Diagrams
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/92
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
1
New cards
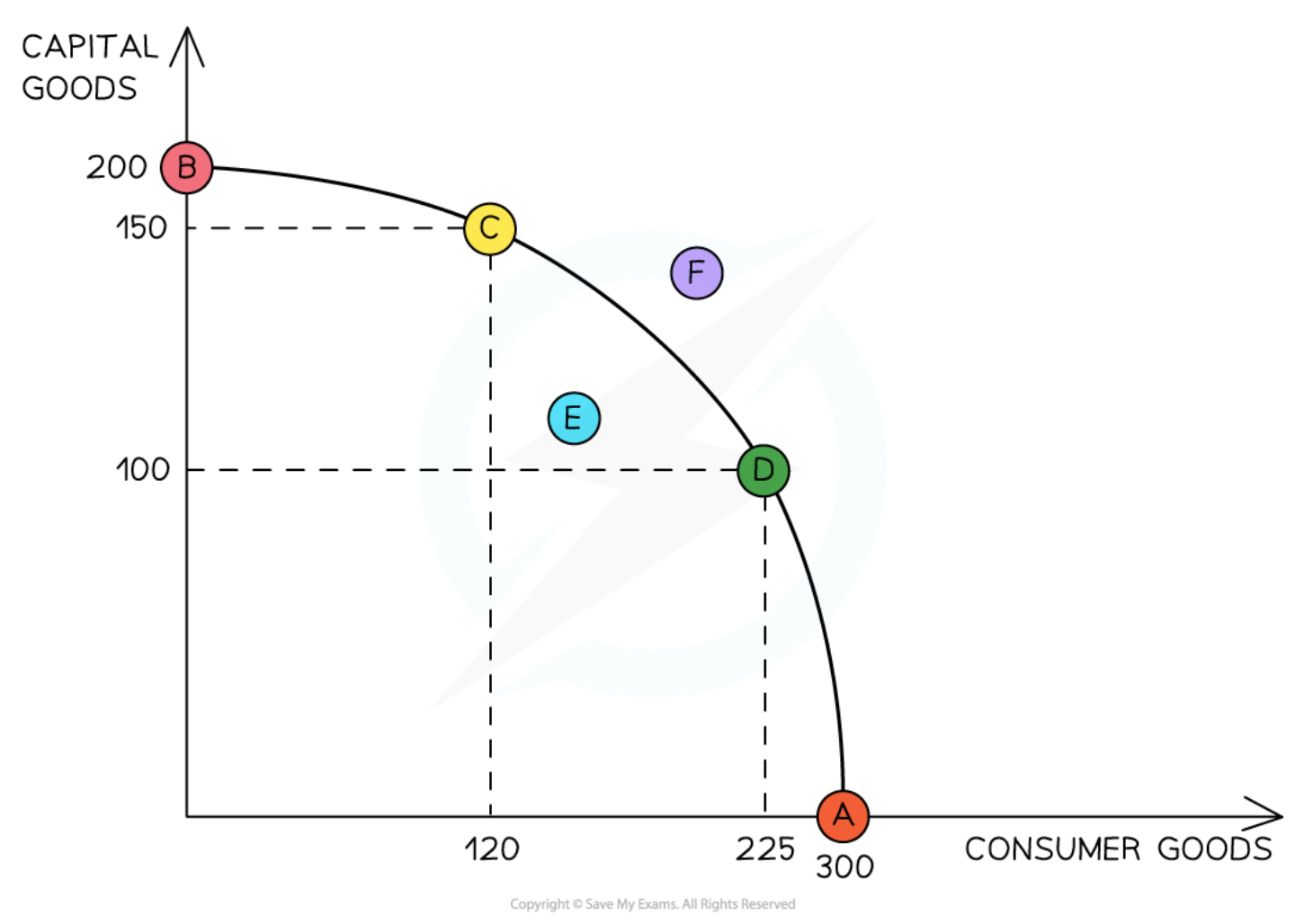
PPC showing maximum productive potential, opportunity cost, (in)efficiency and (un)attainable production
2
New cards
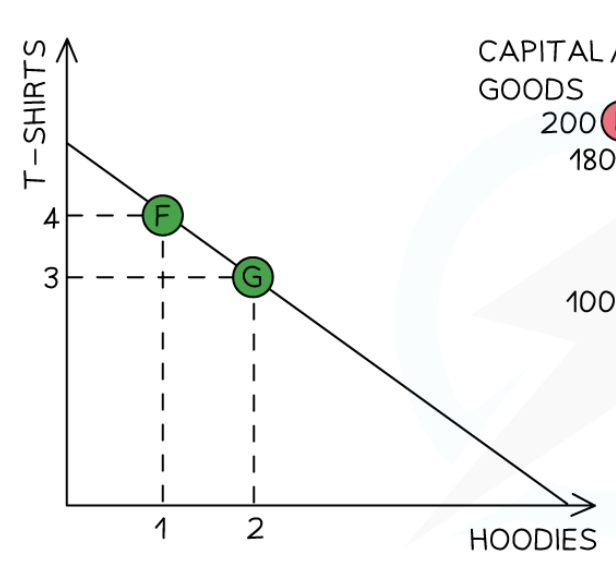
Constant opportunity cost
3
New cards
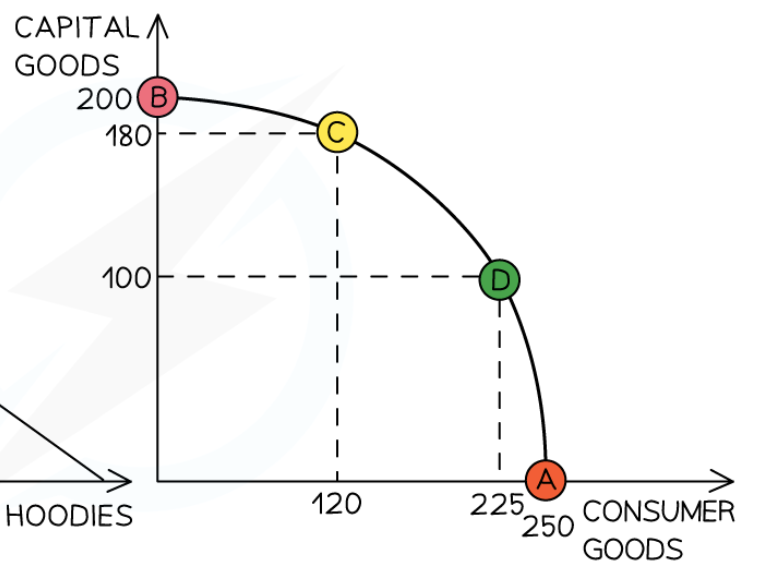
Increasing opportunity cost
4
New cards
Changes in production possibilities
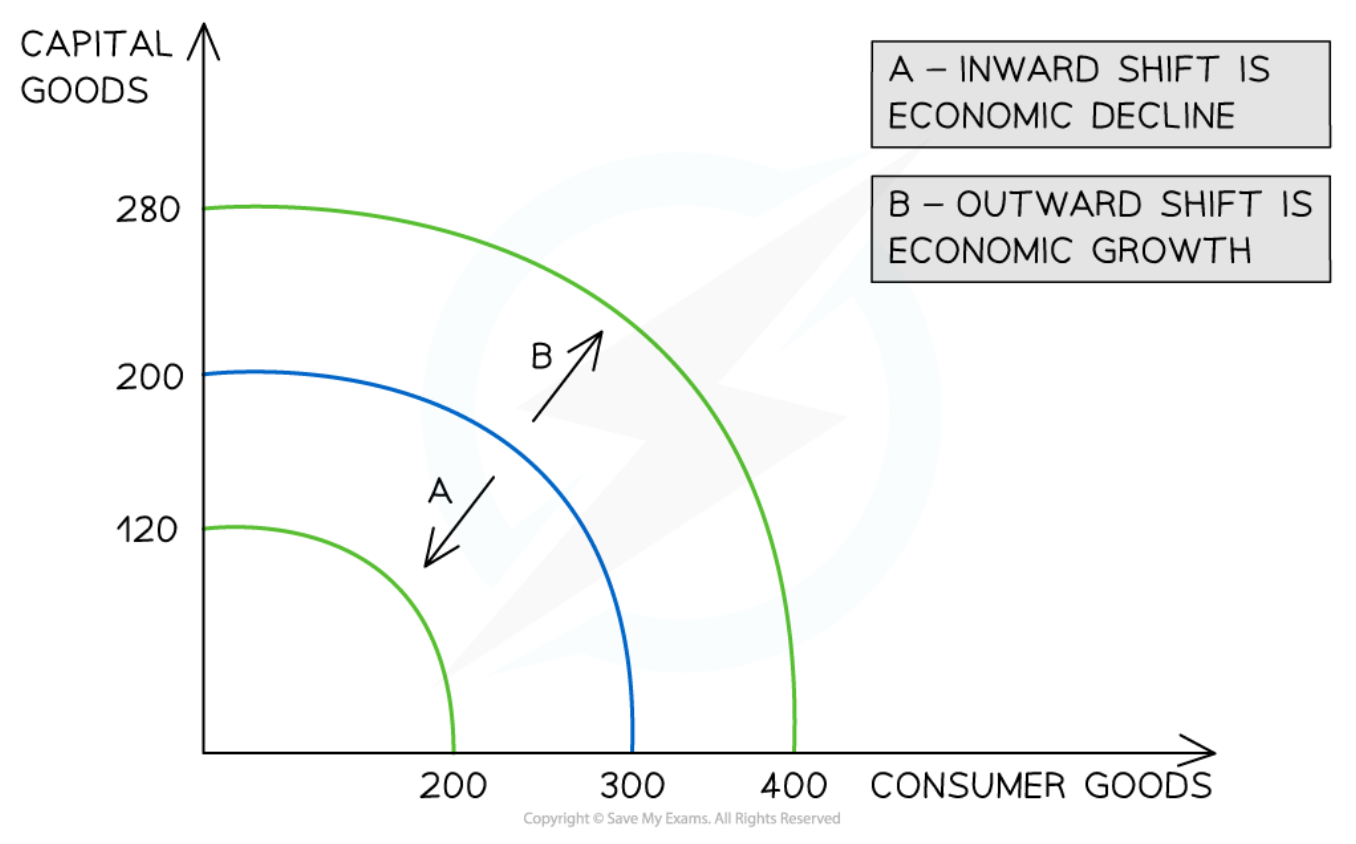
5
New cards
Circular flow of income in a closed economy
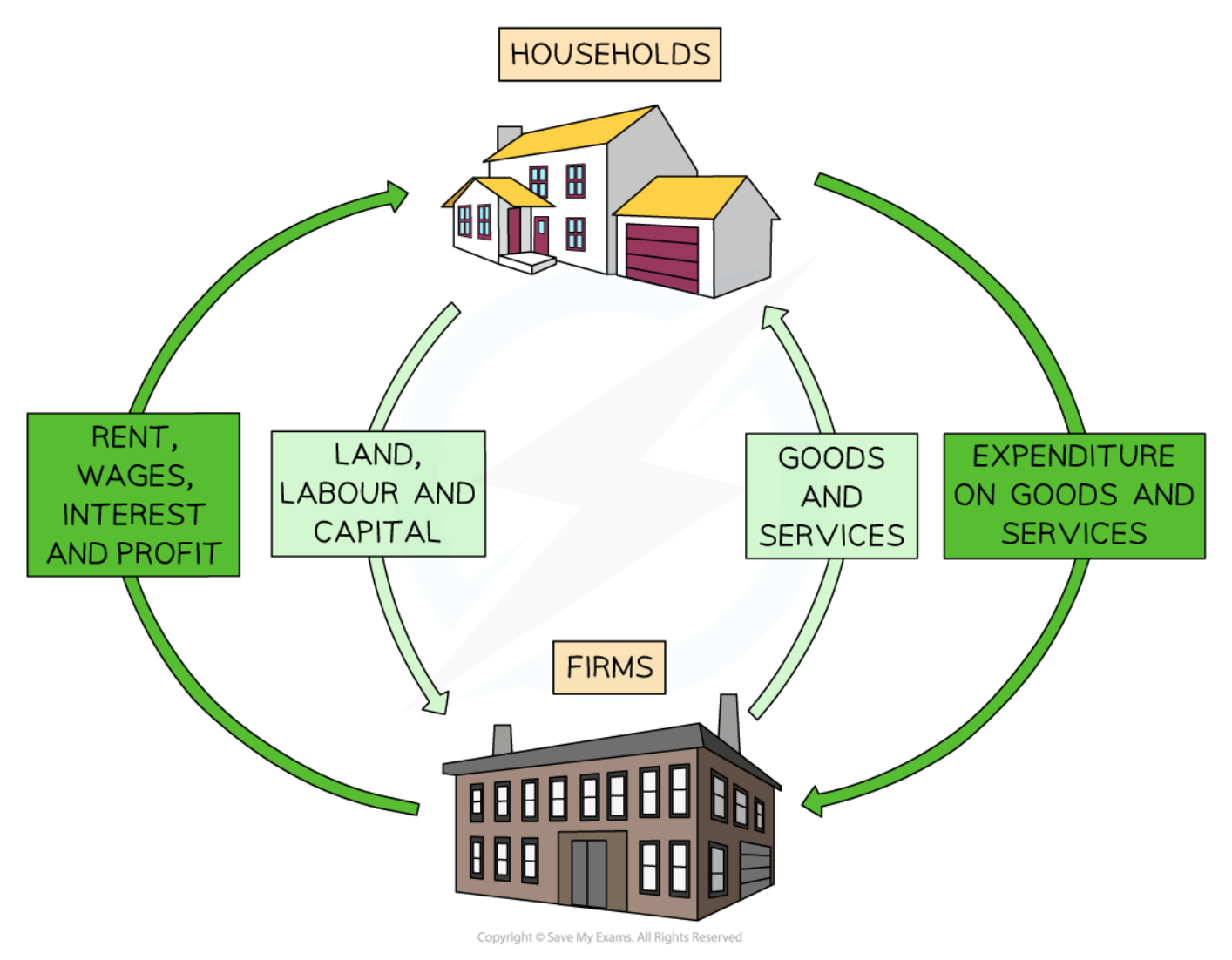
6
New cards
Circular flow of income in an open economy
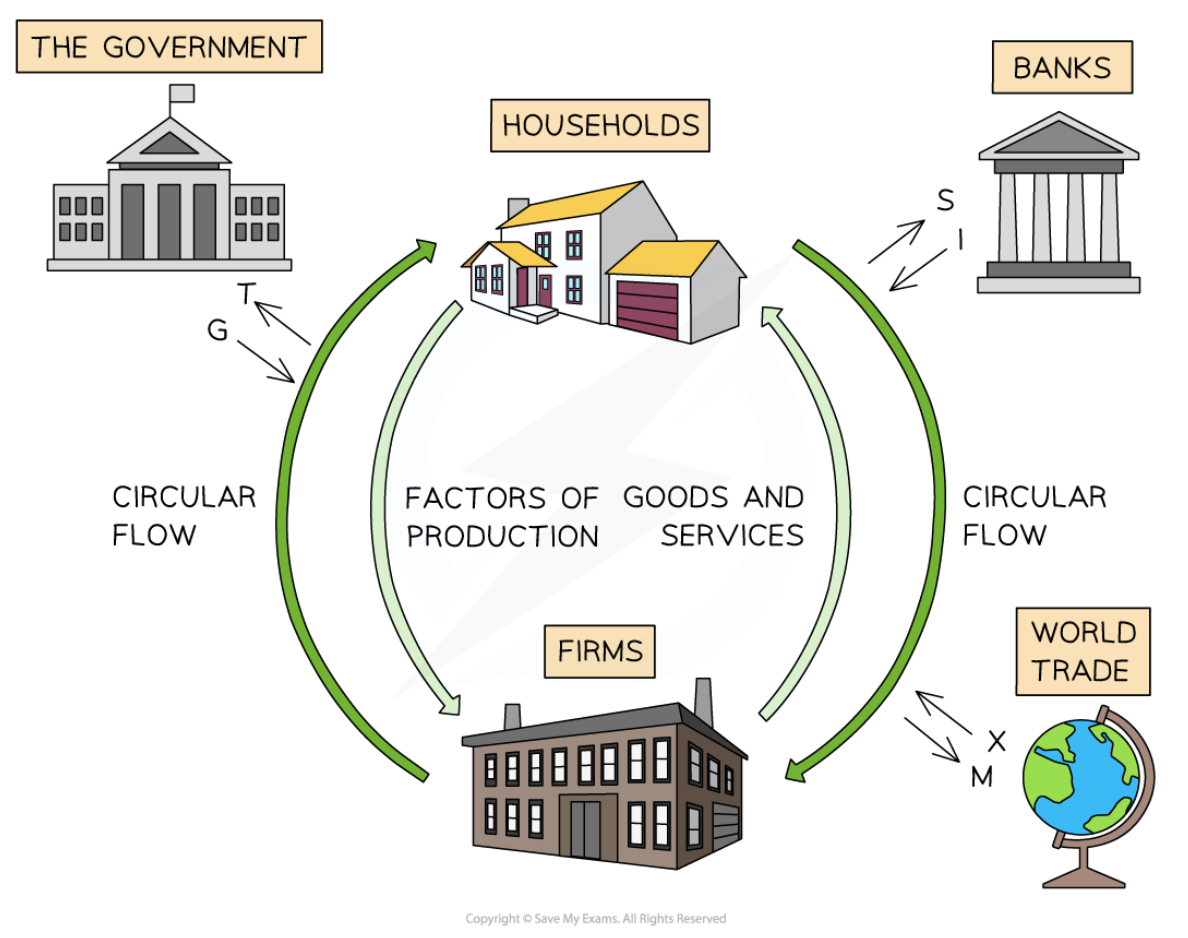
7
New cards
Movements along the demand curve
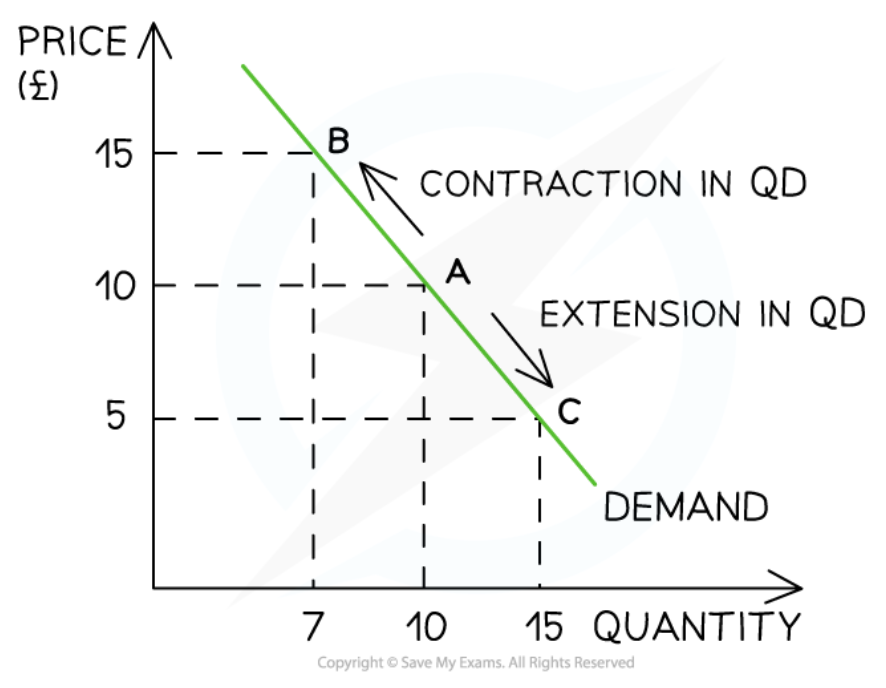
8
New cards
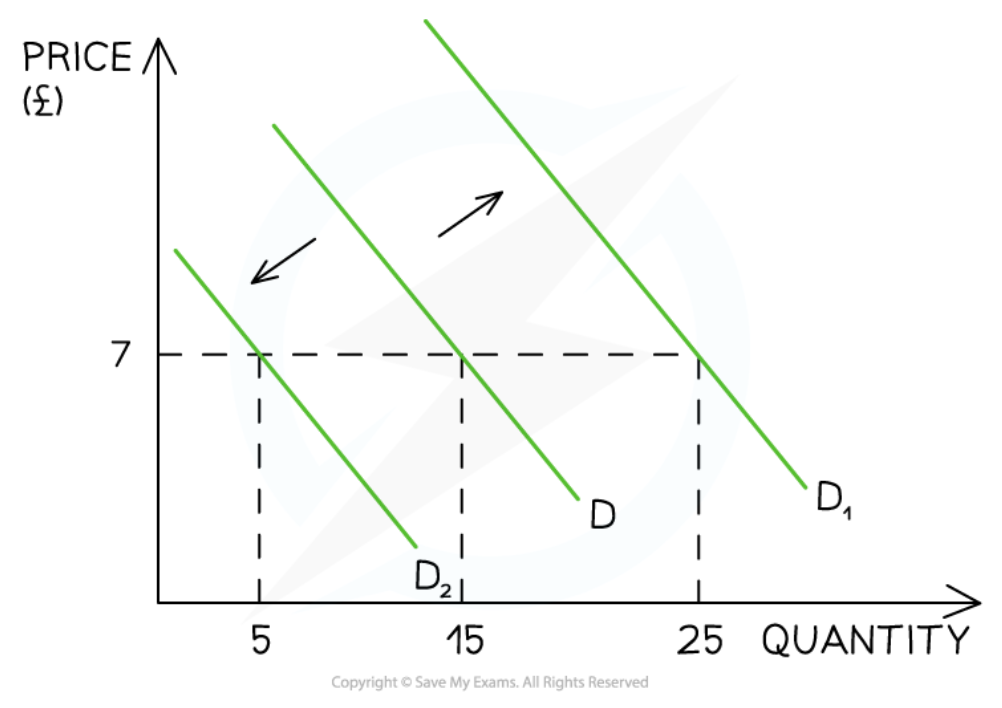
Shifts of the demand curve
9
New cards
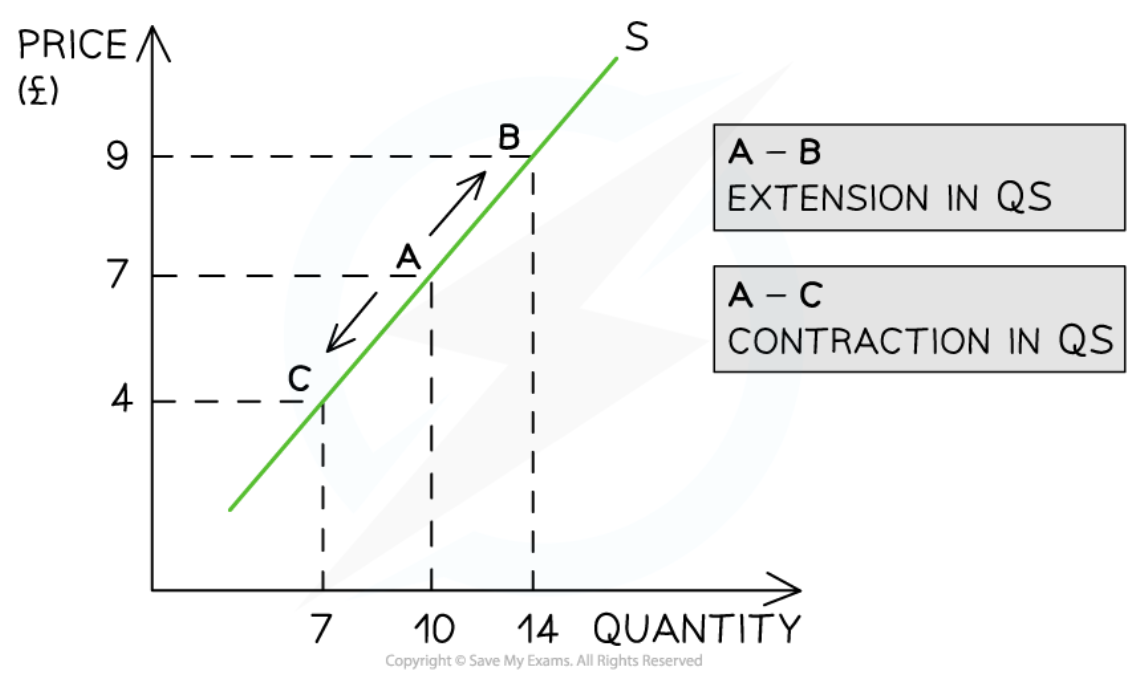
Movements along the supply curve
10
New cards
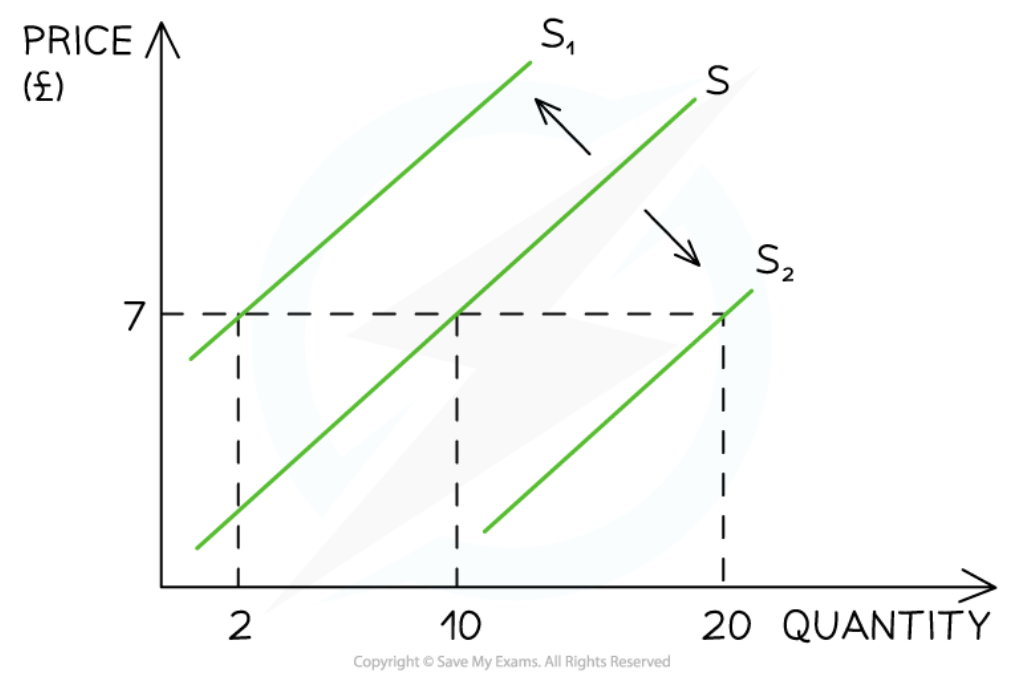
Shifts of the supply curve
11
New cards
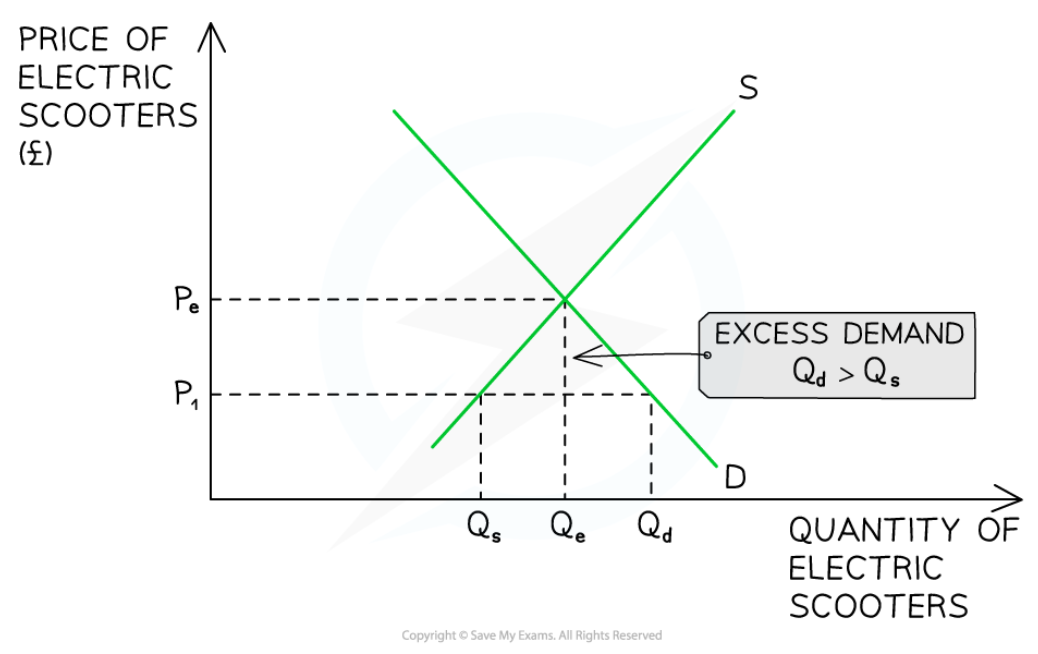
Excess demand
12
New cards
Excess supply
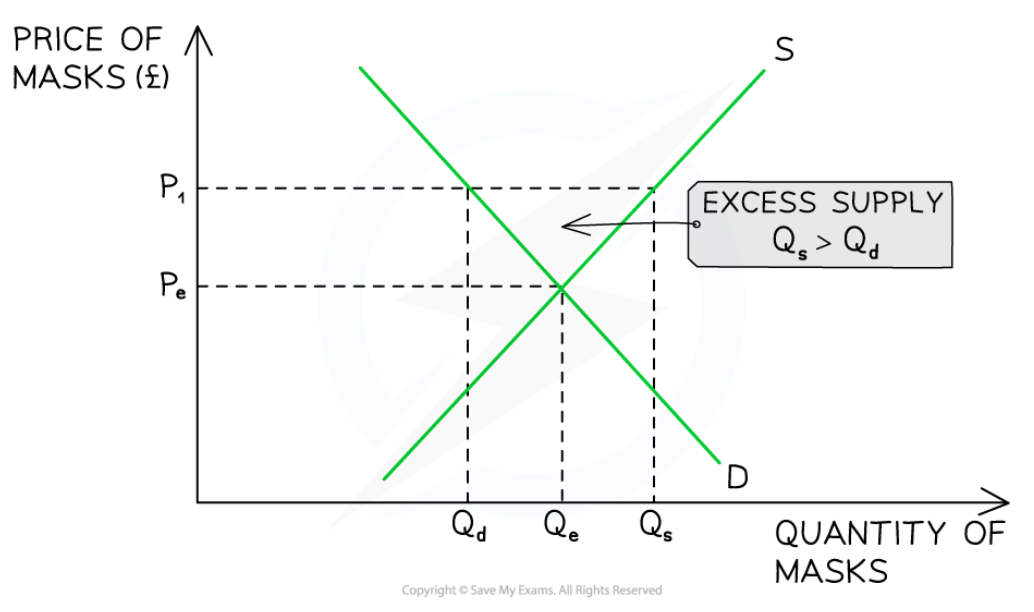
13
New cards
Maximization of community surplus
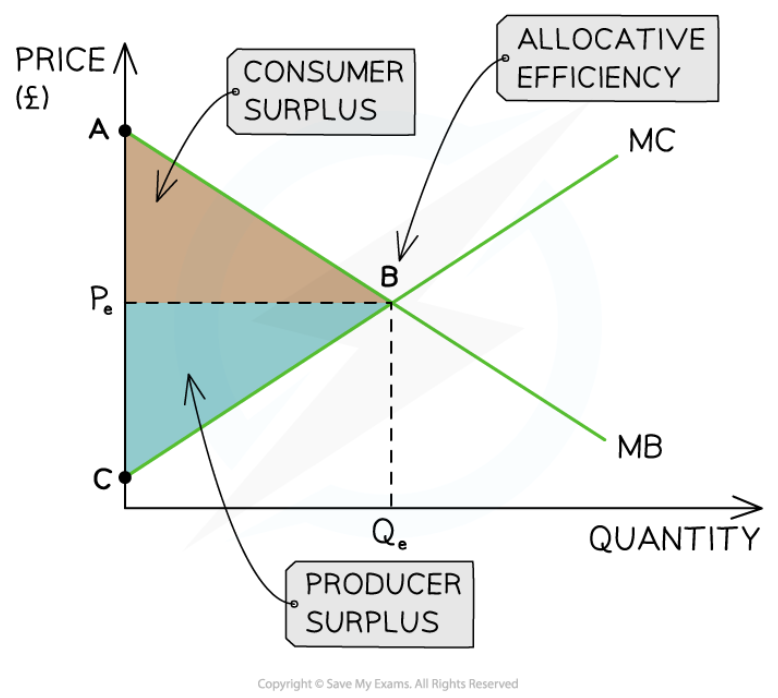
14
New cards
Consumer and produces surplus
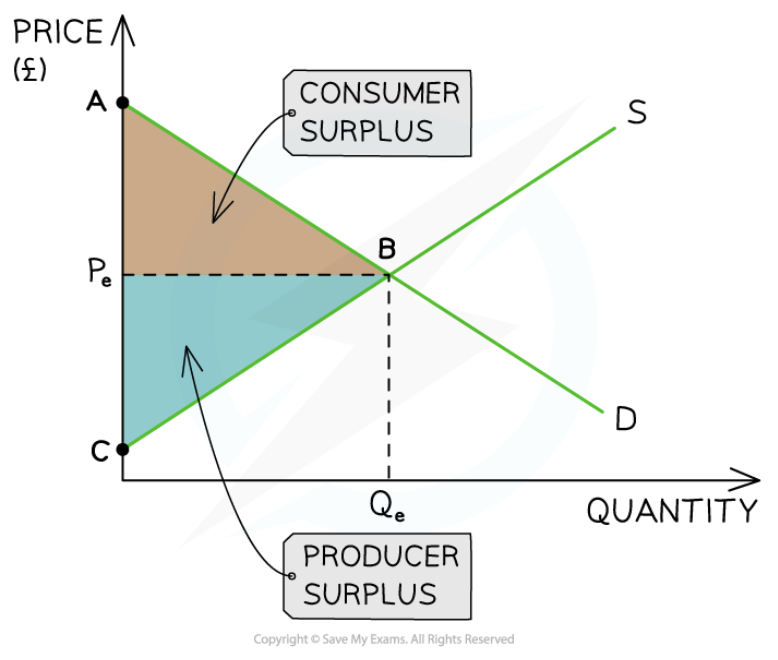
15
New cards
Perfectly inelastic demand
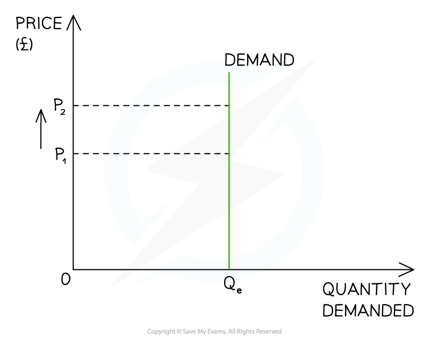
16
New cards
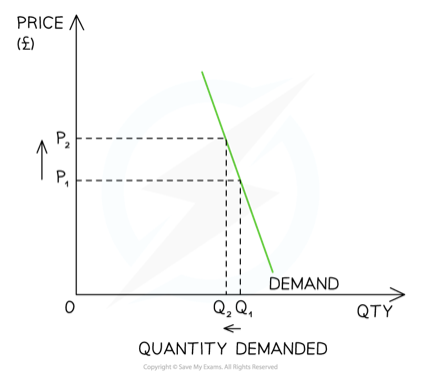
Inelastic demand
17
New cards
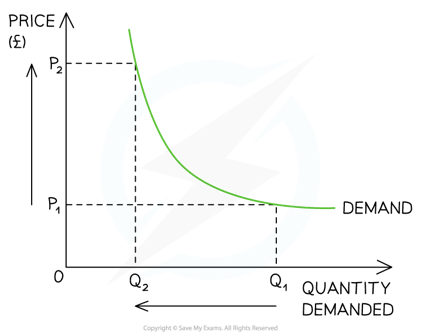
Unitary elastic demand
18
New cards
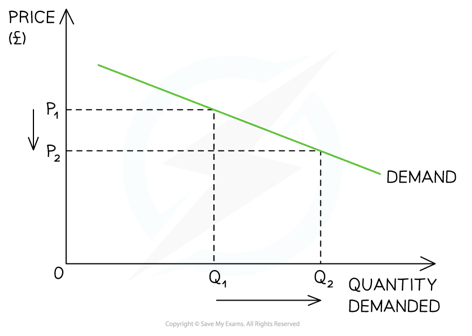
Elastic demand
19
New cards
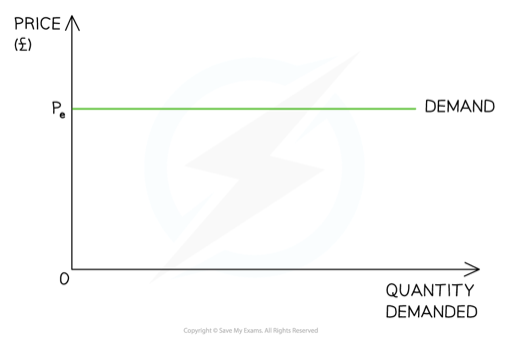
Perfectly elastic demand
20
New cards
Necessity (YED)
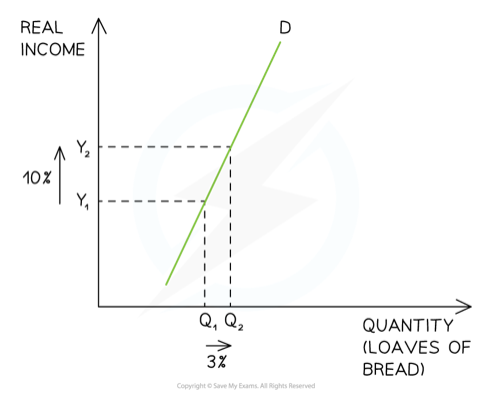
21
New cards
Luxury (YED)
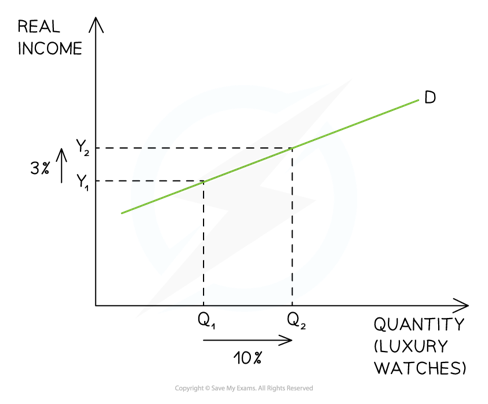
22
New cards
Inferior good (YED)
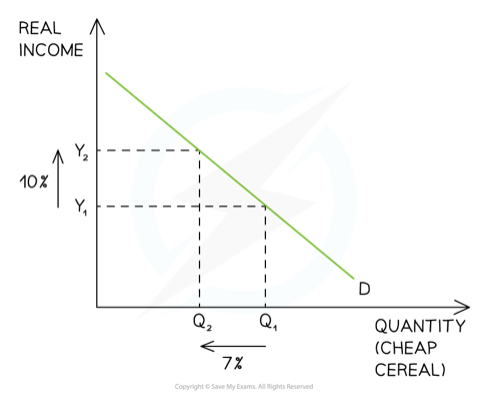
23
New cards
Inelastic supply
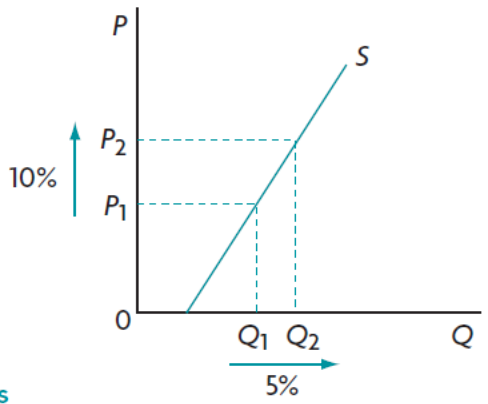
24
New cards
Elastic supply
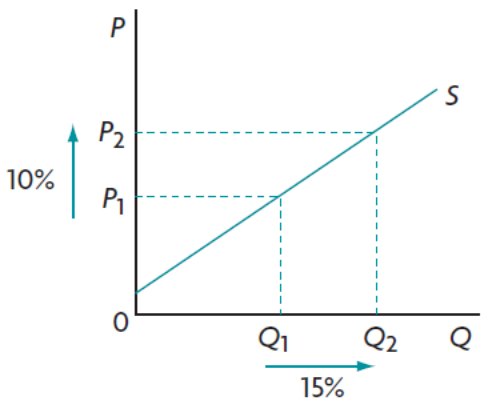
25
New cards
Unitary elastic supply
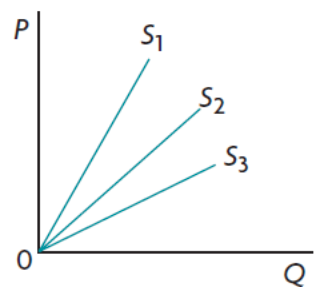
26
New cards
Perfectly inelastic supply
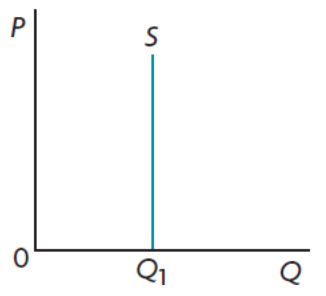
27
New cards
Perfectly elastic supply
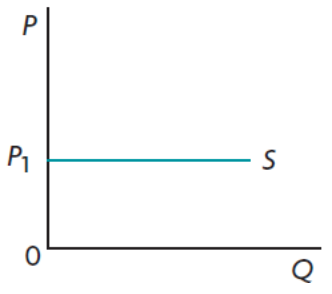
28
New cards
Specific tax
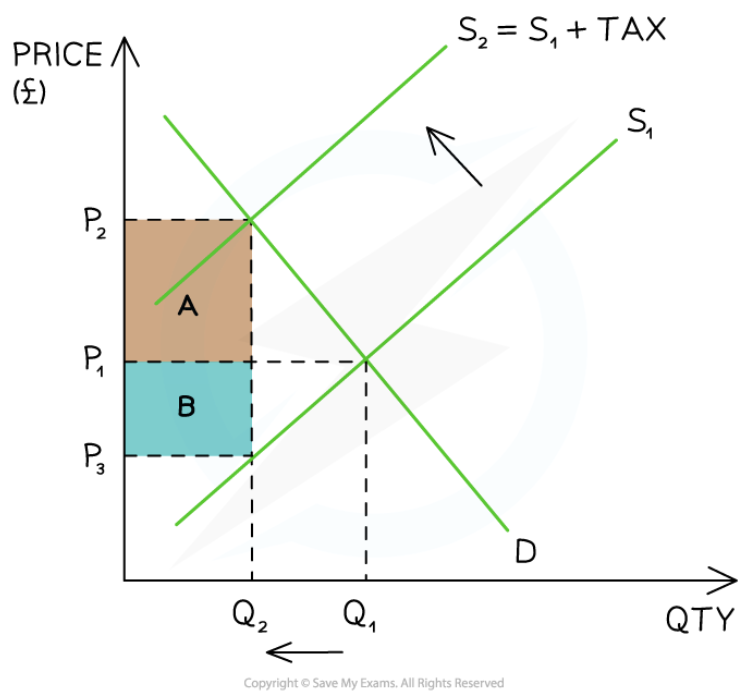
29
New cards
As Valorem tax (VAT)
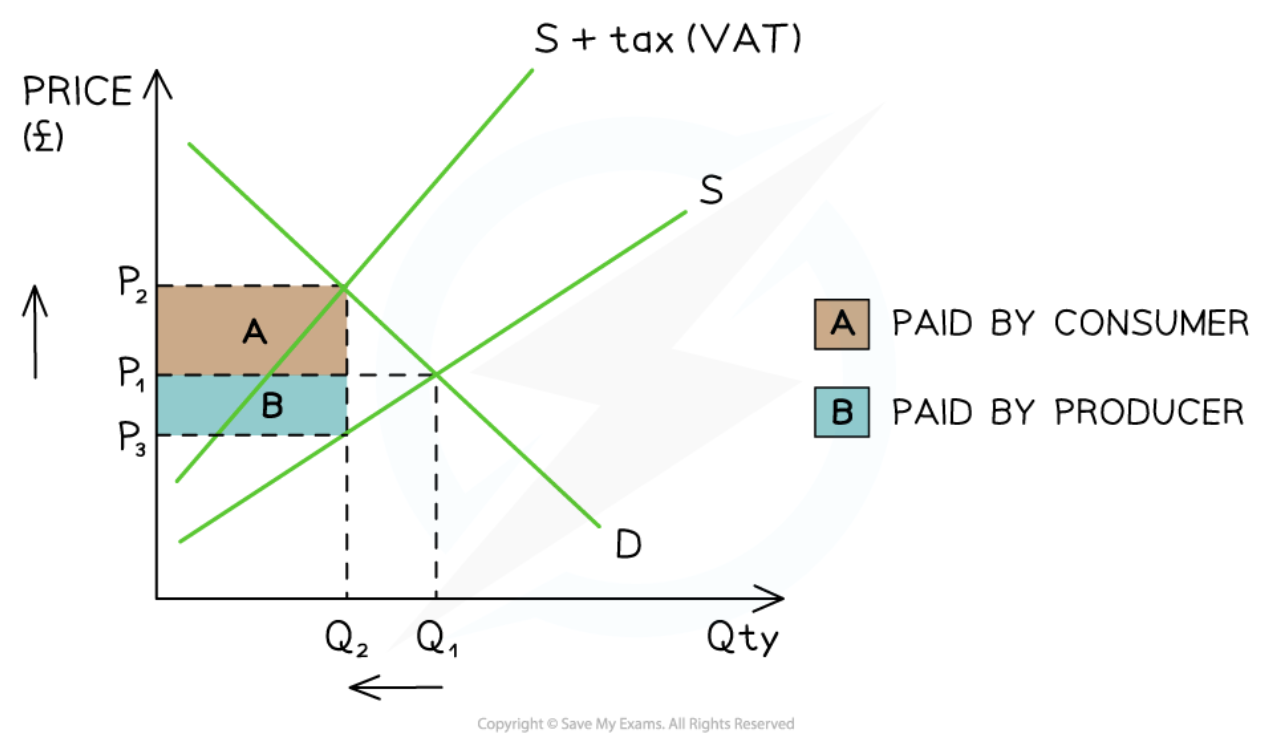
30
New cards
Subsidy
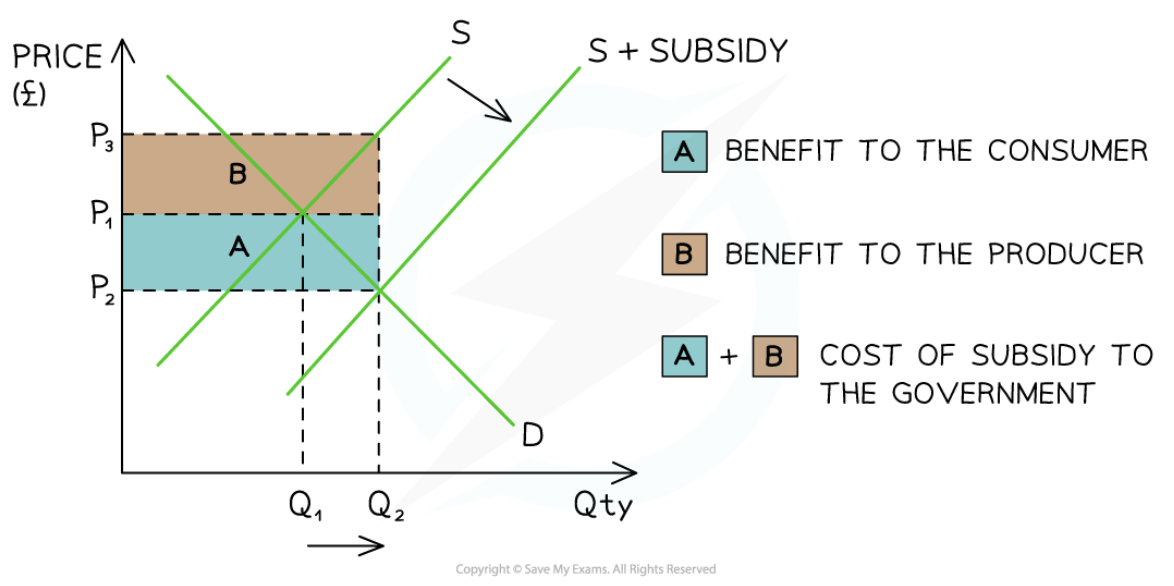
31
New cards
Price ceiling
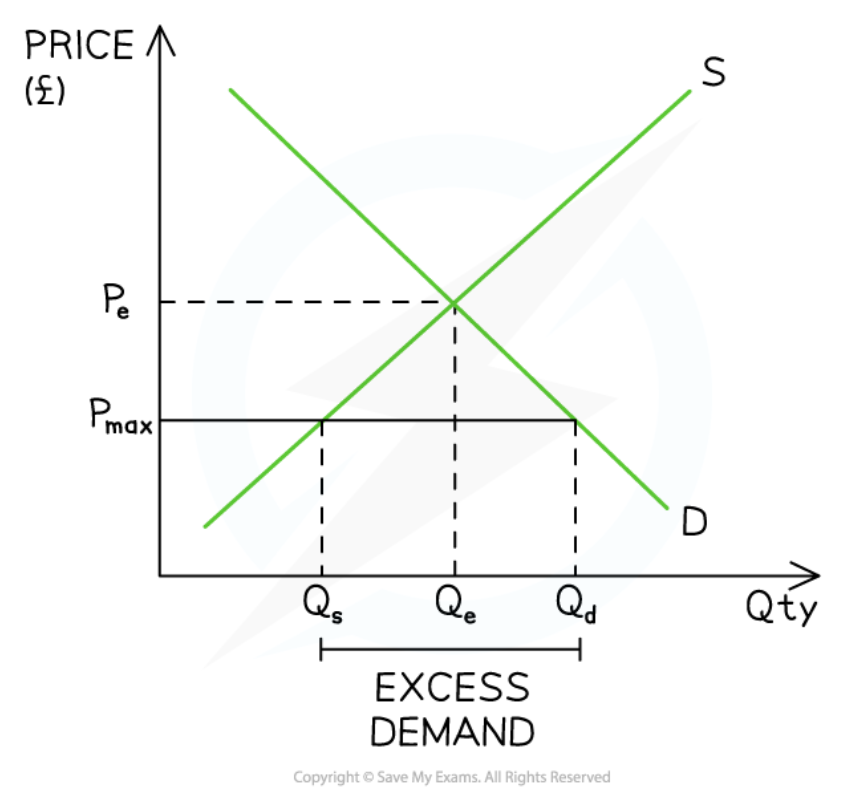
32
New cards
Price floor
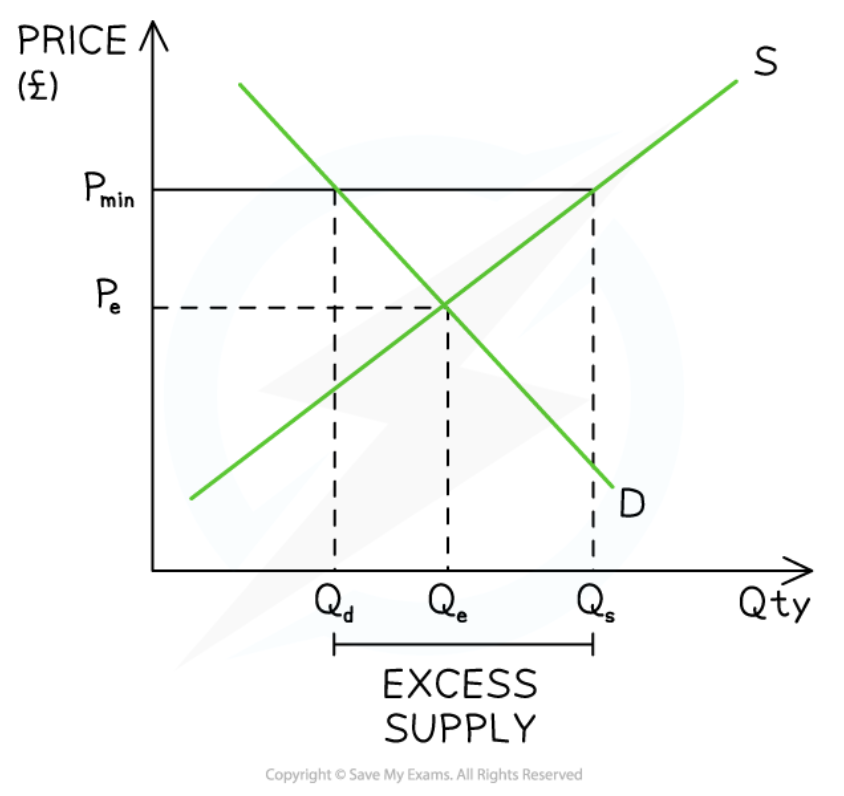
33
New cards
Minimum wage in labour markets
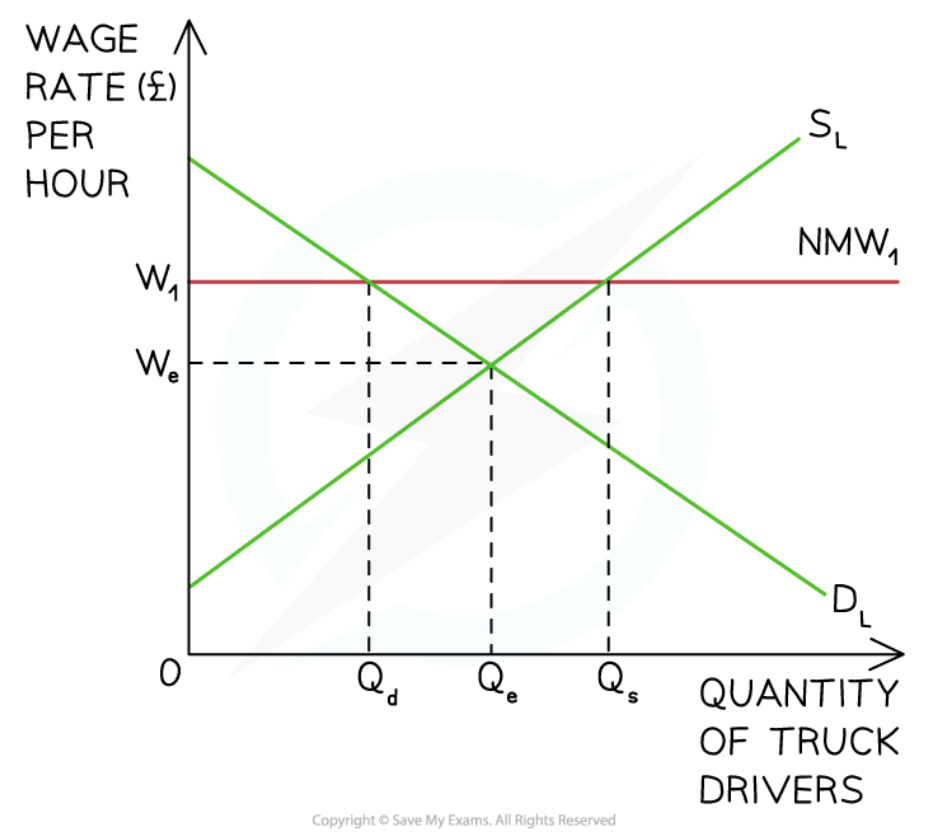
34
New cards
Negative production externality
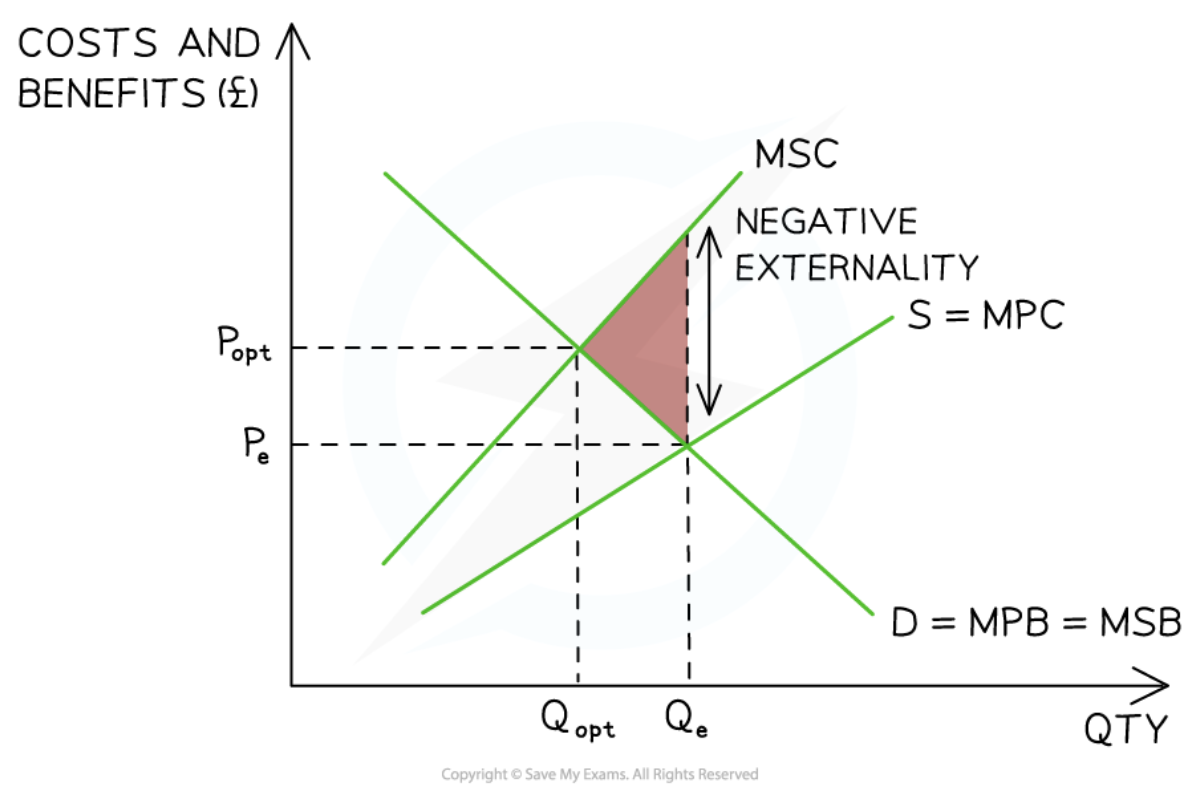
35
New cards
Negative consumption externality
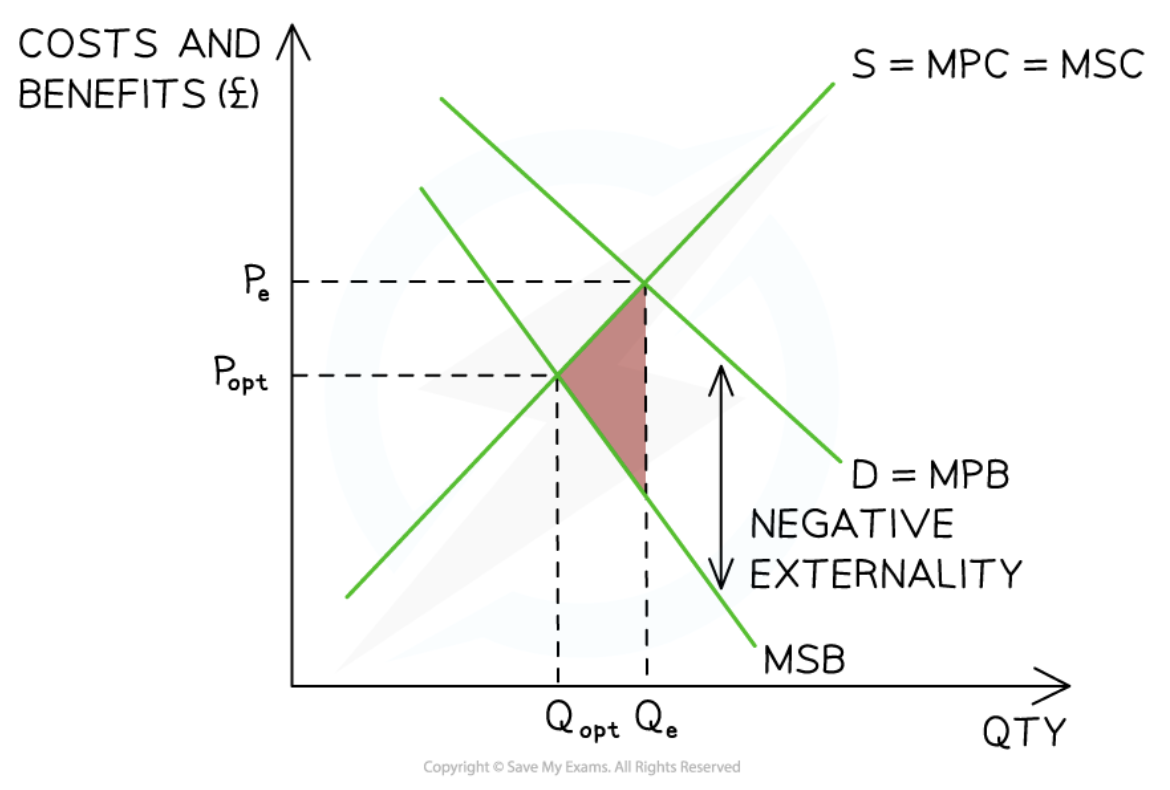
36
New cards
Positive production externality
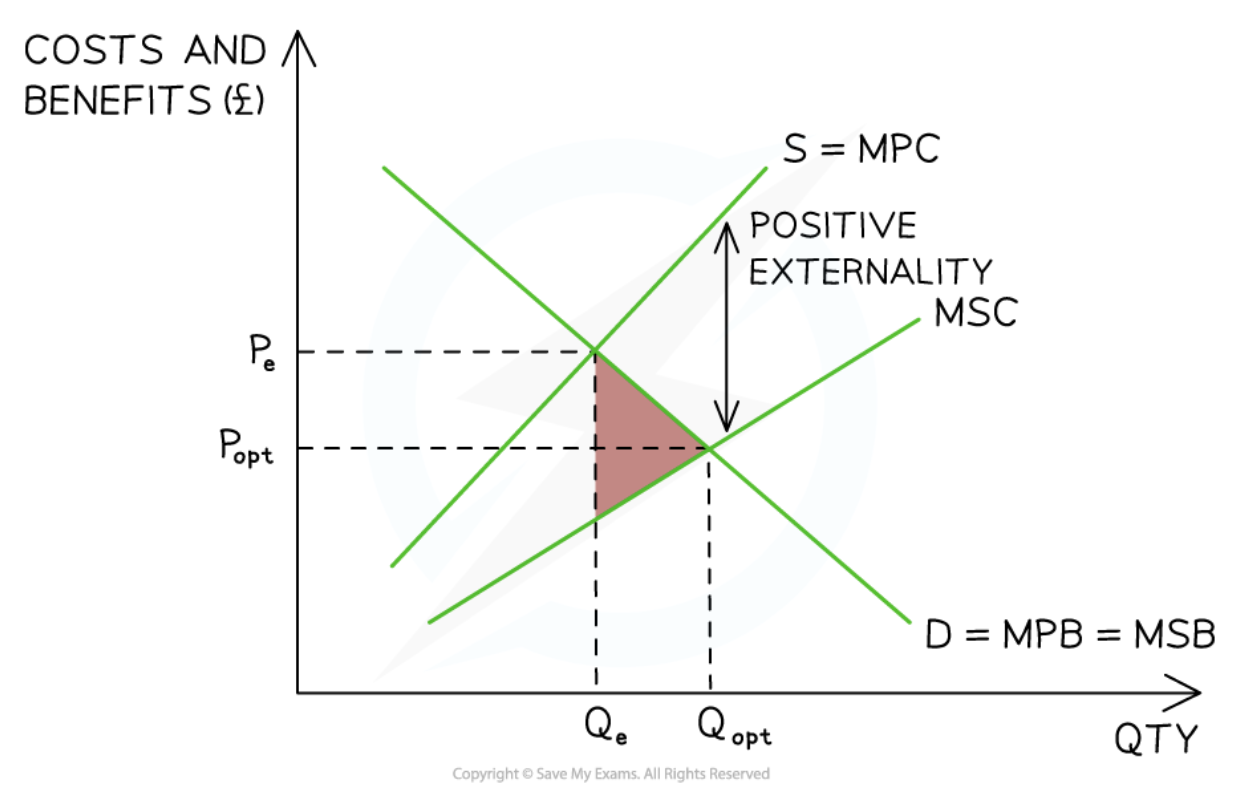
37
New cards
Positive consumption externality
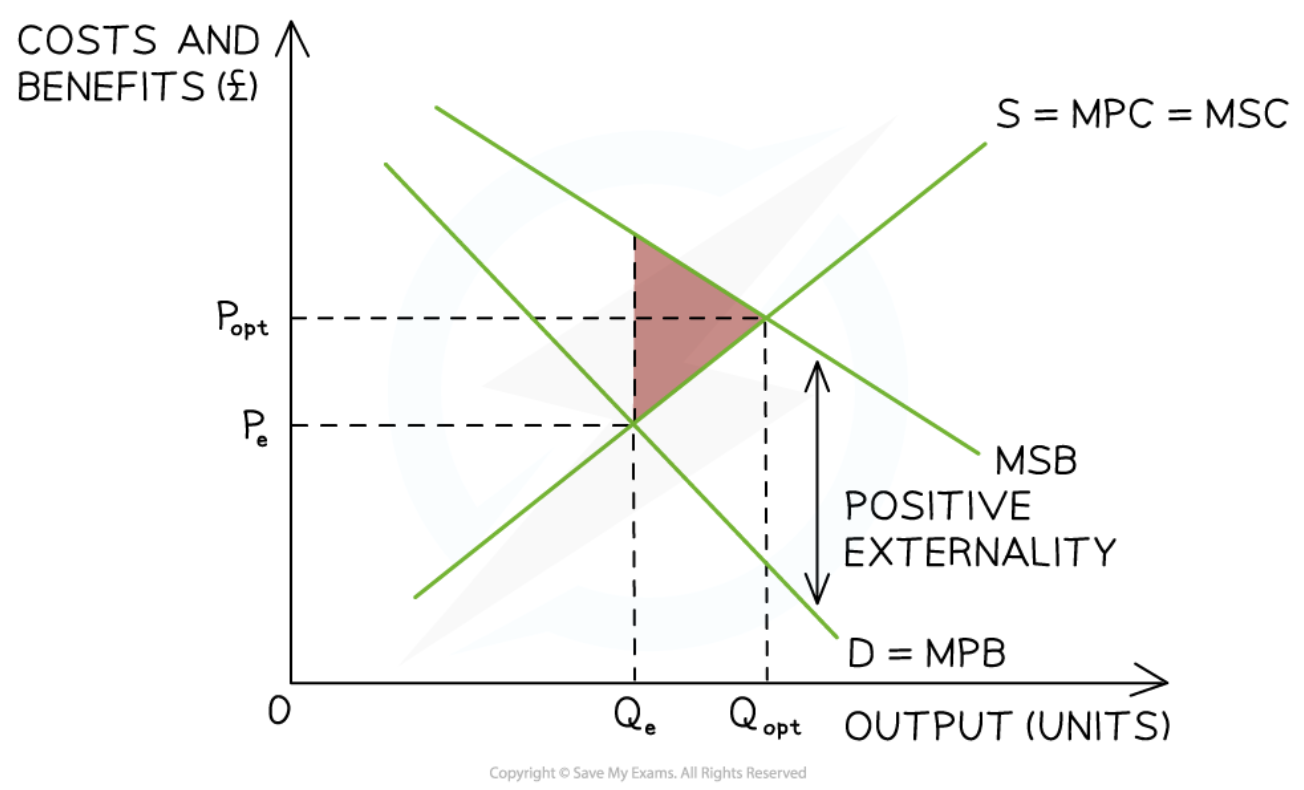
38
New cards
Specific tax on a negative production externality
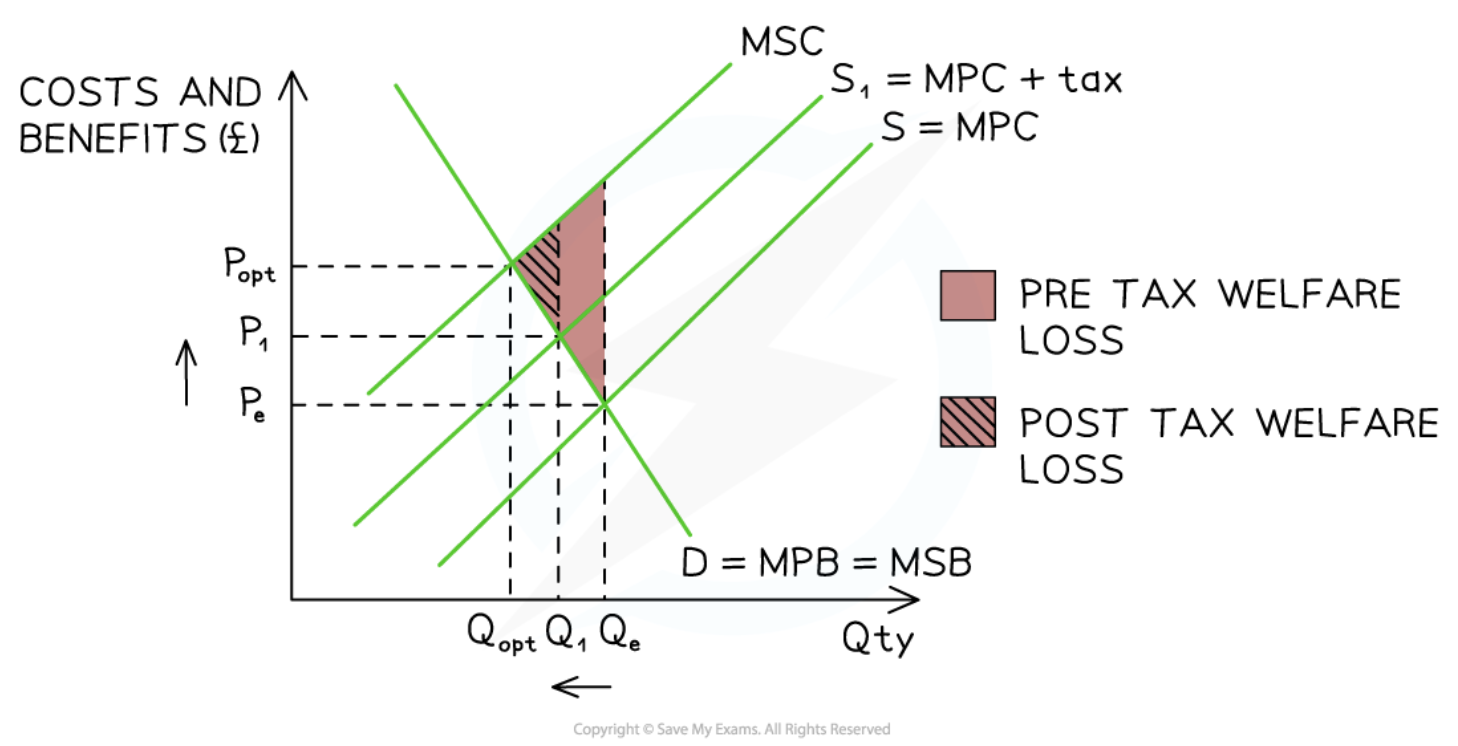
39
New cards
Specific tax on a negative consumption externality
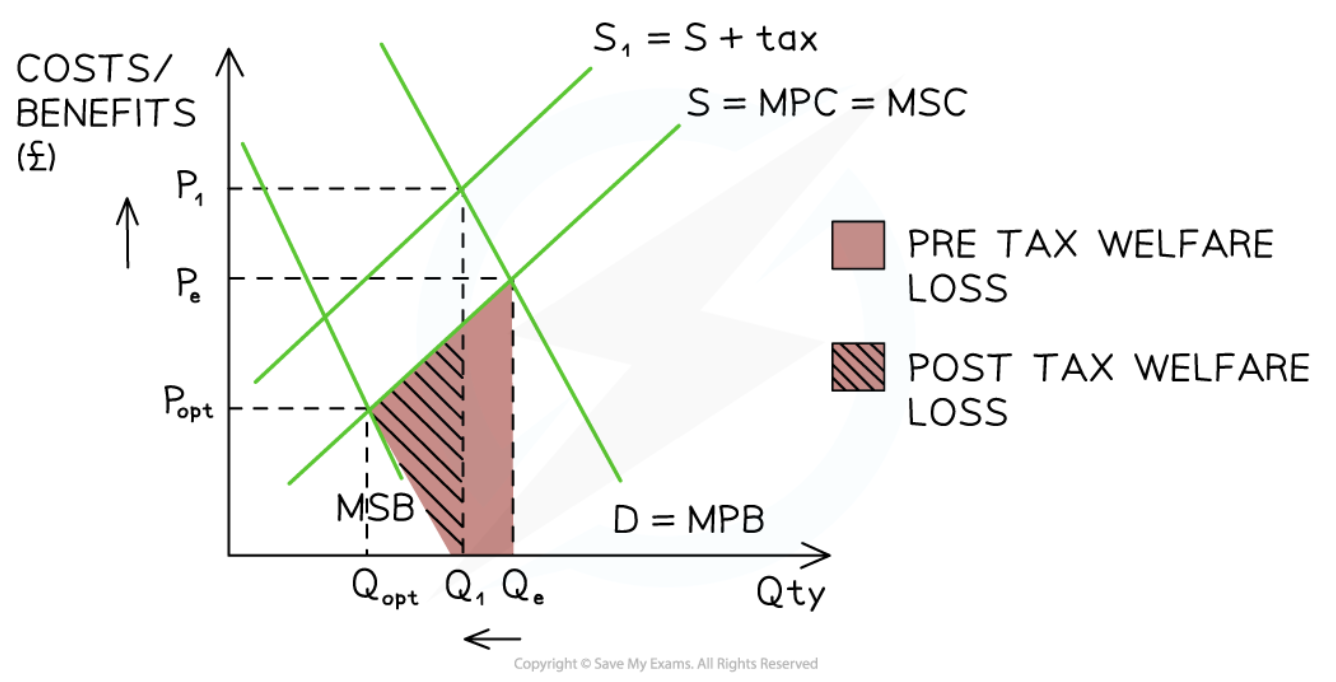
40
New cards
Carbon tax (on a negative production externality)
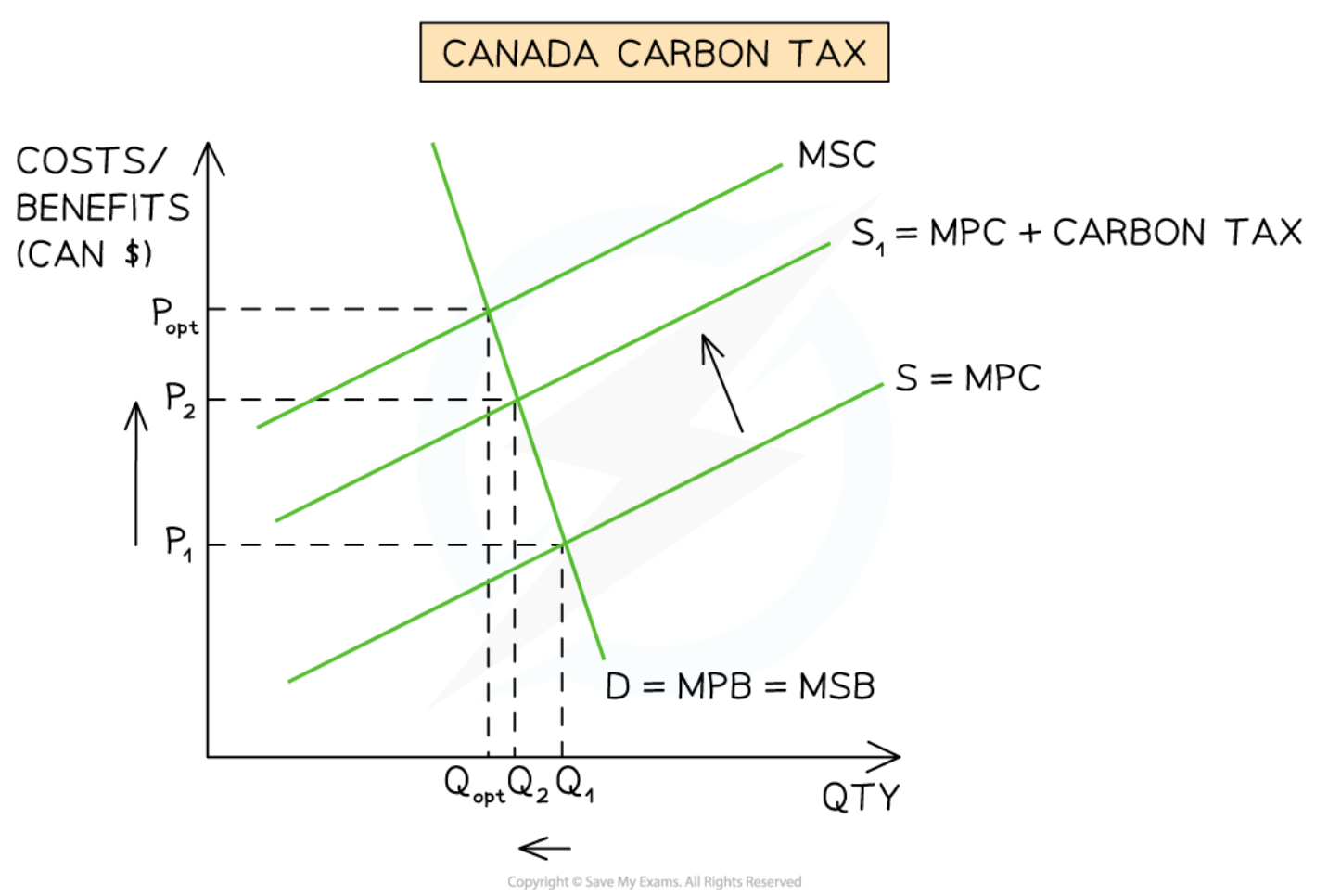
41
New cards
Subsidy on a positive production externality
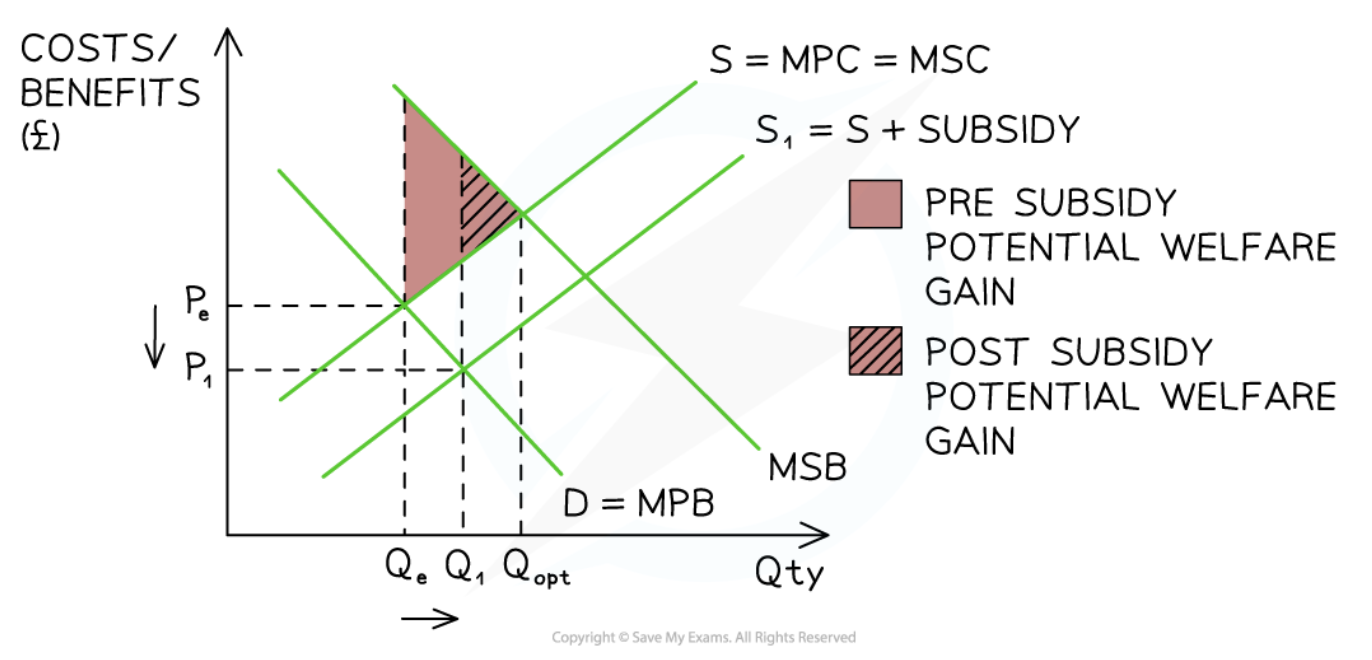
42
New cards
Legislation aimed at the consumer side
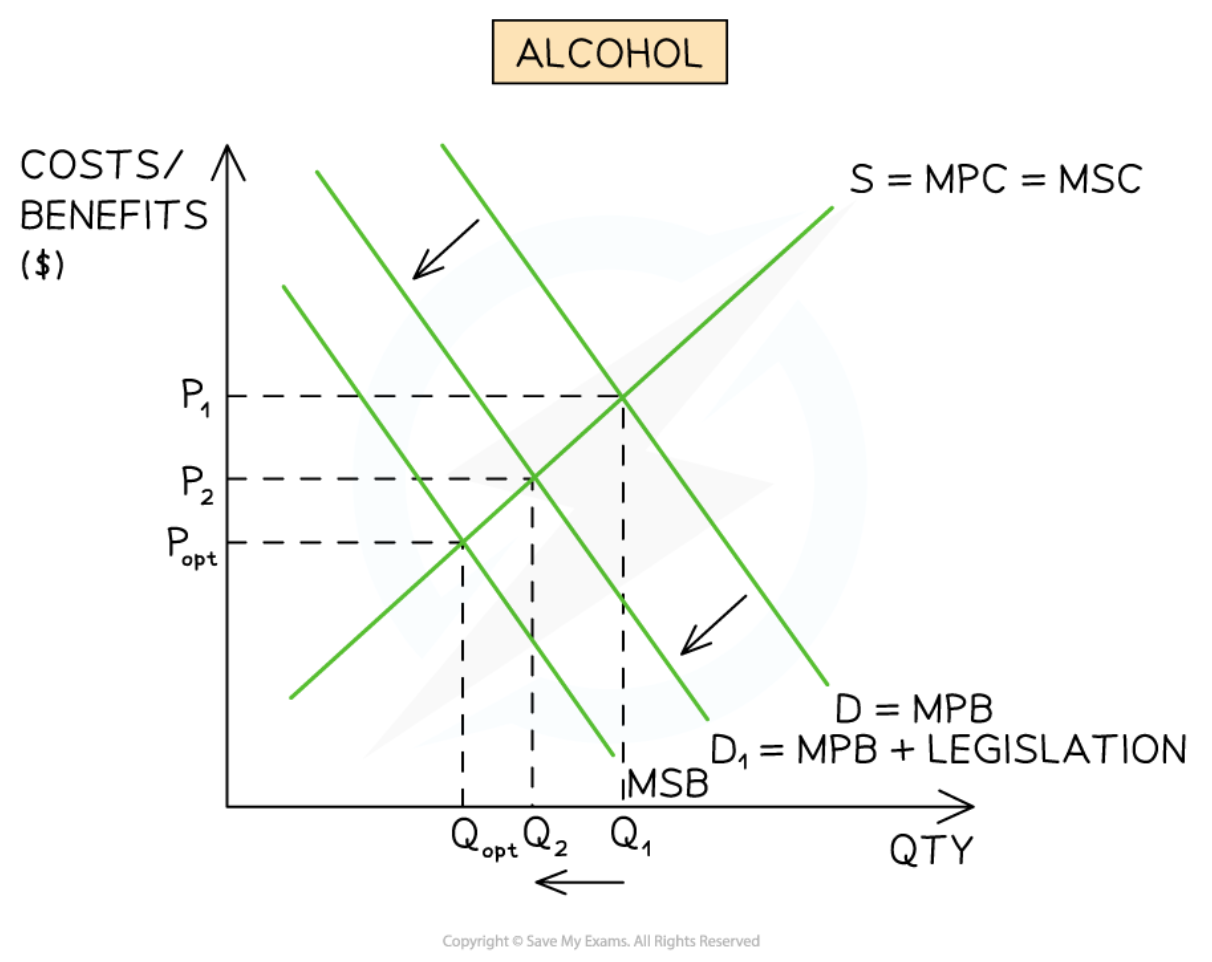
43
New cards
Legislation aimed at the producer side
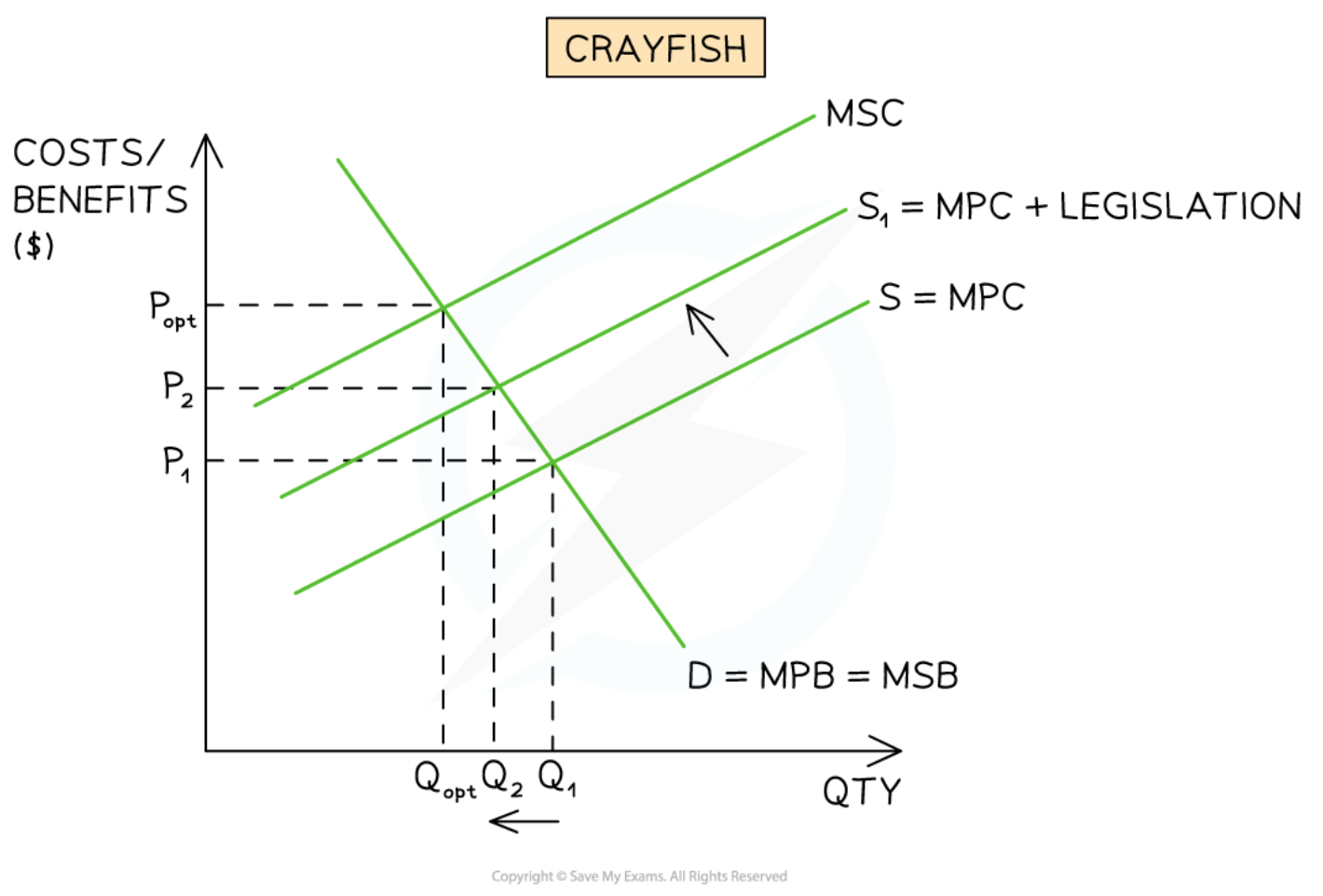
44
New cards
Educating consumers on the benefits of merit goods
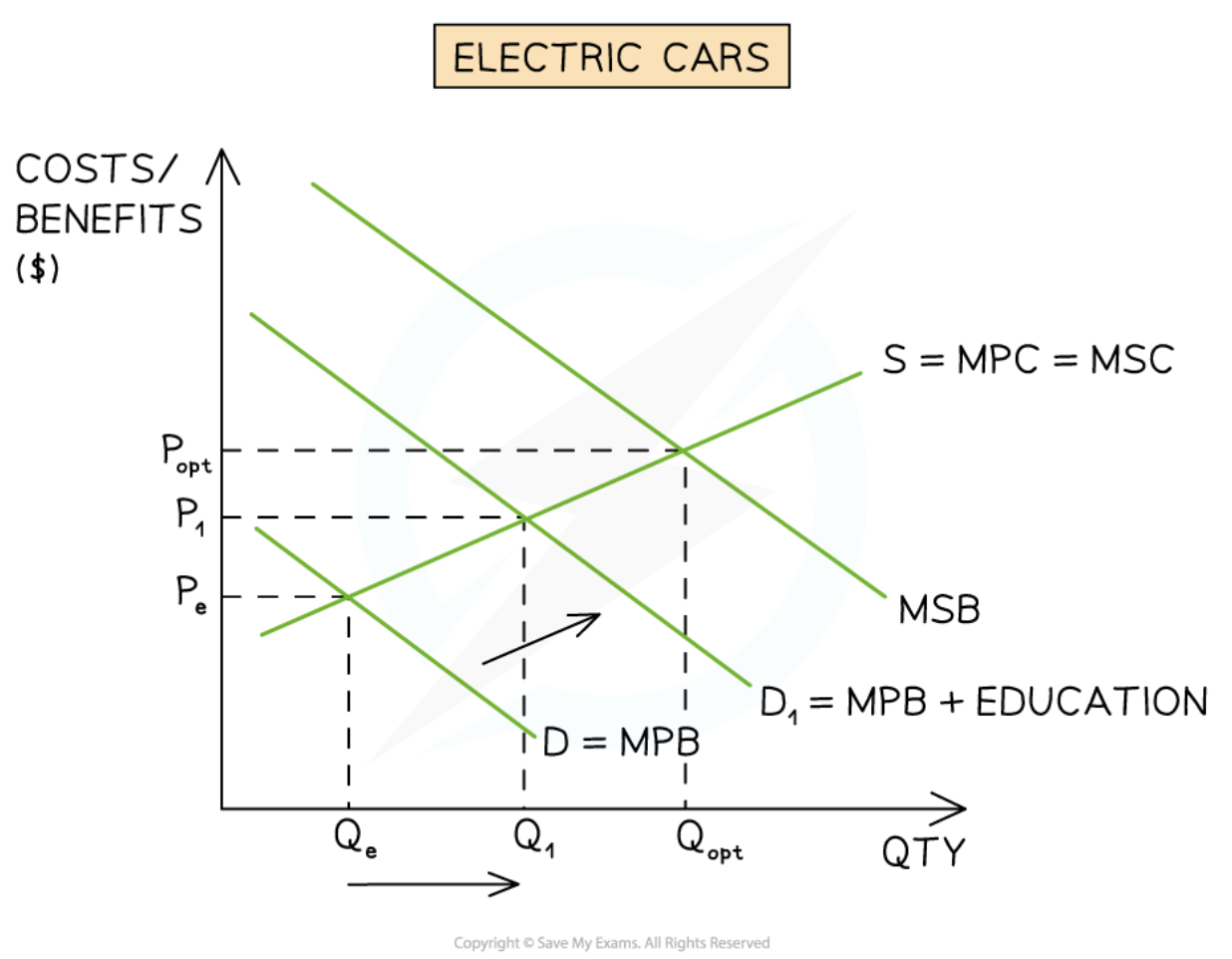
45
New cards
Education consumers on the dangers of consuming demerit goods
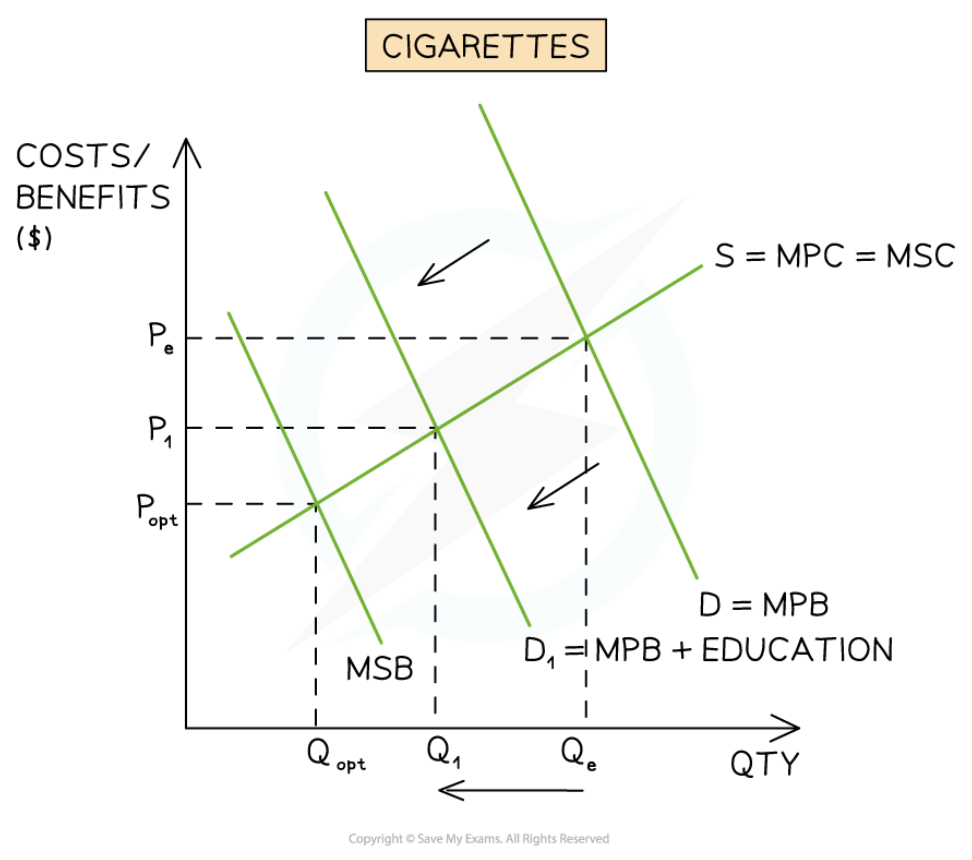
46
New cards
Business cycle
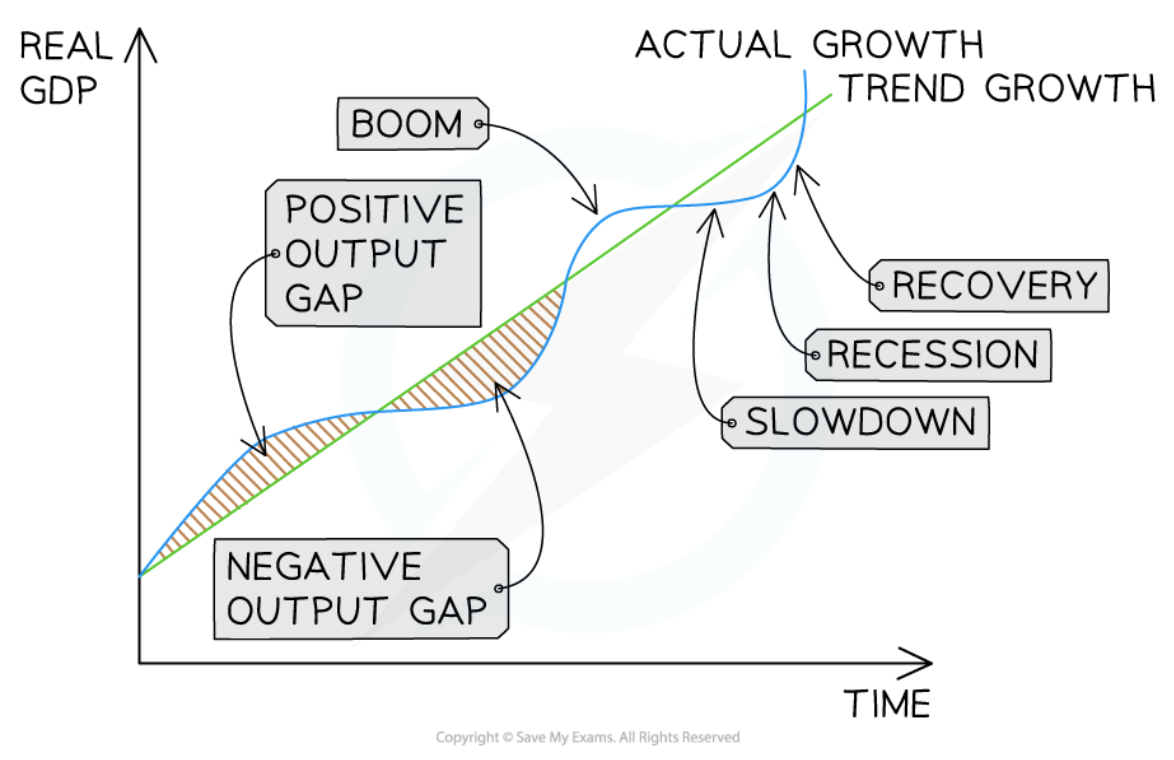
47
New cards
Movements along the AD curve
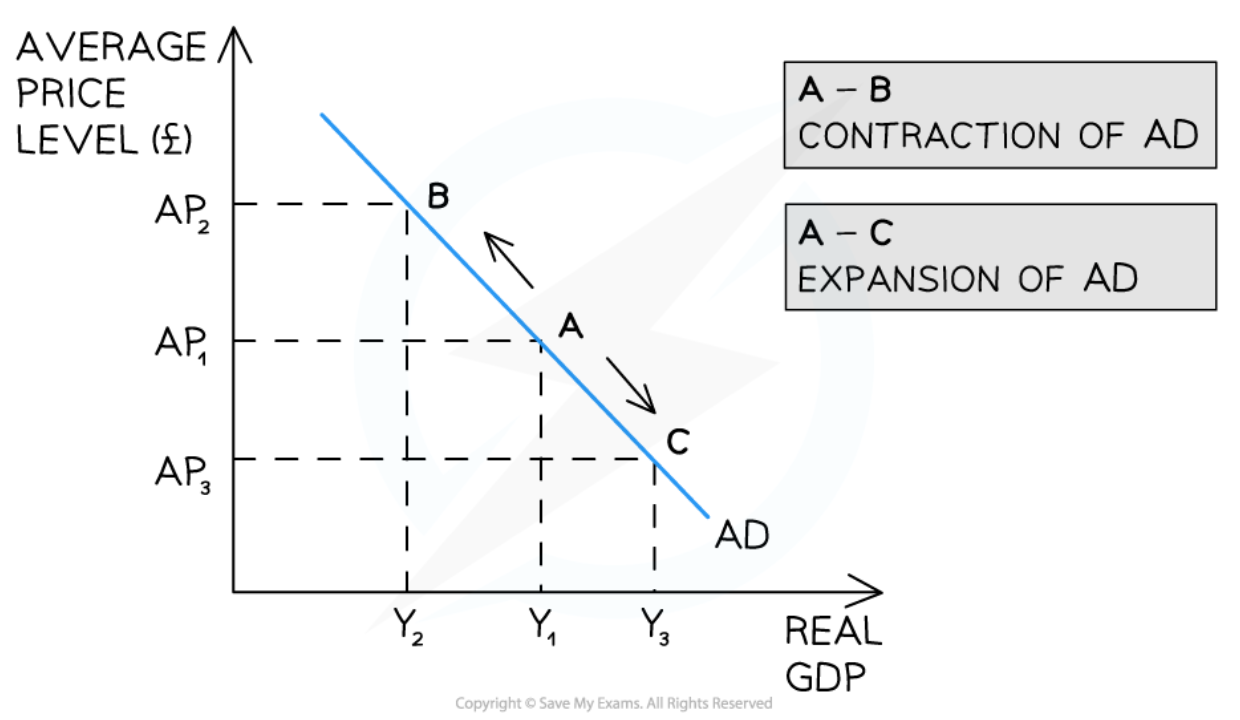
48
New cards
Shifts of the AD curve
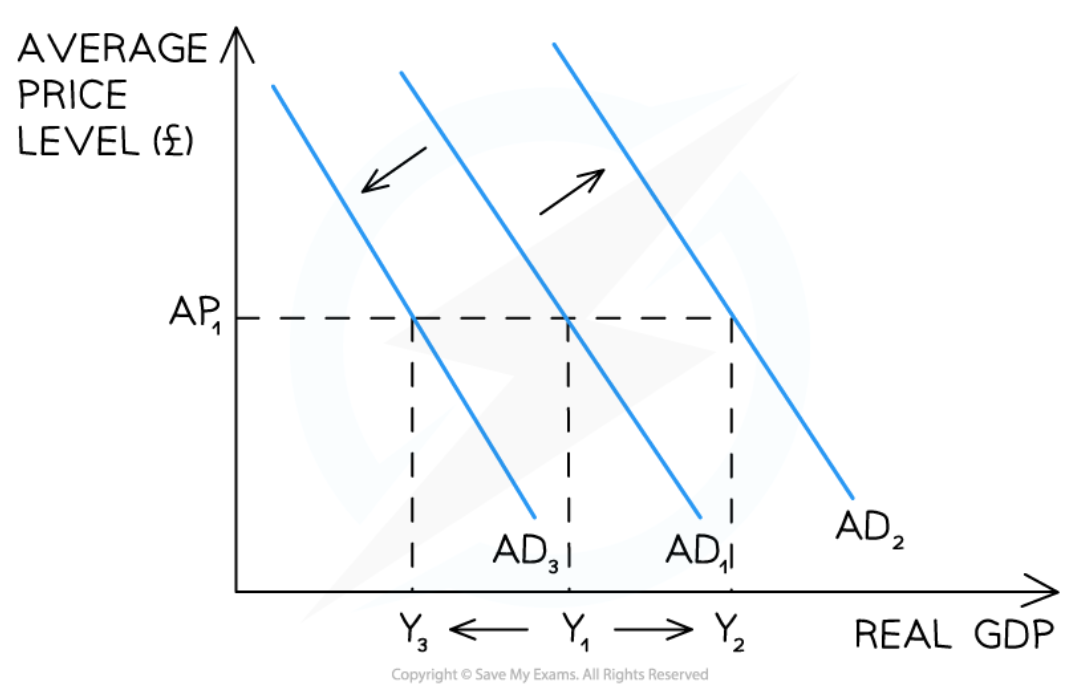
49
New cards
Movements along the SRAS curve
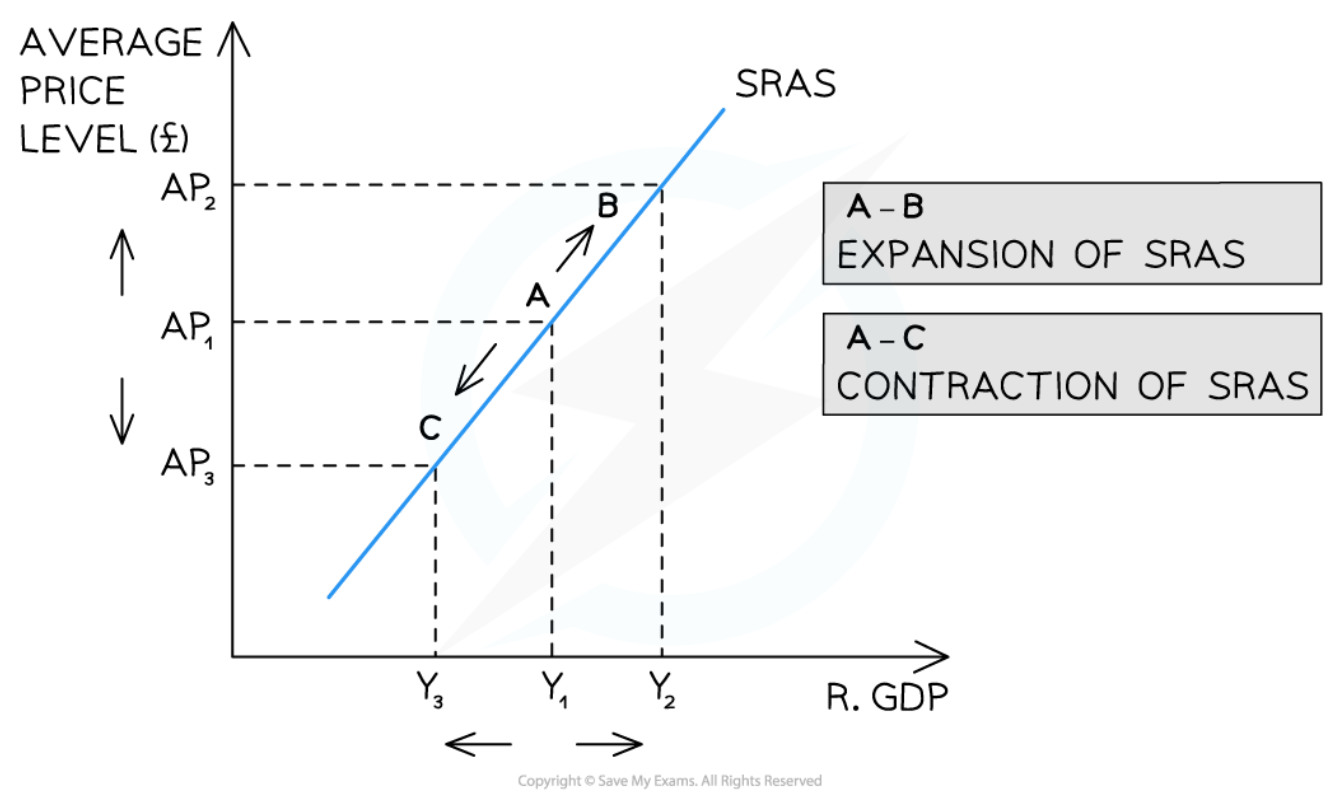
50
New cards
Shifts of the SRAS curve
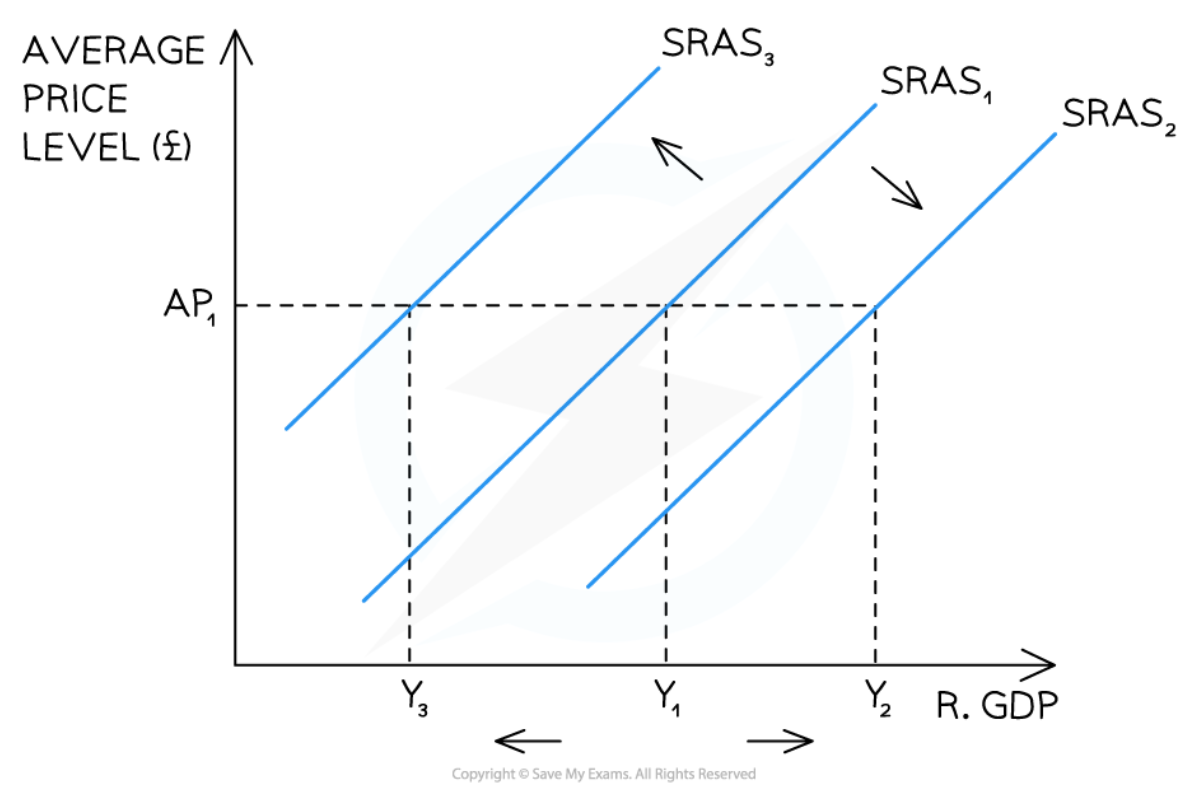
51
New cards
Monetarist/New classical view of the long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve
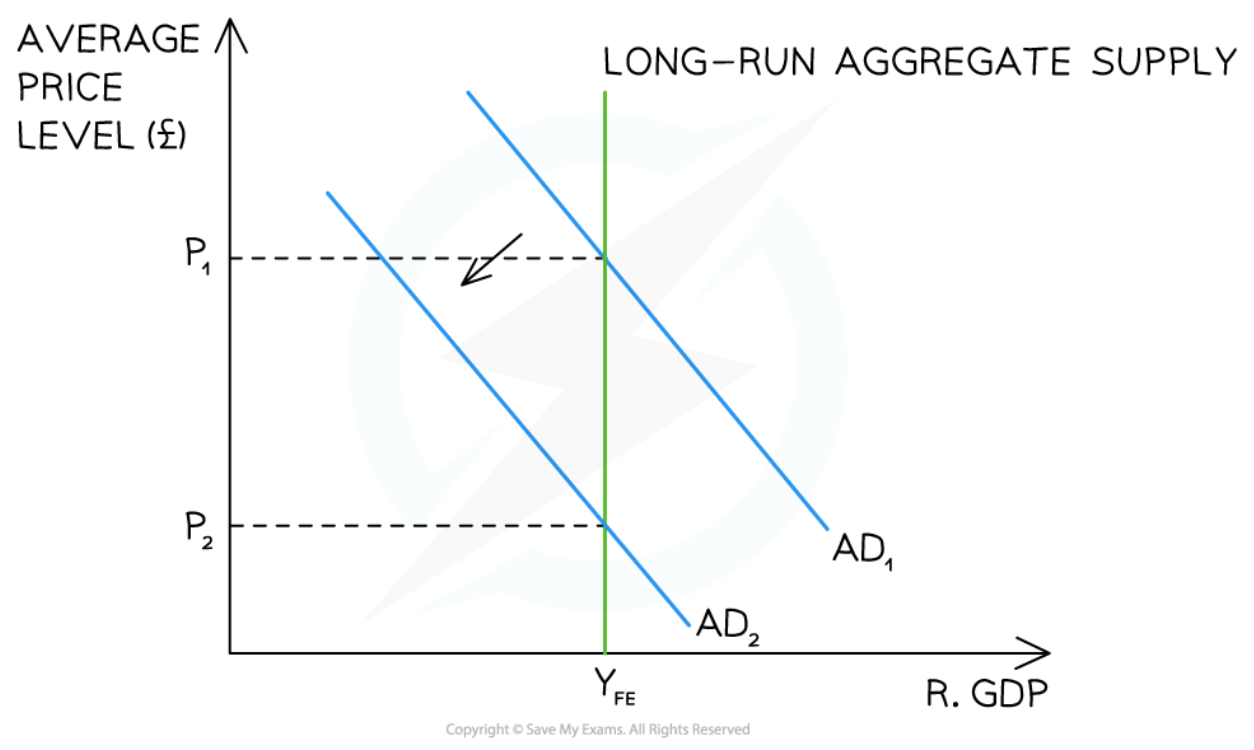
52
New cards
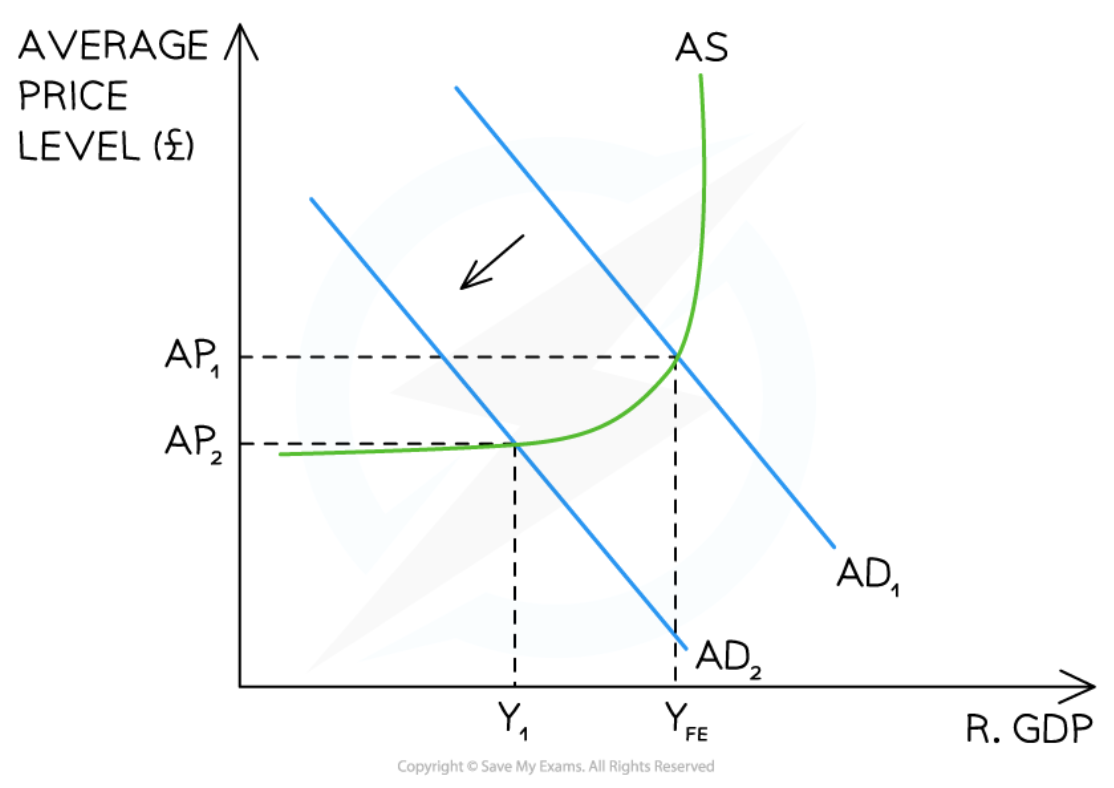
Keynesian view of the AS curve
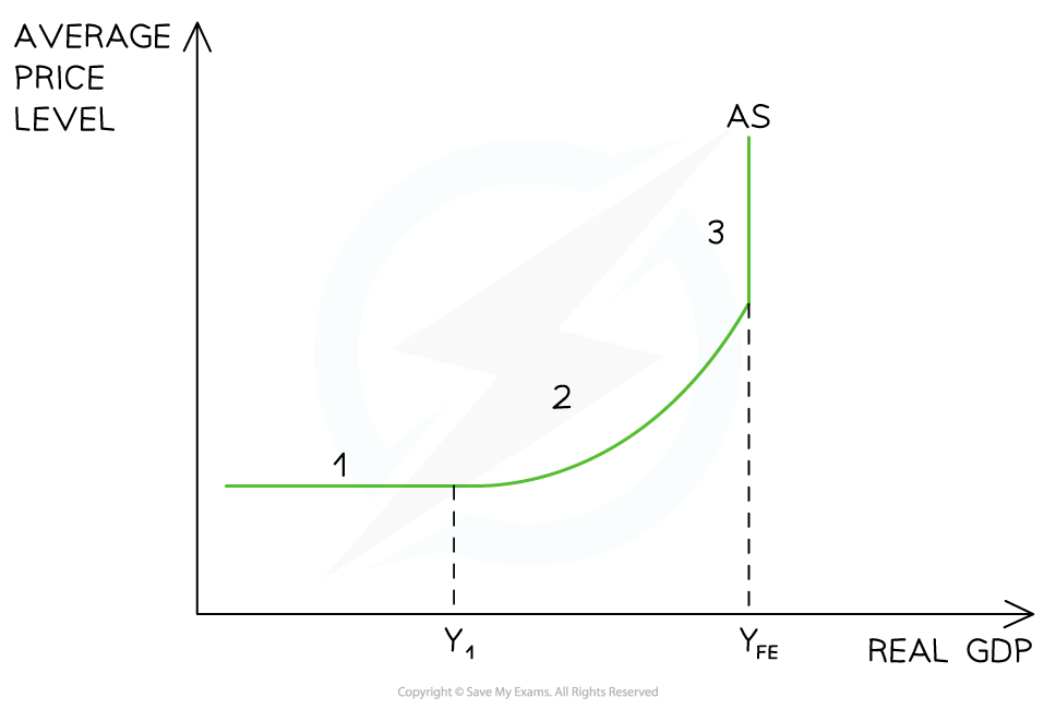
53
New cards
A deflationary gap in the Keynesian model
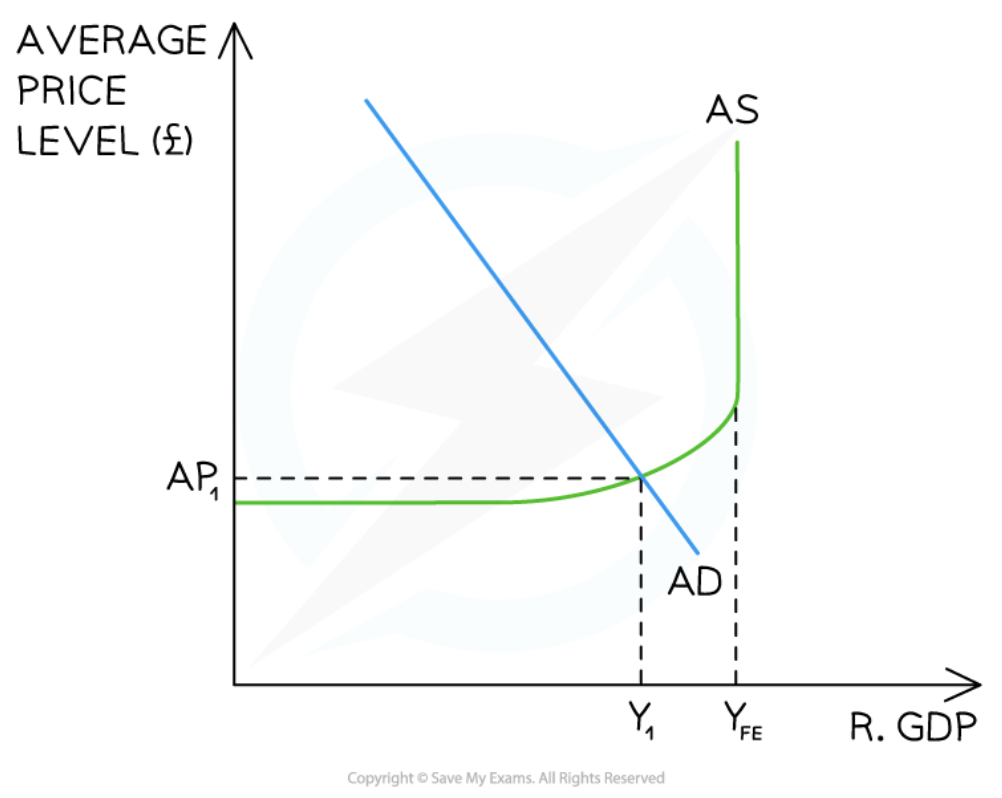
54
New cards
A deflationary gap in the Monetarist/New classical model
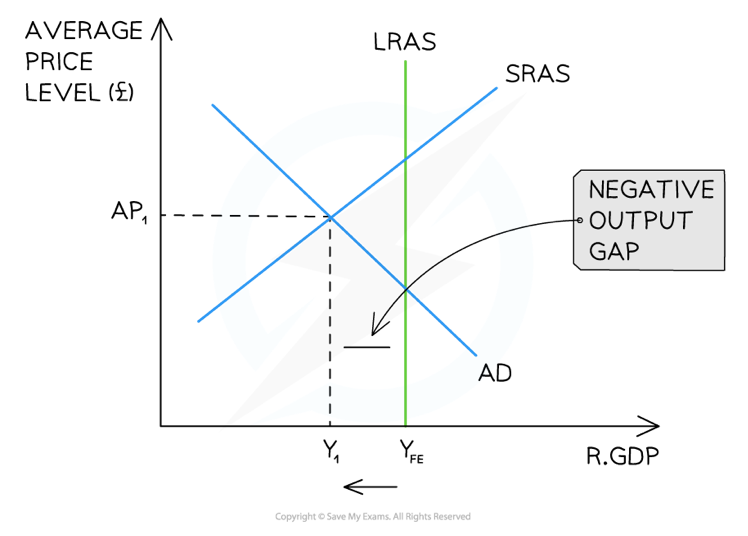
55
New cards
An inflationary gap in the Monetarist/New classical model
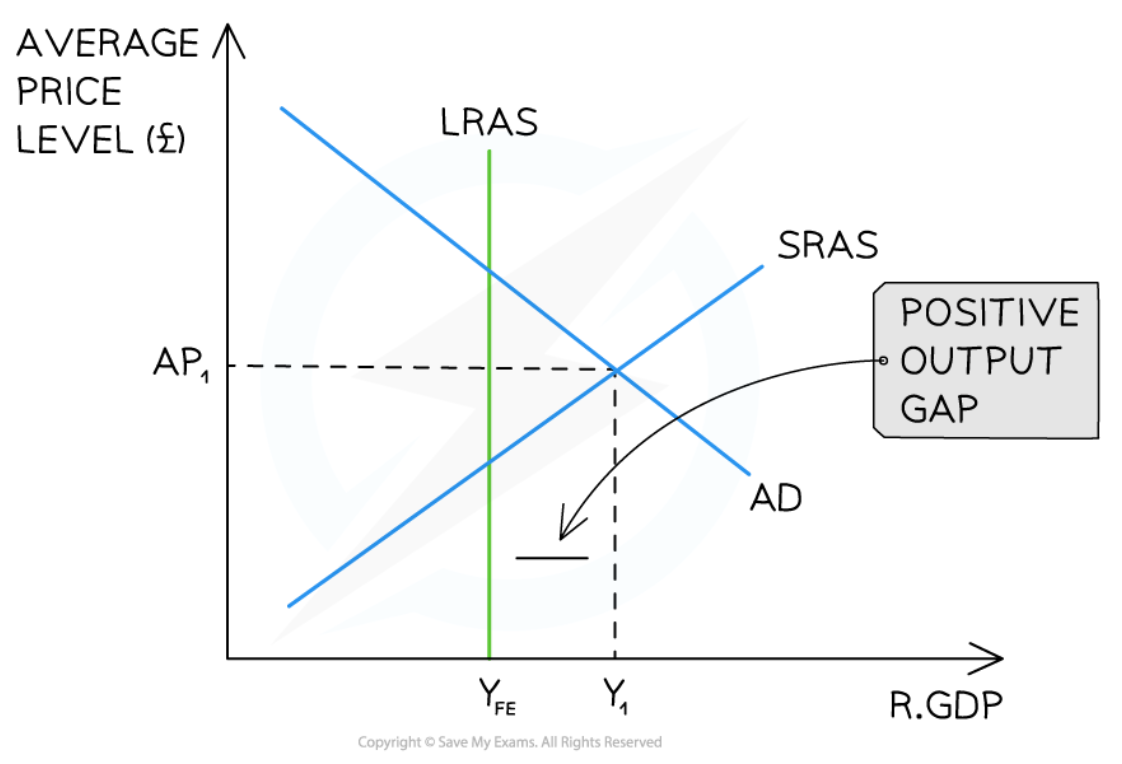
56
New cards
Changes to LRAS in the Monetarist/New classical model
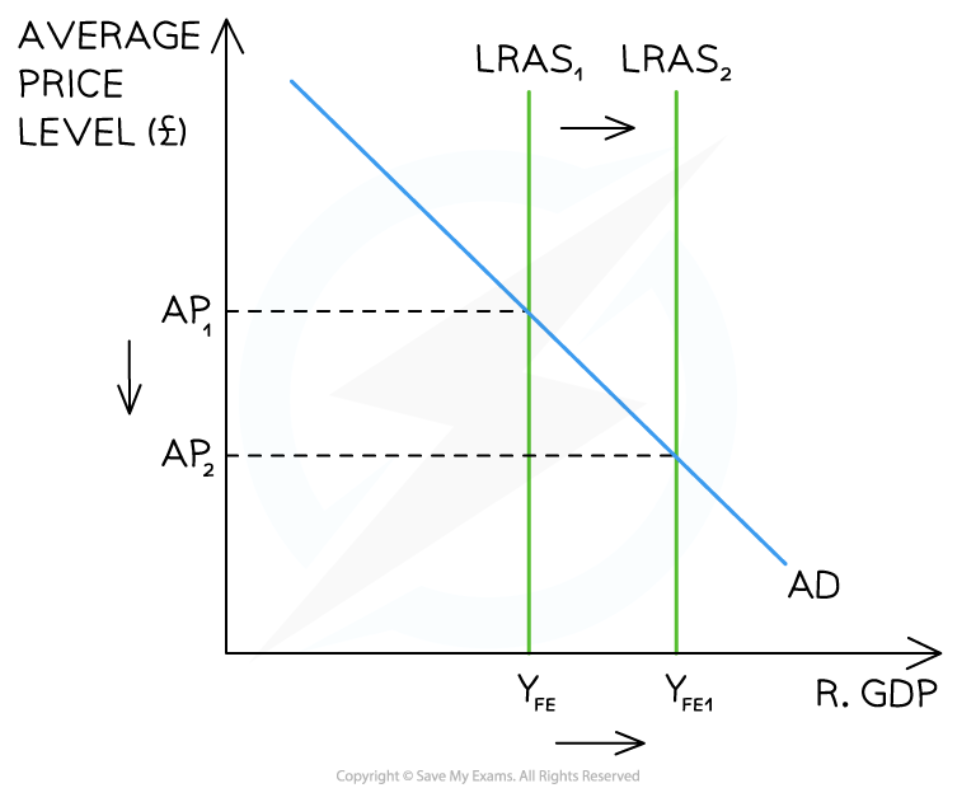
57
New cards
Changes to AS in the Keynesian model
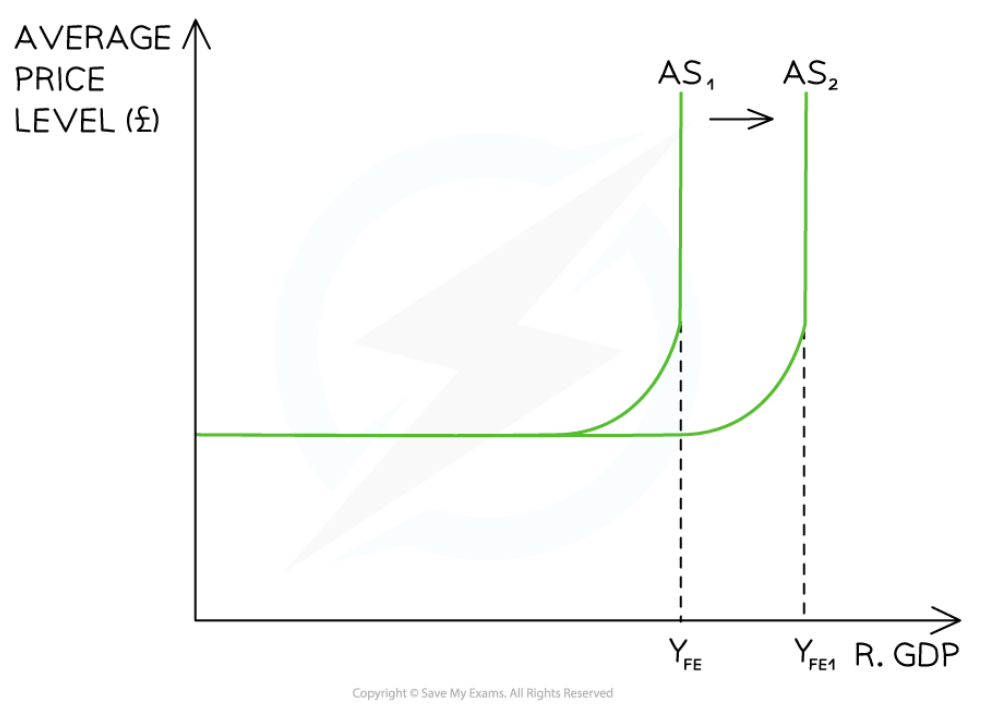
58
New cards
Long-run equilibrium in the Monetarist/New classical model
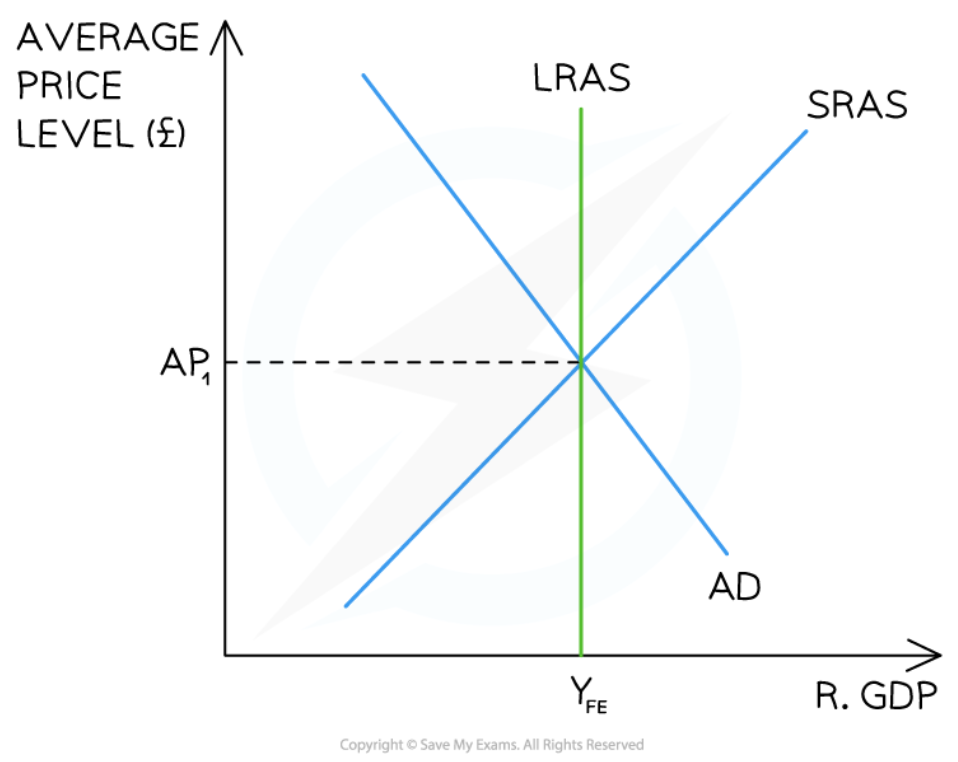
59
New cards
Automatic adjustment from a deflationary output gap
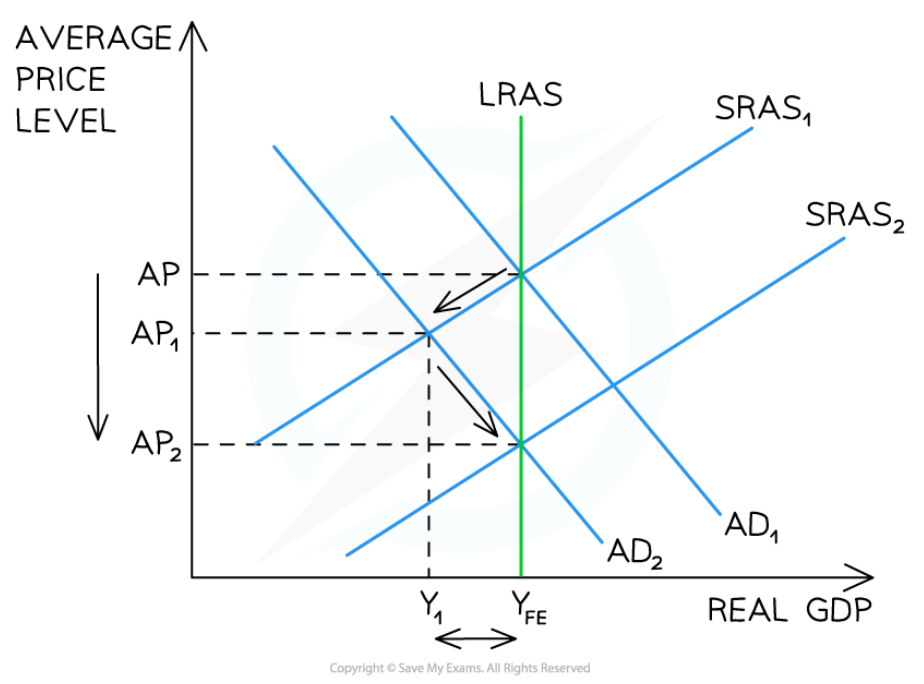
60
New cards
Automatic adjustment from an inflationary output gap
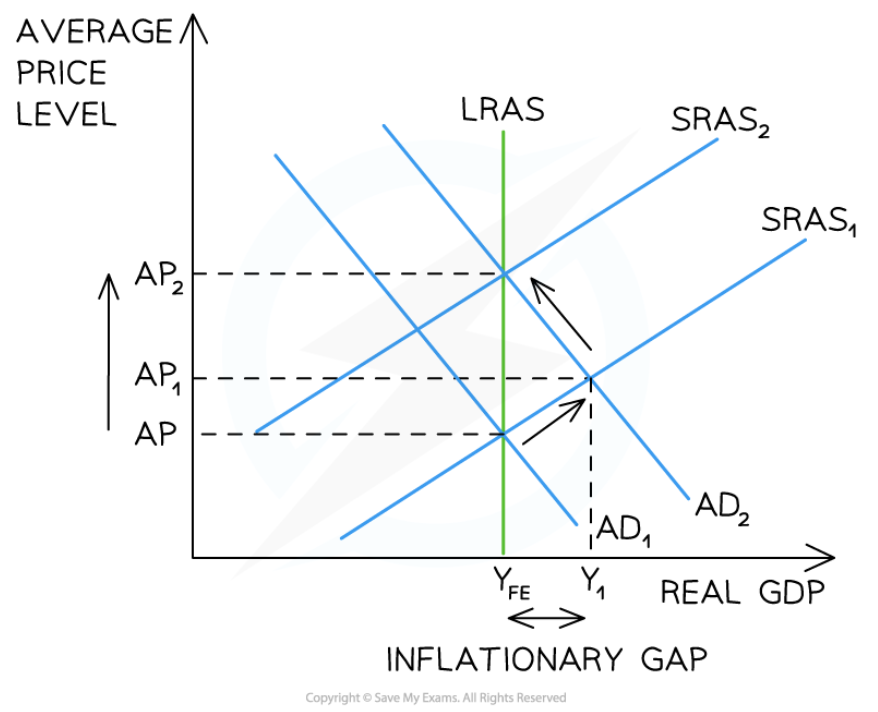
61
New cards
Keynesian economists believe that the economy can be in long term equilibrium at any level of output
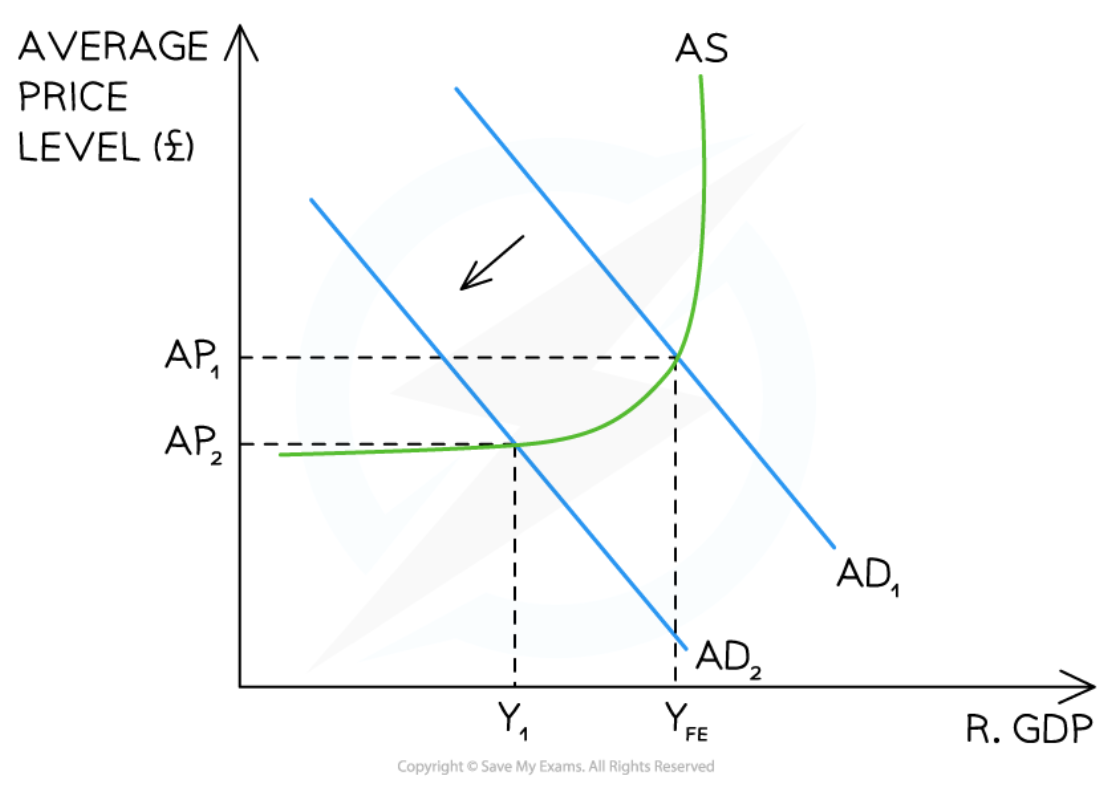
62
New cards
Short-term Economic Growth in the Monetarist/New classical model
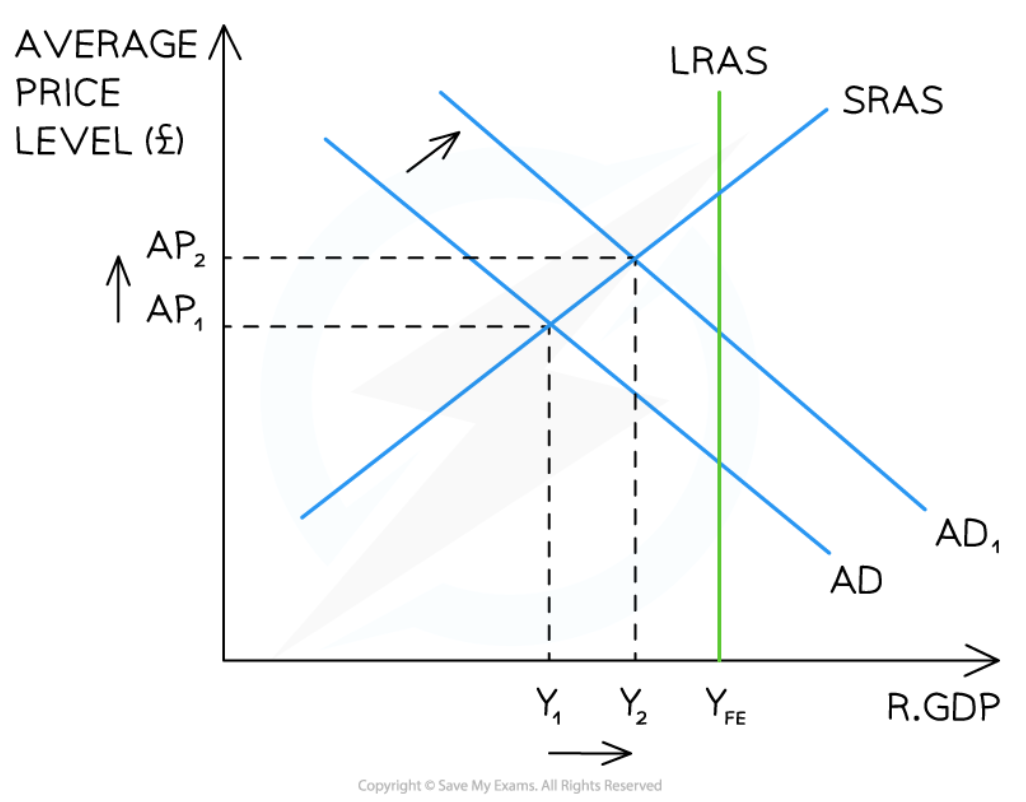
63
New cards
Short-term Economic Growth on a Production Possibilities Curve (PPC)
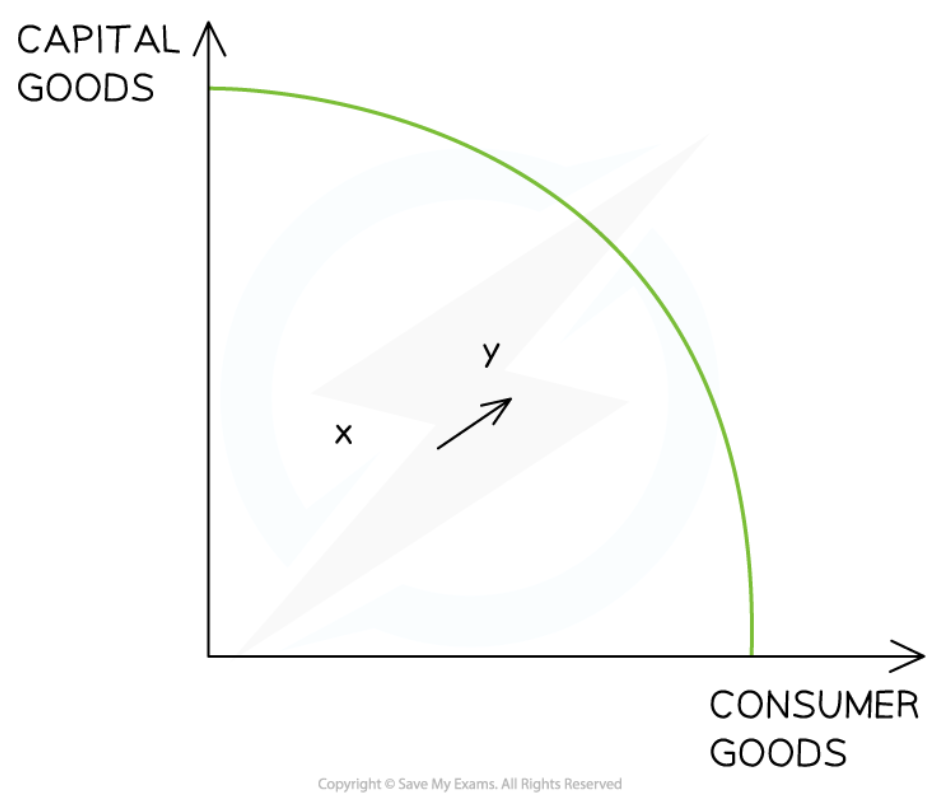
64
New cards
Long-term Economic Growth in the Monetarist/New classical model
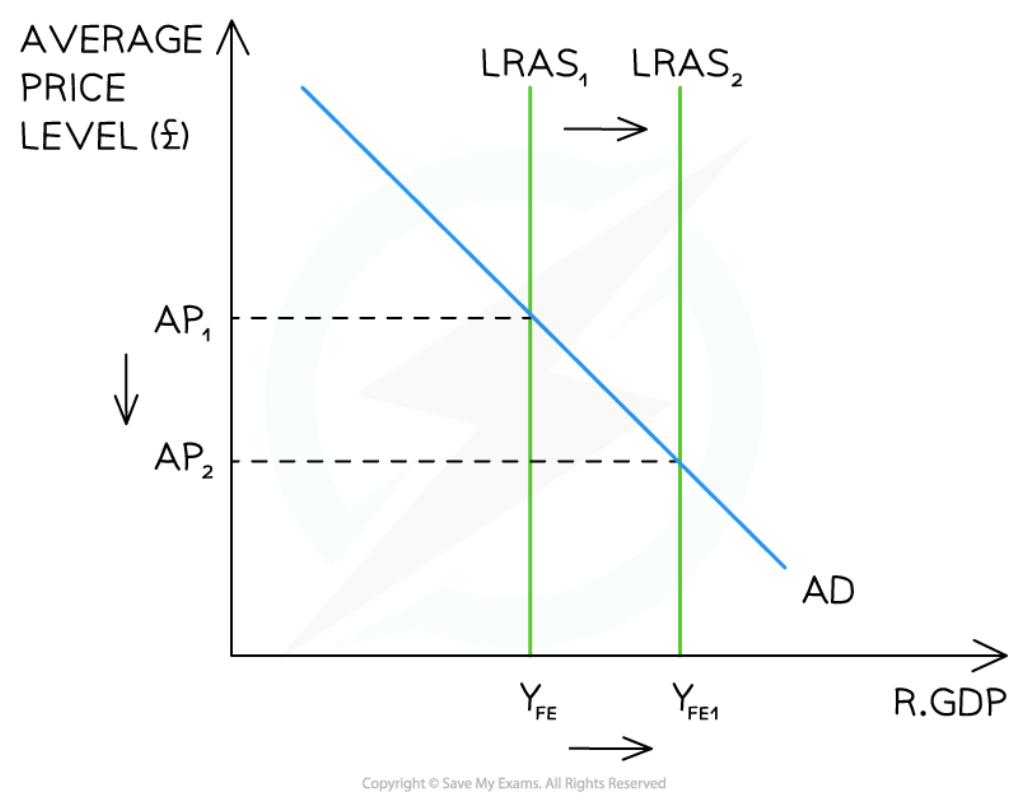
65
New cards
Long-term Economic Growth Using a PPC Model
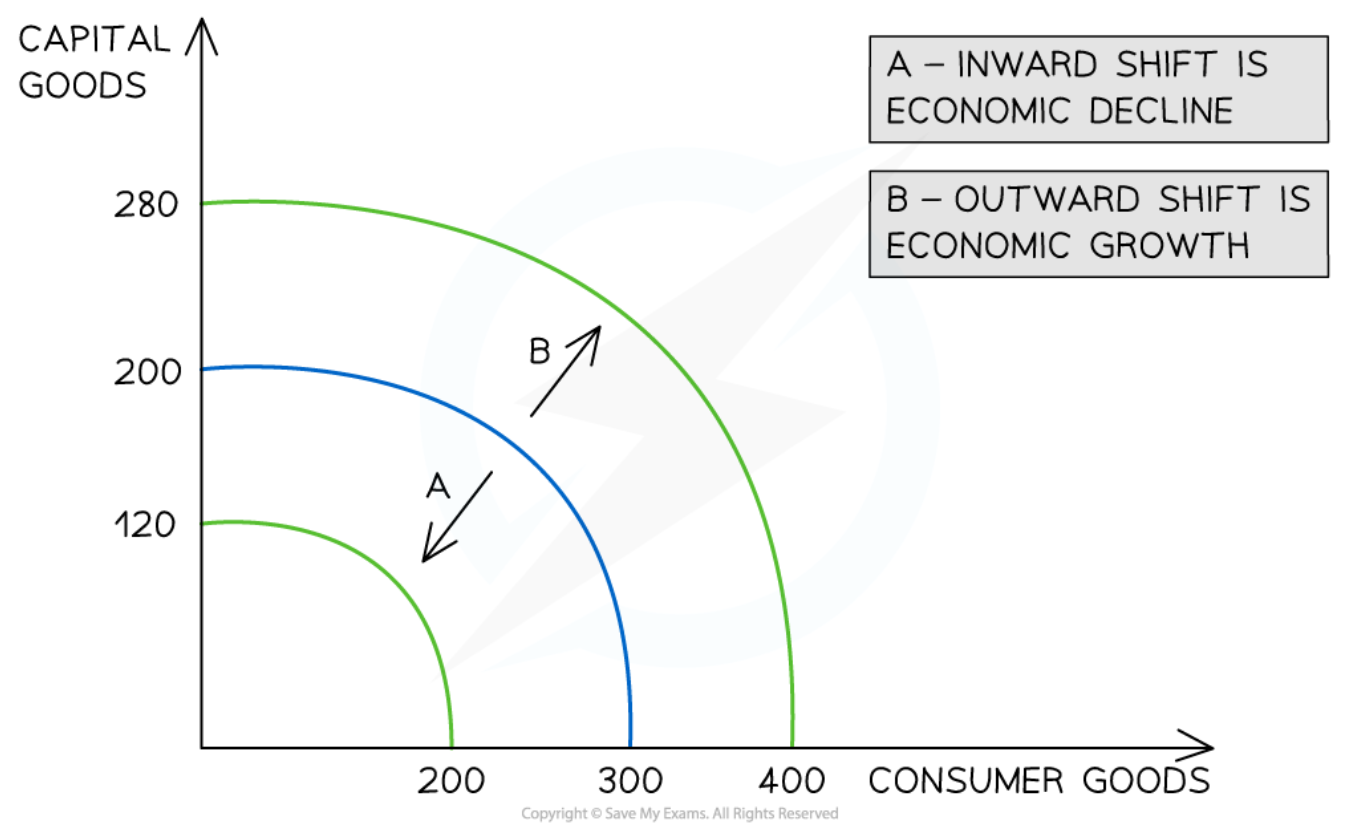
66
New cards
Structural unemployment
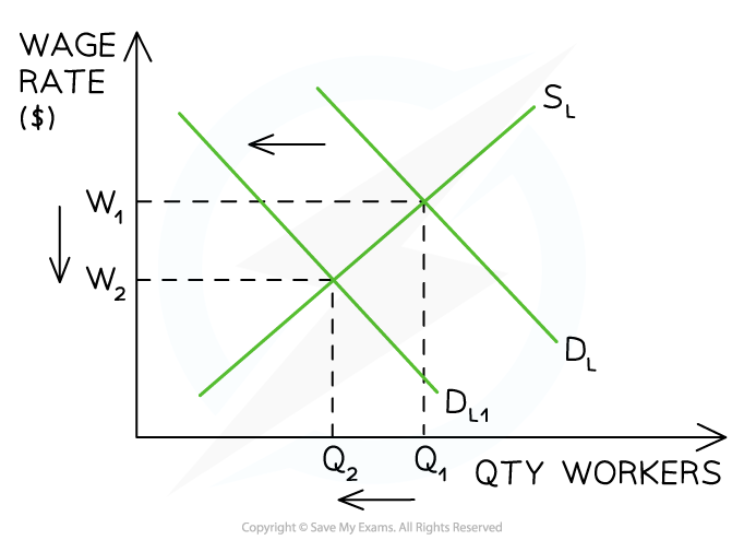
67
New cards
Cyclical unemployment in the Keynesian model
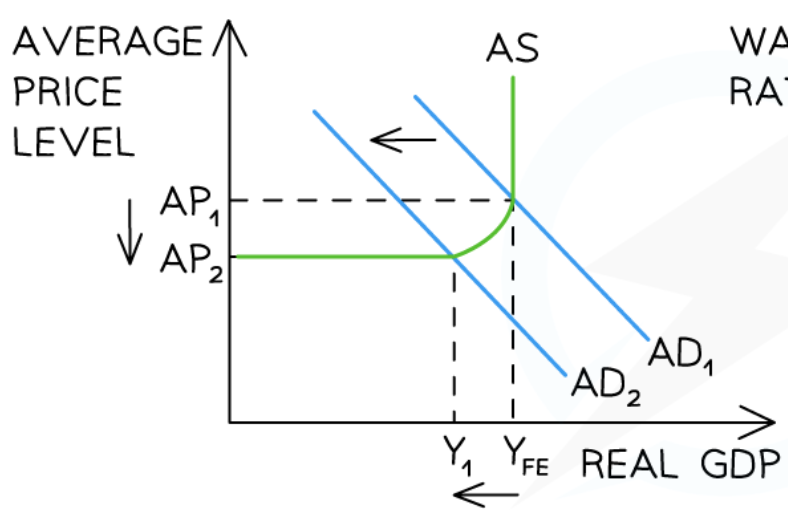
68
New cards
Cyclical unemployment in the Monetarist/New classical model
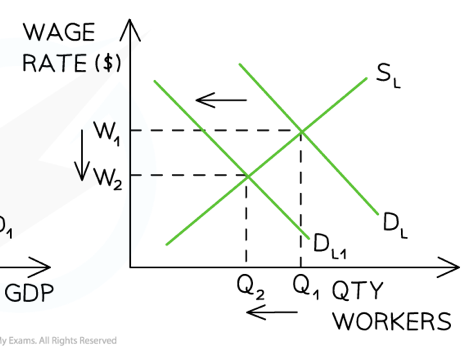
69
New cards
Demand pull inflation
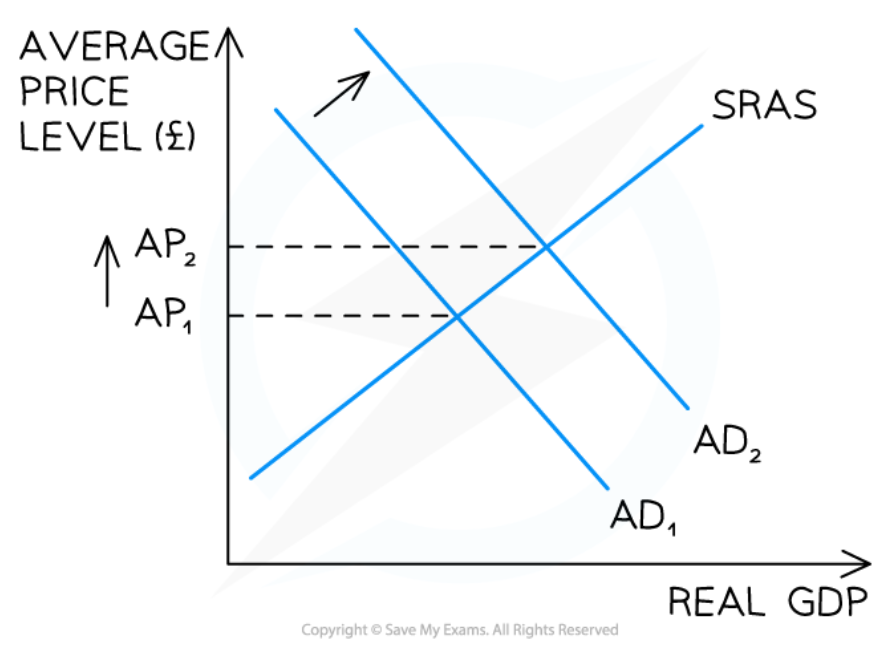
70
New cards
Cost push inflation
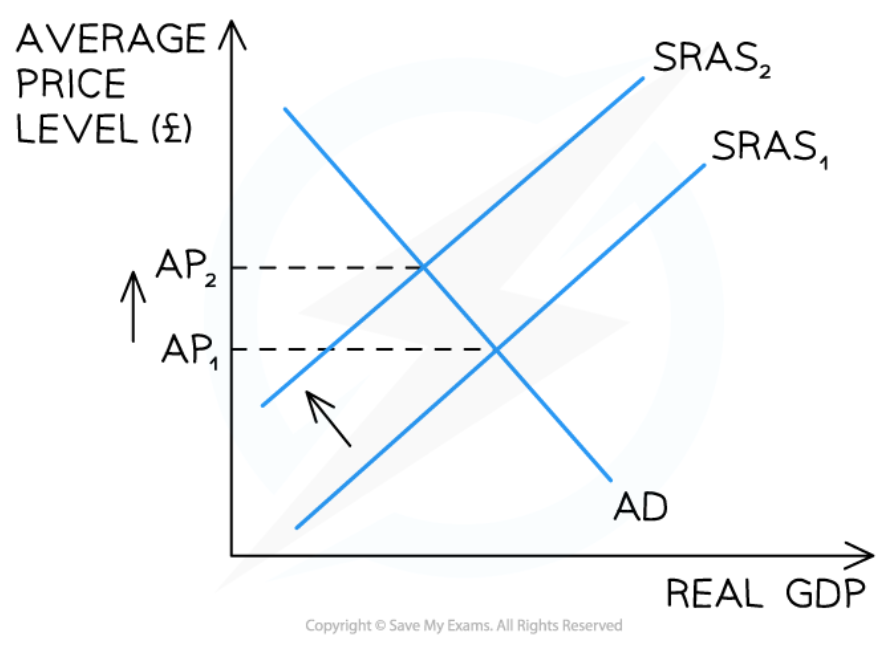
71
New cards
Demand-side deflation
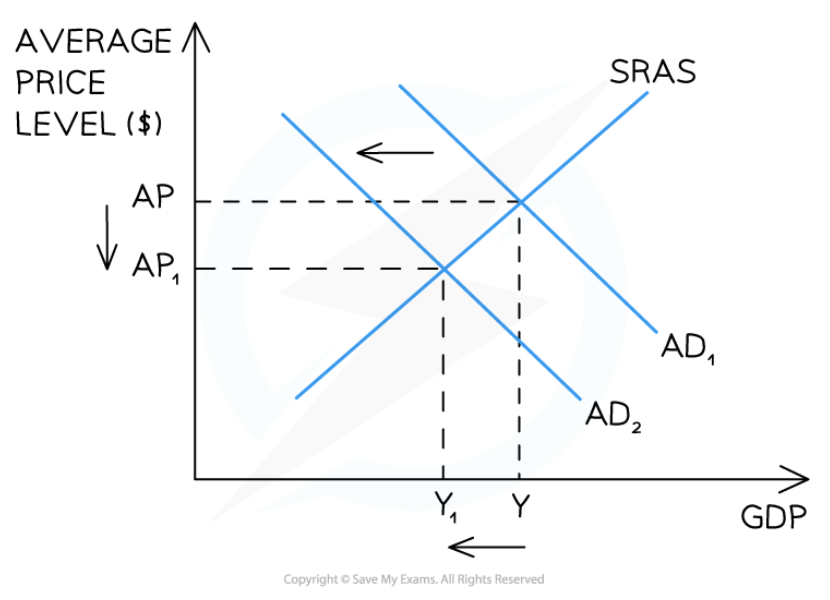
72
New cards
Supply-side deflation
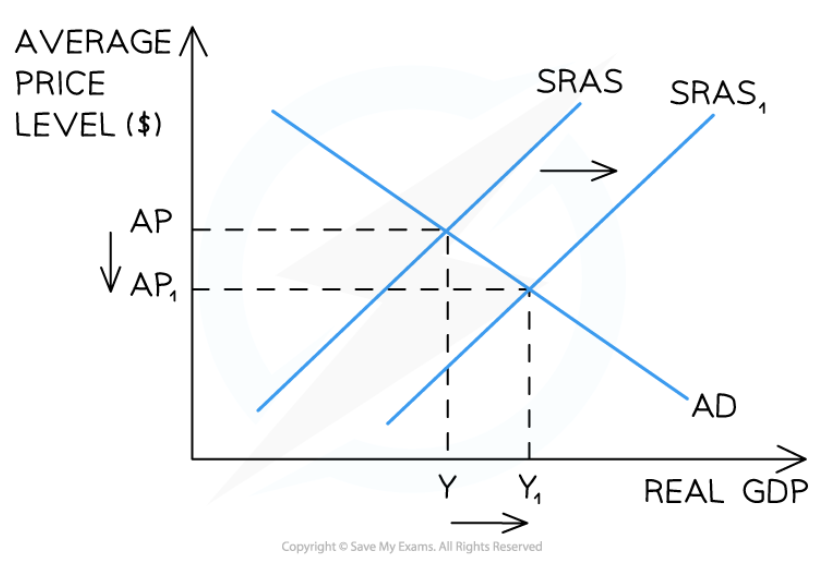
73
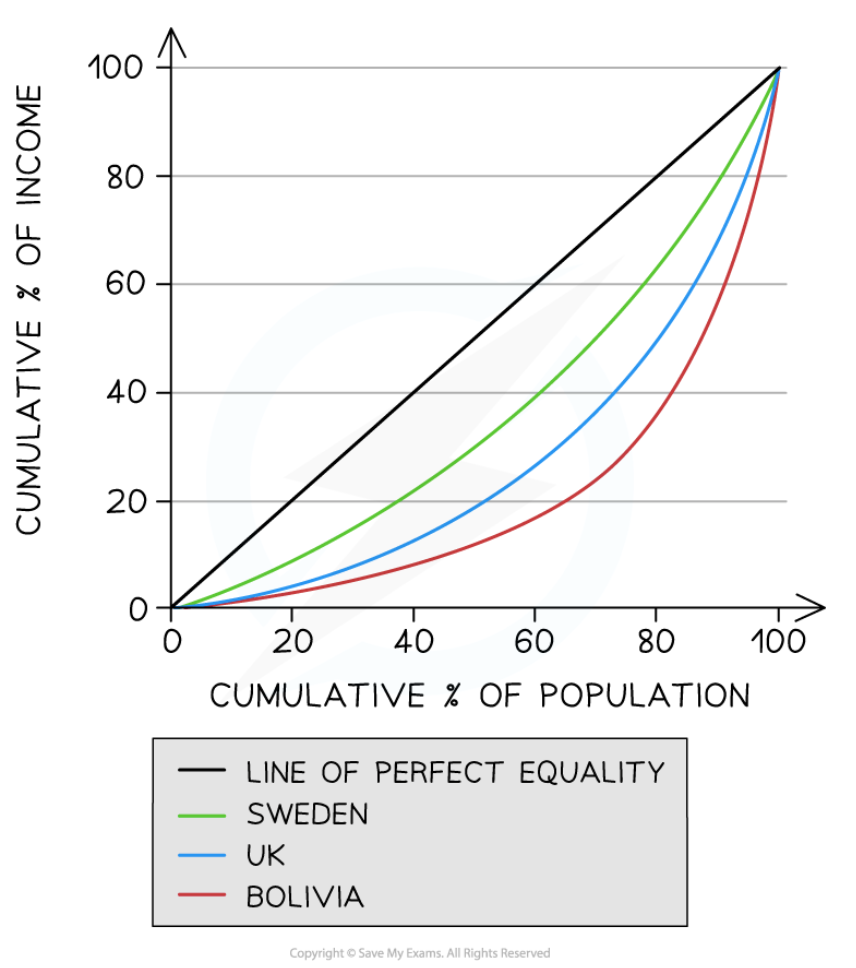
New cards
Lorenz curve for Sweden, UK, and Bolivia
74
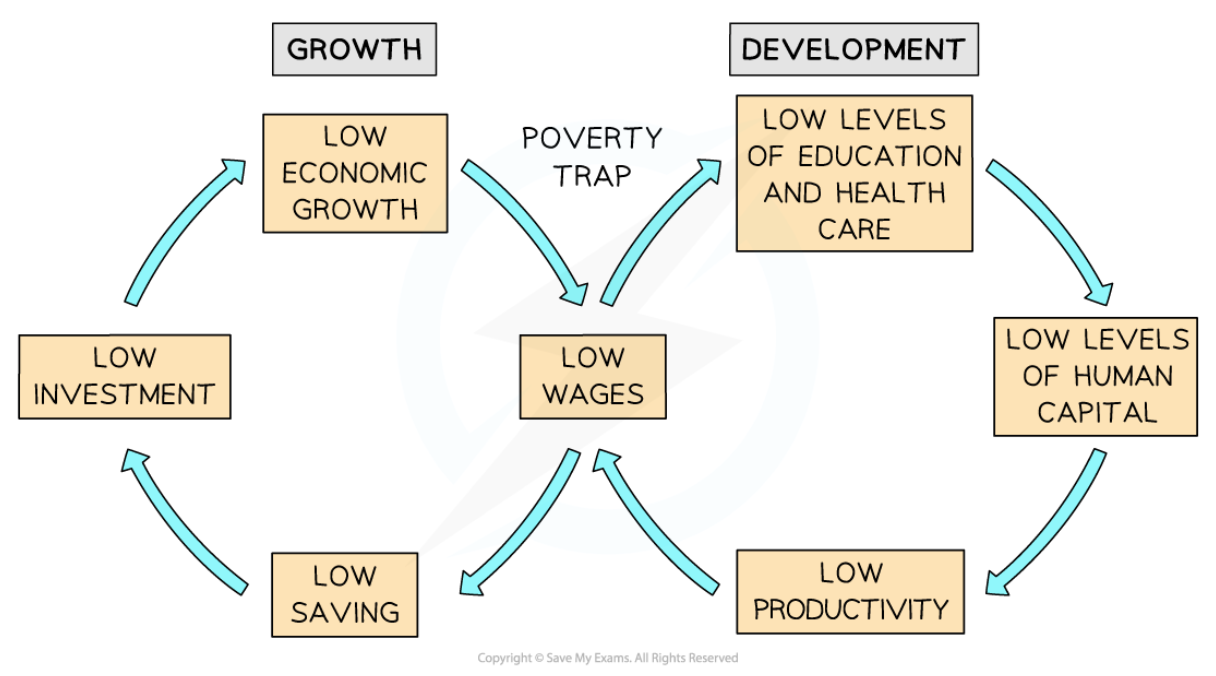
New cards
Poverty trap
75
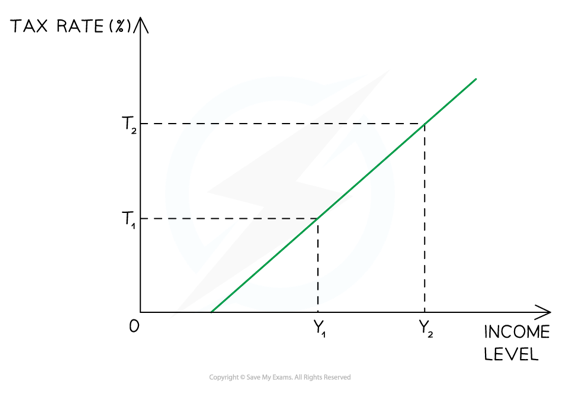
New cards
Progressive tax
76
New cards
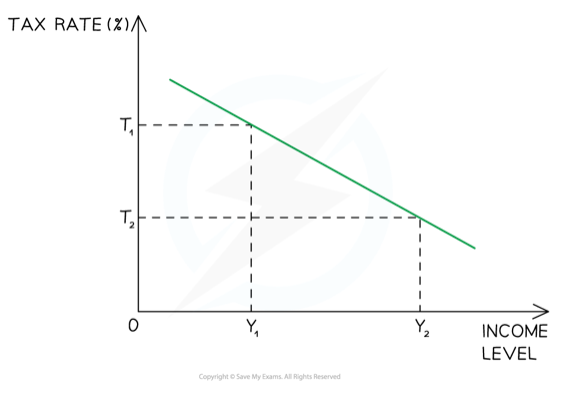
Regressive tax
77
New cards
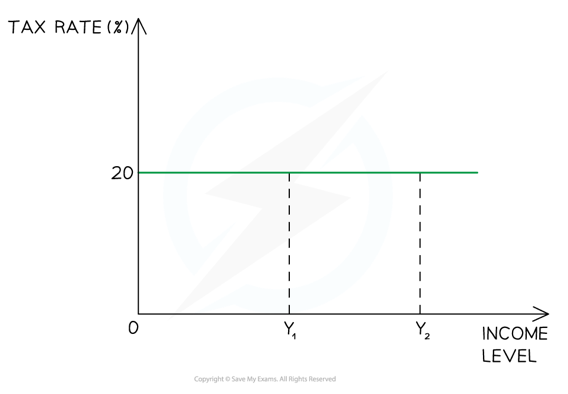
Proportional tax
78
New cards
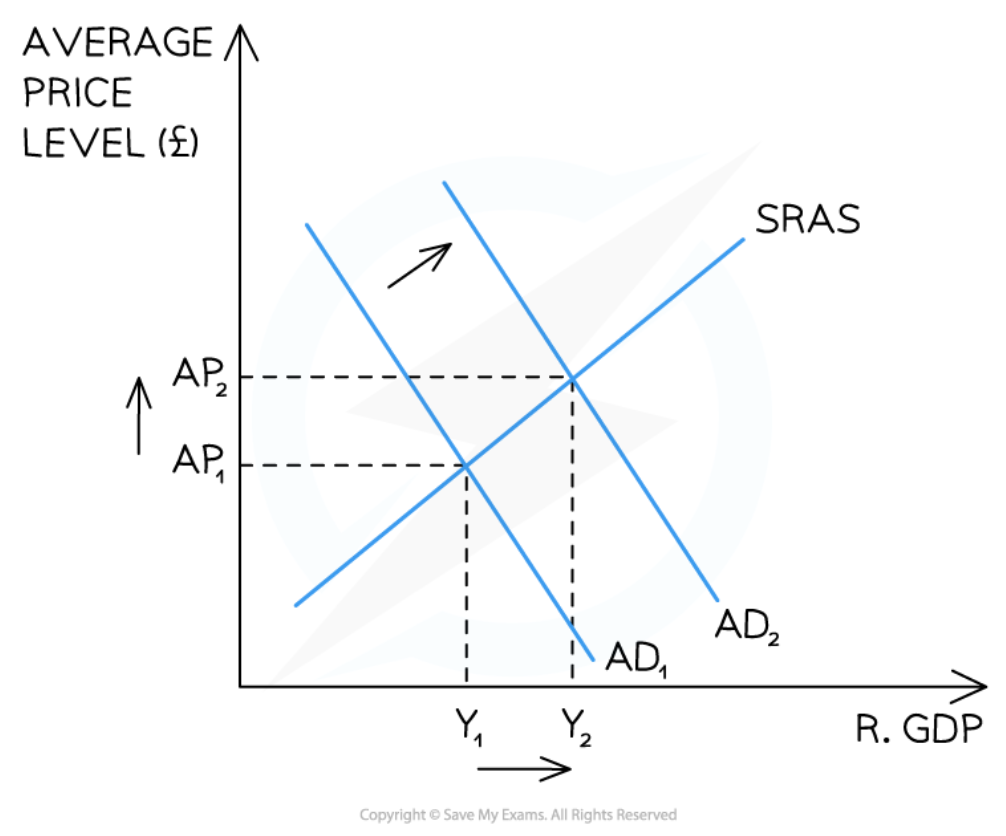
Expansionary monetary policy in the Monetarist/New classical model
79
New cards
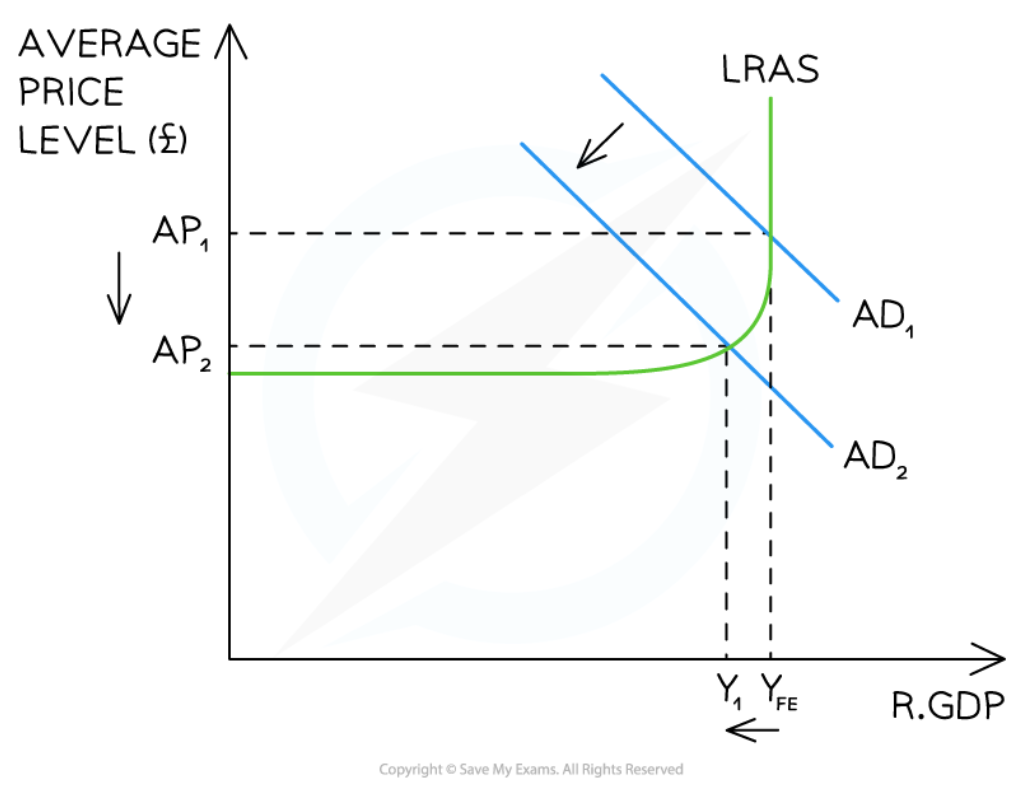
Contractionary monetary policy in the Keynesian model
80
New cards
Expansionary fiscal policy in the Monetarist/New classical model
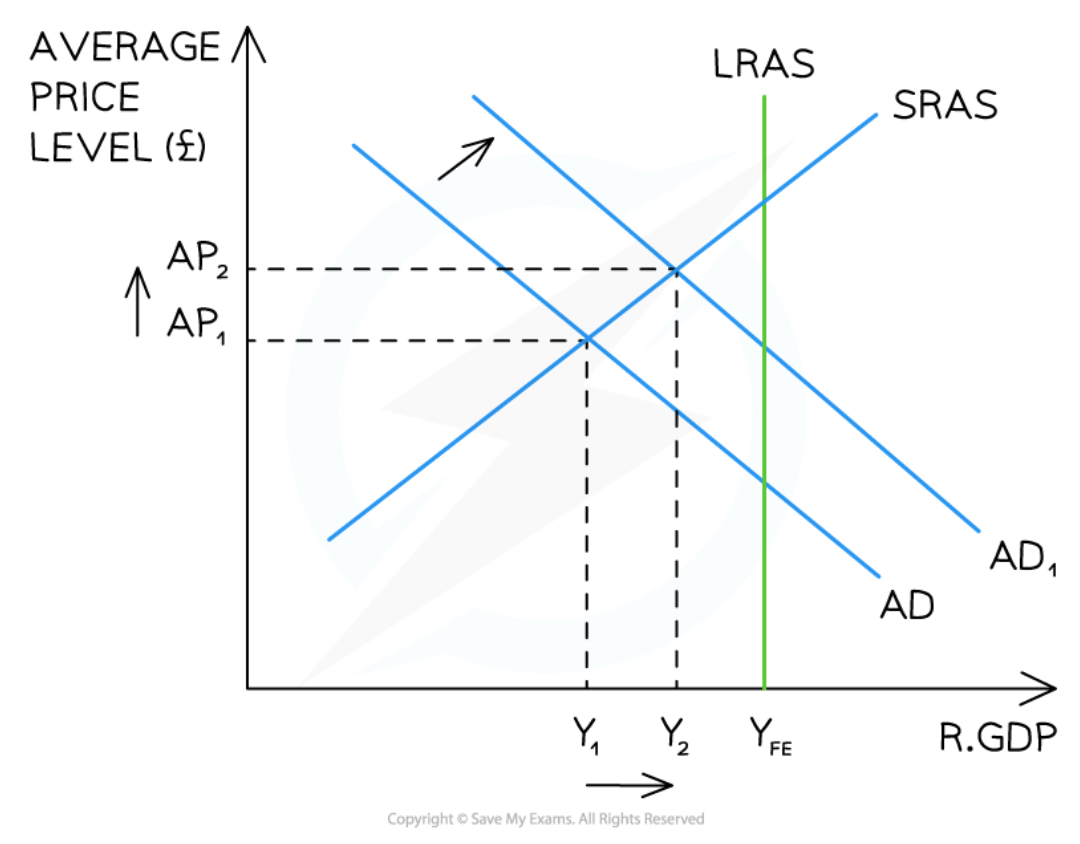
81
New cards
Contractionary fiscal policy in the Keynesian model
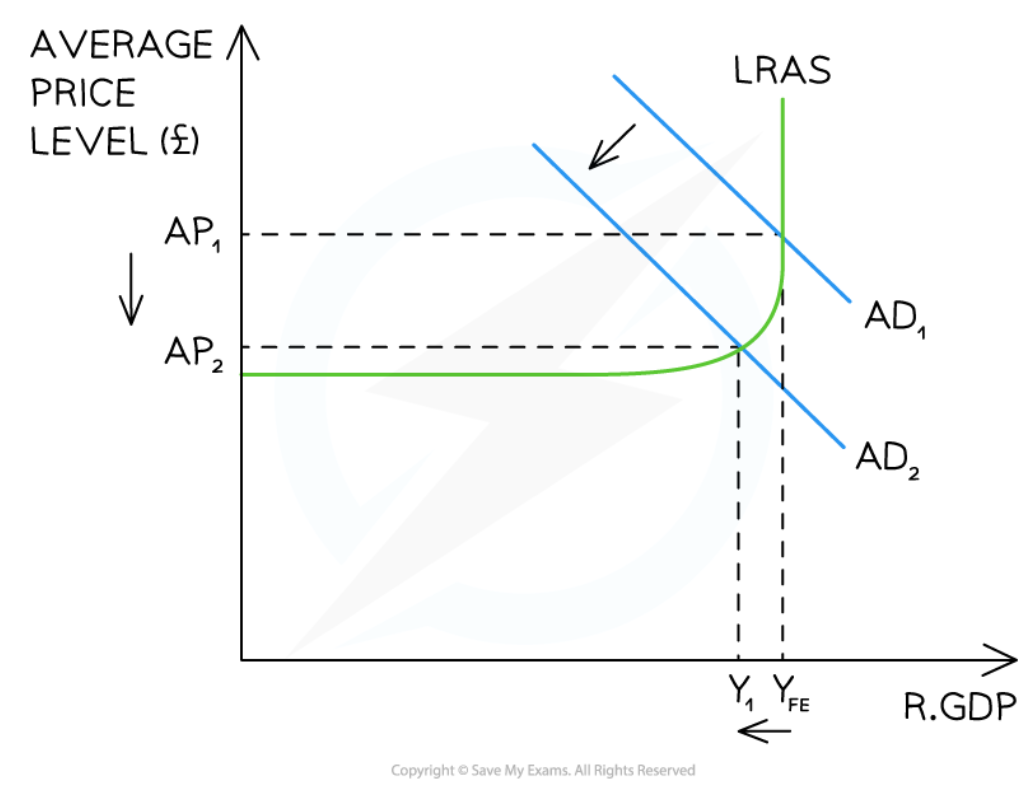
82
New cards
A Monetarist/New classical diagram that illustrates the implementation of a successful supply-side policy
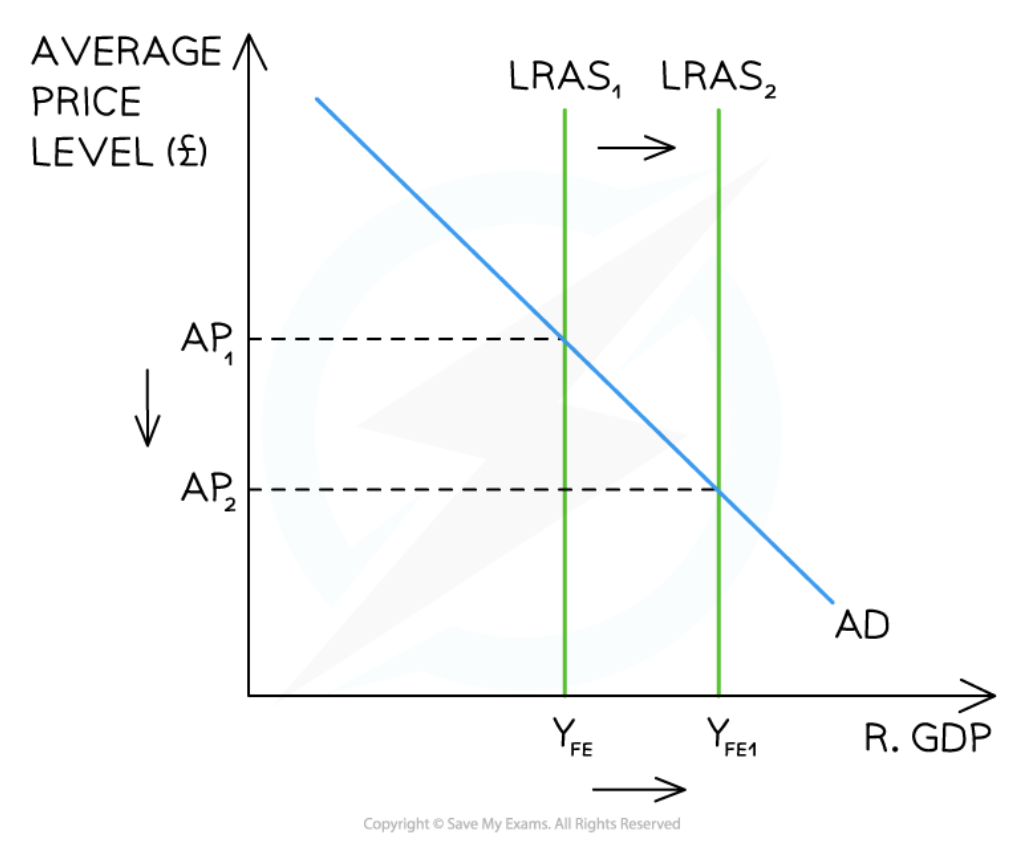
83
New cards
A Keynesian diagram that illustrates the implementation of a successful supply-side policy
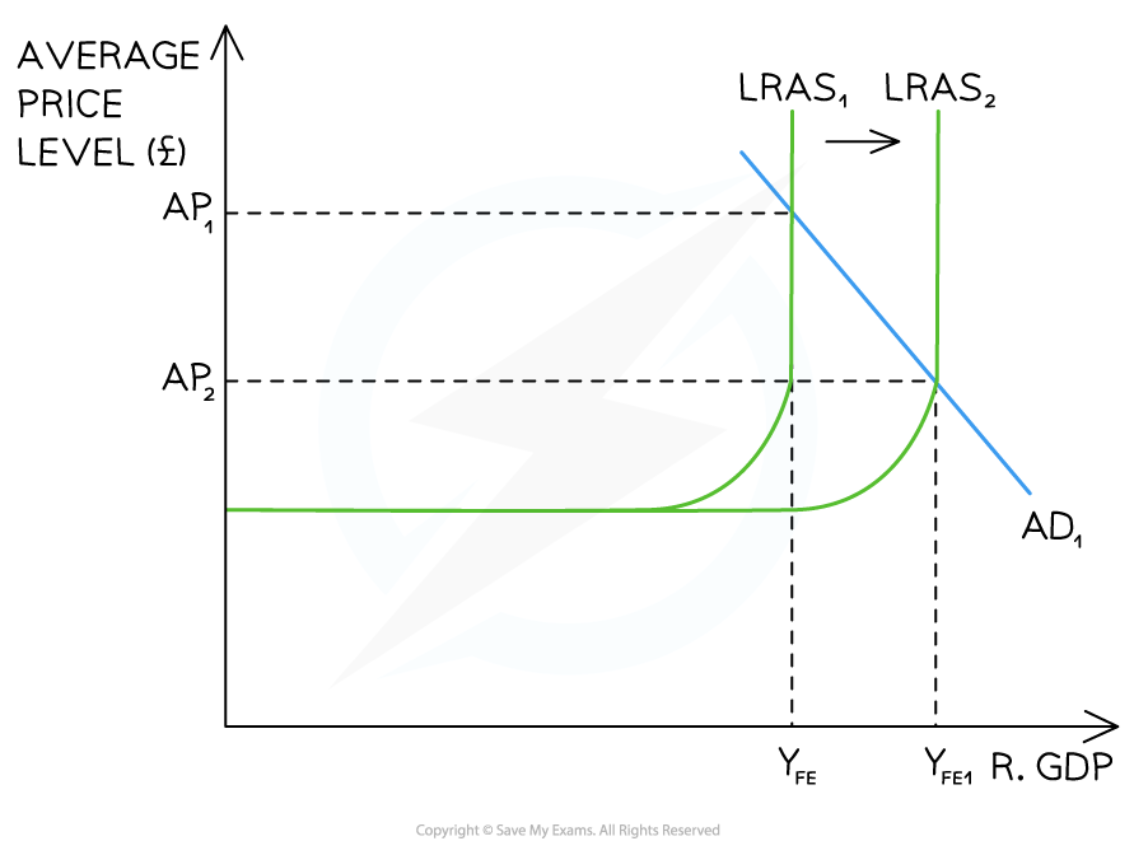
84
New cards
World price is above the domestic price
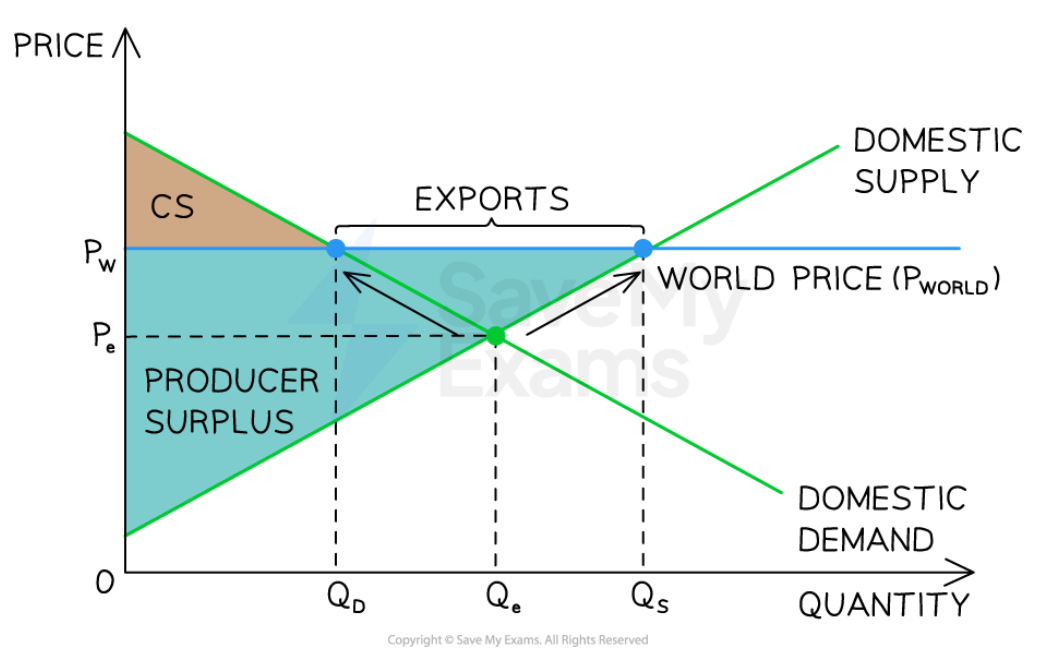
85
New cards
World price is below the domestic price
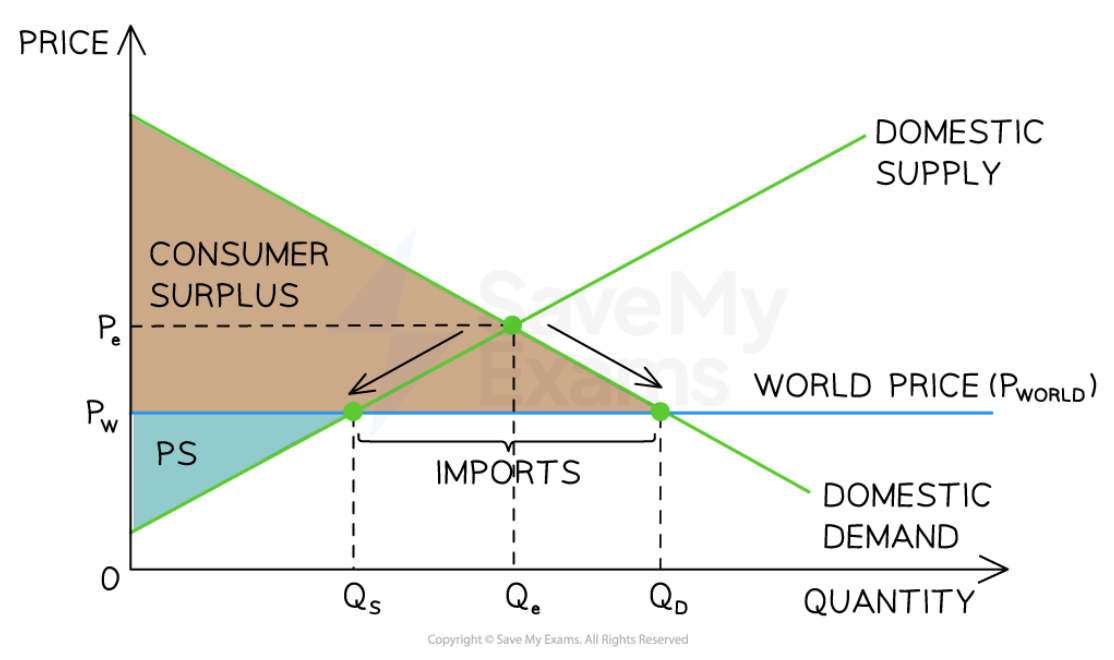
86
New cards
Tariffs
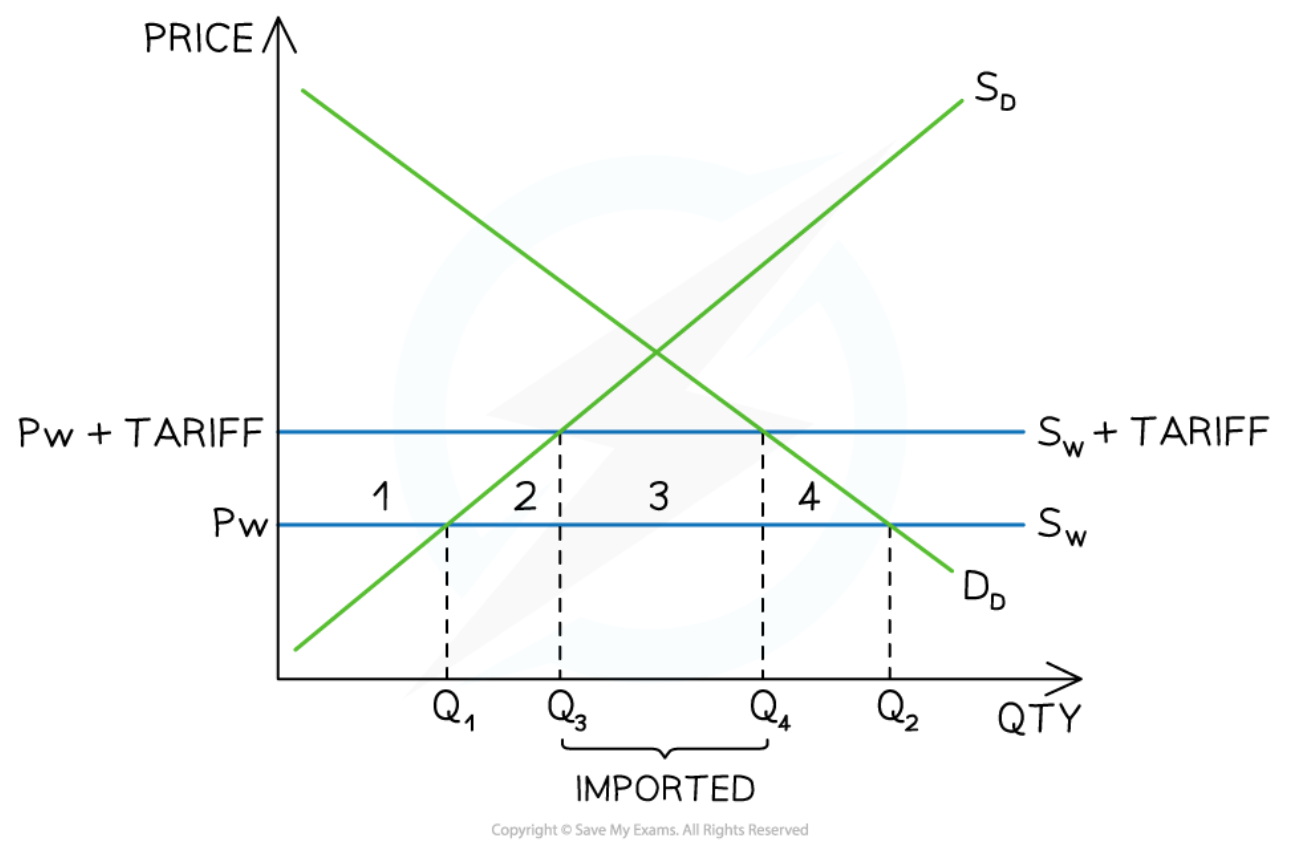
87
New cards
Quotas
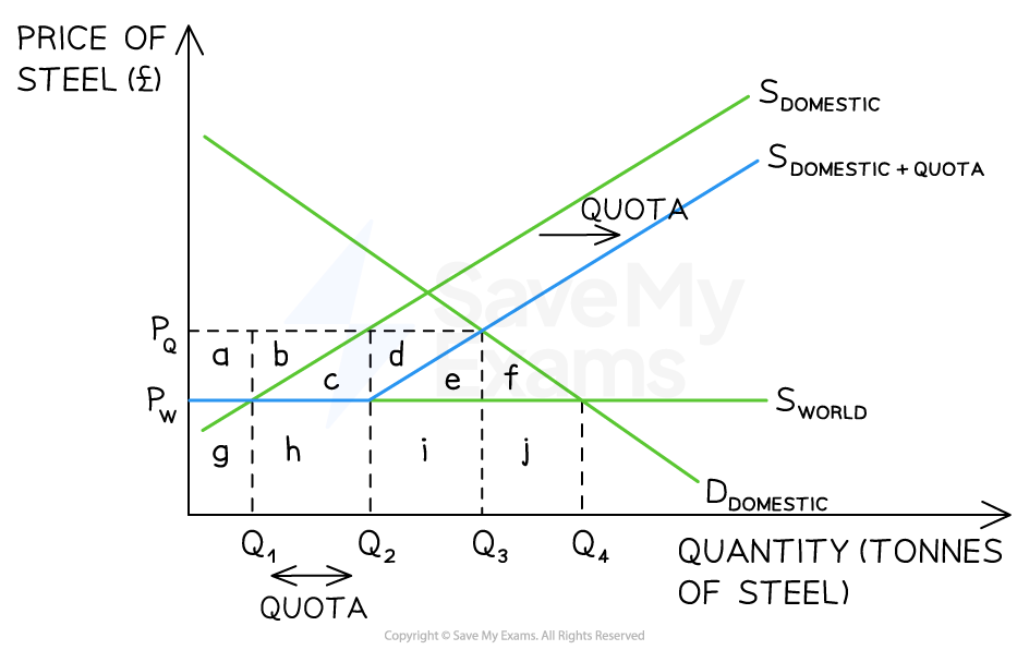
88
New cards
Export subsidies
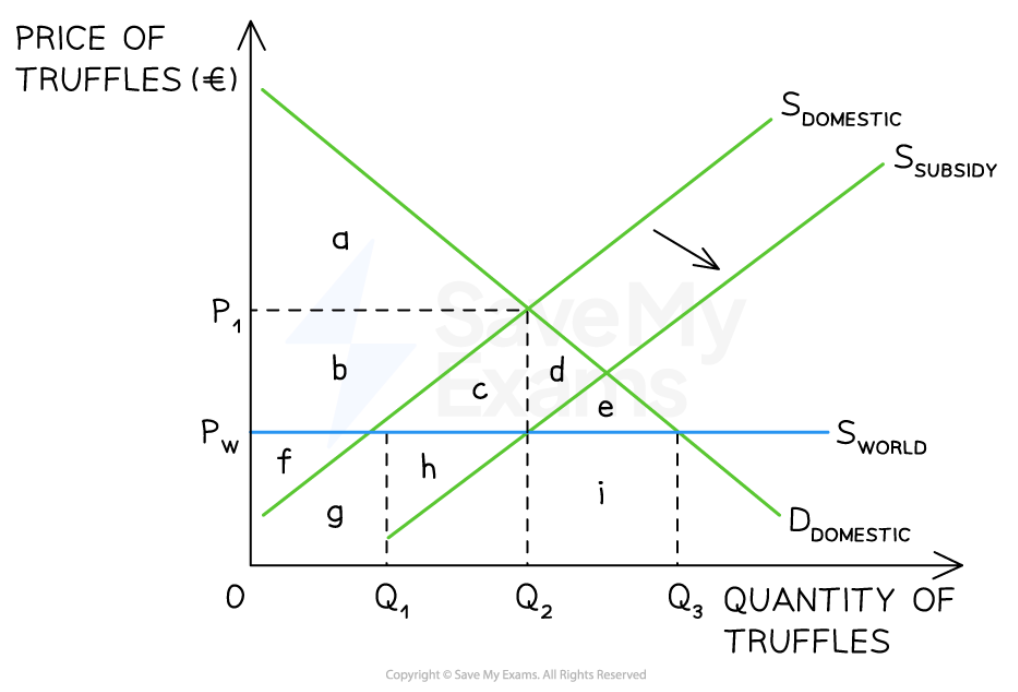
89
New cards
A floating Exchange rate system
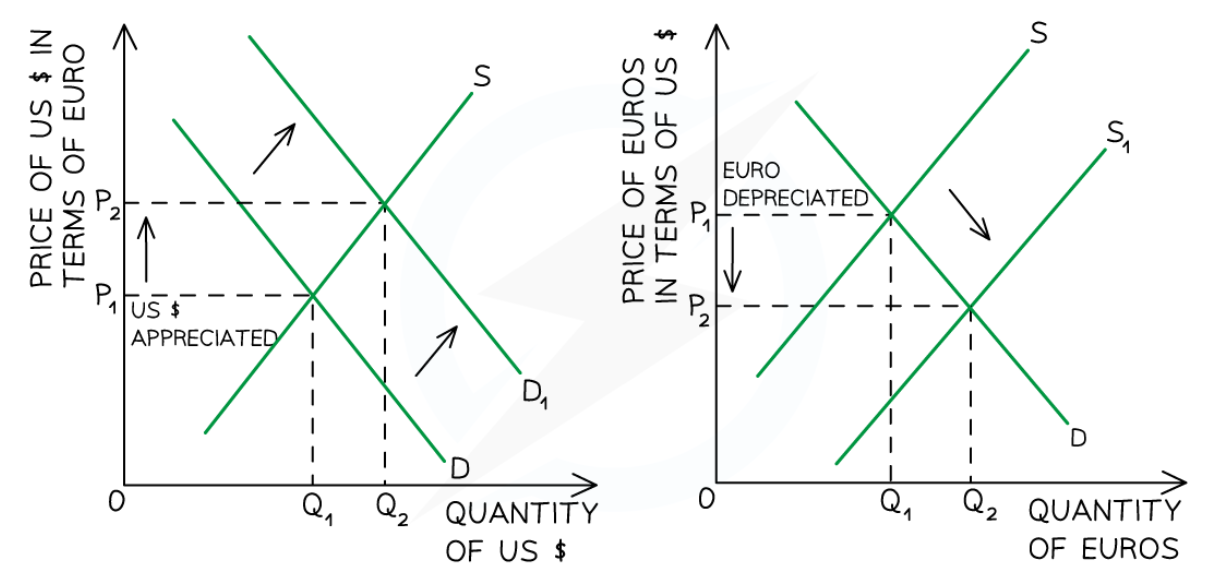
90
New cards
A fixed Exchange rate system
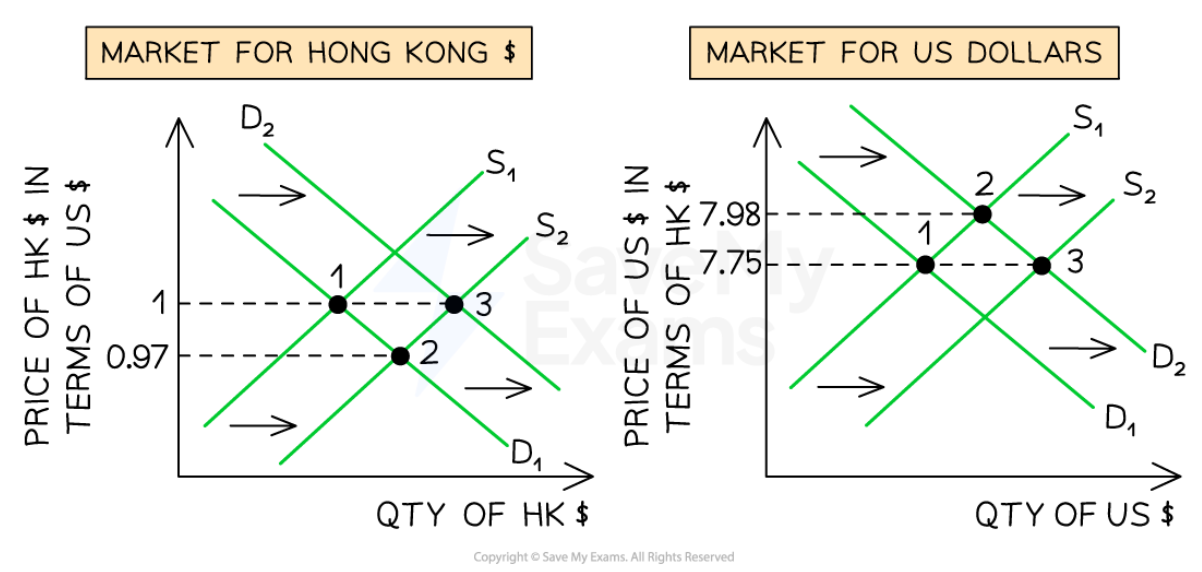
91
New cards
A managed Exchange rate system
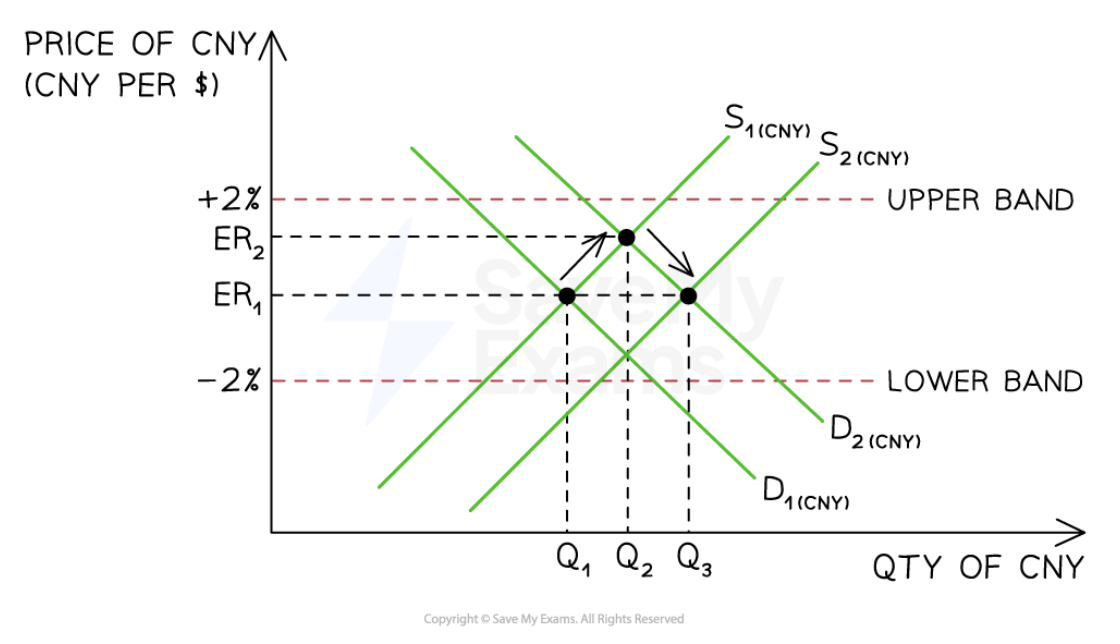
92
New cards
Likely impact on the macro economy of a currency depreciation in the Keynesian model
93
New cards
Likely impact on the macro economy of a currency appreciation in the Monetarist/New classical model