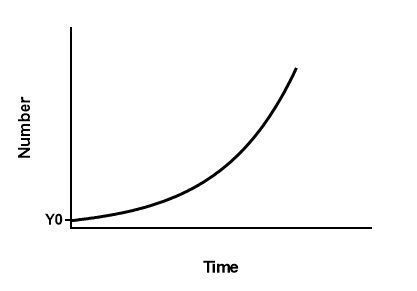
exponential growth
models that assume density-independent growth. J-shaped curve, unlimited resources
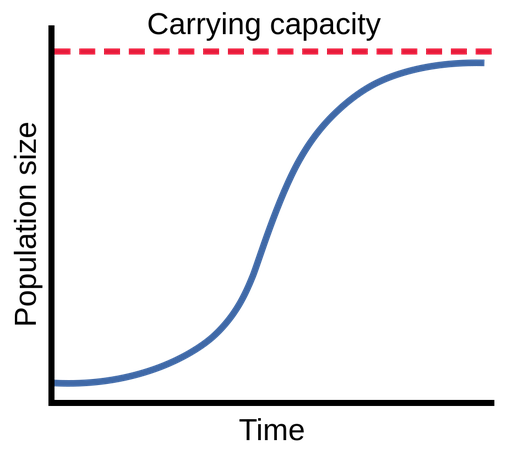
logistic growth
assumes density-dependent growth
time lags
delayed responses between an environmental change (cause) and the corresponding ecological effect
stochasticity
temporal variation due to unexpected events. Increases density-independent mortality
environmental stochasticity
temporary environmental fluctuations that led to changes in population growth rates
endogenous
internal density-dependence
exogenous
external density-independence
demographic stochasticity
within-individual variation in a population across years
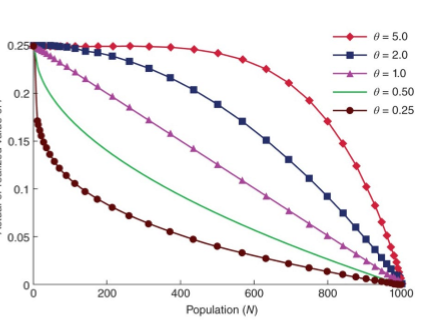
Theta Logistic Model
modifies the logistic model by altering the shape of density dependent relationships
allee effects
positive density dependence; when populations have a minimum population size below which birth rates collapse or death rates are extremely high; affects small populations
population dynamics
changes in size and shape of populations due to survivorship and reproduction