Vocabulary Terms for Chapter 8
1/25
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms

Attentional Capture
Our attention is automatically drawn to salient objects.

Akinetopsia
A condition in which damage to an area of the cortex involved in motion perception causes blindness to motion.
Real Motion
An object is physically moving across our field of view.

Illusory Motion
Perception of motion when there is actually none.

Apparent Motion
An illusion of movement that occurs when two objects separated in space are presented rapidly, one after another, separated by a brief time interval.

Induced Motion
The illusory movement of one object (usually smaller) that is caused by the movement of another object (usually a large one) that is near by.
Motion Aftereffect
An illusion that occurs after a person views a moving stimulus & then sees movement in the opposite direction when viewing a stationary stimulus immediately afterward.

Waterfall Illusion
Aftereffect of movement that occurs after viewing a stimulus moving in one direction, such as a waterfall; viewing the waterfall makes other objects appear to move in the opposite direction.
Optic Array
The structured pattern of light created by the presence of objects, surfaces, & textures in the environment.

Local Disturbance in the Optic Array
Occurs when one object moves relative to the environment, so that the stationary background is covered & uncovered by the moving object. This local disturbance indicates that the object is moving relative to the environment.
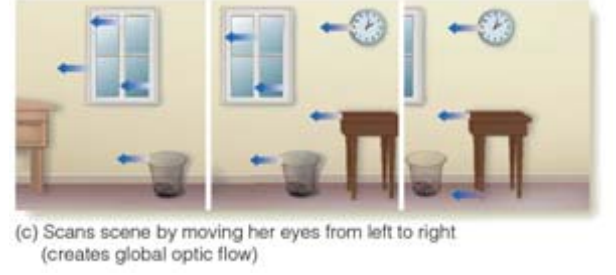
Global Optic Flow
Information for movement that occurs when all elements in a scene move.
Reichardt Detector
Signals caused by movement of a stimulus across the receptors are processed by a delay unit and an output unit so that signals are generated by movement in one direction but not in the opposite direction.
Corollary Discharge Theory
The theory that explains motion perception as being determined both by movement of the image on the retina & by signals that indicate movement of the eyes.
Image Displacement Signal (IDS)
The signal that occurs when an image moves across the visual receptors.
Motor Signal (MS)
The signal that is sent to the eye muscles when the observer moves the eyes.
Corollary Discharge Signal (CDS)
A copy of the motor signal that is sent to the eye muscles to cause movement of the eye.
Comparator
A structure hypothesized by the corollary discharge theory of movement perception.
Striate Cortex
Perception begins here. It is the region of the occipital lobe where information from the retinas first reaches the cortex. Neurons on this cortex respond to movement of the ends of objects.
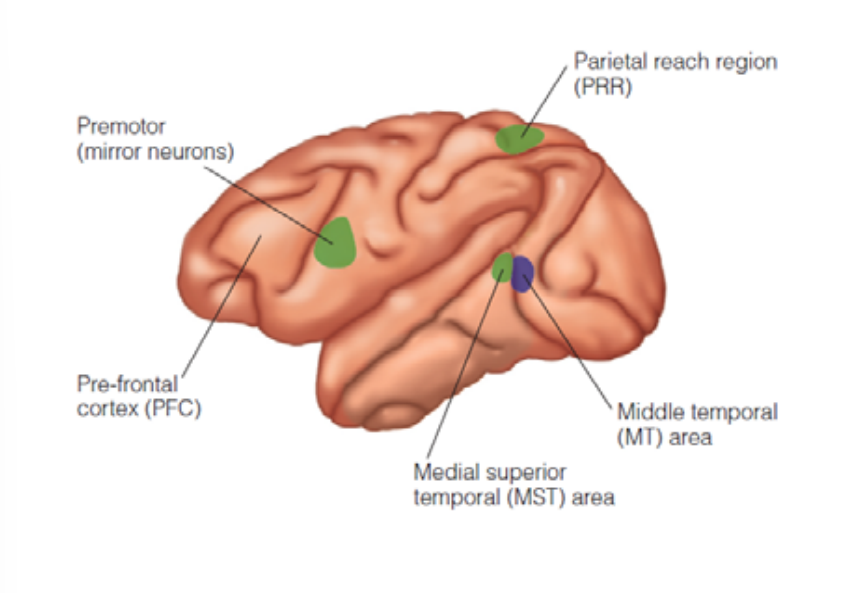
Middle Temporal (MT) Area
Contains many directionally sensitive cells in this area. Evidence comes from experiments that have used moving dot displays in which the direction of motion of individual dots can be varied.
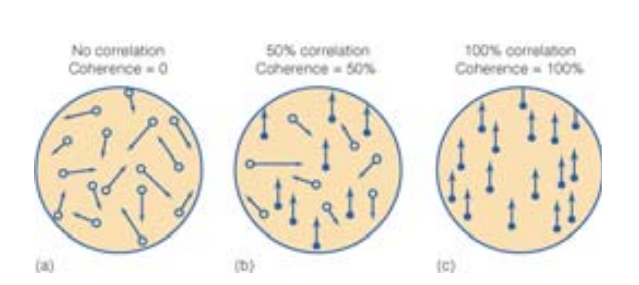
Coherence
Perception in which arrays of moving dots are used as stimuli.
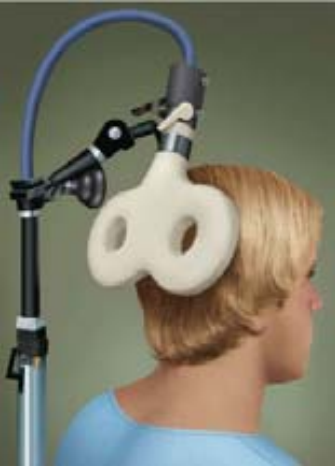
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Presenting a strong magnetic field to the head that temporarily disrupts the functioning of a specific area of the brain.
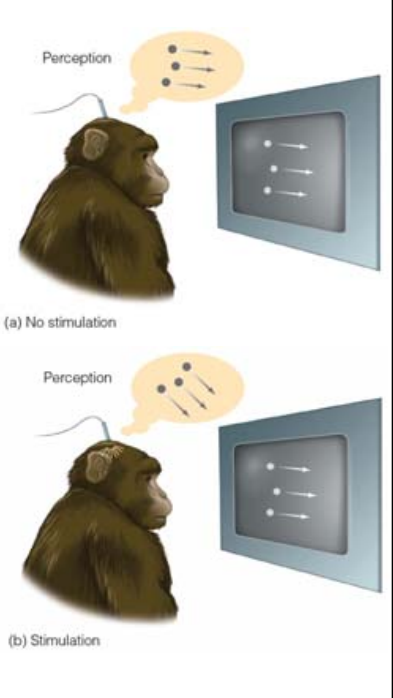
Microstimulation
a small electrode is inserted into the cortex, &
an electrical current passed through the electrode activating specific groups of neurons affects perception
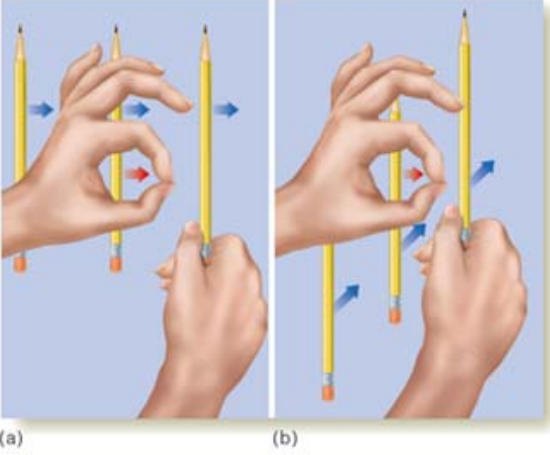
Aperture Problem
Observation of a small portion of a larger stimulus leads to misleading information about direction of movement. This can result
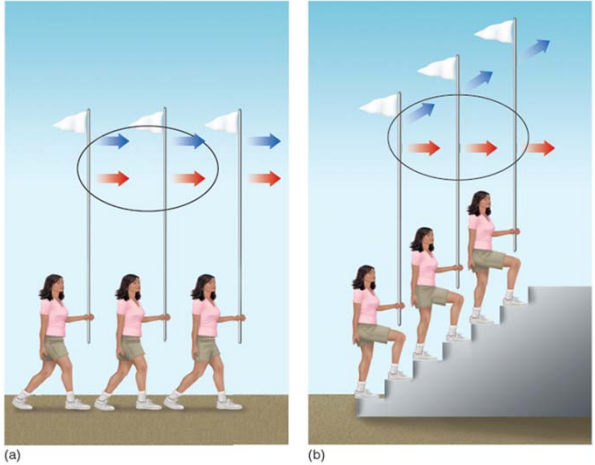
Shortest Path Constraint
In the perception of apparent motion, the principle that apparent movement tends to occur along the shortest path between 2 stimuli.

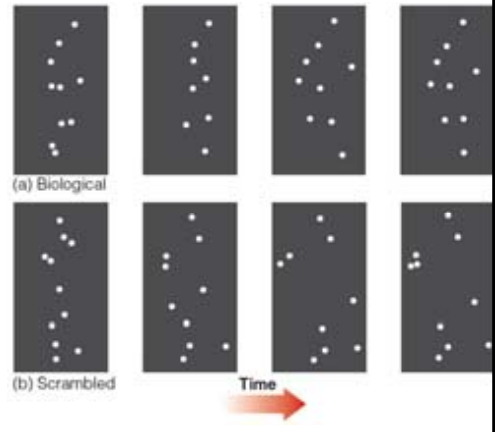
Point-Light Walkers
A biological motion stimulus created by placing small lights on people’s joints & then filming the patterns created by these lights when people walk & carry out other actions in the dark.
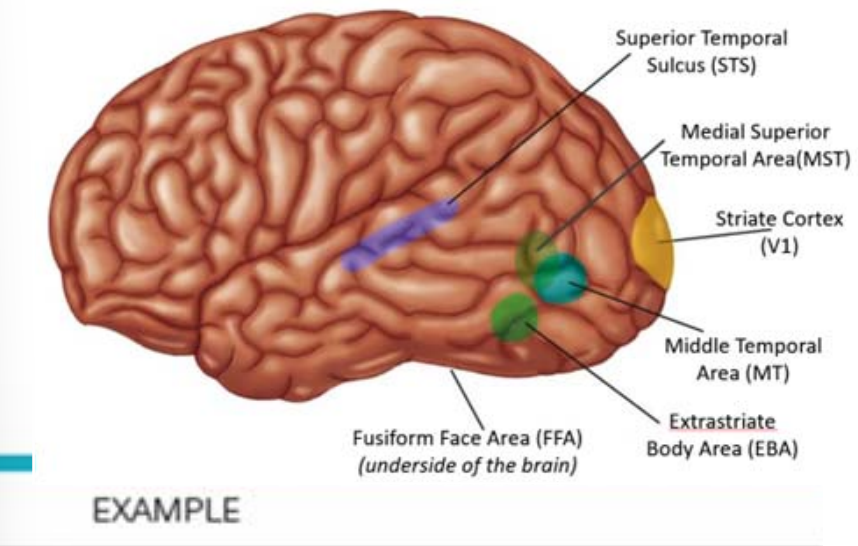
BRAIN REGIONS INVOLVED IN THE PERCEPTION OF MOTION
Striate Cortex (V1): Direction of motion across small receptive fields.
Middle Temporal Area (MT): Direction & speed of object motion.
Medial Superior Temporal Area (MST): Processing optic flow, locating moving objects, & reaching for moving objects.
Superior Temporal Sulcus (STS): Perception of motion related to animals & people (biological motion).
