Lens Abnormalities
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
presbyopia
physiological decrease in amplitude of accommodation associated with aging
cataract
any opacity of the lens, small local opacity or diffuse general loss of transparency
pseudophakia
S/P cataract extraction w/ IOL
aphakia
absence of lens: congenital or acquired
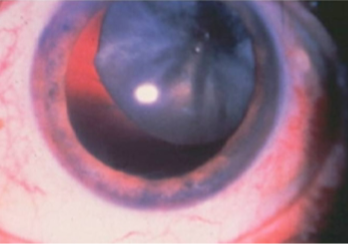
subluxation
partial displacement of lens
luxation
total displacement of lens
Vossius’ ring
pigment left on the anterior lens capsule from the iris after trauma
rosette cataract
anterior or posterior subcapsular cataract due to trauma of the lens
smoking, UV exposure, DM, prolonged steroid use, ocular trauma, high myopia
what are some risk factors for cataract development?
intumescent
swelling of lens
immature cataract
scattered opacities separated by tranparent fibers
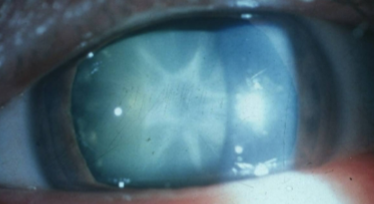
mature cataract
opaque cortex w/ intact capsule
hypermature cataract
liquefication of lens fibers w/ leakage of H2O & protein
sutural opacities/cataracts
congenital cataract
may be small isolated opacity along the Y suture or dense opacities along partial or total branches of Y sutures
do not progress
found in fetal nucleus
cerulean ‘blue dot’ opacities
congenital cataract
small, blush punctate opacities in cortex
non-progressive
no visual loss
symmetrical
lamellar/zonular cataract
congenital cataract
most common infantile cataract
bilateral, non-progressive
secondary to insult during fetal development
opacities occupy spherical lamellae
U shaped “riders”
normally patient still sees fairly well, but if interfering w/ vision needs to be removed quickly to prevent amblyopia
coronary ‘crown’ cataracts
congenital cataract
single/multiple club-shaped peripheral cortical opacities
no vision loss
often associated w/ cerulean opacities
anterior polar cataract
congenital cataract
dense, circular, pyramidal, well-defined opacity
symmetric & bilateral
typically no visual effect
posterior polar cataract
congenital cataract
dense, circular, pyramidal, well-defined opacity
symmetric & bilateral
can affect VA
nuclear sclerosis
change in nucleus
slow development
signs/sx:
poor hue discrimination
reduced contrast sensitivity
myopic shift
monocular diplopia
slight yellowing, expected for age
definite yellowing
yellow ++
yellow-orange
orange-brown
describe the color changes for grades 1-4 of an NS cataract
cortical (cuneiform) cataract
wedge-shaped opacities in anterior & posterior cortex
slowly progressive
begins inferior-nasal quadrant
signs/sx:
increased glare
decreased contrast sensitivity
variable VA reduction (depends on if spokes go through visual axis)
lenticular, lamellar clefts-spoke opacities
sheet-like zones of peripheral opacification
retrodots
secondary to oxidative stress
risk factors:
alcohol consumption
high serum levels of HDL cholesterol
smoking
associated w/ nuclear cataracts
vacuoles
secondary to oxidative stress
clear, spherical, fluid-filled spaces w/in the lens cortex or subcapsular space
vary in size
minimal effect on vision
<10%
10-50%
50-90%
>90%
describe the % obscuring visual axis for cortical cataracts grade 1-4
posterior subcapsular cataract
cataracts that have a significant effect on vision, especially with a small pupil
surgery may be necessary earlier on
no effect on RE
etiology: migration & thickening of lens epithelial cells in the posterior subcapsular space
trauma, chronic uveitis, chronic systemic steroid use
3%
30%
50%
>50%
describe the % of affected posterior capsule in PSC grade 1-4
epicapsular stars
star-shaped deposits on anterior lens capsule
remnants of tunica vasculosa lentis
persistent pupillary membrane
remnant of tunica vasculosa lentis
attached to iris collarette
flow freely or are attached to anterior lens capsule
may have subcapsular lens opacities
Mittendorf’s dot
remnant of tunica vasculosa lentis
remnant of hyaloid artery on posterior capsule
typically inferior-nasal
may have a tail
persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous (aka persistent fetal vasculature)
hyperplasia of tunica vasculosa lentis
unilateral
decreased VA
secondary PSC
strabismus
microphthalmos
leukocoria
coloboma
notch at inferior lens equator
loss of zonules in region (subluxation upward)
congenital primary aphakia
abnormality occurs during 4-5th week of fetal development
failed induction of surface ectoderm during embryogenesis
may be AR (mutations in FOXE3 gene)
may be associated with severe ocular & systemic developmental anomalies
microphthalmia
aniridia
sclerocornea
secondary aphakia
lens has developed but been resorbed or extruded before or during birth
often associated w/ congenital infections like rubella
lenticonus
lens has a cone shape
more common posteriorly
unilateral
etiology: traction of hyaloid remnants or capsule weakness
anterior is associated w/ Alport syndrome
oil droplet appearance on retroillumination
distorted, myopic reflex
lentiglobus
lens has a spherical shape
more common posteriorly
unilateral
etiology: traction of hyaloid remnants or capsule weakness
oil droplet appearance on retroillumination
distorted, myopic reflex
Alport syndrome
what systemic condition is anterior lenticonus associated w/?
microphakia
abnormally small lens diameter
high myopia
subluxation & iridodonesis
potential for pupil block & secondary glaucoma
systemic associations:
Lowe’s syndrome
microspherophakia
abnormally small lens diameter with spherical shape
high myopia
subluxation & iridodonesis
potential for pupil block & secondary glaucoma
systemic associations:
hyperlysinemia
Weill-Marchesani syndrome
Marfan’s syndrome
ectopia lentis
signs/sx:
increased astigmatism
monocular diplopia
cataracts
glaucoma
systemic associations:
aniridia
Marfan’s syndrome
homocystinuria
Weill-Marchesani syndrome
Marfan’s syndrome
etiology: AD w/ variable expression, abnormality of connective tissue
ocular signs/sx:
bilateral, superior subluxation
microspherophakia
angle anomaly → secondary glaucoma
segmental hypoplasia of iris dilator muscle
severe myopia
retinal detachment
systemic associations:
cardiac anomalies
skeletal anomalies
normal intelligence
Weill-Marchesani syndrome
etiology: rare, AR
ocular signs/sx:
microspherophakia
high myopia
inferior subluxation
may precipitate acute glaucoma
systemic associations:
short stature w/ broad hands & fingers
joint sitiffness
decreased mobility
carpal tunnel syndrome
myotonic dystrophy
AD, mutation in mitochondrial DNA
systemic signs:
impaired contraction & relaxation of skeletal muscles
frontal baldness
cardiac anomalies
ocular signs:
polychromatic cortical opacities
christmas tree cataracts
bilateral ptosis
chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia
retinal pigmentary changes
atopic dermatitis
bilateral, posterior/anterior stellate opacities
mature rapidly
chronic keratoconjunctivitis
keratoconus
Down’s syndrome
ocular signs:
punctate lenticular opacities
narrowed & slanted palpebral fissures
esotropia
high RE
keratoconus
systemic signs:
intellectual disability
defective, awkward gait
small stature
congenital heart defects
diabetes
+FHx
ocular signs:
fluctuations in RE
senile cataracts
bilateral, white punctate snowflake opacities that can mature w/in days, due to marked increase in blood sugar
rubella
positive IgM antibodies
15% of women of childbearing age at risk
systemic signs:
deafness
congenital heart defects
intellectual disability
ocular signs:
nuclear/lamellar cataracts
RPE pigmentary retinopathy
high RE
strabismus
microphthalmos
glaucoma
optic atrophy
nystagmus
preventable w/ vaccination
chlorpromazine toxic cataracts
etiology: antipsychotic medication
ocular signs:
fine, stellate pigmentation under anterior capsule w/in the pupillary zone
photosensitive
corneal endothelial & stromal pigmentation
retinopathy with high doses (rare)
dose dependent
corticosteroids (PSC), chlorpromazine (anterior stellate), infrared radiation (glass blower’s cataract), x-ray radiation (PSC), UV radiation (cortical/nuclear cataract)
what things can cause toxic cataracts & what type of cataract is formed?
pseudoexfoliation syndrome
etiology: amyloid amorphous material secreted by CB epithelium, deposited on the anterior lens capsule, posterior iris, ciliary processes, & TM
usually bilateral
can lead to secondary glaucoma
glaucomflecken
diagnosis of previous acute angle closure glaucoma
small gray-white anterior subcapsular or capsular opacities w/in pupillary zone
no visual loss
phacolytic uveitis & glaucoma
etiology:
hypermature cataract or ruptured capsule
inflammation secondary to the release of lens proteins
macrophages respond to the proteins & obstruct the TM
uveitis ocular signs
tx:
initial suppression of immune response w/ corticosteroids, then cataract extraction
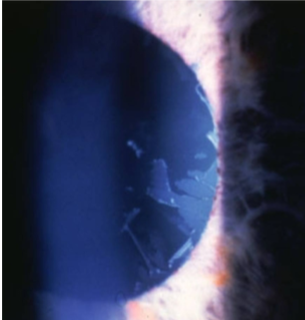
Vossius ring
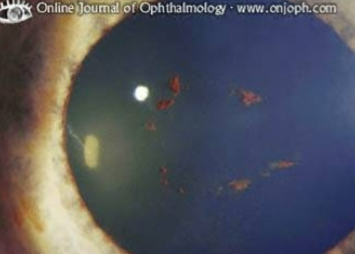
rosette cataract
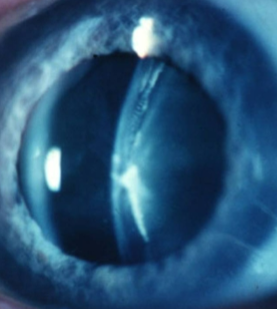
lens subluxation
mature cataract
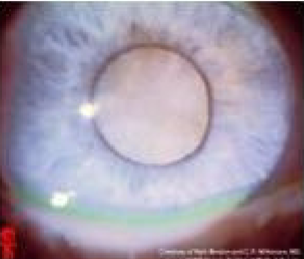
hypermature cataract
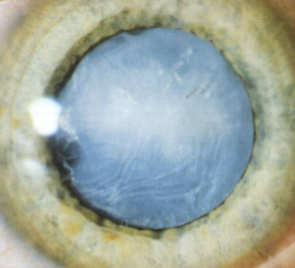
sutural cataract
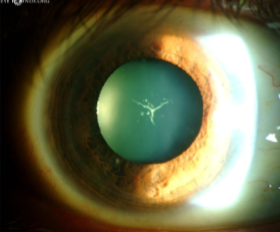
sutural cataract

sutural cataract
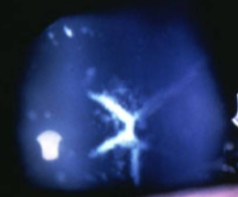
cerulean cataract
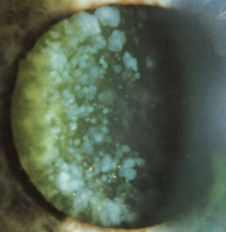
cerulean cataract

lamellar/zonular cataract
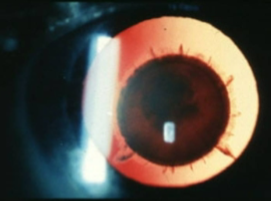
lamellar/zonular cataract
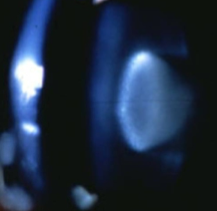
lamellar/zonular cataract

coronary cataract
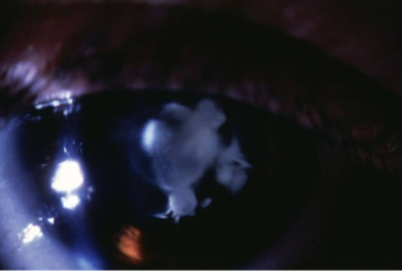
anterior polar cataract

posterior polar cataract
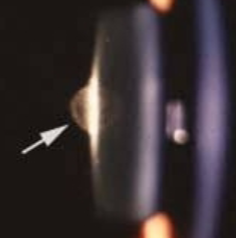
nuclear sclerotic cataract
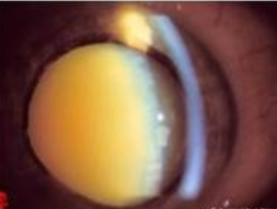
NS cataract
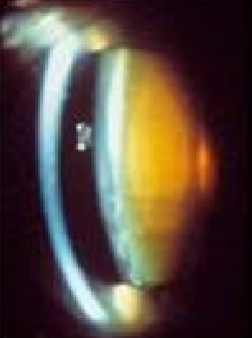
NS cataract
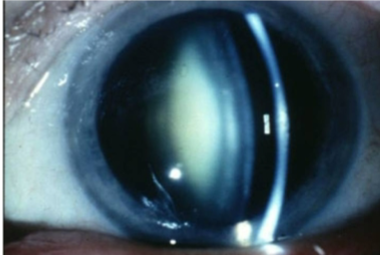
cortical cataract
retrodots
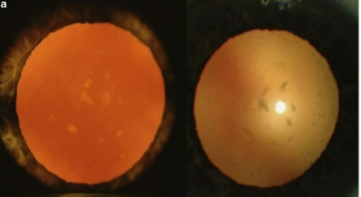
vacuoles

cortical cataract

PSC
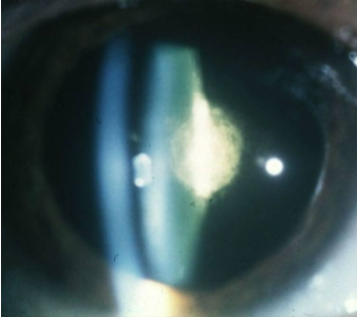
PSC
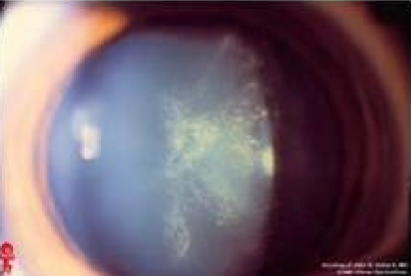
PSC
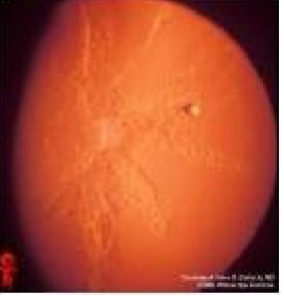
NS & cortical cataract
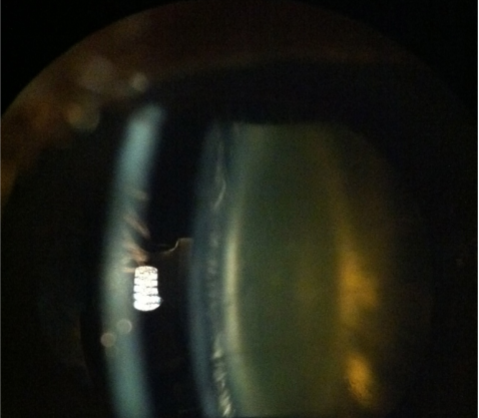
epicapsular stars
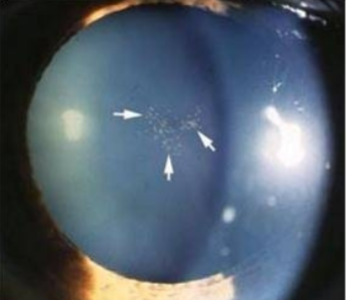
PPM
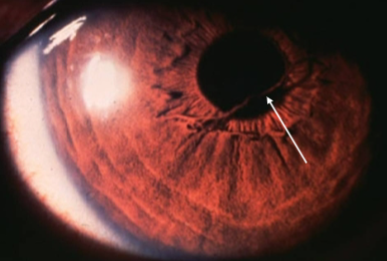
Mittendorf dot
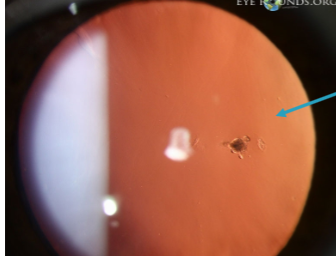
Mittendorf dot & tail

PHPV/PFV

PHPV
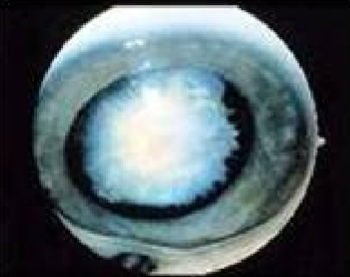
PHPV
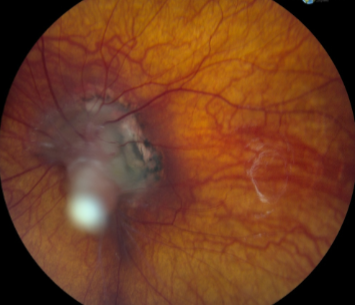
coloboma
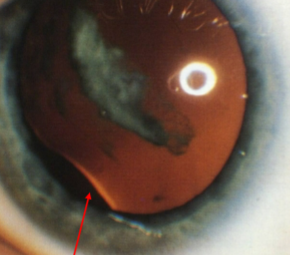
posterior lenticonus & polar cataract
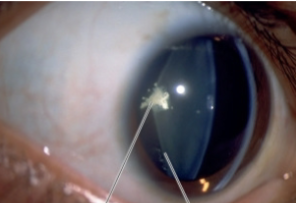
posterior lenticonus
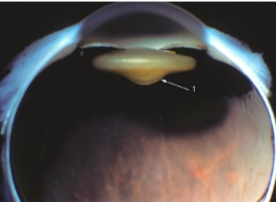
lenticonus
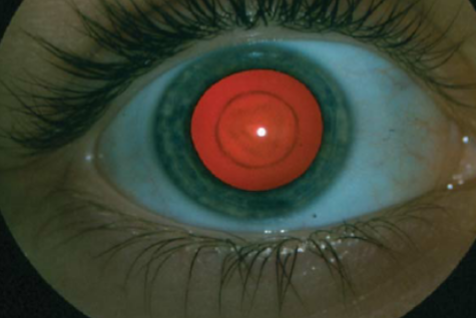
microphakia
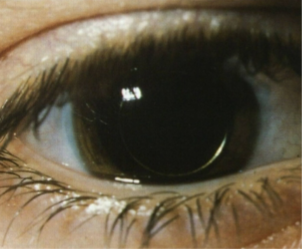
microphakia
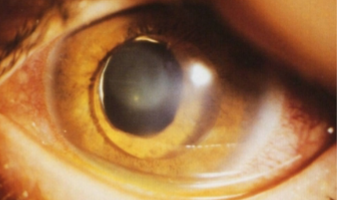
subluxation
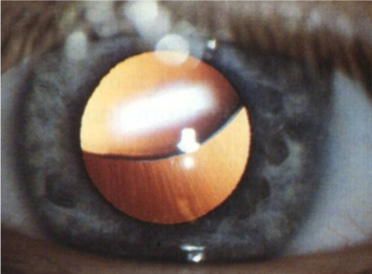
subluxation (Marfan’s)
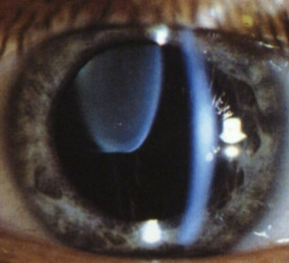
subluxation (Weill-Marchesani)
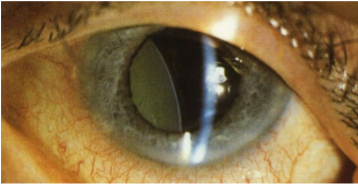
christmas tree cataract (myotonic dystrophy)
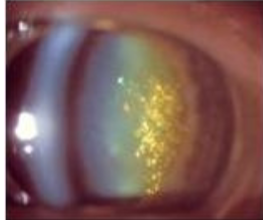
christmas tree cataract (myotonic dystrophy)

christmas tree cataract (myotonic dystrophy)
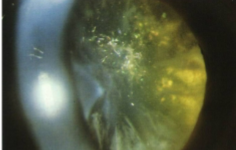
stellate anterior subcapsular cataract (chlorpromazine)
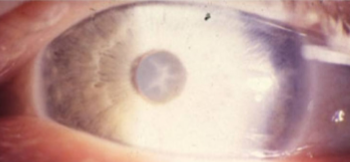
pseudoexfoliation syndrome