NATIONAL MINIMUM WAGE
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
What does the national minimum wage do?
Intro. of a national min. wage seeks to uphold workers' rights, increase pay, & combat income inequality.
It establishes a min. hourly rate that employers are required to pay their staff as a matter of law.
What is the minimum wage?
The National minimum wage rate is currently £8.72 for workers over 25 (from April 2020).
The minimum wage was introduced in April 1999 (at £3.60) and is the legal minimum that employers can pay.
What does the min. wage aim to do?
The aim of the National Minimum Wage is to help increase incomes of the low paid.
It has become more important in a labour market characterised by a decline in trade unions and the growth of low-paid service sector jobs.
What does Friedman argue on min. wage?
Free market economists, such as Milton Friedman argued a National Minimum Wage would lead to unemployment because firms cannot afford to pay the workers.
Does min. wage cause u/e?
Since it was intro. in 1999, the effect on u/e has been negligible.
In the UK, there are record levels of u/e, lower natural rates of unemployment and unemployment only increasing temporarily because of the recession in 2008.
What could future increases of it do?
Although the impact has been less than some economists anticipated, future increases could place a strain on some employers.
What do some argue on the rate?
Others argue that Minimum Wage rates are still too low and do not provide a ‘living wage‘ in certain areas of high housing costs, such as London.
Advantages of a national minimum wage: reduces poverty
The implementation of national min. wage can raise low-paid workers' standards of living & help combat poverty.
It gives workers means to cover their fundamental necessities, such as housing, food, and healthcare, by guaranteeing a min. level of income.
The min. wage increases the wages of the lowest paid. These workers will have increased income & will reduce relative poverty.
Advantages of national minimum wage: reduced income inequality
To close the income gap between high and low earnings is one of the main goals of a national minimum wage.
A minimum wage is set in order to reduce income inequality and advance a more fair allocation of resources.
Advantages of national minimum wage: enhanced productivity and retention
Fair pay can incentivise workers to supply their labour, resulting in improved labour output & productivity, lower turnover of lab. within jobs, & increase job satisfaction.
When workers are paid fairly, they are more likely to be dedicated to their roles, which raises productivity levels across the board in the labour market.
Efficiency wage theory states higher wages can increase incentive for people to work harder & thus higher wages may increase lab. productivity. If firms have to pay higher wages, they may put more focus on increasing labour productivity, which increases efficiency of economy
Advantages of national minimum wage: stimulated consumer spending & economic growth
A national min. wage can enhance consumer spending by giving low-income workers more purchasing power.
This therefore increases D for products & services, causing increase in econ. output, creation of new job roles, especially in industries that depend on domestic consumption.
Advantages of minimum wage: increases incentives to accept a job
With a min. wage, there is a bigger difference between the level of benefits and the income from employment.
A min. wage could also increase participation rate as the benefits of work become greater and more worthwhile.
Advantages of minimum wage: increased investment
Firms will have an increased incentive to invest and increase labour productivity because labour is more costly.
In the long-term, this can encourage greater investment and labour productivity – an economy based on high value added, rather than competing on low wages.
Advantages of minimum wage: knock on effect of min. wage
Although only 5-7% of workers are on the minimum wage, the minimum wage has an indirect effect on the wages of those just above the minimum wage.
If the minimum wage floor rises, firms may need to increase wages for those just above the minimum wage floor – to maintain pay premium for experienced workers.
Advantages of minimum wage: counterbalance the effect of monopoly employers
If firms have Monopsony power they can drive wages down by employing fewer workers.
However, min. wages will make this more difficult.
Therefore min. wage could have positive effect on employment.
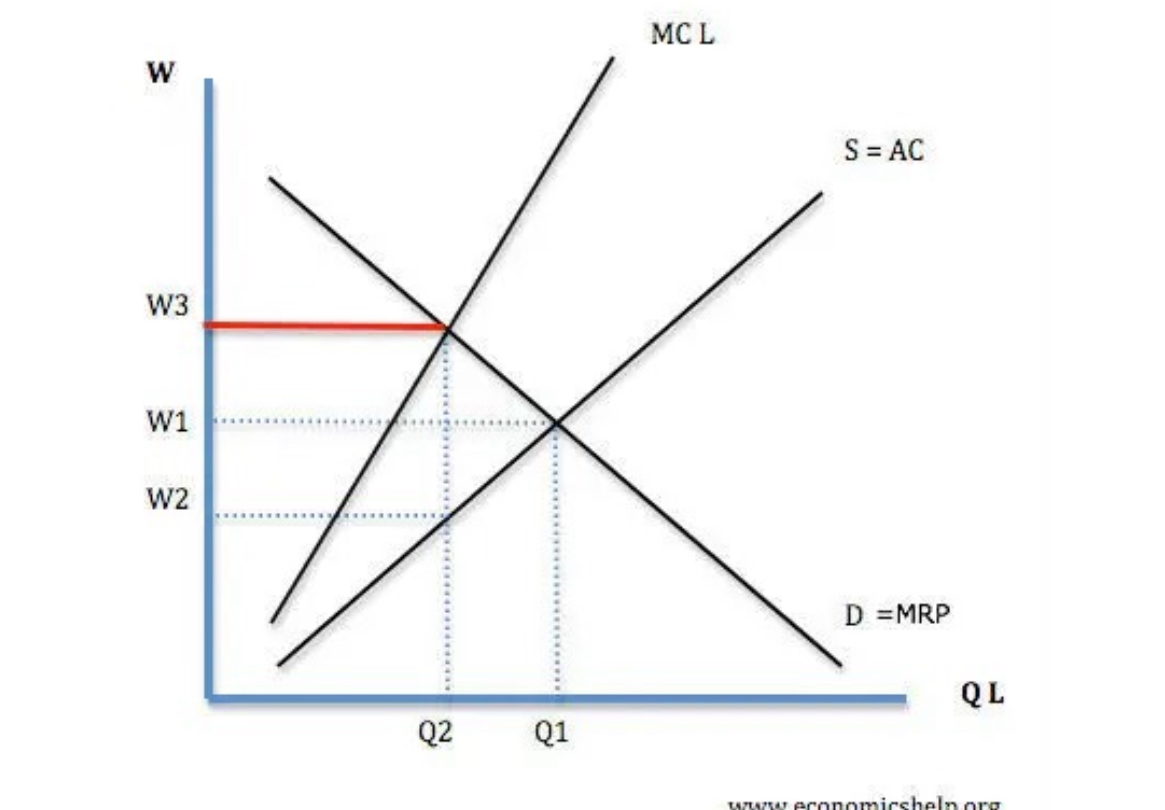
Draw diagram of minimum wage on monopsony.
monopsony pays wage of W2 & employs Q2. if a min. wage was placed equal to W1, would increase employment to Q1. Thus, in some circumstances, it is feasible that min. wage could actually increase employment – or at least not cause any employment.
Arguably many firms can afford to pay higher wages, a minimum wage helps redistribute income in society.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: potential job losses and reduced hiring
Critics (especially free market economists) say that national min. wage could result in job losses, especially in sectors with slim profit margins or those that depend significantly on low-skilled labour.
Some businesses might not be able to afford greater labour costs, which would force them to decrease the rate at which they hire new employees, or possibly even lay off employees altogether.
If labour markets are competitive, a minimum wage above the equilibrium could cause a fall in demand for workers, and excess supply
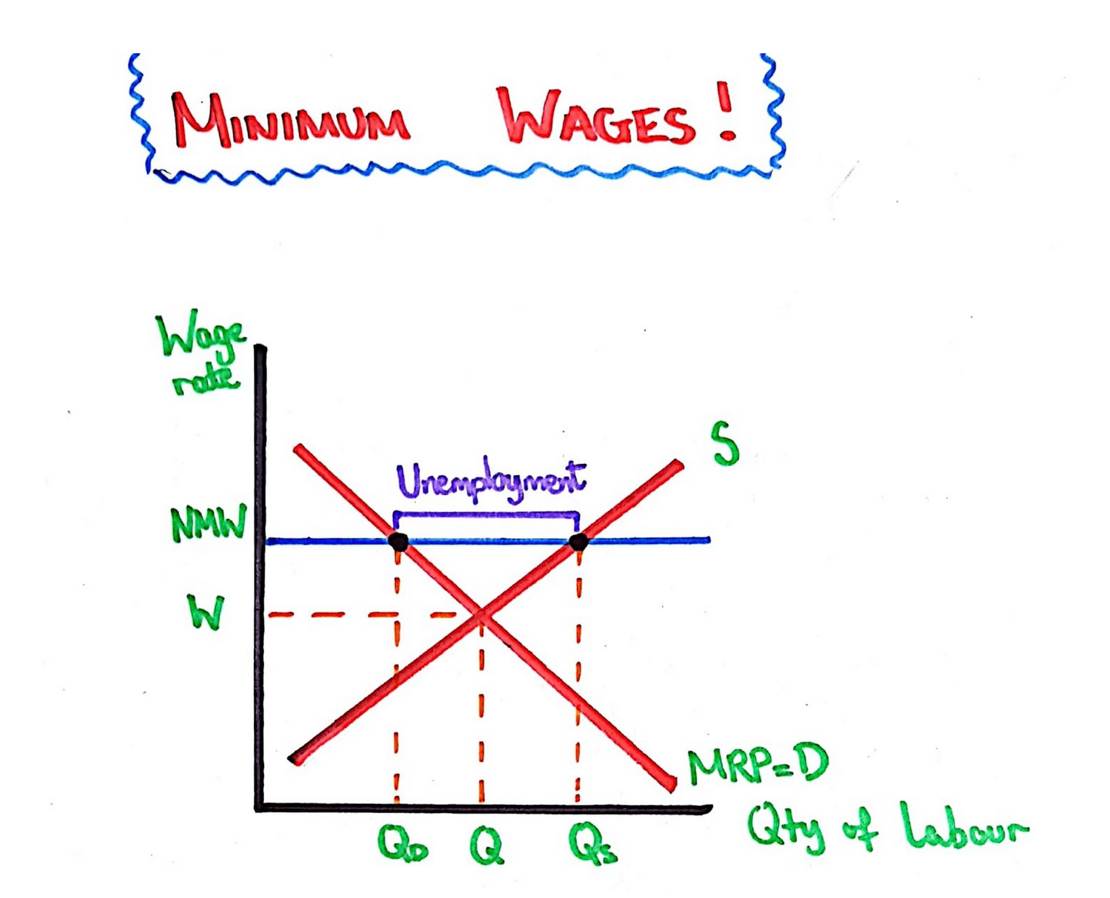
Draw diagram showing u/e as result of minimum wage.
Above the equilibrium, the national minimum wage can cause unemployment of Q3-Q2
Disadvantages of national minimum wage: increased cost of business operations
Following a national min. wage standard may result in large increases in operational costs for firms.
Particularly small enterprises may struggle to adapt to rising wage standards, which could have an effect on their viability and survival.
Disadvantages of national minimum wage: potential negative impact on small businesses
Smaller businesses with fewer resources may experience more challenges in adhering to national min. wage.
Might find it difficult to compete with bigger businesses that have more financial wiggle room & negotiating power over prices - this could increase risk of business failure & decrease competitiveness within mkts.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: inflationary pressures
Implementation of a national minimum wage may increase pressures for inflation in a given country
greater salaries may cause firms to incur greater production expenses, which might then be passed on to customers as higher prices for goods and services.
Can cause cost-push inflation - because firms face increase in costs which are likely to be passed on to consumers. even more likely if wage differentials are maintained.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: Certain industries vulnerable to a ‘living wage’
It is argued labour-intensive industries, where labour costs are a high percentage of overall costs could be hit by a high National Minimum Wage.
In particular care workers for old people are often paid the Minimum Wage. With a rise in number of old people needing care, could sig. increase costs for old-age care.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: reduced variations in wages
A big problem with a national minimum wage is that wages vary enormously within the UK.
In London, with higher costs of living, not many people get minimum wage because wages are relatively higher.
However, in some areas, minimum wage of £9 could cause sig. u/e, especially in labour-intensive industries.
It is estimated that in 10 hot spot low pay areas 30% of workers are on the Minimum Wage.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: higher wages passed onto consumers
An increase in the minimum wage could cause firms to increase prices and pass the costs onto consumers
Disadvantages of minimum wage: more and more workers are getting stuck on the minimum wage
More than 1 million workers receive the minimum wage.
The highest proportion are amongst women, ethnic minorities and young people.
The fear is that a minimum wage encourages firms to keep more workers on the lowest band of wages.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: incentive to work in black market
A high min. wage may create incentive for firms to find ways to avoid declaring wages to govt but offer cash-in-hand work in the unofficial/underground economy.
This can lead to exploitation of labour & is concern in some industries – especially with higher rates of migrant labour.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: firms may become uncompetitive
In some cases, higher min. wage could push up costs causing a firm to go out of business because they may not be able to afford wage costs.
This might be a particular problem if firm is competing in a global market and higher wage costs make them uncompetitive compared to low-wage cost countries.
E.g. higher min. wage may encourage firms to manufacture clothes in China or Taiwan where labour is cheaper than the UK.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: poorest don’t benefit
A limitation of the minimum wage is that it doesn’t increase the incomes of the lowest income groups.
This is because the poorest have to rely on benefits and are therefore not affected by minimum wages.
Disadvantages of minimum wage: limited impact on relative poverty
Many who benefit from the minimum wage are second income earners, and therefore the household is unlikely to be below the poverty line.
A household with a single income earner just above the minimum wage is likely to be relatively poorer.
But they will not benefit from the minimum wage.
Evaluation of min. wage - uncertainty
The effect of a min wage on unemployment is uncertain, the structure of the labour market is very important.
E.g. if the labour market is a monopsony, a minimum wage may not cause unemployment.
Evaluation of min. wage - cause u/e?
Empirical evidence from the US and the UK suggests that a moderate increase in the minimum wage doesn’t cause a fall in employment.
Therefore the key question is how high the minimum wage can rise before causing unemployment.
Evaluation of min. wage - wage differentials
Impact of min. wage on wage differential is important.
E.g. skilled workers just above the minimum wage may feel they deserve more.
Therefore, increase in min. wage may lead to wage increases for all pay grades.
However, increasing min. wage tends to have limited impacts on wage differentials.
Evaluation of min. wage - regional
There may be good case for regional min. wage because actual wages tend to be lower in north than south.
In London, v. few workers benefit from minimum wage, and in this region, the minimum wage could increase.
What does desirability of min. wage depend on?
State of the economy. During strong growth and falling u/e, it is easier for firms to pay higher wages.
Elasticity of demand. Is D for labour wage inelastic? or will some firms be v. sensitive to higher wages? Some service sector jobs like hairdressers/cleaners may argue small increase in their wage bill could lead to u/e.
Regional wage rates. Could you allow for regional differences in wages? (e.g. London specific min. wage)
Type of labour market. Are lab. mkts comp. or monopsonistic?
Is there scope for firms to increase labour productivity? and therefore be able to afford the wage increases.
Percent of Median wages.
What did one study find on rate of min. wage? (% of median wages)
One study found that rate of min. wage compared to median wages is important.
E.g. Effect of minimum wages on low wage jobs, Jan 2019 found that a min wage set ” between 37% & 59% of the median wage—have yet to reach a point where the job losses become sizable.”
Arguments for enforcing a living wage - inequality
Helps to reduce inequality in society
Arguments for enforcing a living wage - higher wage rates
Firms can afford higher wage rates for lowest paid workers by reducing wage rates of top paid workers.
Arguments for enforcing a living wage - productivity
Higher pay can help to increase labour productivity, motivation and reduce labour turnover rates.
Arguments for enforcing a living wage - monopsony
Firms have a degree of monopsony power in employing workers.
This enables them to pay wages lower than marginal revenue product (see: monopsony theory)
Arguments against enforcing a living wage - already high
Min. wage rate is already quite high
There is a danger setting a min. wage rate significantly higher could cause u/e.
Although some firms like KPMG & Tesco might be able to afford higher wages, other firms like hairdressers, & cafes may find 20% increase in wages could be diff. between survival & bankruptcy in current recession.
Arguments against enforcing a living wage - campaign
Greater campaign to encourage voluntary uptake may be a better alternative.
Firms who pay higher wages may benefit from improved public relations and better labour productivity.
In theory, does increasing min. wage for 16-18 year olds encourage labour market participation?
In theory, increasing the minimum wage for 16-18 year old workers would increase the incentive to join the labour market because work will become more attractive compared to studying at school and not earning.
In reality, will increase in min. wage for 16-18 year olds encourage labour market participation?
Min. wage for 16 & 17 year-olds still relatively low. Thus, benefit of working on min. wage may still seem insig. compared to benefits from studying & getting qualifications which enable higher lifetime earnings.
Many 16 and 17 year-olds live rent free therefore there is not same economic necessity to go out and get a job.
Can’t think of many students who would give up A-levels so they could go & work in McDonald’s for £4.20.
Most likely is increase in participation of young workers doing part-time jobs in addition to studying full time.
What is the case for increasing the min. wage rate for 16-18 year olds?
Unfair firms can pay a lower wage rate to young workers doing the same job as people over 21.
Efficiency Wage Theory – idea if you pay a higher wage, you will get greater motivation and labour productivity.
Problems of increasing min. wage rate for young workers?
Could lead to u/e & fewer job opportunities. Many firms may be unwilling to employ workers if there is a sig. increase in min. wage rate. Would particularly affect labour-intensive industries like hairdressers and cafes.
Arguably young workers lack experience, & so firms need to spend time & money on training them. Thus a lower min. wage rate is justified to pay for costs of on-the-job training.
What balance is there?
Promoting sustainable economic growth and ensuring the well-being of both workers and businesses depend on striking a balance between fair salaries and the general health of labour markets.
What is there difference between ?
there is a difference between the national minimum wage and the national living wage
critics argue that the minimum wage rate in the UK is below the living wage
the living wage is the wage somebody needs to support a minimum acceptable standard of living
How is the living wage calculated?
the living wage is calculated by the living wage foundation
“As of April 2023, the NLW is £10.42 per hour for those aged 23 & over, £10.18 for those aged 21–22, £7.49 for ages 18–20, £5.28 for under-18s, and £5.28 for apprentices. The London living wage is currently set at £11.95.”
Has minimum wage in UK caused u/e?
despite adopting national min. wage in Uk, is little evidence to suggest it has specifically created u/e
though this could because maj. of employers are making sup. profits & have budgets to meet national minimum wage rates
also, don’t forget min. wage is below living wage - unlikely that firms will get away with paying far lower wages than the living wage anyway
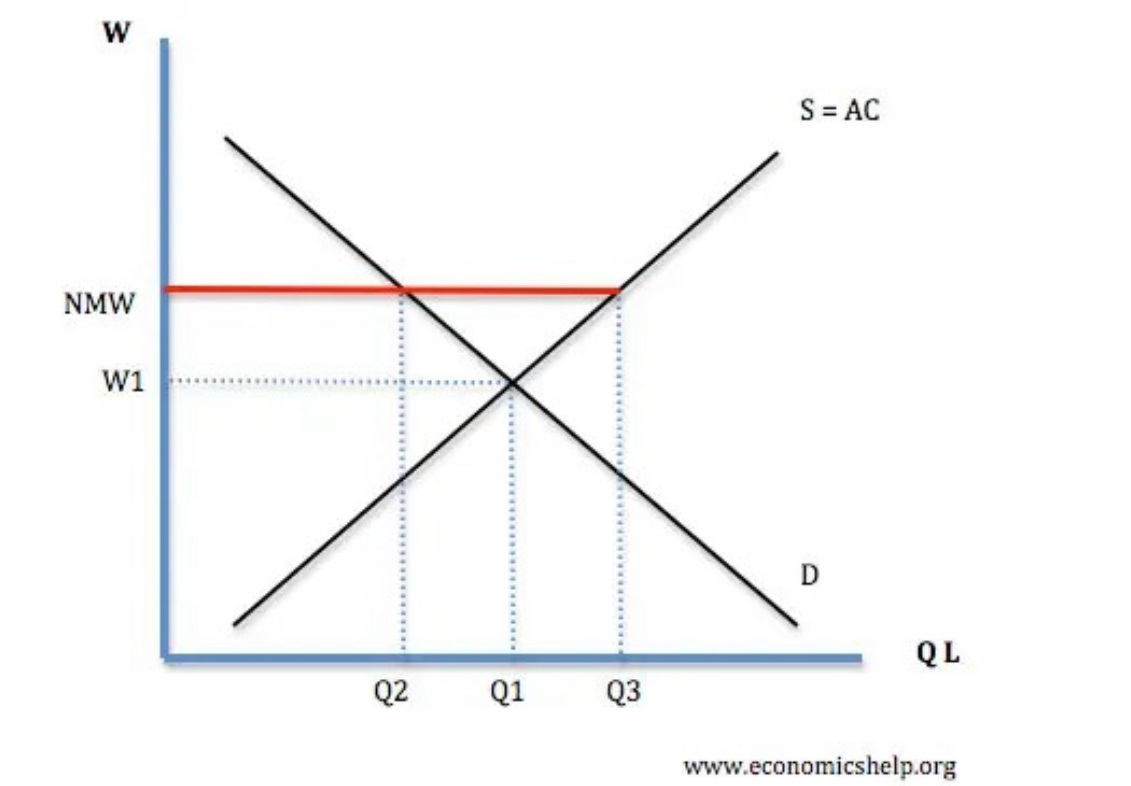
Draw diagram to show minimum wage.
diagram to show how national minimum wages (NMW) creates additional u/e
NMW increases market wage above equilibrium level
this creates an additional S of labour relative to D
this creates u/e between Qd and Qs
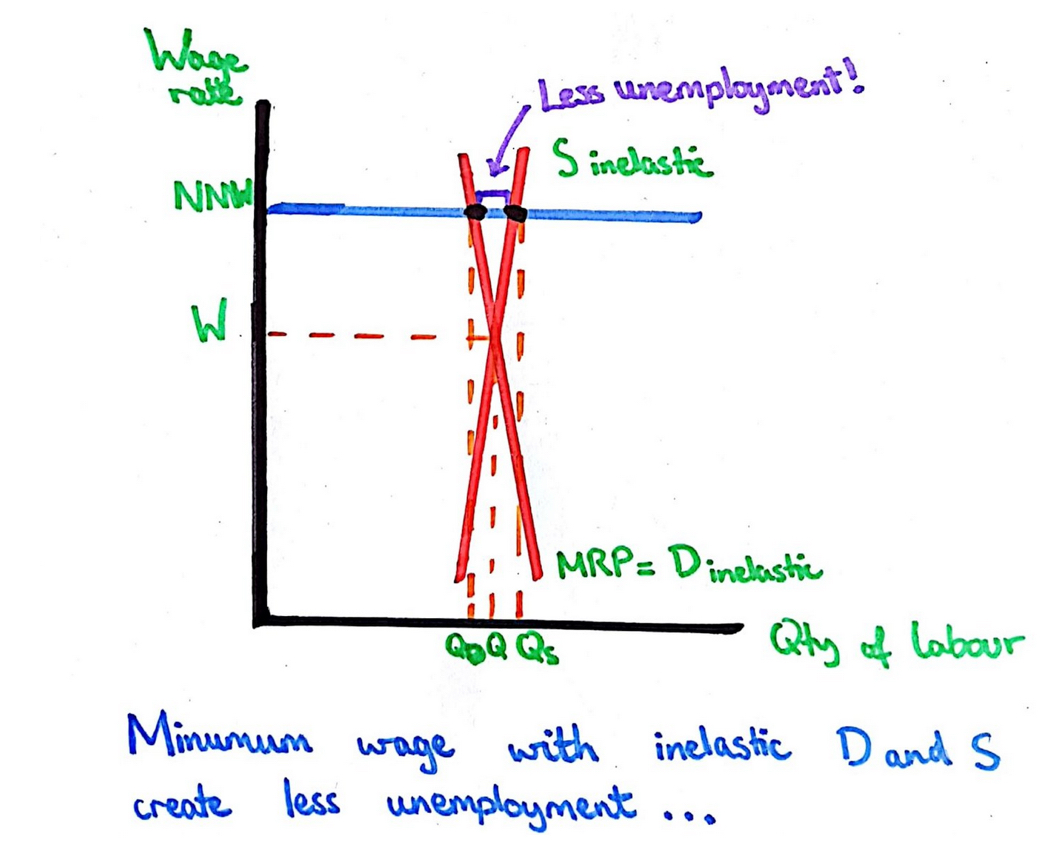
Draw diagram to show minimum wage on inelastic.
note if labour demand and supply are inelastic, then the national minimum wage has less of an impact and creates less unemployment
What is the purpose of implementing a national minimum wage?
To create a legal wage floor on the hourly wages, govt must impose a NMW.
It attempts to defend workers' rights, increase wages to a fairer level, lessen economic inequality, and raise low-wage workers' standards of living.
It’s particularly important to have in industries where there are large monopsony employers.
What are some potential drawbacks of a national minimum wage?
risk of job losses is one of the potential negatives of NMW, particularly in sectors with slim profit margins or those dependent on low-skilled labour.
This is especially case for small businesses, as it might raise operating costs.
There might be inflationary pressures and significant harm to the competitiveness of small enterprises.
How does a national minimum wage impact the economy positively?
economy may be impacted by a NMW in both positive and negative ways.
on the plus side, it can increase consumer spending as lower-income households earn higher wages.
can boost employee retention rates as employees are less likely to seek higher paid work.
can boost productivity, and lessen income inequality.
How does a national minimum wage impact the economy negatively?
might result in employment losses if min. wage set too high.
can raise corporate expenses, and possibly even create inflationary pressures if firms choose to pass on increased costs to their customers via prices.
to minimise any negative consequences and encourage sustainable economic growth, critical to evaluate state of local lab. mkt and put suitable regulations in place.